Abstract
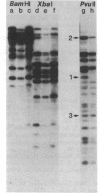
We have used genomic blotting with DNA from a human cell line that has a small deletion on chromosome 6 (6.3.6) and from its parent cell line (T5-1) to map DNA fragments complementary to cloned DNA sequences encoding the HLA-B7 antigen (class I) and the alpha chain of the HLA-DR antigen (class II). The 6.3.6 variant fails to express the HLA-A, -B, -C, and -DR and MB specificities associated with one of the parental T5-1 haplotypes and has a visible deletion in the short arm of one chromosome 6 (1). The gene locus assignment was based on the expectation that, if the chromosomal location of the DNA sequences used as a hybridization probe were within the deletion, then the relative amount or size (or both) of genomic restriction fragments that hybridize to the probe in T5-1 and in 6.3.6 DNAs should differ predictably. By comparing the genomic blot patterns from T5-1 and 6.3.6 DNAs, we have shown directly that the loss of haplotype expression was due to deletion of the structural genes and have mapped the structural gene for the HLA-DR alpha chain to the chromosomal location (6p2105-6p23) defined by the 6.3.6 deletion. A cDNA clone encoding the alpha chain of the HLA-DR antigen hybridized to two genomic fragments, 4.2 and 3.8 kilobases long, generated by Bgl II digestion of T5-1 DNA. The 4.2-kilobase fragment was absent from DNA derived from the 6.3.6 deletion variant. Thus, this fragment could be assigned to the parental chromosome 6 with the A1, B8, DR3 haplotype, and the 3.8-kilobase fragment, to the chromosome 6 with the A2, B27, DR1 haplotype. In addition, comparison of the T5-1 and 6.3.6 genomic blot patterns obtained with the HLA-B7 probe revealed dosage differences for all of the class I genomic fragments generated by BamHI digestion, suggesting that all of the class I loci map to the region 6p2105-6p23.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodmer W. F., Bodmer J. G. Evolution and function of the HLA system. Br Med Bull. 1978 Sep;34(3):309–316. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., Aellen-Schulz M. F., St Geme J., 3rd, Erlich H. A., McDevitt H. O. Biochemical characterization of an invariant polypeptide associated with Ia antigens in human and mouse. Mol Immunol. 1983 Jan;20(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., McDevitt H. O. Characterization of HLA-D-region antigens by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Molecular-genotyping. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):18s–36s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotner T., Mashimo H., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Strominger J. L. Human T cell surface antigens bearing a structural relationship to HLA antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3858–3862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Camerini-Otero R. D., Ozato K., Seidman J. G. Structure and expression of a mouse major histocompatibility antigen gene, H-2Ld. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1994–1998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladstone P., Fueresz L., Pious D. Gene dosage and gene expression in the HLA region: evidence from deletion variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1235–1239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyert S. M., Shively J. E., Silver J. Biochemical characterization of a second family of human Ia molecules, HLA-DS, equivalent to murine I-A subregion molecules. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):550–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., Hewgill D., McDevitt H. O. Detection of a common polypeptide chain in I--A and I--E sub-region immunoprecipitates. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jan;16(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Andersen R. L., Strominger J. L. HLA-DR antigens have polymorphic light chains and invariant heavy chains as assessed by lysine-containing tryptic peptide analysis. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):37s–53s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavathas P., Bach F. H., DeMars R. Gamma ray-induced loss of expression of HLA and glyoxalase I alleles in lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. The major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):516–521. doi: 10.1126/science.104386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Knudsen P. J., Kaufman J. F., Strominger J. L. cDNA clones for the heavy chain of HLA-DR antigens obtained after immunopurification of polysomes by monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Swan D., Ruddle F., D'Eustachio P., Leder P. Dispersion of alpha-like globin genes of the mouse to three different chromosomes. Nature. 1981 Sep 17;293(5829):196–200. doi: 10.1038/293196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Trowsdale J., Bodmer W. F. cDNA clones coding for the heavy chain of human HLA-DR antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):545–549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López de Castro J. A., Strominger J. L., Strong D. M., Orr H. T. Structure of crossreactive human histocompatibility antigens HLA-A28 and HLA-A2: possible implications for the generation of HLA polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3813–3817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Malissen B., Jordan B. R. Exon/intron organization and complete nucleotide sequence of an HLA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):893–897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson J., Flaherty L., Vitetta E., Poulik M. D. Molecular similarities between the Qa-2 alloantigen and other gene products of the 17th chromosome of the mouse. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):1066–1070. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes are localized to a homogeneously staining region of a single chromosome in a methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5553–5556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr H. T., Bach F. H., Ploegh H. L., Strominger J. L., Kavathas P., DeMars R. Use of HLA loss mutants to analyse the structure of the human major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):454–456. doi: 10.1038/296454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Rutter W. J., Shows T. B., Gray P., Goeddel D. V., Lawn R. M. Leukocyte and fibroblast interferon genes are located on human chromosome 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Molecular cloning of a human histocompatibility antigen cDNA fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. The evolutionary past of the major histocompatibility complex and the future of cellular immunology. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):629–632. doi: 10.1038/297629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Slesinski R. S., Littlefield J. W. Chemical mutagenesis at the phosphoribosyltransferase locus in cultured human lymphoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1244–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Mann D. L., van Rood J. J., Ferrara G. B., Strominger J. L. Human B-cell alloantigens DC1, MT1, and LB12 are identical to each other but distinct from the HLA-DR antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4566–4570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. L. Demonstration of structural polymorphism among HLA-DR light chains by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):144–165. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. H., Hood L. Biochemical identification of the Qa-1 alloantigen. Immunogenetics. 1980;11(3):309–314. doi: 10.1007/BF01567797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D., Das H., Nunberg J. H., Saiki R., Sheng-Dong R., Mullis K. B., Weissman S. M., Erlich H. A. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the human HLA-DR antigen alpha chain by using a synthetic oligonucleotide as a hybridization probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5966–5970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W., Capra J. D., Vitetta E. S., Cook R. G. Organization of the immune response genes. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):292–297. doi: 10.1126/science.113876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman K., Larhammar D., Claesson L., Gustafsson K., Schenning L., Bill P., Böhme J., Denaro M., Dobberstein B., Hammerling U. Isolation and identification of a cDNA clone corresponding to an HLA-DR antigen beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1703–1707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A., Milstein C. A small polypeptide different from beta2-microglobin associated with a human cell surface antigen. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):243–244. doi: 10.1038/279243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]