Abstract
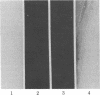
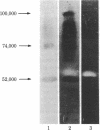
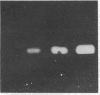
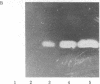
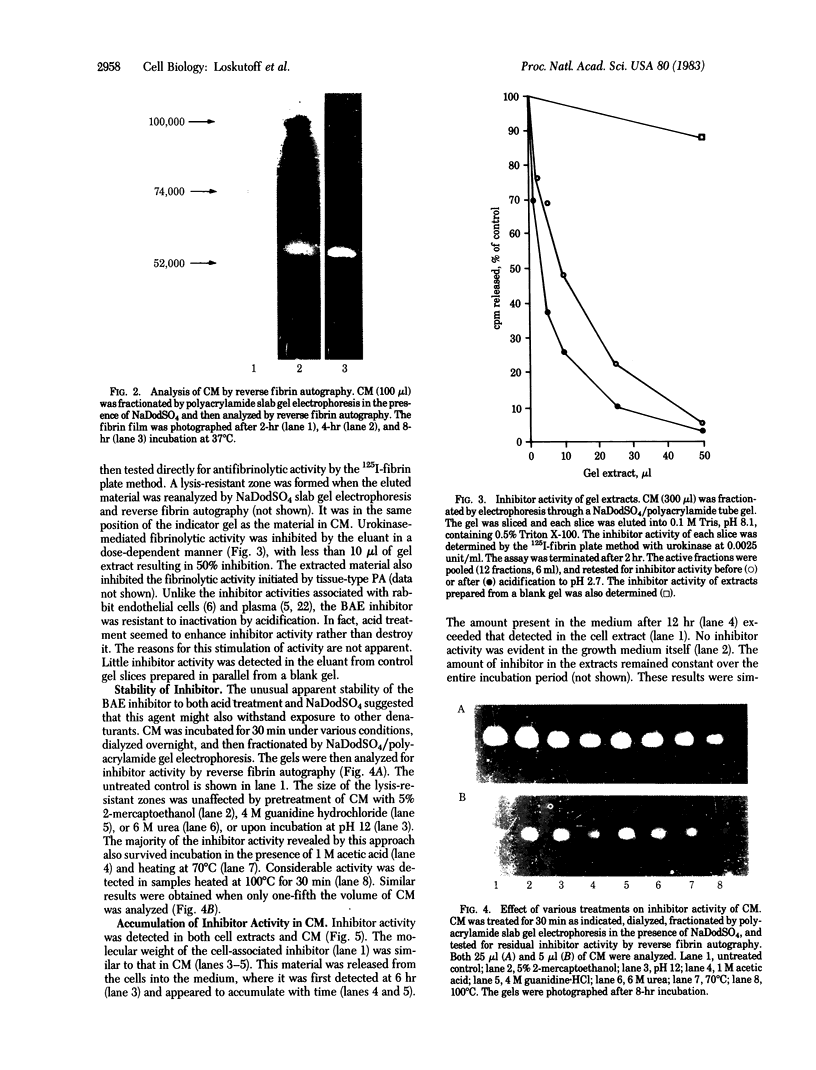
Fibrin/agar films were prepared and used to detect plasminogen activators produced by cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells (fibrin autography). One preparation of fibrin underwent spontaneous lysis upon incubation at 37 degrees C. This lysis was prevented by antibodies to tissue-type plasminogen activator but not by antibodies to urokinase. Conditioned medium from the confluent endothelial cells was fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of NaDodSO4. The gels were analyzed on indicator films prepared with the spontaneously lysing fibrin (reverse fibrin autography). Unexpectedly, as the opaque fibrin film cleared, a distinct lysis-resistant zone appeared in the indicator gel at a region corresponding to Mr 55,000. Experiments were devised to determine whether the lysis-resistant zone in the indicator film reflected the presence of a cellular inhibitor in the polyacrylamide gel. The corresponding region was excised from a polyacrylamide gel, extracted with buffer, and tested directly for antifibrinolytic activity by the 125I-labeled fibrin plate method. Urokinase-mediated fibrinolytic activity was inhibited by the gel extract in a dose-dependent manner indicating the presence of such an inhibitor. Inhibitor activity was detected in Triton X-100 extracts of washed monolayers and in conditioned medium, where it accumulated with time. The endothelial cell inhibitor not only survived exposure to NaDodSO4 but also was active after incubation at pH 12 or treatment with 5% (vol/vol) 2-mercaptoethanol, 6 M urea, 4 M guanidine hydrochloride, or 1 M acetic acid. Considerable activity also remained after heating at 100 degrees C for 30 min. These results indicate that cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells synthesize and secrete a previously undetected, unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor of Mr 55,000. Reverse fibrin autography offers a convenient approach for studying such molecules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barouski-Miller P. A., Gelehrter T. D. Paradoxical effects of glucocorticoids on regulation of plasminogen activator activity of rat hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2319–2322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Scheinbuks J., Radek J., Osikowicz G., Feder S., Quarfoot A. J. Immunological identification and comparison of plasminogen activator forms in cultured normal human endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Thromb Res. 1981 Dec 1;24(5-6):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Vavrin Z., Hibbs J. B., Jr Macrophage fibrinolytic activity: identification of two pathways of plasmin formation by intact cells and of a plasminogen activator inhibitor. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Acs G. Purification and characterization of a cellular fibrinolytic factor associated with oncogenic transformation: the plasminogen activator from SV-40-transformed hamster cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 27;340(3):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90279-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosne A. M., Dupuy E., Bodevin E. Production of a fibrinolytic inhibitor by cultured endothelial cells derived from human umbilical vein. Thromb Res. 1978 Mar;12(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnard F., Dupuy E., Dosne A. M., Bodevin E. Partial characterization of a fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by cultured endothelial cells derived from human umbilical vein. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):128–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laug W. E. Secretion of plasminogen activators by cultured bovine endothelial cells: partial purification, characterization and evidence for multiple forms. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Jun 30;45(3):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laug W. E., Tokes Z. A., Benedict W. F., Sorgente N. Anchorage independent growth and plasminogen activator production by bovine endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):281–293. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Comparative studies of the fibrinolytic activity of cultured vascular cells. Thromb Res. 1979;15(5-6):869–878. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Cultured bovine endothelial cells produce both urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):631–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of plasminogen activator production by cultured endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;401:184–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Serum-mediated suppression of cell-associated plasminogen activator activity in cultured endothelial cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):701–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Interaction of plasminogen activators and inhibitors with plasminogen and fibrin. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1982 Jan;8(1):2–10. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Edgington T. E. Synthesis of a fibrinolytic activator and inhibitor by endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Edgington T. S. An inhibitor of plasminogen activator in rabbit endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4142–4145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J. Effect of thrombin on the fibrinolytic activity of cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):329–332. doi: 10.1172/JCI109457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J. Effects of acidified fetal bovine serum on the fibrinolytic activity and growth of cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Sep;96(3):361–369. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040960312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Jaffe E., Rifkin D. B. Tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate stimulates latent collagenase production by cultured human endothelial cells. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90620-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins D. E., Bazer F. W., Roberts R. M. Secretion of a progesterone-induced inhibitor of plasminogen activator by the porcine uterus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):865–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roblin R. O., Young P. L., Bell T. E. Concomitant secretion by transformed SVWI38-VA13-2RA cells of plasminogen activator(s) and substance (s) which prevent their detection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 15;82(1):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90591-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlich S. T., Rifkin D. B. Isolation of the major serine protease inhibitor from the 5-day serum-free conditioned medium of human embryonic lung cells and demonstration that it is fetuin. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Oct;109(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharoni Y., Topal M. C., Tuttle P. R., Berger H., Jr A comparison of plasminogen activators derived from rat plasma, primary rat hepatocytes and isolated perfused rat liver. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):166–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S., Glas-Greenwalt P., Astrup T. Differences in the binding to fibrin of urokinase and tissue plasminogen activator. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Aug 31;28(1):65–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. L., Becker M. L., Hoal E. G., Dowdle E. B. Molecular species of plasminogen activators secreted by normal and neoplastic human cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):933–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]