Abstract
We describe a method that can be used to produce equimolar amounts of two or more specific proteins in a cell. In this approach, termed the ubiquitin/protein/reference (UPR) technique, a reference protein and a protein of interest are synthesized as a polyprotein separated by a ubiquitin moiety. This tripartite fusion is cleaved, cotranslationally or nearly so, by ubiquitin-specific processing proteases after the last residue of ubiquitin, producing equimolar amounts of the protein of interest and the reference protein bearing a C-terminal ubiquitin moiety. In applications such as pulse-chase analysis, the UPR technique can compensate for the scatter of immunoprecipitation yields, sample volumes, and other sources of sample-to-sample variation. In particular, this method allows a direct comparison of proteins' metabolic stabilities from the pulse data alone. We used UPR to examine the N-end rule (a relation between the in vivo half-life of a protein and the identity of its N-terminal residue) in L cells, a mouse cell line. The increased accuracy afforded by the UPR technique underscores insufficiency of the current "half-life" terminology, because in vivo degradation of many proteins deviates from first-order kinetics. We consider this problem and discuss other applications of UPR.
Full text
PDF

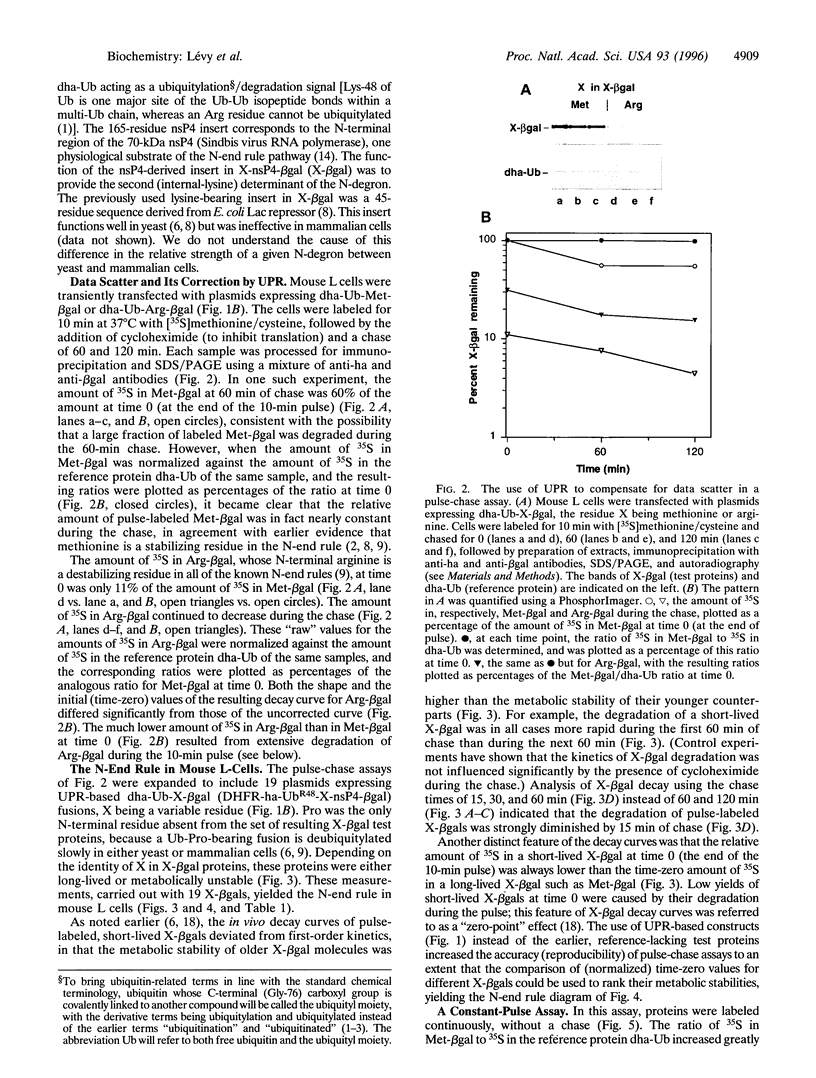
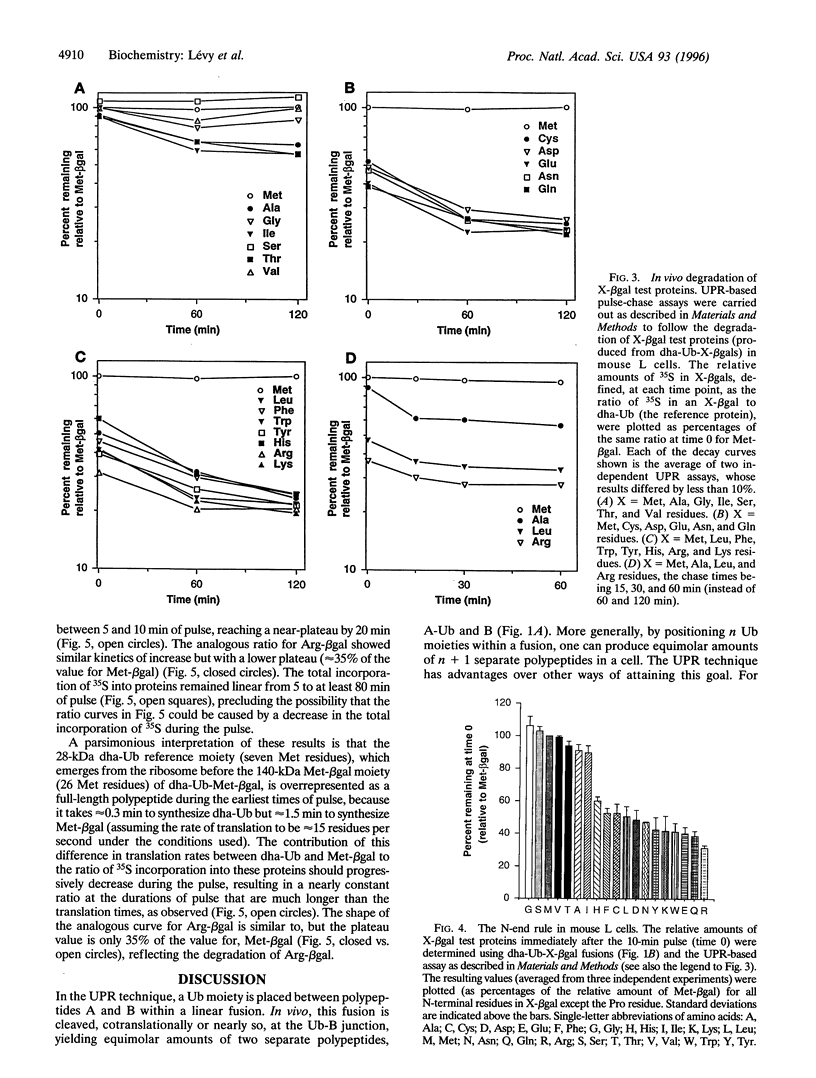

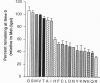
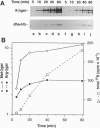
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alagramam K., Naider F., Becker J. M. A recognition component of the ubiquitin system is required for peptide transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Jan;15(2):225–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arfin S. M., Bradshaw R. A. Cotranslational processing and protein turnover in eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):7979–7984. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Varshavsky A. The degradation signal in a short-lived protein. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1019–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90635-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Tobias J. W., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin-specific proteases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cloning of UBP2 and UBP3, and functional analysis of the UBP gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23364–23375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Varshavsky A. Inhibition of the N-end rule pathway in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1090–1094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Varshavsky A. Yeast N-terminal amidase. A new enzyme and component of the N-end rule pathway. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):12065–12074. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.12065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda D. K., Bachmair A., Wünning I., Tobias J. W., Lane W. S., Varshavsky A. Universality and structure of the N-end rule. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16700–16712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim R., Cubitt A. B., Tsien R. Y. Improved green fluorescence. Nature. 1995 Feb 23;373(6516):663–664. doi: 10.1038/373663b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M., Varshavsky A. In vivo degradation of a transcriptional regulator: the yeast alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90481-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., Schlenker S. Selective protein degradation: a journey's end within the proteasome. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):881–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson N., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin-assisted dissection of protein transport across membranes. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2686–2698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06559.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemm J. A., Rümenapf T., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H., Rice C. M. Polypeptide requirements for assembly of functional Sindbis virus replication complexes: a model for the temporal regulation of minus- and plus-strand RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2925–2934. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madura K., Varshavsky A. Degradation of G alpha by the N-end rule pathway. Science. 1994 Sep 2;265(5177):1454–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.8073290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa F. R., Hochstrasser M. The yeast DOA4 gene encodes a deubiquitinating enzyme related to a product of the human tre-2 oncogene. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):313–319. doi: 10.1038/366313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. mRNA stability in mammalian cells. Microbiol Rev. 1995 Sep;59(3):423–450. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.3.423-450.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. D., Drew J. Foot-and-mouth disease virus 2A oligopeptide mediated cleavage of an artificial polyprotein. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):928–933. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias J. W., Shrader T. E., Rocap G., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule in bacteria. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.1962196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. The N-end rule. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1995;60:461–478. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1995.060.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Rümenapf T., Kuhn R. J., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sindbis virus RNA polymerase is degraded by the N-end rule pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8967–8971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]