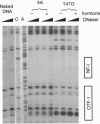
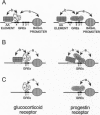
Abstract
We have previously characterized a regulatory element located between -294 and -200 within the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) long terminal repeat (LTR). This element termed AA element cooperates with the glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) for glucocorticoid activation. Here we show that in a MMTV LTR wild type context, the deletion of this element significantly reduces both glucocorticoid and progestin activation of the promoter. Deletion of the two most distal GREs forces the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and the progestin receptor (PR) to bind the same response elements and results in a dramatic decrease in the inducibility of the MMTV promoter by the two hormones. The simultaneous deletion of the two distal GREs and of the AA element abolishes completely the glucocorticoid-induced activation of the promoter. In contrast it restores a significant level of progestin-induced activation. This different effect of the double deletion on glucocorticoid- and progestin-induced MMTV promoter activation is not cell specific because it is also observed, and is even stronger, when either GR or PR is expressed in the same cell line (NIH 3T3). This is the first description of a mutated MMTV promoter that, although retaining GREs, is activated by progestins and not by glucocorticoids. This suggests a different functional cooperation between protein(s) interacting with the AA element and GR or PR. Cotransfections with constructs containing wild-type or mutated MMTV LTR with either PR lacking its C-terminal domain or GR/PR chimeras in which the N-terminal domains have been exchanged demonstrate that the N-terminal domains of the receptors specify the different behavior of GR and PR regarding the AA element.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler A. J., Danielsen M., Robins D. M. Androgen-specific gene activation via a consensus glucocorticoid response element is determined by interaction with nonreceptor factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11660–11663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler A. J., Scheller A., Robins D. M. The stringency and magnitude of androgen-specific gene activation are combinatorial functions of receptor and nonreceptor binding site sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6326–6335. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., Glaser T. M., Handelin B. L., Housman D. E., Evans R. M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E., Lasnizki I., Robel P. Metabolism of testosterone and action of metabolites on prostate glands grown in organ culture. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1155–1156. doi: 10.1038/2191155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Beato M. Nuclear factor I acts as a transcription factor on the MMTV promoter but competes with steroid hormone receptors for DNA binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Miksicek R., Schütz G., Arnemann J., Beato M. The hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumour virus mediates progesterone induction. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2237–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Skroch P., Weinmann J., Butkeraitis P., Ponta H. DNA sequences outside the receptor-binding sites differently modulate the responsiveness of the mouse mammary tumour virus promoter to various steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Weinmann J. Mineralocorticoid regulation of transcription of transfected mouse mammary tumor virus DNA in cultured kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):2119–2125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Arnemann J., Slater E., Brüller H. J., Gross B., Beato M. Differential gene activation by glucocorticoids and progestins through the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbre P., Page M., King R. J. Androgen regulation by the long terminal repeat of mouse mammary tumor virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2847–2854. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Pearce P. T., Smith R., Smith A. I. Mineralocorticoid action: target tissue specificity is enzyme, not receptor, mediated. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):583–585. doi: 10.1126/science.2845584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Sola B., Couette B., Richard-Foy H. Cooperation between structural elements in hormono-regulated transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1563–1569. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowland P. L., Buetti E. Mutations in the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus differentially affect the response to progestins, androgens, and glucocorticoids. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3999–4008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzburg W. H., Salmons B. Factors controlling the expression of mouse mammary tumour virus. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):625–632. doi: 10.1042/bj2830625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. L., Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of the Ha-MuSV p21 gene conferred by sequences from mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalff M., Gross B., Beato M. Progesterone receptor stimulates transcription of mouse mammary tumour virus in a cell-free system. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):360–362. doi: 10.1038/344360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Mulligan R., Berg P., Ringold G. Glucocorticoids regulate expression of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA in mouse mammary tumour virus chimaeric plasmids. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):228–232. doi: 10.1038/294228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. E., Pornon A., Ji J. W., Bocquel M. T., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Agonistic and antagonistic activities of RU486 on the functions of the human progesterone receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3923–3932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen V. T., Morange M., Bensaude O. Firefly luciferase luminescence assays using scintillation counters for quantitation in transfected mammalian cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jun;171(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90505-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce D., Yamamoto K. R. Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor activities distinguished by nonreceptor factors at a composite response element. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1161–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.8382376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Boshart M., Klock G., Stewart F., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid- and progesterone-specific effects are determined by differential expression of the respective hormone receptors. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):629–632. doi: 10.1038/339629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Janich S., Scheidereit C., Renkawitz R., Schütz G., Beato M. Glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors bind to the same sites in two hormonally regulated promoters. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):706–709. doi: 10.1038/313706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]