Abstract
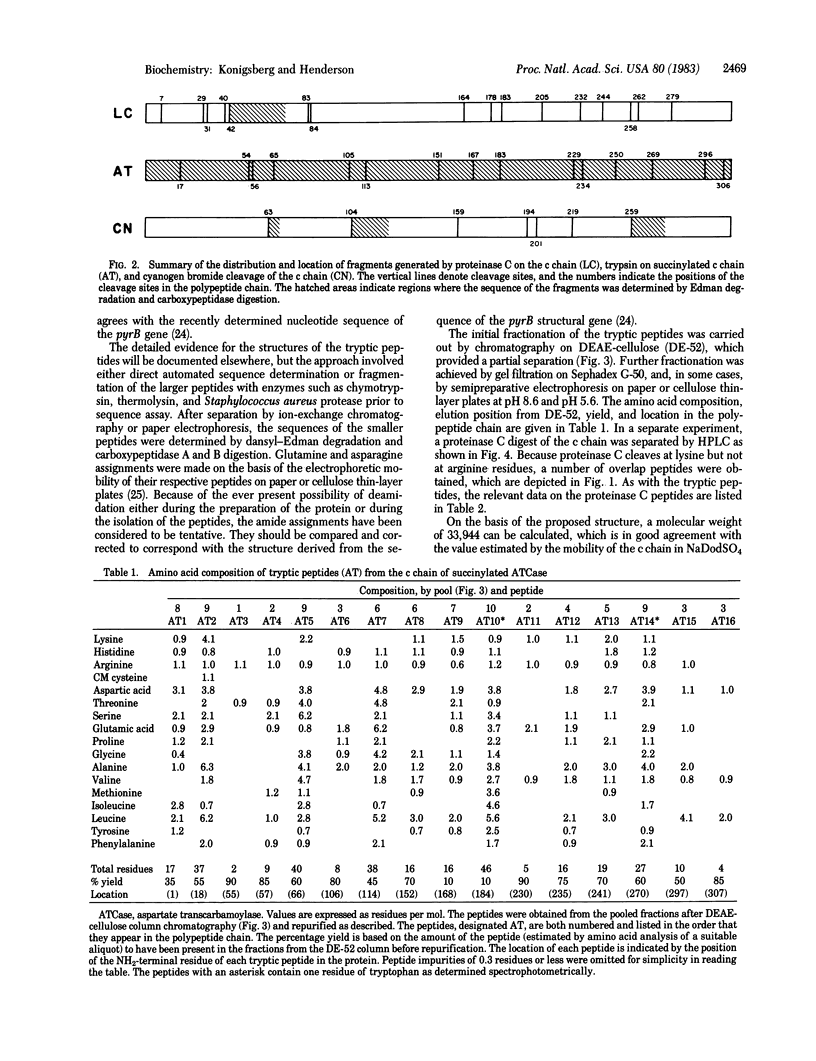
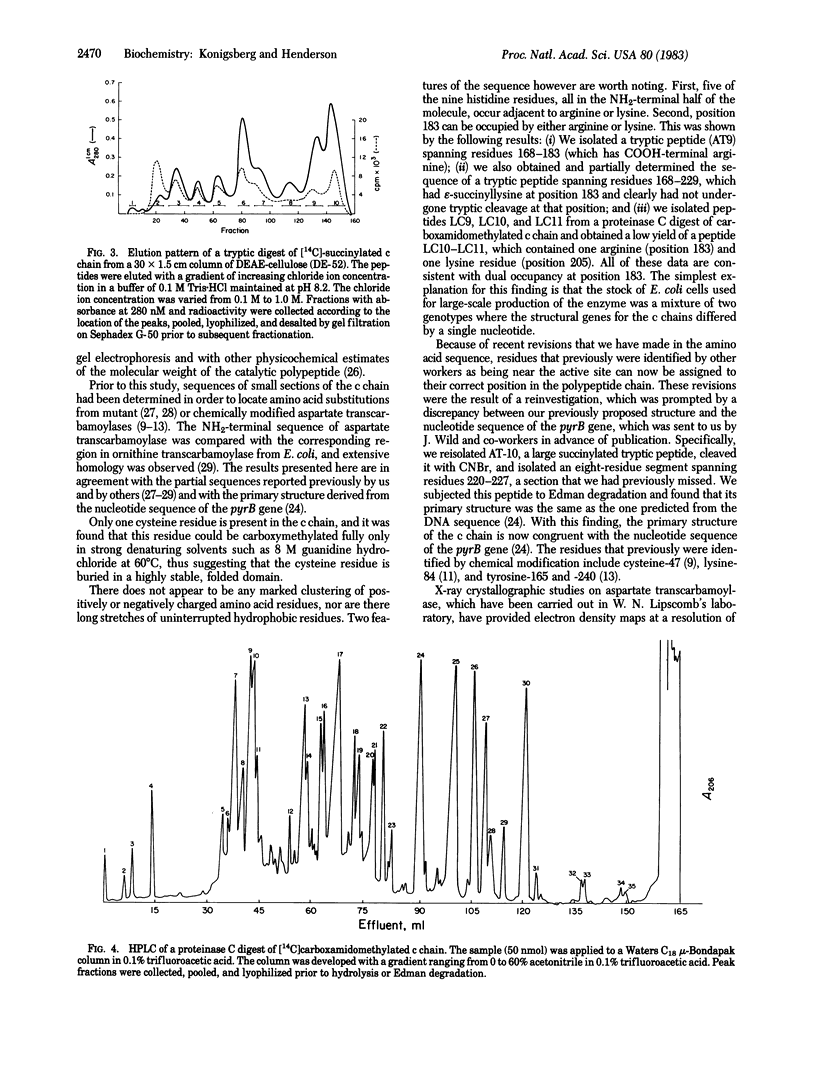
We propose a primary structure for the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamoylase (aspartate carbamoyltransferase; carbamoylphosphate: L-aspartate carbamoyltransferase, EC 2.1.3.2) from Escherichia coli based on amino acid sequences of fragments obtained by cyanogen bromide cleavage, by tryptic digestion of the succinylated polypeptide, and by chymotryptic and proteinase C digestion of the intact catalytic chain. The protein contains 310 amino acids and has a calculated molecular weight of 33,944. The negatively and positively charged residues are distributed uniformly, and there is no indication of charge clustering in the linear sequence.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benisek W. F. Reaction of the catalytic subunit of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase with permanganate ion, a reactive structural analogue of phosphate ion. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3151–3159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHART J. C., PARDEE A. B. The enzymology of control by feedback inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Holoubek H. The purification of aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli and separation of its protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2886–2892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Distinct subunits for the regulation and catalytic activity of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigot D., Glansdorff N., Legrain C., Piérard A., Stalon V., Konigsberg W., Caplier I., Strosberg A. D., Hervé G. Comparison of the N-terminal sequences of aspartate and ornithine carbamoyltransferases of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 1;81(1):28–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80920-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwell P., Jewett S. L., Stark G. R. Aspartate transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. The use of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate as a probe in the active site. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):5994–6001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honzatko R. B., Crawford J. L., Monaco H. L., Ladner J. E., Ewards B. F., Evans D. R., Warren S. G., Wiley D. C., Ladner R. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal and molecular structures of native and CTP-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):219–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honzatko R. B., Monaco H. L., Lipscomb W. N. A 3.0-A resolution study of nucleotide complexes with aspartate carbamoyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5105–5109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. A., Roof W. D., Foltermann K. F., O'Donovan G. A., Bencini D. A., Wild J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the structural gene (pyrB) that encodes the catalytic polypeptide of aspartate transcarbamoylase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2462–2466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz E. R., Lipscomb W. N. An essential residue at the active site of aspartate transcarbamylase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2688–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempe T. D., Stark G. R. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, a fluorescent probe in the active site of aspartate transcarbamylase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6861–6869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladner J. E., Kitchell J. P., Honzatko R. B., Ke H. M., Volz K. W., Kalb A. J., Ladner R. C., Lipscomb W. N. Gross quaternary changes in aspartate carbamoyltransferase are induced by the binding of N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate: A 3.5-A resolution study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3125–3128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritzen A. M., Landfear S. M., Lipscomb W. N. Inactivation of the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamylase by nitration with tetranitromethane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):602–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A., Pigiet V., Schachman H. K. Hybridization of native and chemically modified enzymes. 3. The catalytic subunits of aspartate transcarbamylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco H. L., Crawford J. L., Lipscomb W. N. Three-dimensional structures of aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli and of its complex with cytidine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5276–5280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanaman T. C., Stark G. R. A study of the sulfhydryl groups of the catalytic subunit of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase. The use of enzyme--5-thio-2-nitrobenzoate mixed disulfides as intermediates in modifying enzyme sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3565–3573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall K. A., Flatgaard J. E., Schachman H. K., Gibbons I. Purification and characterization of a mutant aspartate transcarbamoylase lacking enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11910–11916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall K. A., Schachman H. K. Primary structure and properties of an inactive mutant aspartate transcarbamoylase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11917–11926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. Aspartate transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. Characterization of the polypeptide chains by molecular weight, amino acid composition, and amino-terminal residues. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):543–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. New structural model of E. coli aspartate transcarbamylase and the amino-acid sequence of the regulatory polypeptide chain. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1116–1119. doi: 10.1038/2181116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystallographic determination of symmetry of aspartate transcarbamylase. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1119–1121. doi: 10.1038/2181119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., LoPresti M. B., Setoguchi M., Konigsberg W. H. Amino acid sequence of the T4 DNA helix-destabilizing protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4614–4617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


