Abstract
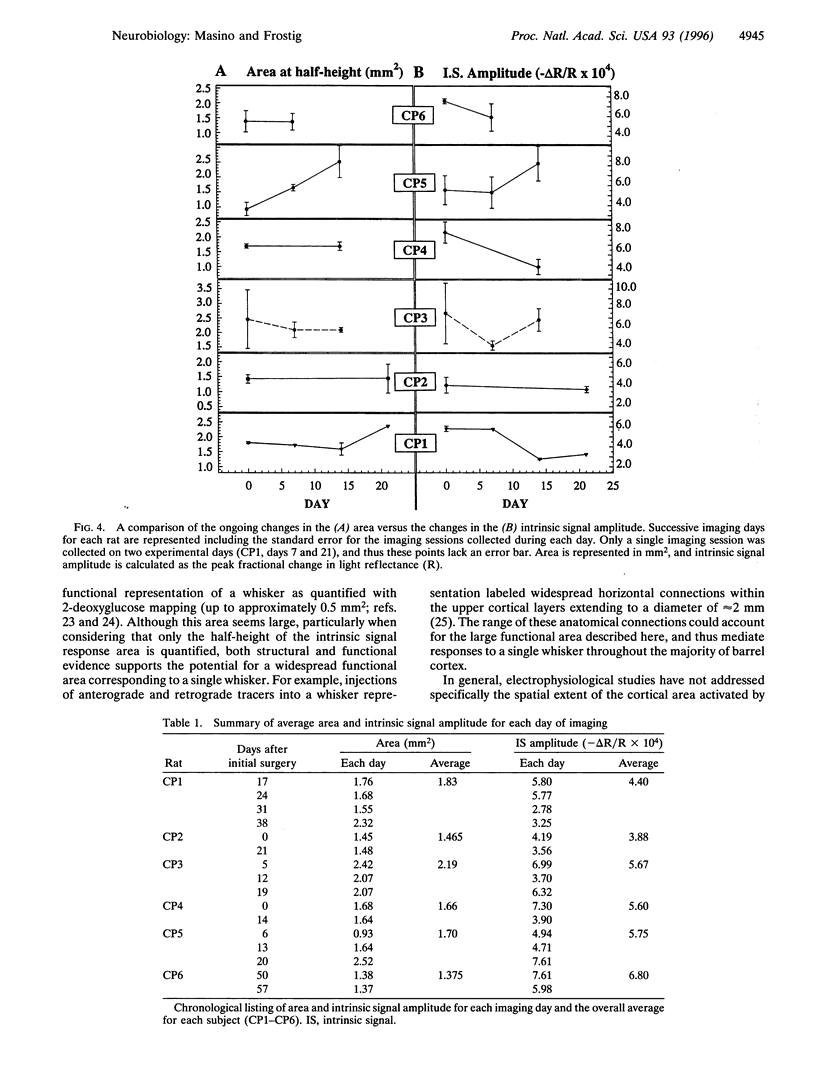
In this study, we implement chronic optical imaging of intrinsic signals in rat barrel cortex and repeatedly quantify the functional representation of a single whisker over time. The success of chronic imaging for more than 1 month enabled an evaluation of the normal dynamic range of this sensory representation. In individual animals for a period of several weeks, we found that: (i) the average spatial extent of the quantified functional representation of whisker C2 is surprisingly large--1.71 mm2 (area at half-height); (ii) the location of the functional representation is consistent; and (iii) there are ongoing but nonsystematic changes in spatiotemporal characteristics such as the size, shape, and response amplitude of the functional representation. These results support a modified description of the functional organization of barrel cortex, where although a precisely located module corresponds to a specific whisker, this module is dynamic, large, and overlaps considerably with the modules of many other whiskers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong-James M., Fox K., Das-Gupta A. Flow of excitation within rat barrel cortex on striking a single vibrissa. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Oct;68(4):1345–1358. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.4.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong-James M., Fox K. Spatiotemporal convergence and divergence in the rat S1 "barrel" cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Sep 8;263(2):265–281. doi: 10.1002/cne.902630209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Code R. A., Eslin D. E., Juliano S. L. Expansion of stimulus-evoked metabolic activity in monkey somatosensory cortex after peripheral denervation. Exp Brain Res. 1992;88(2):341–344. doi: 10.1007/BF02259109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Gilbert C. D. Long-range horizontal connections and their role in cortical reorganization revealed by optical recording of cat primary visual cortex. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):780–784. doi: 10.1038/375780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Lieke E., Frostig R. D., Gilbert C. D., Wiesel T. N. Functional architecture of cortex revealed by optical imaging of intrinsic signals. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):361–364. doi: 10.1038/324361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeflinger B. F., Bennett-Clarke C. A., Chiaia N. L., Killackey H. P., Rhoades R. W. Patterning of local intracortical projections within the vibrissae representation of rat primary somatosensory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1995 Apr 17;354(4):551–563. doi: 10.1002/cne.903540406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Ferrier lecture. Functional architecture of macaque monkey visual cortex. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Jul 28;198(1130):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins W. M., Merzenich M. M., Ochs M. T., Allard T., Guíc-Robles E. Functional reorganization of primary somatosensory cortex in adult owl monkeys after behaviorally controlled tactile stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jan;63(1):82–104. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey H. P. Anatomical evidence for cortical subdivisions based on vertically discrete thalamic projections from the ventral posterior nucleus to cortical barrels in the rat. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 15;51:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killackey H. P., Belford G., Ryugo R., Ryugo D. K. Anomalous organization of thalamocortical projections consequent to vibrissae removal in the newborn rat and mouse. Brain Res. 1976 Mar 12;104(2):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90623-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. S., Bonhoeffer T. Reverse occlusion leads to a precise restoration of orientation preference maps in visual cortex. Nature. 1994 Aug 4;370(6488):370–372. doi: 10.1038/370370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossut M., Hand P. J., Greenberg J., Hand C. L. Single vibrissal cortical column in SI cortex of rat and its alterations in neonatal and adult vibrissa-deafferented animals: a quantitative 2DG study. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Aug;60(2):829–852. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.2.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land P. W., Simons D. J. Cytochrome oxidase staining in the rat SmI barrel cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Aug 8;238(2):225–235. doi: 10.1002/cne.902380209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. E., Craik R. L., Hand P. J. The role of norepinephrine in adult rat somatosensory (SmI) cortical metabolism and plasticity. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 8;443(1-2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91620-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masino S. A., Kwon M. C., Dory Y., Frostig R. D. Characterization of functional organization within rat barrel cortex using intrinsic signal optical imaging through a thinned skull. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9998–10002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Nelson R. J., Kaas J. H., Stryker M. P., Jenkins W. M., Zook J. M., Cynader M. S., Schoppmann A. Variability in hand surface representations in areas 3b and 1 in adult owl and squirrel monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Apr 8;258(2):281–296. doi: 10.1002/cne.902580208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan S. M., Santori E. M., Toga A. W. Mapping functional activity in rodent cortex using optical intrinsic signals. Cereb Cortex. 1994 Mar-Apr;4(2):195–204. doi: 10.1093/cercor/4.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolelis M. A., Lin R. C., Woodward D. J., Chapin J. K. Dynamic and distributed properties of many-neuron ensembles in the ventral posterior medial thalamus of awake rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2212–2216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach H. S., Cohen L. B., Grinvald A. Optical mapping of electrical activity in rat somatosensory and visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1985 Jul;5(7):1886–1895. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-07-01886.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson B. E., Goldreich D. A new approach to optical imaging applied to rat barrel cortex. J Neurosci Methods. 1994 Sep;54(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(94)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recanzone G. H., Merzenich M. M., Jenkins W. M., Grajski K. A., Dinse H. R. Topographic reorganization of the hand representation in cortical area 3b owl monkeys trained in a frequency-discrimination task. J Neurophysiol. 1992 May;67(5):1031–1056. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.5.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons D. J. Response properties of vibrissa units in rat SI somatosensory neocortex. J Neurophysiol. 1978 May;41(3):798–820. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.3.798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryker M. P., Jenkins W. M., Merzenich M. M. Anesthetic state does not affect the map of the hand representation within area 3b somatosensory cortex in owl monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Apr 8;258(2):297–303. doi: 10.1002/cne.902580209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger N. M. Dynamic regulation of receptive fields and maps in the adult sensory cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1995;18:129–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.18.030195.001021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker C. Receptive fields of barrels in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Mar 15;166(2):173–189. doi: 10.1002/cne.901660205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker C. Receptive fields of barrels in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Mar 15;166(2):173–189. doi: 10.1002/cne.901660205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolsey T. A., Van der Loos H. The structural organization of layer IV in the somatosensory region (SI) of mouse cerebral cortex. The description of a cortical field composed of discrete cytoarchitectonic units. Brain Res. 1970 Jan 20;17(2):205–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xerri C., Stern J. M., Merzenich M. M. Alterations of the cortical representation of the rat ventrum induced by nursing behavior. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 2):1710–1721. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01710.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]