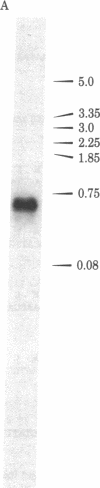
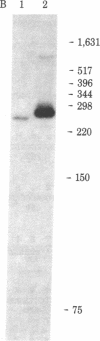
Abstract
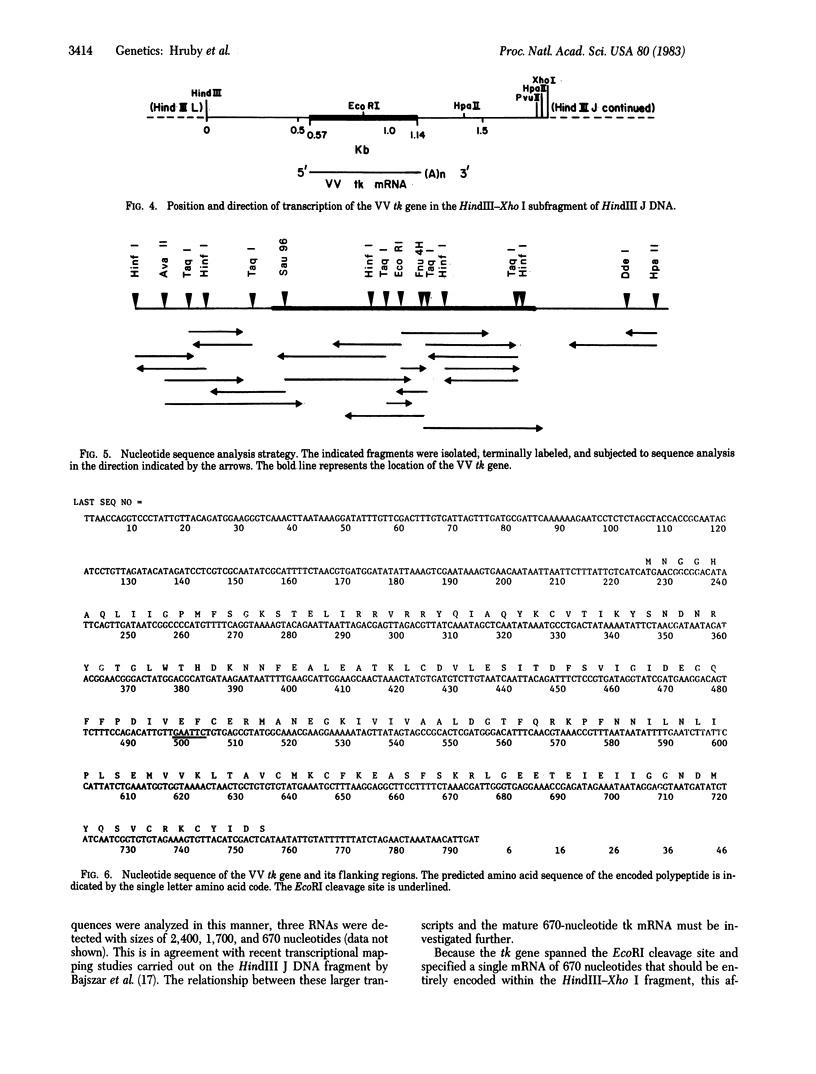
The thymidine kinase (ATP:thymidine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.21) gene of vaccinia virus has previously been mapped near the middle of the viral DNA, within the 4.85-kilobase HindIII J fragment, and shown to encode a Mr 19,000 polypeptide [Hruby, D. E. & Ball, L. A. (1982) J. Virol. 43, 403-409]. To locate the gene more precisely and to determine the structure of the basic transcriptional unit, the positions of cleavage sites for several restriction endonucleases were mapped within the HindIII J DNA fragment. Four appropriate subfragments of HindIII J DNA were inserted into plasmid pBR322 derivatives and cloned in Escherichia coli. These recombinant plasmid DNAs were tested for their ability to inhibit the cell-free synthesis of active thymidine kinase and to retain the mRNA for this enzyme when immobilized on nitrocellulose filters. The data showed that the gene spanned an EcoRI cleavage site that lies 850 base pairs from the left-hand end of the HindIII J fragment (the HindIII L-J boundary). Because hybridization of vaccinia virus DNA to partially purified thymidine kinase mRNA detected only a single 670-nucleotide RNA species capable of hybridizing to this region of the genome, nuclease S1 mapping experiments were carried out with thymidine kinase mRNA to protect DNA fragments that were terminally labeled at this EcoRI site. The results indicated that the gene extended from about 550 to 1,150 base pairs from the left end of HindIII J, was transcribed in a rightward direction, and contained no intervening sequences. Hence, a 1.04-kilobase Ava II-Hpa II restriction fragment containing this region of DNA was isolated and subjected to nucleotide sequence analysis. An examination of this nucleotide sequence revealed the presence of an open reading frame of 531 nucleotides capable of encoding a protein of 177 amino acids with a Mr of 20,077.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajszár G., Wittek R., Weir J. P., Moss B. Vaccinia virus thymidine kinase and neighboring genes: mRNAs and polypeptides of wild-type virus and putative nonsense mutants. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):62–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.62-72.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFilippes F. M. Restriction enzyme mapping of vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):136–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.136-149.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardies S. C., Patient R. K., Klein R. D., Ho F., Reznikoff W. S., Wells R. D. Construction and mapping of recombinant plasmids used for the preparation of DNA fragments containing the Escherichia coli lactose operator and promoter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5527–5534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield V., Boyer H. W., Yanofsky C., Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Plasmid ColEl as a molecular vehicle for cloning and amplification of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Cell-free synthesis of enzymatically active vaccinia virus thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):594–601. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Control of expression of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):456–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.456-464.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Mapping and identification of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):403–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.403-409.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isle H. B., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Cell-free translation of early and late mRNAs selected by hybridization to cloned DNA fragments derived from the left 14 million to 72 million daltons of the vaccinia virus genome. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Joklik W. K. Poly (A) sequences of vaccinia virus messenger RNA: nature, mode of addition and function during translation in vitra and in vivo. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Gershowitz A., Moss B. Complete nucleotide sequences of two adjacent early vaccinia virus genes located within the inverted terminal repetition. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):637–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.637-646.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. A paranuclear extract contains a unique set of viral transcripts late in SV40 infection. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Bajszár G., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene by marker rescue and by cell-free translation of selected mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R. C., Wu R. BK virus DNA sequence coding for the amino-terminus of the T-antigen. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]