Abstract
Objective To examine whether an association exists between maternal dietary patterns and risk of preterm delivery.
Design Prospective cohort study.
Setting Norway, between 2002 and 2008.
Participants 66 000 pregnant women (singletons, answered food frequency questionnaire, no missing information about parity or previously preterm delivery, pregnancy duration between 22+0 and 41+6 gestational weeks, no diabetes, first enrolment pregnancy).
Main outcome measure Hazard ratio for preterm delivery according to level of adherence to three distinct dietary patterns interpreted as “prudent” (for example, vegetables, fruits, oils, water as beverage, whole grain cereals, fibre rich bread), “Western” (salty and sweet snacks, white bread, desserts, processed meat products), and “traditional” (potatoes, fish).
Results After adjustment for covariates, high scores on the “prudent” pattern were associated with significantly reduced risk of preterm delivery hazard ratio for the highest versus the lowest third (0.88, 95% confidence interval 0.80 to 0.97). The prudent pattern was also associated with a significantly lower risk of late and spontaneous preterm delivery. No independent association with preterm delivery was found for the “Western” pattern. The “traditional” pattern was associated with reduced risk of preterm delivery for the highest versus the lowest third (hazard ratio 0.91, 0.83 to 0.99).
Conclusion This study showed that women adhering to a “prudent” or a “traditional” dietary pattern during pregnancy were at lower risk of preterm delivery compared with other women. Although these findings cannot establish causality, they support dietary advice to pregnant women to eat a balanced diet including vegetables, fruit, whole grains, and fish and to drink water. Our results indicate that increasing the intake of foods associated with a prudent dietary pattern is more important than totally excluding processed food, fast food, junk food, and snacks.
Introduction
Preterm delivery, defined as spontaneous or iatrogenic delivery before gestational week 37,1 is associated with significant short term and long term neonatal morbidity and almost 75% of all neonatal deaths.2 3 4 In the Nordic countries, the prevalence is quite low at about 6%,5 whereas the United States, for instance, has a prevalence of about 12%.6 Several potential risk factors have been identified,3 but in most cases of preterm delivery the cause is unknown.7
Maternal dietary habits can directly affect the growing fetus,8 and awareness has increased during recent years that maternal diet may influence the outcome of pregnancy as well as the long term health of the child.9 10 Several studies indicate associations between maternal diet and preterm delivery.11 12 13 14 15
The habitual diet contains thousands of nutrients and other bioactive substances acting together, making studying the potential influence of single substances or food items in relation to different phenotypes, such as preterm delivery, difficult. Many substances are found in the same food, and foods are not consumed independently of each other.
The study of dietary patterns offers a broader view of food and nutrient consumption and overcomes the methodological limitations related to the study of single nutrients or foods.16 17 These patterns reflect overall dietary behaviour and can be characterised on the basis of a priori knowledge (hypothesis oriented approach) or by the use of data driven techniques (empirically derived dietary patterns).18 Dietary patterns are population specific and are influenced by sociocultural factors and food availability.19 20 21
Dietary patterns in pregnant women have been described in several populations,22 23 24 25 but few studies have examined the role of dietary patterns in pregnancy outcomes.26 The aim of this study was therefore to examine the association between maternal dietary patterns and the risk of preterm delivery, including subanalysis of spontaneous and iatrogenic preterm delivery and preterm delivery at early, moderate, and late preterm gestations, in a large prospective cohort of pregnant women.
Methods
Population and study design
The dataset in this study is part of the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study, a population based pregnancy cohort conducted by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health.27 In the overall study, participants were recruited from all over Norway during 1999-2008, and 40.6% (108 264) of the women invited consented to participate. Women were recruited by postal invitation in connection with their first routine ultrasound examination at gestational week 17-18. The cohort now includes 114 500 children, 95 200 mothers, and 75 200 fathers. Follow-up is done by questionnaires at regular intervals and by linkage to national health registries.27 28 The data included in this study were from two questionnaires answered at gestational weeks 15 (questionnaire 1) and 17-22 (questionnaire 2). Questionnaire 1 was a general questionnaire covering lifestyle, background, illness, and health related factors. Questionnaire 2 was a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire, in which women reported their dietary habits from the start of the pregnancy. Pregnancy and birth outcomes recorded in the Medical Birth Registry of Norway were linked to the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study database.28 All participants gave written consent.
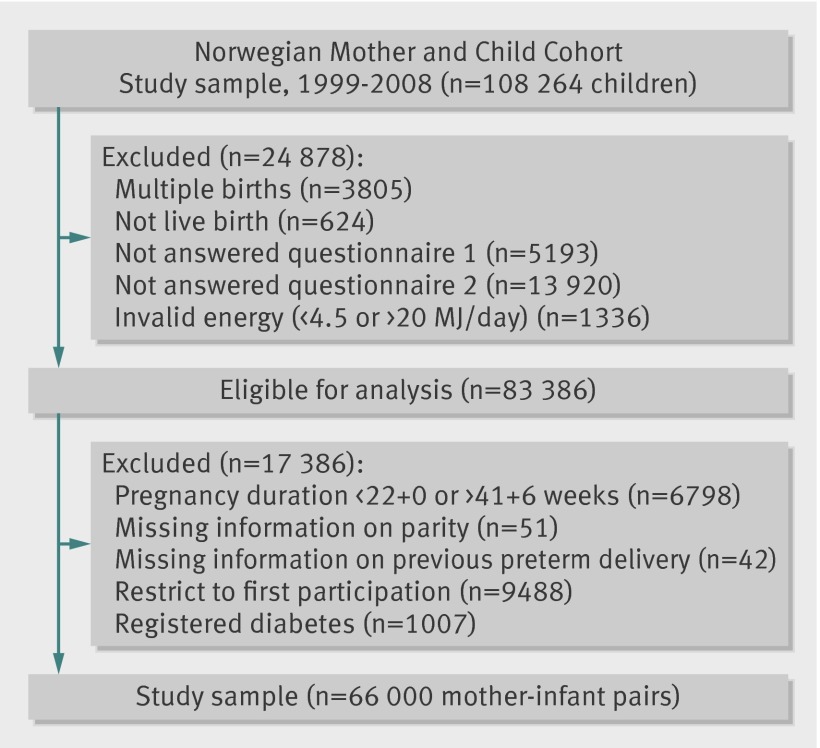
We used the quality validated data files released for research in 2010 (version 5) in this study. To be included, participants had to have delivered a live, singleton baby and to have answered the first general questionnaire as well as the food frequency questionnaire, and had a valid energy intake between 4.5 and 20 MJ/day, resulting in 83 386 women. We excluded women with a duration of pregnancy less than 22+0 or more than 41+6 gestational weeks, as well as those with missing information about parity or previously preterm delivery. To avoid the use of multiple dependent observations, we included women enrolled in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study more than once only with their first participation. Finally, we excluded women with diabetes mellitus on the basis of an a priori decision, because dietary modification is a vital part of the management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes as well as gestational diabetes. This resulted in a total study sample of 66 000 women (fig 1). The prevalence of preterm delivery was higher in the study population than in the 17 386 excluded pregnancies (5.3% (3505 cases) v 3.8% (660 cases)). Women in the study sample were younger (30.1 v 30.9 years) and more often pregnant for the first time (51.8% (34 217) v 25% (4347)) than were those excluded.
Fig 1 Flow chart showing selection of study participants from Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
Dietary information
Data from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study food frequency questionnaire (www.fhi.no/dokumenter/011fbd699d.pdf) were collected from February 2002 onwards. The study food frequency questionnaire is a validated semi-quantitative questionnaire designed to compile information on dietary habits during the first four to five months of pregnancy. 29 30 The food frequency questionnaire was validated in a subsample of cohort participants, showing that relative to a dietary reference method and several biological markers, it produces a realistic estimate of the habitual diet and is a valid tool for ranking pregnant women according to high and low intakes of energy, nutrients, and foods.31 32 The food frequency questionnaire was read optically. We converted food frequencies into daily intakes (g/day) and used FoodCalc to calculate nutrient and energy intakes.33 The food frequency questionnaire covered 255 food and beverage items. We compiled these items into 58 non-overlapping food groups, based on nutrients, common characteristics, or culinary use, as described in more detail previously.24 Dietary energy density is the ratio of energy (kcal) to weight (g); this ratio remains constant regardless of the amount consumed. We calculated a variable denoting energy density by dividing each woman’s daily energy intake by the weight of all foods consumed, excluding all beverages.34
Extraction of dietary patterns
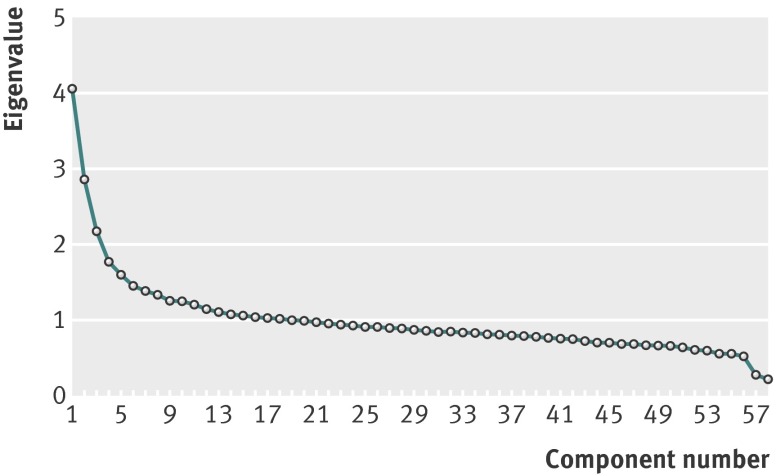
We used principal component analysis to extract dietary patterns. This is a data driven technique that reduces the dimension of the data and groups correlated variables, in this case the food intake variables, to form new linear factors or components. The components (dietary patterns) derived by principal component analysis reflect the combinations of foods consumed by individual participants. The coefficients defining the components are called factor loadings and describe the correlation between each food variable and the components. (table 1) As described above, we aggregated food intakes from the food frequency questionnaire into 58 non-overlapping food groups and standardised them to reduce the influence of food intakes with large variances at the expense of those with minor variances. The number of components retained was based on interpretation of the factor loading matrix after orthogonal (varimax) rotation and a scree plot (fig 2) that shows the proportion of the variance in total consumption of the food variables.18 We tested the analysis with the Bartlett test of sphericity and Kaiser-Mayer-Olkin tests. We considered food and drink items with loadings of 0.25 or higher on a factor to be important for the interpretability of each pattern.
Table 1.
Structures of three orthogonally rotated factors identified by principal component analysis in 66 000 pregnant women in Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
| Dietary pattern | Food | Factor loadings coefficient* | Cumulative variance explained (%)† |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Prudent” | Raw vegetables | 0.60 | 7 |
| Cooked vegetables | 0.57 | ||
| Salad | 0.56 | ||
| Onion, leek, garlic | 0.55 | ||
| Cooking oil‡ | 0.50 | ||
| Fruit, berries | 0.48 | ||
| Mushrooms | 0.45 | ||
| Olive oil | 0.43 | ||
| Dried fruit | 0.35 | ||
| Rice | 0.34 | ||
| Nuts | 0.33 | ||
| Herbal tea | 0.32 | ||
| Water as beverage | 0.32 | ||
| Whole grain cereals | 0.32 | ||
| Yoghurt§ | 0.32 | ||
| Poultry | 0.27 | ||
| Fibre rich bread | 0.25 | ||
| White bread | −0.27 | ||
| Pizza, tacos | −0.27 | ||
| Processed meat products¶ | −0.43 | ||
| “Western” | Salty snacks | 0.49 | 12 |
| Chocolates and sweets | 0.49 | ||
| French fries | 0.44 | ||
| Cakes | 0.41 | ||
| White bread | 0.38 | ||
| Ketchup | 0.38 | ||
| Dairy desserts | 0.38 | ||
| Sugar sweetened drinks | 0.36 | ||
| Buns | 0.33 | ||
| Gravy | 0.32 | ||
| Mayonnaise spreads | 0.31 | ||
| Processed meat products¶ | 0.29 | ||
| Waffles, pancakes | 0.28 | ||
| Cookies | 0.27 | ||
| Pasta | 0.25 | ||
| Lean fish | −0.27 | ||
| Fibre rich bread | −0.25 | ||
| “Traditional” | Boiled potatoes | 0.64 | 16 |
| Fish products | 0.58 | ||
| Gravy | 0.44 | ||
| Lean fish | 0.43 | ||
| Margarine | 0.31 | ||
| Rice pudding | 0.29 | ||
| Low fat milk | 0.27 | ||
| Cooked vegetables | 0.25 | ||
| Pizza, tacos | −0.30 | ||
| Poultry | −0.42 |
*Factor loadings are correlation coefficients (r) between input variables (food intakes) and extracted factors. Food groups are sorted by size of loading coefficients. Food groups with factor loadings between 0.25 and −0.25 are not listed. Food items can be included in more than one pattern.
†Percentage of variance in total food intake explained by patterns.
‡Denotes soybean oil, canola oil, corn oil, and sunflower oil.
§Denotes all yoghurt, including probiotic yoghurt and cured milk enriched with Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5, Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12, and/or Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.
¶Denote hot dogs, hamburgers, and sausages.
Fig 2 Scree plot for identification of dietary patterns (components) by principal component analysis. Food intakes (g/day) were aggregated into 58 food groups and used as input variables. Factors considered appropriate for patterns shown in table 1 are the three factors with eigenvalues >2
We named the new linear components after the nature of the input variables with the highest factor loadings. We assigned participants factor scores for each of the dietary patterns (dietary patterns scores). We derived these factor scores by multiplying factor loadings by the corresponding standardised intake value of each food item and adding all these items. The mean factor score for each pattern is zero. Positive factor scores indicate higher consumption of foods and drinks in that pattern, and negative factor scores indicate low consumption. We divided each extracted dietary pattern into thirds, with the lowest third as the reference.
Preterm delivery
The primary outcome was preterm delivery, defined as delivery between gestational week 22+0 and 36+6. We calculated gestational age on the basis of ultrasound measurements at 17-18 weeks of gestation in 64 846 cases. In 1154 cases, information about gestational length from ultrasound was missing, so we calculated it from last menstruation period. Information about gestational age at birth came from the Medical Birth Registry of Norway.28 We divided preterm delivery into spontaneous or iatrogenic, defining iatrogenic preterm delivery as induced or caesarean delivery, on maternal or fetal indications. We also divided preterm delivery into late (34+0 to 36+6 weeks), moderately (32+0 to 33+6 weeks), and early preterm (22+0 to 31+6 weeks).
Covariates
We selected 10 covariates for their known association with preterm delivery. Information about maternal age and previous preterm delivery came from the Medical Birth Registry of Norway. We treated maternal age as a continuous variable, except in the case of descriptive statistics, for which we divided it into four groups (<20 years, 20-29 years, 30-39 years, and ≥40 years). We analysed history of previous preterm delivery as a dichotomous variable (yes/no). In questionnaire 1, women reported their pre-pregnancy weight and height, from which we calculated body mass index. We included only women who reported weight in the range 35-180 kg and height above 1.40 m. We used body mass index as a categorical variable, divided into four categories (<18.5, 18.5-24.9, 25-29.9, and ≥30). We analysed height as categorical data and divided into thirds (<1.66 m, 1.66-1.70 m, and ≥1.71 m). Information about marital status came from questionnaire 1; we categorised it as either living alone or cohabiting. Information about parity came from questionnaire 1 and from the Medical Birth Registry of Norway. We divided parity into two categories (nulliparous or parous). We categorised smoking as non-smoker, occasional smoker, or daily smoker on the basis of women’s answers in questionnaire 1. We divided maternal education into three categories (<13 years, 13-16 years, and ≥17 years), regardless of the kind of education. We used total energy intake (kJ) as a continuous variable but present it as quarters in table 2. We divided household income into three categories (both partners <300 000 Norwegian Krone (£29 648; €35 660; $48 406) per year, participant or partner ≥300 000 Norwegian Krone per year, and both partners ≥300 000 Norwegian Krone per year) on the basis of information provided in questionnaire 1 and analysed it as categorical data.
Table 2.
Dietary pattern scores*, according to maternal characteristics, in 66 000 pregnant women in Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
| Characteristics | No (%) | Dietary pattern | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Prudent” | “Western” | “Traditional” | ||
| Maternal age at delivery (years) | ||||
| <20 | 641 (1.0) | −0.66 | 0.57 | 0.26 |
| 20-29 | 29 351 (44.5) | −0.17 | 0.10 | −0.05 |
| 30-39 | 34 664 (52.5) | 0.14 | −0.09 | 0.02 |
| ≥40 | 1344 (2.0) | 0.47 | −0.31 | 0.31 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Maternal education (years) | ||||
| <13 | 20 472 (31.0) | −0.26 | 0.27 | 0.19 |
| 13-16 | 27 423 (41.6) | −0.02 | −0.04 | −0.02 |
| ≥17 | 16 704 (25.3) | 0.35 | −0.27 | −0.20 |
| Missing information | 1401 (2.1) | 0.00 | 0.02 | −0.03 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| History of preterm delivery | ||||
| No | 63 667 (96.5) | 0.00 | −0.01 | −0.01 |
| Yes | 2333 (3.5) | −0.08 | 0.14 | 0.28 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Parity | ||||
| Nulliparous | 34 217 (51.8) | 0.03 | −0.08 | −0.22 |
| Parous | 31 783 (48.2) | −0.03 | 0.09 | 0.24 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Pre-pregnancy body mass index | ||||
| <18.5 | 2029 (3.1) | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.08 |
| 18.5-24.9 | 42 704 (64.7) | 0.08 | −0.05 | −0.01 |
| 25-29.9 | 13 754 (20.8) | −0.12 | 0.07 | 0.00 |
| ≥30 | 5824 (8.8) | −0.25 | 0.12 | −0.01 |
| Missing information | 1689 (2.6) | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.11 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Smoking during pregnancy | ||||
| No | 60 321 (91.4) | 0.03 | −0.05 | −0.03 |
| Occasional | 1748 (2.6) | −0.14 | 0.40 | 0.17 |
| Daily | 3553 (5.4) | −0.42 | 0.57 | 0.34 |
| Missing information | 378 (0.6) | 0.10 | −0.02 | 0.06 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Household income | ||||
| Both <300 000‡ | 18 352 (27.8) | −0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| Either ≥300 000§ | 27 051 (41.0) | −0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Both ≥300,000¶ | 18 698 (28.3) | 0.23 | −0.21 | −0.24 |
| Missing information | 1899 (2.9) | −0.09 | 0.18 | 0.25 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Total energy intake (kJ) | ||||
| Quarter 1 | 16 500 (25) | −0.37 | −0.60 | −0.48 |
| Quarter 2 | 16 500 (25) | −0.13 | −0.25 | −0.15 |
| Quarter 3 | 16 500 (25) | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.10 |
| Quarter 4 | 16 500 (25) | 0.44 | 0.78 | 0.53 |
| P value† | — | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
*Dietary pattern scores created by multiplying factor loadings by corresponding standardised value for intake of each food and adding all these items. Values are mean factor scores, derived by extraction of three dietary factors. Not adjusted for confounders.
†Non-parametric test, Mann-Whitney (two groups) or Kruskal-Wallis (more than two groups).
‡Both partners have annual income of <300 000 Norwegian Krone.
§Either participant or partner has an annual income of ≥300 000 Norwegian Krone.
¶Both participant and partner have an annual income of ≥300 000 Norwegian Krone.
We also ran analyses for additional confounders. We analysed physical activity during pregnancy as categorical data divided into one of four categories (none, less than weekly, 1-2 times weekly, and ≥3 times weekly), as reported at gestational week 17. We analysed information from the food frequency questionnaire about nausea and vomiting during pregnancy as dichotomous data (yes/no) and energy density calculated from the food frequency questionnaire as continuous data. We used alcohol intake as both categorical and continuous data (g/day) and collected information from the food frequency questionnaire. We analysed passive smoking as dichotomous data (yes/no) from questionnaire 1 and used information about planned pregnancy as dichotomous data (yes/no) collected from questionnaire 1.
Statistical methods
We used PASW Statistics software version 19 for Windows for statistical analyses. We used principal component analysis with orthogonal (varimax) rotation to derive dietary patterns. To avoid higher influence of variables with different size and large variance, as is often the case with foods, SPSS standardises the input variables before extraction of the linear components. Extraction of dietary patterns (factors) was based on the correlation matrix. To test the analysis, we used the Bartlett test of sphericity (P<0.001) and the Kaiser-Mayer-Olkin test (0.672), denoting statistically correlated variables and adequate sampling size. We calculated factor scores for three patterns and used them as the exposure variables. The factor scores were not normally distributed, but we describe them as mean (SD) when analysed by maternal characteristics. We tested differences in factor scores between groups by using non-parametric tests (Mann-Whitney for two groups and Kruskal-Wallis for more than two groups). For adjusted analyses, we used the factor scores as ranked numerical data (continuous variables) in linear regression and ranked into thirds (categorical data) for risk estimation. We used a Cox regression model to examine the associations between dietary patterns and preterm delivery for overall preterm delivery as well as in subanalyses. We did regression analyses with all three dietary patterns entered into the same model. Variables included in the adjusted models were maternal age, history of previous preterm delivery, height, body mass index, marital status, parity, smoking, maternal education, household income, and total energy intake. In additional analyses, we also adjusted for physical activity, nausea, alcohol intake, passive smoking, planned pregnancy, and energy density, but as these variables had P values greater than 0.1 we did not include them in the final models. P values were two sided, and we considered values below 0.05 to be statistically significant. We obtained P for trend by incorporating the categorical variables as linear terms into the Cox regression models.
Results
Dietary patterns
We extracted three distinct dietary patterns with eigenvalues above 2 from the scree plot, as well as factor loadings (table 1 and fig 2); these three patterns accounted for 16% of the total variation in food intakes. The first pattern (eigenvalue 4.1) had high positive factor loadings for raw and cooked vegetables, salad, onion/leek/garlic, fruit and berries, nuts, vegetables oils, water as beverage, whole grain cereals, poultry, and fibre rich bread, as well as negative factor loadings for processed meat products (hot dogs, hamburgers, and so on), white bread, and pizza/tacos; we denoted this “prudent.” The second pattern (eigenvalue 2.9) had positive factor loadings for salty snacks, chocolate and sweets, cakes, French fries, white bread, ketchup, sugar sweetened drinks, processed meat products, and pasta, as well as negative factor loadings for lean fish and fibre rich bread; we denoted this “Western.” The third pattern (eigenvalue 2.2) had positive factor loadings for boiled potatoes, fish products, gravy, lean fish, margarine, rice pudding, low fat milk, and cooked vegetables, as well as negative factor scores for poultry and pizza/tacos; we denoted this “traditional.”
Spearman correlations between the pattern scores and nutrients indicative of diet quality confirmed that these pattern labels were appropriate.35 For instance, the prudent pattern scores correlated with folic acid (r=0.61), dietary fibre (r=0.57), β carotene (r=0.53), potassium (r=0.52), and ascorbic acid (r=0.48); the Western dietary pattern scores correlated with total fat (r=0.55), saturated fat (r=0.55), and added sugar (r=0.59); and the traditional pattern scores correlated with potassium (r=0.42), magnesium (r=0.39), protein (r=0.38), and dietary fibre (r=0.33). Furthermore, the energy density correlated inversely with the prudent pattern scores (r=−0.48), correlated positively with the Western pattern scores (r=0.30), and was not associated with the traditional pattern scores (r=0.01).
Dietary patterns in relation to maternal characteristics
The distribution of mean dietary pattern scores differed according to maternal characteristics (table 2). The prudent pattern score increased with increasing maternal age and education and was lower in women with higher body mass index. Furthermore, the prudent pattern score was slightly higher in nulliparous women, in non-smokers, and in women with no previous preterm delivery. The Western pattern score was higher in younger women, in smokers, in women with less education, in parous women, and in those with previous preterm delivery. Both underweight and overweight women had higher scores on the Western pattern than did normal weight women. For the traditional pattern, mean factor scores were higher in the young (<20 years) and the older (≥40 years) age groups than in the intermediate age groups. The traditional pattern scores also increased with decreasing education and were higher in parous women, in smokers, and in women with a history of preterm delivery. The mean factor scores for all three patterns increased with increasing energy intake.
Deliveries
Among the 66 000 pregnant women, preterm delivery occurred in 3505 (5.3%) cases, of which 2003 (3.1%) were spontaneous and 1414 (2.2%) were iatrogenic. In 88 (0.13%) cases, information about start of delivery was missing. Late preterm delivery occurred in 2558 (3.9%) of total deliveries, 478 (0.7%) were moderately preterm, and 469 (0.7%) were early preterm.
Dietary patterns in relation to preterm delivery
In the unadjusted linear regression analysis, women with preterm delivery had significantly lower scores on the prudent and traditional dietary patterns and significantly higher scores on the Western pattern (table 3). Women with spontaneous preterm delivery had significantly lower scores on the prudent dietary pattern and significantly higher scores on the Western pattern. We also observed significantly higher scores on the Western pattern for women who had an iatrogenic preterm delivery. After stratification for time of delivery, women with late preterm delivery had significantly lower scores on the prudent pattern and higher scores on the Western pattern. We observed no significant differences in pattern scores for moderately and early preterm delivery, compared with term deliveries, but the numbers of preterm deliveries in these subgroups were low. When we restricted the study sample to overweight women (body mass index ≥25), we saw no significant difference between scores on any of the patterns. In the adjusted analysis with pattern scores as continuous variables, the scores on the prudent pattern remained significantly lower in overall, spontaneous, and late preterm deliveries (table 3).
Table 3.
Mean factor scores* of dietary patterns in 66 000 pregnant women in subgroups of preterm delivery in Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. Values are mean (SD) unless stated otherwise
| No (%) | Dietary pattern | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Prudent” | “Western” | “Traditional” | ||
| Overall preterm delivery | ||||
| No† | 62 495 (94.7) | 0.002 (0.998) | −0.003 (0.998) | 0.002 (0.999) |
| Yes | 3505 (5.3) | −0.029 (1.027) | 0.057 (1.027) | −0.027 (1.016) |
| Crude P value‡ | — | 0.011 | 0.002 | 0.025 |
| Adjusted P value§ | — | 0.026 | 0.466 | 0.095 |
| Spontaneous preterm delivery | ||||
| No† | 62 495 (96.9) | 0.002 (0.998) | −0.003 (0.998) | 0.002 (0.999) |
| Yes | 2003 (3.1) | −0.055 (1.026) | 0.048 (1.014) | −0.028 (1.022) |
| Crude P value‡ | — | 0.001 | 0.033 | 0.094 |
| Adjusted P value§ | — | 0.016 | 0.226 | 0.769 |
| Iatrogenic preterm delivery | ||||
| No† | 62 495 (97.8) | 0.002 (0.998) | −0.003 (0.998) | 0.002 (0.999) |
| Yes | 1414 (2.2) | −0.001 (1.018) | 0.093 (1.044) | −0.008 (1.016) |
| Crude P value‡ | — | 0.773 | 0.001 | 0.430 |
| Adjusted P value§ | — | 0.618 | 0.483 | 0.102 |
| Late preterm delivery | ||||
| No† | 62 495 (94.7) | 0.002 (0.998) | −0.003 (0.998) | 0.002 (0.999) |
| Yes | 2558 (3.9) | −0.022 (1.038) | 0.075 (1.029) | −0.026 (1.008) |
| Crude P value‡ | — | 0.049 | <0.001 | 0.071 |
| Adjusted P value§ | — | 0.025 | 0.244 | 0.102 |
| Moderately preterm delivery | ||||
| No† | 62 495 (94.7) | 0.002 (0.998) | −0.003 (0.998) | 0.002 (0.999) |
| Yes | 478 (0.7) | −0.061 (0.972) | −0.053 (1.017) | −0.058 (1.001) |
| Crude P value‡ | — | 0.159 | 0.144 | 0.206 |
| Adjusted P value§ | — | 0.586 | 0.120 | 0.642 |
| Early preterm delivery | ||||
| No† | 62 495 (94.7) | 0.002 (0.998) | −0.003 (0.998) | 0.002 (0.999) |
| Yes | 469 (0.7) | −0.034 (1.027) | 0.070 (1.022) | −0.003 (1.077) |
| Crude P value‡ | — | 0.324 | 0.150 | 0.480 |
| Adjusted P value§ | — | 0.611 | 0.427 | 0.734 |
| Preterm delivery in overweight women | ||||
| No¶ | 18 393 (93.9) | −0.159 (0.950) | 0.081 (0.987) | −0.001 (1.011) |
| Yes** | 1185 (6.1) | −0.140 (1.019) | 0.097 (1.045) | −0.011 (1.024) |
| Crude P value‡ | 0.958 | 0.969 | 0.603 | |
| Adjusted P value§ | 0.905 | 0.838 | 0.848 | |
*Dietary pattern scores created by multiplying factor loadings with corresponding standardised value for intake of each food and adding all these items. Values are mean (SD) factor scores for three dietary patterns extracted by principal component analysis. Overall mean factor score for each pattern is zero. Positive factor scores indicate high consumption of foods and drinks in that pattern, and negative factor scores indicate low consumption. The scores are not adjusted for other variables.
†Term deliveries.
‡Non-parametric test (Mann-Whitney).
§Linear regression of ranked factor scores (continuous) adjusted for maternal age, pre-pregnancy body mass index, height, parity, total energy intake, maternal education, marital status, smoking, previous preterm delivery, household income, and other dietary patterns.
¶Term deliveries in overweight women (body mass index ≥25).
**Preterm deliveries in overweight women (body mass index ≥25).
The incidence of preterm delivery was highest (1249 cases; 5.7%) in the lowest third of the prudent dietary pattern scores and lowest (1110 cases; 5.0%) in the lowest third of the Western pattern and the highest third of the traditional pattern scores (1110 cases; 5.0%) (table 4). Mean scores for the prudent pattern were negative in the lowest third (denoting low intake of foods from the prudent pattern), with the highest incidence of preterm delivery, and positive for the highest third (denoting high intake), in which the incidence of preterm delivery was lower (1115 cases; 5.1%). For the Western pattern, factor scores were positive (high intake of foods belonging to this pattern), and the incidence of preterm delivery peaked in the highest third (1229 cases; 5.6%).
Table 4.
Associations between thirds of dietary pattern scores* and preterm delivery in 66 000 pregnant women in Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
| Dietary pattern | Preterm delivery—No (%†) | Mean‡ (min, max) | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1§ | Model 2¶ | |||
| All | 3505 (5.3) | — | — | — |
| “Prudent”: | ||||
| Third 1 | 1249 (5.7) | −0.97 (−2.69, −0.51) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 1141 (5.2) | −0.14 (−0.51, 0.27) | 0.92 (0.85 to 0.99) | 0.94 (0.86 to 1.02) |
| Third 3 | 1115 (5.1) | 1.10 (0.27, 10.52) | 0.89 (0.82 to 0.97) | 0.88 (0.80 to 0.97) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.007 | 0.006 |
| “Western”: | ||||
| Third 1 | 1110 (5.0) | −0.99 (−3.77, −0.47) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 1166 (5.3) | −0.10 (−0.47, 0.29) | 1.04 (0.95 to 1.12) | 1.04 (0.95 to 1.13) |
| Third 3 | 1229 (5.6) | 1.09 (0.29, 12.04) | 1.10 (1.01 to 1.19) | 1.02 (0.92 to 1.13) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.021 | 0.695 |
| “Traditional”: | ||||
| Third 1 | 1224 (5.6) | −1.04 (−3.46, −0.49) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 1171 (5.3) | −0.08 (−0.49, 0.35) | 0.96 (0.88 to 1.04) | 0.98 (0.90 to 1.06) |
| Third 3 | 1110 (5.0) | 1.12 (0.35, 6.05) | 0.90 (0.83 to 0.98) | 0.91 (0.83 to 0.99) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.015 | 0.043 |
*Dietary pattern scores created by multiplying factor loadings by corresponding standardised value for intake of each food and adding all these items.
²Percentage of preterm delivery in each third.
‡Mean (minimum, maximum) of scores for each dietary pattern.
§Adjusted for other dietary patterns; hazard ratio and 95% CI calculated by Cox regression.
¶Adjusted for maternal age, pre-pregnancy body mass index, height, parity, total energy intake, maternal education, marital status, smoking, previous preterm delivery, household income, and other dietary patterns; hazard ratio and 95% CI calculated by Cox regression.
**P values for linear trend obtained by incorporating variable as linear term in Cox regression models.
The Cox regression analysis showed that the association between the prudent dietary pattern and lower risk of preterm delivery was statistically significant after adjustment for covariates including maternal age, history of preterm delivery, pre-pregnancy body mass index, height, marital status, parity, smoking, maternal education, household income, total energy intake, and the other dietary patterns. The adjusted hazard ratio for the highest third compared with the lowest third was 0.88 (95% confidence interval 0.80 to 0.97; P for trend=0.006) (table 4). We found no significant association in the adjusted analysis for the Western pattern, but the hazard ratio for the highest third compared with the lowest third of the traditional dietary pattern was significant (0.91, 0.83 to 0.99; P for trend=0.043).
In additional analyses, we examined physical activity, nausea, alcohol intake, passive smoking, and planned pregnancy as potential confounders, but these variables had no significant association with the dietary patterns (data not shown) and preterm delivery. Likewise, adjustment for energy density did not change the results, confirming that properties reflected by the energy density variable were already represented by the dietary patterns.
The variables most influencing the association between dietary patterns and preterm delivery were time of delivery, body mass index, and parity. We did sensitivity analyses in the strata of these variables.
We stratified women into two groups according to pre-pregnancy body mass index (<25 and ≥25). The adjusted hazard ratio between the prudent dietary pattern and preterm delivery in the low body mass index group was 0.88 (0.78 to 0.99) for the highest third. For the higher body mass index group, the corresponding adjusted hazard ratio did not reach statistical significance (0.92, 0.78 to 1.08) for the highest third. For women with high adherence to the traditional dietary pattern, we found a significantly reduced risk of preterm delivery in the low body mass index group (hazard ratio 0.87, 0.78 to 0.98), but also no significant association in the high body mass index group.
We further stratified women by parity (nulliparous versus parous). The dataset contained 34 217 (51.8%) nulliparous women. We found a stronger association between high scores on the prudent dietary pattern and reduced risk of preterm delivery in nulliparous women than in the whole cohort. In the nulliparous group, the adjusted hazard ratio for the middle and highest thirds were 0.86 (0.78 to 0.96) and 0.75 (0.67 to 0.85), with a significant P for trend (<0.001). The adjusted hazard ratio for the Western dietary pattern and preterm delivery was significantly increased only in the middle third (1.12, 1.01 to 1.25), with a non-significant test for trend. In parous women, the associations between the dietary patterns and preterm delivery did not reach statistical significance.
In the adjusted analysis, we also found a significantly reduced risk of late preterm delivery for women with high adherence to the prudent dietary pattern. Hazard ratios for the middle and highest thirds compared with the lowest third were 0.91 (0.82 to 0.99) and 0.86 (0.78 to 0.96), with a significant P for trend (0.007). We also found a significant association between the highest third of the traditional dietary pattern and late preterm delivery (hazard ratio 0.89, 0.80 to 0.99). The risk estimates for moderately and early preterm delivery were comparable to those for late preterm delivery but did not reach statistical significance (table 5).
Table 5.
Subanalysis for gestational length—associations between thirds of dietary pattern scores* and subgroups of preterm delivery in 66 000 pregnant women in Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
| Dietary pattern | No | Preterm delivery—No (%†) | Mean‡ (min, max) | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1§ | Model 2¶ | ||||
| Late preterm | |||||
| “Prudent”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 666 | 915 (4.2) | −0.97 (−2.69, −0.51) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 678 | 819 (3.8) | −0.13 (−0.51, 0.27) | 0.90 (0.82 to 0.99) | 0.91 (0.82 to 0.99) |
| Third 3 | 21 709 | 824 (3.8) | 1.10 (0.27, 10.52) | 0.91 (0.82 to 0.99) | 0.86 (0.78 to 0.96) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.036 | 0.007 | |
| “Western”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 676 | 786 (3.6) | −0.99 (−3.77, −0.47) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 668 | 854 (3.9) | −0.10 (−0.47, 0.29) | 1.07 (0.97 to 1.18) | 1.06 (0.96 to 1.17) |
| Third 3 | 21 689 | 918 (4.2) | 1.08 (0.29, 12.04) | 1.16 (1.05 to 1.28) | 1.06 (0.94 to 1.19) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.002 | 0.323 | |
| “Traditional”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 666 | 890 (4.1) | −1.04 (−3.46, −0.49) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 692 | 863 (4.0) | −0.08 (−0.49, 0.35) | 0.97 (0.88 to 1.07) | 0.98 (0.89 to 1.08) |
| Third 3 | 21 695 | 805 (3.7) | 1.12 (0.35, 6.05) | 0.90 (0.82 to 0.99) | 0.89 (0.80 to 0.99) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.033 | 0.032 | |
| Moderately preterm | |||||
| ”Prudent”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 20 926 | 175 (0.8) | −0.97 (−2.69, −0.51) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 013 | 154 (0.7) | −0.13 (−0.51, 0.27) | 0.86 (0.69 to 1.07) | 0.94 (0.75 to 1.17) |
| Third 3 | 21 034 | 149 (0.7) | 1.10 (0.27, 10.52) | 0.82 (0.66 to 1.03) | 0.91 (0.71 to 1.17) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.101 | 0.485 | |
| “Western”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 074 | 184 (0.9) | −0.99 (−3.77, −0.47) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 20 978 | 144 (0.7) | −0.10, (−0.47, 0.29) | 0.77 (0.62 to 0.96) | 0.81 (0.64 to 1.02) |
| Third 3 | 20 921 | 150 (0.7) | 1.08 (0.29, 12.04) | 0.81 (0.65 to 1.00) | 0.79 (0.60 to 1.04) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.050 | 0.074 | |
| “Traditional”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 20 942 | 166 (0.8) | −1.04 (−3.45, −0.49) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 20 986 | 157 (0.7) | −0.08 (−0.49, 0.35) | 0.93 (0.75 to 1.16) | 1.02 (0.81 to 1.28) |
| Third 3 | 21 045 | 155 (0.7) | 1.11 (0.35, 6.05) | 0.92 (0.74 to 1.14) | 1.02 (0.79 to 1.32) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.479 | 0.869 | |
| Early preterm | |||||
| ”Prudent”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 20 910 | 159 (0.8) | −0.97 (−2.69, −0.51) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 027 | 168 (0.8) | −0.13 (−0.51, 0.27) | 1.07 (0.86 to 1.33) | 1.10 (0.88 to 1.38) |
| Third 3 | 21 027 | 142 (0.7) | 1.10 (0.27, 10.52) | 0.90 (0.72 to 1.13) | 0.92 (0.71 to 1.19) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.345 | 0.521 | |
| “Western”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 030 | 140 (0.7) | −0.99 (−3.77, −0.47) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 002 | 168 (0.8) | −0.10 (−0.47, 0.29) | 1.19 (0.95 to 1.49) | 1.21 (0.95 to 1.53) |
| Third 3 | 20 932 | 161 (0.8) | 1.08 (0.29, 12.04) | 1.15 (0.92 to 1.45) | 1.09 (0.82 to 1.44) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.245 | 0.541 | |
| “Traditional”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 20 944 | 168 (0.8) | −1.04 (−3.46, −0.49) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 20 980 | 151 (0.7) | −0.08 (−0.49, 0.35) | 0.90 (0.72 to 1.12) | 0.93 (0.74 to 1.16) |
| Third 3 | 21 040 | 150 (0.7) | 1.12 (0.35, 6.05) | 0.89 (0.72 to 1.11) | 0.90 (0.69 to 1.15) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.292 | 0.414 | |
*Dietary pattern scores created by multiplying factor loadings by corresponding standardised value for intake of each food and adding all these items.
†Percentage of preterm delivery in each third.
‡Mean (minimum, maximum) of scores for each dietary pattern.
§Adjusted for other dietary patterns; hazard ratio and 95% CI calculated by Cox regression.
¶Adjusted for maternal age, pre-pregnancy body mass index, height, parity, total energy intake, maternal education, marital status, smoking, previously preterm delivery, household income, and other dietary patterns; hazard ratio and 95% CI calculated by Cox regression.
**P values for linear trend obtained by incorporating the variable as linear term in Cox regression models.
[We need denominators for the percentages – this also applies to table 6, now added in tables, see red figures. Denominators are now presented in the second column, in table 5 and table 6.]
When we analysed spontaneous preterm delivery separately, we found a significantly lower risk of spontaneous preterm delivery for women with high adherence to the prudent dietary pattern: the adjusted hazard ratio for the highest versus the lowest third was 0.85 (0.75 to 0.96). We also found a significant association for reduced risk of iatrogenic preterm delivery with high adherence to the traditional dietary pattern: the adjusted hazard ratio for the highest versus lowest third was 0.85 (0.74 to 0.99) (table 6).
Table 6.
Subanalysis for start of delivery: associations between thirds of dietary pattern scores* and subgroups of preterm delivery in 65 912 pregnant women in Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
| Dietary pattern | No | Preterm delivery—No (%†) | Mean‡ (min, max) | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1§ | Model 2¶ | ||||
| Spontaneous | |||||
| ”Prudent”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 491 | 740 (3.4) | −0.97 (−2.69, −0.51) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 499 | 640 (3.0) | −0.14 (−0.51, 0.27) | 0.87 (0.78 to 0.97) | 0.90 (0.81 to 1.01) |
| Third 3 | 21 508 | 623 (2.9) | 1.10 (0.27, 10.52) | 0.84 (0.76 to 0.94) | 0.85 (0.75 to 0.96) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.001 | 0.008 | |
| “Western”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 519 | 629 (2.9) | −0.99 (−3.77, −0.47) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 523 | 689 (3.2) | −0.10 (−0.47, 0.29) | 1.07 (0.96 to 1.20) | 1.10 (0.98 to 1.23) |
| Third 3 | 21 456 | 685 (3.2) | 1.09 (0.29, 12.04) | 1.08 (0.97 to 1.20) | 1.04 (0.91 to 1.19) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.171 | 0.504 | |
| “Traditional”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 483 | 707 (3.3) | −1.04 (−3.46, −0.49) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 479 | 650 (3.0) | −0.08 (−0.49, 0.35) | 0.92 (0.83 to 1.02) | 0.96 (0.86 to 1.07) |
| Third 3 | 21 536 | 646 (3.0) | 1.12 (0.35, 6.05) | 0.91 (0.82 to 1.02) | 0.96 (0.85 to 1.09) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.079 | 0.512 | |
| Iatrogenic | |||||
| ”Prudent”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 230 | 479 (2.3) | −0.97 (−2.69, −0.51) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 335 | 476 (2.2) | −0.14 (−0.51, 0.27) | 1.00 (0.88 to 1.14) | 1.00 (0.88 to 1.15) |
| Third 3 | 21 344 | 459 (2.2) | 1.10 (0.27, 10.52) | 0.96 (0.84 to 1.09) | 0.93 (0.80 to 1.08) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.560 | 0.328 | |
| “Western”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 328 | 438 (2.1) | −0.99 (−3.77, −0.47) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 285 | 451 (2.1) | −0.10 (−0.47, 0.29) | 1.03 (0.90 to 1.17) | 1.00 (0.87 to 1.15) |
| Third 3 | 21 296 | 525 (2.5) | 1.09 (0.29, 12.04) | 1.20 (1.06 to 1.37) | 1.05 (0.90 to 1.23) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.005 | 0.548 | |
| “Traditional”: | |||||
| Third 1 | 21 255 | 479 (2.3) | −1.04 (−3.46, −0.49) | 1 | 1 |
| Third 2 | 21 318 | 489 (2.3) | −0.08 (−0.49, 0.35) | 1.02 (0.90 to 1.16) | 1.01 (0.89 to 1.15) |
| Third 3 | 21 336 | 446 (2.1) | 1.12 (0.35, 6.05) | 0.92 (0.81 to 1.05) | 0.85 (0.74 to 0.99) |
| P for trend** | — | — | 0.260 | 0.042 | |
*Dietary pattern scores created by multiplying factor loadings by corresponding standardised value for intake of each food and adding all these items.
†Percentage of preterm delivery in each third.
‡Mean (minimum, maximum) scores for each dietary pattern.
§Adjusted for other dietary patterns; hazard ratio and 95% CI calculated by Cox regression.
¶Adjusted for maternal age, pre-pregnancy body mass index, height, parity, total energy intake, maternal education, marital status, smoking, previously preterm delivery, household income, and other dietary patterns; hazard ratio and 95% CI calculated by Cox regression.
**P values for linear trend obtained by incorporating variable as linear term in Cox regression models.
Discussion
In this study, we found that an overall “prudent” dietary pattern was associated with a reduced risk of preterm delivery, especially in the subgroups of late preterm delivery and spontaneous preterm delivery and in nulliparous women. We also found a significantly reduced risk of preterm delivery for the “traditional” dietary pattern. These findings are important, as prevention of preterm delivery is of major importance in modern obstetrics. The “Western” dietary pattern was not independently associated with preterm delivery.
Strengths
The major strengths of this study are the large number of participants from all over Norway, the prospective design, and the detailed information on a wide range of potential confounding factors. All age and socioeconomic groups are represented in the study group. Women were also unaware of the outcome of pregnancy when they filled in the food frequency questionnaire, so outcome could not affect the reporting. In the food frequency questionnaire, women were asked to report intake since the beginning of pregnancy. The food frequency questionnaire covers the period from becoming pregnant until gestational week 22, meaning that responses covered embryogenesis, a period that is important when it comes to epigenetic mechanisms and for possible later preterm delivery.36 The food frequency questionnaire used in our study has been extensively validated and shown to be a valuable tool for ranking pregnant women according to high and low intakes of energy, nutrients, and foods.29 32 37 One of the most important risk factor for preterm delivery is previous preterm delivery,37 which we adjusted for in this study. Smoking also increases the risk of preterm delivery,38 and the fact that smoking is commonly underreported, especially in pregnant women,39 constitutes a major challenge in all epidemiological studies. In this study, we divided smoking into non-smoking, occasional smoking, and daily smoking. This categorisation of the smoking variable has been validated in a subsample of 2997 women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study with plasma cotinine as an objective reference, showing a high degree of agreement between plasma cotinine and self reported smoking during pregnancy.40 Our findings are likely to be generalisable outside of Norway and thus contribute to the general body of research on diet and health. Studies do not show that a typical Nordic diet, either in the general population or in pregnant women, contain more “prudent” foods than elsewhere.41 42
Limitations
Our study also has limitations. The results are observational, and no causal inference is possible. Despite careful consideration of known risk factors and potential confounding factors, residual confounding cannot be ruled out. The low participation rate (40%) in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study is a concern. Women in the study are older, better educated, and less often smokers compared with the general pregnant population, which might have affected the outcome in our study. However, the incidence of preterm delivery in the general population is comparable to that in the study cohort.27 Furthermore, a study focusing on the potential self selection bias in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort showed no significant differences between eight evaluated exposure-outcome associations (of which preterm delivery was one) in the cohort and the total pregnant population in Norway during the same period.43 Bias might also have arisen in the exclusion process, but the prevalence of preterm delivery was actually higher in the study population than in the 17 386 excluded pregnancies (5.3% (3505 cases) v 3.8% (660 cases)) owing to exclusion of women participating in the study with more than one pregnancy, resulting in a higher proportion of nulliparous women in the study sample.
Possible explanations for findings
The association between the prudent dietary pattern and a reduced risk of preterm delivery was stronger in nulliparous women than for the whole group. Women who were pregnant with their first child had significantly higher scores on the prudent dietary pattern than did the multiparous women. This difference may be explained by nulliparous women being more health conscientious than parous women or by diet being of less importance in later pregnancies than in the first, as the overall risk of preterm delivery is significantly lower in women who have experienced a previous pregnancy.44
Furthermore, after stratification according to time of delivery, we found only a significantly reduced risk of late preterm delivery related to high adherence to the prudent dietary pattern. Although results point in the same direction, no significant associations were found between this pattern and moderately or early preterm delivery. This might be due to the low number of cases in these subgroups, or more serious mechanisms might underlie early and moderately preterm delivery—for example, amniotic infections that a prudent dietary pattern cannot prevent. An alternative explanation is that the prudent dietary pattern might reduce the progression to preterm delivery only marginally, in the order of a few days, and that the effect is therefore most easily detectable in late preterm delivery, but this is only speculation.
We did not find any independent association between high scores on the Western pattern and preterm delivery in this study. This pattern explained only 5% of the variance in total food intakes. A low score on the prudent pattern is interpreted as an unwholesome diet, as the dietary pattern scores are negative in this group (see tables 4, 5, and 6). Foods perceived to be unhealthy tend to be underreported to a larger degree than foods regarded as healthy.45 The interplay between dietary behaviour, body mass, and health outcome is complex, and the effects are difficult to disentangle. Other studies have shown the importance of limiting the intake of food items typical of the Western pattern.46 47 48 In a previous study in the same study population, we found that high intakes of both sugar sweetened and artificially sweetened drinks were associated with an increased risk of preterm delivery.13 Sugar sweetened drinks loaded positively on the Western pattern. Although no independent association with preterm delivery was observed for this pattern, we cannot rule out the possibility that high consumption of single items in a pattern may be associated with the outcome. However, as found in a previous study on healthy food intake and mortality in women,49 the overall findings indicate that focusing on regular consumption of healthy food is more important than focusing on reducing consumption of unhealthy food.
Delivery starts as a result of a complex paracrine and autocrine dynamic, biochemical event in involving the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, resulting in increased adrenal cortisol production and subsequent inflammation.32 50 Altering the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is one way that food can influence gestational length. Animal studies have found that a high fat diet can act as a stressor in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system, increasing production of glucocorticosteroids.51 Whether high adherence to a prudent pattern can have an anti-stressor effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is as yet unknown, but it is an interesting hypothesis. A diet characterised by high intake of vegetables, fruit, and berries and rich in antioxidants and vitamins can reduce both systemic and local inflammation (through gut flora),52 which might also be one explanation for the reduced risk of preterm delivery associated with adhering to a prudent diet.53 54 55 56 57 This dietary pattern is also low in saturated fat, which is also associated with reduced inflammation.58
Comparison with other studies
To the best of our knowledge, no previous study has investigated dietary patterns in relation to preterm delivery by principal component analysis. Most other studies have focused on specific foods or nutrients in relation to preterm delivery, but distinguishing the foods in a mixed diet that are responsible for the effect can be difficult. Therefore, studying overall dietary patterns in relation to outcomes might be an important alternative approach.
Some food items found to be associated with the risk of preterm delivery were part of the food pattern identified by principal component analysis. Milk and yoghurt products enriched with probiotic Lactobacillus (probiotic milk products) have been reported to be associated with a reduced risk of preterm delivery,15 59 and probiotic milk products had positive loading on the prudent dietary pattern in our study. Also, two large cohort studies found aspects of Mediterranean-type dietary patterns, characterised by high intake of fruit, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, to be associated with a reduced risk of preterm delivery.11 60 We found these food items to be positively loaded on the prudent pattern, associated with reduced risk of preterm delivery. A prudent diet comparable to ours has been found in studies to be associated with other beneficial obstetric outcomes. Brantsaeter and co-workers found that a similar dietary pattern was associated with reduced risk of pre-eclampsia in nulliparous women.24 In addition to preterm delivery and pre-eclampsia, an overall healthy diet is also beneficial for other obstetric outcomes, such as to prevent excessive weight gain and reduce the incidence of gestational diabetes, especially in overweight women.61 62
The reduced risk of preterm delivery related to high scores on the prudent dietary pattern was apparent only in the normal weight group. Different findings in normal weight and overweight women were also observed in a study by Magnus et al, in which physical activity was associated with a reduced risk of pre-eclampsia in normal weight, but not in obese (body mass index ≥30), women.63 The negative effect of overweight may have been much greater than the positive effect of a prudent diet in our study. Overweight is a well known risk factor for preterm delivery.64 65 In our study, pre-pregnancy overweight and obese women had significantly lower scores on the prudent dietary pattern than did normal weight women (table 2) and might therefore not have benefited from this pattern. Also, overweight pregnant women tend to underreport dietary intake to a larger degree, which may be another explanation for the results.66
Conclusions and policy implications
Our study is observational, and conclusions about causality cannot be drawn; intervention trials would be needed. Because carrying out intervention trials with “normal diets” as the exposure is virtually impossible, studies of associations between overall dietary behaviour and health outcomes contribute valuable evidence to serve as a basis for dietary guidelines.67 Furthermore, the results of the factor analysis could be used to identify foods that characterised or were very specific for a certain pattern. These foods might warrant further investigation and could be studied in more detail, for example in the form of a randomised controlled trial. This study adds knowledge concerning this and indicates that preterm delivery might actually be modified by maternal diet.
In conclusion, we found a significantly reduced risk of both preterm delivery, especially late preterm delivery and spontaneous preterm delivery, in women choosing a “prudent” or a “traditional” dietary pattern, characterised by, for example, vegetables, cooking oil, fruit, berries, olive oil, rice, water as beverage, whole grain cereals, yoghurt, poultry, lean fish, and boiled potatoes, as well as low intake of processed meat products, white bread, and pizza/tacos. Our findings suggest that diet matters, when it comes to the risk of preterm delivery. This may reassure medical practitioners that the current dietary recommendations are sound but also inspire them to pay more attention to dietary counselling. We saw no independent association between the “Western” dietary pattern and preterm delivery, indicating that low adherence to a prudent pattern is a stronger indicator of unhealthy dietary behaviour than intake of processed food, fast food, junk food, and snacks.
What is already known on this topic
Awareness has increased in recent years that maternal diet may influence the outcome of pregnancy as well as the long term health of the child
Several studies indicate associations between maternal diet and preterm delivery
What this study adds
Diet matters for the risk of preterm delivery, which may reassure medical practitioners that the current dietary recommendations are sound but also inspire them to pay more attention to dietary counselling
We are grateful to all the families in Norway participating in this ongoing cohort study.
Contributors: All the authors participated in the planning and conduct of this study and approved the final version. ALB, LE-Ö, BEB, BJ, and VS conceived the study. ALB, VS, and LE-Ö did the statistical analyses. LE-Ö, ALB, and BJ wrote the first draft of this manuscript. ALB, MH, BEB, VS, RM, HMM, and BJ revised several versions of this manuscript. LE-Ö is the guarantor.
Funding: This work was supported by grants from the Freemasons Directorate board for Children, the Adlerbertska Foundation, the Hjalmar Svensson Foundation, the Norwegian Research Council (FUGE 183220/S10, FRIMEDKLI-05 ES236011), the Jane and Dan Olsson Foundation, the Swedish Medical Society (SLS 2008-21198), and Swedish government grants to researchers in public health service (ALFGBG-2863, ALFGBG-11522). The Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study was also supported by the Norwegian Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Education and Research, NIH/NIEHS (contract No N01-ES-75558), NIH/NINDS (grant No.1 UO1 NS 047537-01 and grant No.2 UO1 NS 047537-06A1), and the Norwegian Research Council/FUGE (grant No. 151918/S10). All authors are independent from funders.
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author) and declare: no support from any organisation for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Regional Committee for Ethics in Medical Research (REK/S-06075a and REK/S-06077a/2008/19291) and the Data Inspectorate in Norway. All participants gave written consent.
Transparency declaration: The lead author (the manuscript’s guarantor) affirms that the manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the study being reported; that no important aspects of the study have been omitted; and that any discrepancies from the study as planned have been explained.
Data sharing: No additional data available.
Cite this as: BMJ 2014;348:g1446
References
- 1.Pennell CE, Jacobsson B, Williams SM, Buus RM, Muglia LJ, Dolan SM, et al. Genetic epidemiologic studies of preterm birth: guidelines for research. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007;196:107-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Morken NH, Kallen K, Jacobsson B. Outcomes of preterm children according to type of delivery onset: a nationwide population-based study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 2007;21:458-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nour NM. Premature delivery and the millennium development goal. Rev Obstet Gynecol 2012;5:100-5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Feng Y, Abdel-Latif ME, Bajuk B, Lui K, Oei JL. Causes of death in infants admitted to Australian neonatal intensive care units between 1995 and 2006. Acta Paediatr 2013;102:17-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Morken NH, Vogel I, Kallen K, Skjaerven R, Langhoff-Roos J, Kesmodel US, et al. Reference population for international comparisons and time trend surveillance of preterm delivery proportions in three countries. BMC Women’s Health 2008;8:16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Howse JL, Katz M. Conquering prematurity. Pediatrics 2013;131:1-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yuan W, Duffner AM, Chen L, Hunt LP, Sellers SM, Bernal AL. Analysis of preterm deliveries below 35 weeks’ gestation in a tertiary referral hospital in the UK: a case-control survey. BMC Res Notes 2010;3:119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Blumfield ML, Hure AJ, Macdonald-Wicks LK, Smith R, Simpson SJ, Giles WB, et al. Dietary balance during pregnancy is associated with fetal adiposity and fat distribution. Am J Clin Nutr 2012;96:1032-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kind KL, Moore VM, Davies MJ. Diet around conception and during pregnancy—effects on fetal and neonatal outcomes. Reprod Biomed Online 2006;12:532-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Godfrey KM, Barker DJ. Fetal programming and adult health. Public Health Nutr 2001;4:611-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haugen M, Meltzer HM, Brantsaeter AL, Mikkelsen T, Osterdal ML, Alexander J, et al. Mediterranean-type diet and risk of preterm birth among women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa): a prospective cohort study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2008;87:319-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Myhre R, Brantsaeter AL, Myking S, Eggesbø M, Meltzer HM, Haugen M, et al. Intake of garlic and dried fruits is associated with lower risk of spontaneous preterm delivery. J Nutr 2013;143:1100-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Englund-Ogge L, Brantsaeter AL, Haugen M, Sengpiel V, Khatibi A, Myhre R, et al. Association between intake of artificially sweetened and sugar-sweetened beverages and preterm delivery: a large prospective cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr 2012;96:552-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Halldorsson TI, Strom M, Petersen SB, Olsen SF. Intake of artificially sweetened soft drinks and risk of preterm delivery: a prospective cohort study in 59,334 Danish pregnant women. Am J Clin Nutr 2010;92:626-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Myhre R, Brantsaeter AL, Myking S, Gjessing HK, Sengpiel V, Meltzer HM, et al. Intake of probiotic food and risk of spontaneous preterm delivery. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;93:151-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jacques PF, Tucker KL. Are dietary patterns useful for understanding the role of diet in chronic disease? Am J Clin Nutr 2001;73:1-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hu FB. Dietary pattern analysis: a new direction in nutritional epidemiology. Curr Opin Lipidol 2002;13:3-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Newby PK, Tucker KL. Empirically derived eating patterns using factor or cluster analysis: a review. Nutr Rev 2004;62:177-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mishra GD, McNaughton SA, Ball K, Brown WJ, Giles GG, Dobson AJ. Major dietary patterns of young and middle aged women: results from a prospective Australian cohort study. Eur J Clin Nutr 2010;64:1125-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mishra GD, McNaughton SA, Bramwell GD, Wadsworth ME. Longitudinal changes in dietary patterns during adult life. Br J Nutr 2006;96:735-44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Balder HF, Virtanen M, Brants HA, Krogh V, Dixon LB, Tan F, et al. Common and country-specific dietary patterns in four European cohort studies. J Nutr 2003;133:4246-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Arkkola T, Uusitalo U, Kronberg-Kippila C, Männistö S, Virtanen M, Kenward MG, et al. Seven distinct dietary patterns identified among pregnant Finnish women—associations with nutrient intake and sociodemographic factors. Public Health Nutr 2008;11:176-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Crozier SR, Robinson SM, Borland SE, Inskip HM, for the SWS Study Group. Dietary patterns in the Southampton Women’s Survey. Eur J Clin Nutr 2006;60:1391-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brantsaeter AL, Haugen M, Samuelsen SO, Torjusen H, Trogstad L, Alexander J, et al. A dietary pattern characterized by high intake of vegetables, fruits, and vegetable oils is associated with reduced risk of preeclampsia in nulliparous pregnant Norwegian women. J Nutr 2009;139:1162-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Northstone K, Emmett PM, Rogers I. Dietary patterns in pregnancy and associations with nutrient intakes. Br J Nutr 2008;99:406-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Meltzer HM, Brantsaeter AL, Nilsen RM, Magnus P, Alexander J, Haugen M. Effect of dietary factors in pregnancy on risk of pregnancy complications: results from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;94(6 suppl):1970-4S. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Magnus P, Irgens LM, Haug K, Nystad W, Skjaerven R, Stoltenberg C. Cohort profile: the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Int J Epidemiol 2006;35:1146-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Irgens LM. The Medical Birth Registry of Norway: epidemiological research and surveillance throughout 30 years. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2000;79:435-9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brantsaeter AL, Haugen M, Alexander J, Meltzer HM. Validity of a new food frequency questionnaire for pregnant women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Matern Child Nutr 2008;4:28-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Meltzer HM, Brantsaeter AL, Ydersbond TA, Alexander J, Haugen M. Methodological challenges when monitoring the diet of pregnant women in a large study: experiences from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Matern Child Nutr 2008;4:14-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brantsaeter AL, Haugen M, Julshamn K, Alexander J, Meltzer HM. Evaluation of urinary iodine excretion as a biomarker for intake of milk and dairy products in pregnant women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Eur J Clin Nutr 2009;63:347-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kota SK, Gayatri K, Jammula S, Kota SK, Krishna SV, Meher LK, et al. Endocrinology of parturition. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2013;17:50-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rimestad AH, Borgejordet Å, Vesterhus KN, Sygnestveit K, Løken EB, Trygg K, et al. Den store matvaretabellen/the Norwegian food composistion table. Statens råd for ernæring og fysisk aktivitet, Statens næringsmiddeltilsyn, Institutt for ernæringsforskning, 2001.
- 34.Ledikwe JH, Blanck HM, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Seymour JD, Tohill BC, et al. Dietary energy density determined by eight calculation methods in a nationally representative United States population. J Nutr 2005;135:273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lobstein T, Davies S. Defining and labelling ‘healthy’ and ‘unhealthy’ food. Public Health Nutr 2009;12:331-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cutfield WS, Hofman PL, Mitchell M, Morison IM. Could epigenetics play a role in the developmental origins of health and disease? Pediatr Res 2007;61(5 pt 2):68-75R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Iams JD, Berghella V. Care for women with prior preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010;203:89-100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bouras G, Theofanopoulou N, Mexi-Bourna P, Poulios A, Michopoulos I, Tassiopoulou I, et al. Preterm birth and maternal psychological health. J Health Psychol 2013; published online 9 Dec. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 39.Lawrence T, Aveyard P, Croghan E. What happens to women’s self-reported cigarette consumption and urinary cotinine levels in pregnancy? Addiction 2003;98:1315-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kvalvik LG, Nilsen RM, Skjaerven R, Vollset SE, Midttun O, Ueland PM, et al. Self-reported smoking status and plasma cotinine concentrations among pregnant women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. Pediatr Res 2012;72:101-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mendez MA, Kogevinas M. A comparative analysis of dietary intakes during pregnancy in Europe: a planned pooled analysis of birth cohort studies. Am J Clin Nutr 2011;94(6 suppl):1993-9S. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Slimani N, Fahey M, Welch AA, Wirfält E, Stripp C, Bergström E, et al. Diversity of dietary patterns observed in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) project. Public Health Nutr 2002;5:1311-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nilsen RM, Vollset SE, Gjessing HK, Skjaerven R, Melve KK, Schreuder P, et al. Self-selection and bias in a large prospective pregnancy cohort in Norway. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 2009;23:597-608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Morken NH, Kallen K, Hagberg H, Jacobsson B. Preterm birth in Sweden 1973-2001: rate, subgroups, and effect of changing patterns in multiple births, maternal age, and smoking. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005;84:558-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fricker J, Baelde D, Igoin-Apfelbaum L, Huet JM, Apfelbaum M. Underreporting of food intake in obese “small eaters”. Appetite 1992;19:273-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Radesky JS, Oken E, Rifas-Shiman SL, Kleinman KP, Rich-Edwards JW, Gillman MW. Diet during early pregnancy and development of gestational diabetes. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 2008;22:47-59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Najafian M, Cheraghi M. Occurrence of fetal macrosomia rate and its maternal and neonatal complications: a 5-year cohort study. ISRN Obstet Gynecol 2012;2012:353791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Alsammani MA, Ahmed SR. Fetal and maternal outcomes in pregnancies complicated with fetal macrosomia. N Am J Med Sci 2012;4:283-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Michels KB, Wolk A. A prospective study of variety of healthy foods and mortality in women. Int J Epidemiol 2002;31:847-54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Iliodromiti Z, Antonakopoulos N, Sifakis S, Tsikouras P, Daniilidis A, Dafopoulos K, et al. Endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine placental mediators in labor. Hormones (Athens) 2012;11:397-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shin AC, MohanKumar SM, Sirivelu MP, Claycombe KJ, Haywood JR, Fink GD, et al. Chronic exposure to a high-fat diet affects stress axis function differentially in diet-induced obese and diet-resistant rats. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010;34:1218-26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jeffery IB, O’Toole PW. Diet-microbiota interactions and their implications for healthy living. Nutrients 2013;5:234-52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kwiatkowski S, Torbe A, Dolegowska B, Błogowski W, Czajka R, Chlubek D, et al. Isoprostanes 8-iPF2alpha-III: risk markers of premature rupture of fetal membranes? Biomarkers 2009;14:406-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wei SQ, Fraser W, Luo ZC. Inflammatory cytokines and spontaneous preterm birth in asymptomatic women: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol 2010;116:393-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sahnoun Z, Jamoussi K, Zeghal KM. [Free radicals and antioxidants: physiology, human pathology and therapeutic aspects (part II)]. Therapie 1998;53:315-39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Andriantsitohaina R, Duluc L, Garcia-Rodriguez JC, Gil-del Valle L, Guevara-Garcia M, Simard G, et al. Systems biology of antioxidants. Clin Sci (Lond) 2012;123:173-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Clerici G, Slavescu C, Fiengo S, Kanninen TT, Romanelli M, Biondi R, et al. Oxidative stress in pathological pregnancies. J Obstet Gynaecol 2012;32:124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Peairs AD, Rankin JW, Lee YW. Effects of acute ingestion of different fats on oxidative stress and inflammation in overweight and obese adults. Nutr J 2011;10:122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Stojanovic N, Plecas D, Plesinac S. Normal vaginal flora, disorders and application of probiotics in pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2012;286:325-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mikkelsen TB, Osterdal ML, Knudsen VK, Haugen M, Meltzer HM, Bakketeig L, et al. Association between a Mediterranean-type diet and risk of preterm birth among Danish women: a prospective cohort study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2008;87:325-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Quinlivan JA, Lam LT, Fisher J. A randomised trial of a four-step multidisciplinary approach to the antenatal care of obese pregnant women. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2011;51:141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Thangaratinam S, Rogozinska E, Jolly K, Glinkowski S, Duda W, Borowiack E, et al. Interventions to reduce or prevent obesity in pregnant women: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess 2012;16(31):iii-iv, 1-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Magnus P, Trogstad L, Owe KM, Olsen SF, Nystad W. Recreational physical activity and the risk of preeclampsia: a prospective cohort of Norwegian women. Am J Epidemiol 2008;168:952-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Khatibi A, Brantsaeter AL, Sengpiel V, Kacerovsky M, Magnus P, Morken NH, et al. Prepregnancy maternal body mass index and preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207:e211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cnattingius S, Villamor E, Johansson S, Edstedt Bonamy AK, Persson M, Wikström AK, et al. Maternal obesity and risk of preterm delivery. JAMA 2013;309:2362-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Olafsdottir AS, Thorsdottir I, Gunnarsdottir I, Thorgeirsdottir H, Steingrimsdottir L. Comparison of women’s diet assessed by FFQs and 24-hour recalls with and without underreporters: associations with biomarkers. Ann Nutr Metab 2006;50:450-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.World Cancer Research Fund, Food, nutrition, physical activity and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective. American Institute for Cancer Research, 2009.