Abstract
Phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and other second messenger-activated protein kinases modulates the activity of a variety of effector proteins including ion channels. Anti-peptide antibodies specific for the alpha 1 subunits of the class B, C or E calcium channels from rat brain specifically recognize a pair of polypeptides of 220 and 240 kDa, 200 and 220 kDa, and 240 and 250 kDa, respectively, in hippocampal slices in vitro. These calcium channels are localized predominantly on presynaptic and dendritic, somatic and dendritic, and somatic sites, respectively, in hippocampal neurons. Both size forms of alpha 1B and alpha 1E and the full-length form of alpha 1C are phosphorylated by PKA after solubilization and immunoprecipitation. Stimulation of PKA in intact hippocampal slices also induced phosphorylation of 25-50% of the PKA sites on class B N-type calcium channels, class C L-type calcium channels and class E calcium channels, as assessed by a back-phosphorylation method. Tetraethylammonium ion (TEA), which causes neuronal depolarization and promotes repetitive action potentials and neurotransmitter release by blocking potassium channels, also stimulated phosphorylation of class B, C and E alpha 1 subunits, suggesting that these three classes of channels are phosphorylated by PKA in response to endogenous electrical activity in the hippocampus. Regulation of calcium influx through these calcium channels by PKA may influence calcium-dependent processes within hippocampal neurons, including neurotransmitter release, calcium-activated enzymes and gene expression.
Full text
PDF


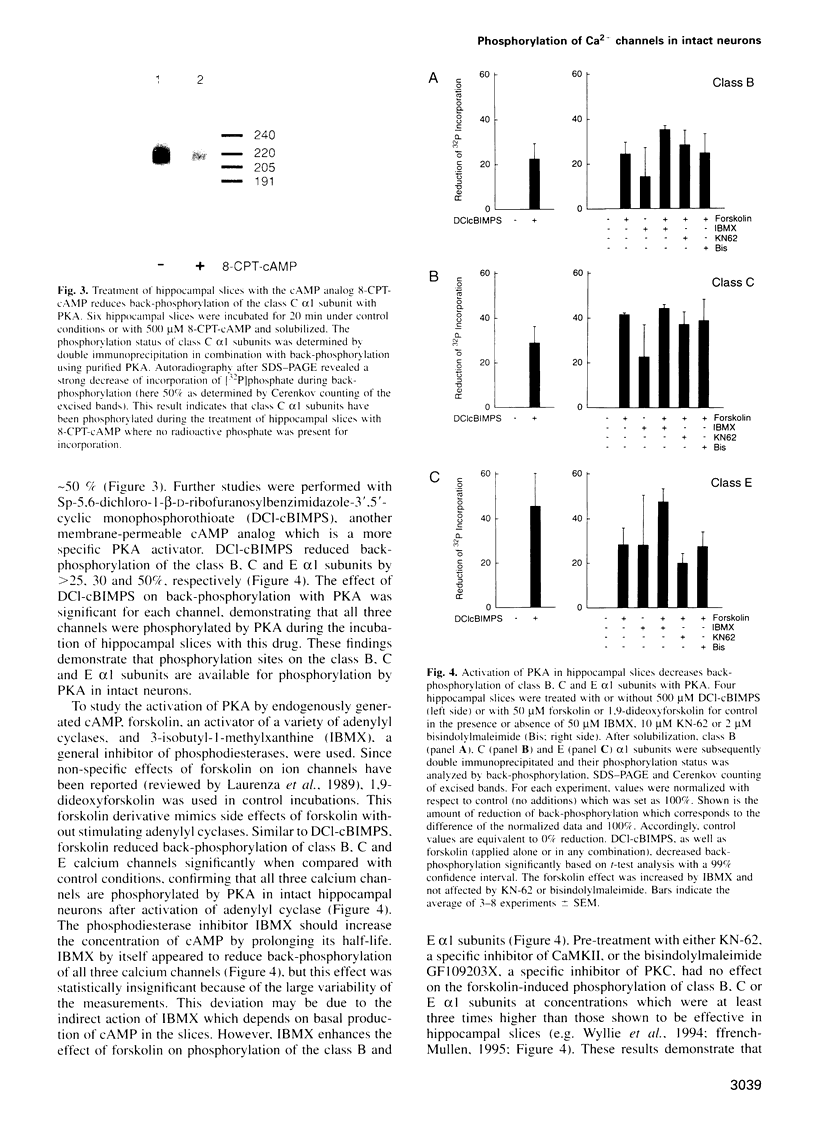
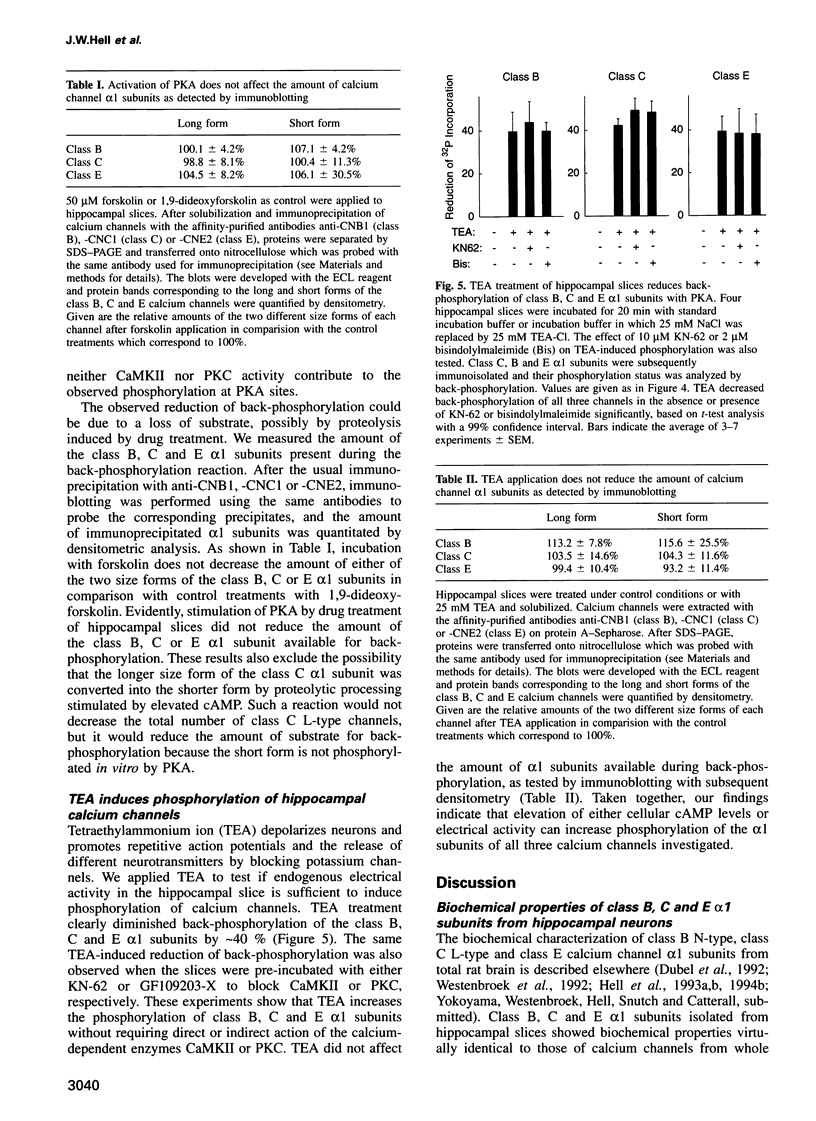




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlijanian M. K., Striessnig J., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of an alpha 1-like subunit of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive brain calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20192–20197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlijanian M. K., Westenbroek R. E., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure and localization of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in mammalian brain, spinal cord, and retina. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):819–832. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aniksztejn L., Ben-Ari Y. Novel form of long-term potentiation produced by a K+ channel blocker in the hippocampus. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):67–69. doi: 10.1038/349067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aosaki T., Kasai H. Characterization of two kinds of high-voltage-activated Ca-channel currents in chick sensory neurons. Differential sensitivity to dihydropyridines and omega-conotoxin GVIA. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):150–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00580957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Eckert R. Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Ariano M. A., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Activation of facilitation calcium channels in chromaffin cells by D1 dopamine receptors through a cAMP/protein kinase A-dependent mechanism. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):239–242. doi: 10.1038/348239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Rossie S., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Voltage-dependent phosphorylation may recruit Ca2+ current facilitation in chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):63–66. doi: 10.1038/358063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bading H., Ginty D. D., Greenberg M. E. Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.8097060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear M. F., Malenka R. C. Synaptic plasticity: LTP and LTD. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Jun;4(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourinet E., Charnet P., Tomlinson W. J., Stea A., Snutch T. P., Nargeot J. Voltage-dependent facilitation of a neuronal alpha 1C L-type calcium channel. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5032–5039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., Leung A. T., Sharp A. H. The biochemistry and molecular biology of the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo P. E., Weisskopf M. G., Nicoll R. A. The role of Ca2+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chad J. E., Eckert R. An enzymatic mechanism for calcium current inactivation in dialysed Helix neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:31–51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chetkovich D. M., Gray R., Johnston D., Sweatt J. D. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation increases cAMP levels and voltage-gated Ca2+ channel activity in area CA1 of hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6467–6471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin H. M., Kozak C. A., Kim H. L., Mock B., McBride O. W. A brain L-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit gene (CCHL1A2) maps to mouse chromosome 14 and human chromosome 3. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):914–919. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jongh K. S., Merrick D. K., Catterall W. A. Subunits of purified calcium channels: a 212-kDa form of alpha 1 and partial amino acid sequence of a phosphorylation site of an independent beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8585–8589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jongh K. S., Warner C., Colvin A. A., Catterall W. A. Characterization of the two size forms of the alpha 1 subunit of skeletal muscle L-type calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10778–10782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. G protein modulation of calcium currents in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:243–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doroshenko P. A., Kostyuk P. G., Martynyuk A. E., Kursky M. D., Vorobetz Z. D. Intracellular protein kinase and calcium inward currents in perfused neurones of the snail Helix pomatia. Neuroscience. 1984 Jan;11(1):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90229-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubel S. J., Starr T. V., Hell J., Ahlijanian M. K., Enyeart J. J., Catterall W. A., Snutch T. P. Molecular cloning of the alpha-1 subunit of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5058–5062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F. Purification of a functional receptor for calcium-channel blockers from rabbit skeletal-muscle microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarizing agents and cyclic nucleotides regulate the phosphorylation of specific neuronal proteins in rat cerebral cortex slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey U., Huang Y. Y., Kandel E. R. Effects of cAMP simulate a late stage of LTP in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.8389057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Mynlieff M., Dirksen R. T., Kim M. S., Niidome T., Nakai J., Friedrich T., Iwabe N., Miyata T., Furuichi T. Primary structure and functional expression of the omega-conotoxin-sensitive N-type calcium channel from rabbit brain. Neuron. 1993 Apr;10(4):585–598. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90162-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Striessnig J. Molecular properties of calcium channels. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;114:1–105. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R., Johnston D. Noradrenaline and beta-adrenoceptor agonists increase activity of voltage-dependent calcium channels in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):620–622. doi: 10.1038/327620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L. Cyclic AMP selectively reduces the N-type calcium current component of mouse sensory neurons in culture by enhancing inactivation. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Jan;61(1):97–105. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L. Reduction of the same calcium current component by A and C kinases: differential pertussis toxin sensitivity. Neurosci Lett. 1988 May 16;88(1):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Uhler M. D., Macdonald R. L. The cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit selectively enhances calcium currents in rat nodose neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:483–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell J. W., Appleyard S. M., Yokoyama C. T., Warner C., Catterall W. A. Differential phosphorylation of two size forms of the N-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit which have different COOH termini. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7390–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell J. W., Westenbroek R. E., Elliott E. M., Catterall W. A. Differential phosphorylation, localization, and function of distinct alpha 1 subunits of neuronal calcium channels. Two size forms for class B, C, and D alpha 1 subunits with different COOH-termini. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Dec 15;747:282–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell J. W., Westenbroek R. E., Warner C., Ahlijanian M. K., Prystay W., Gilbert M. M., Snutch T. P., Catterall W. A. Identification and differential subcellular localization of the neuronal class C and class D L-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunits. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):949–962. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell J. W., Yokoyama C. T., Wong S. T., Warner C., Snutch T. P., Catterall W. A. Differential phosphorylation of two size forms of the neuronal class C L-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19451–19457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P. Calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:337–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Y., Li X. C., Kandel E. R. cAMP contributes to mossy fiber LTP by initiating both a covalently mediated early phase and macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Y., Malenka R. C. Examination of TEA-induced synaptic enhancement in area CA1 of the hippocampus: the role of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the induction of LTP. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):568–576. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00568.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., Ellinor P. T., Krizanova O., Wang J. J., Diebold R. J., Schwartz A. Molecular cloning of multiple subtypes of a novel rat brain isoform of the alpha 1 subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymel L., Striessnig J., Glossmann H., Schindler H. Purified skeletal muscle 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor forms phosphorylation-dependent oligomeric calcium channels in planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4290–4294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn H., Nastainczyk W., Röhrkasten A., Schneider T., Hofmann F. Site-specific phosphorylation of the purified receptor for calcium-channel blockers by cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases, protein kinase C, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and casein kinase II. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 15;178(2):535–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. D., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Voltage-dependent potentiation of L-type Ca2+ channels in skeletal muscle cells requires anchored cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11492–11496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L. K., Jennings K. R., Strumwasser F., Nairn A. C., Walter U., Wilson F. D., Greengard P. Microinjection of catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase enhances calcium action potentials of bag cell neurons in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7487–7491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y., Seagar M. J., Takahashi M., Catterall W. A. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of two size forms of alpha 1 subunits of L-type calcium channels in rat skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20839–20848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenza A., Sutkowski E. M., Seamon K. B. Forskolin: a specific stimulator of adenylyl cyclase or a diterpene with multiple sites of action? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Nov;10(11):442–447. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(89)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Lin J. W., Cherksey B. Blocking and isolation of a calcium channel from neurons in mammals and cephalopods utilizing a toxin fraction (FTX) from funnel-web spider poison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1689–1693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. NMDA-receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity: multiple forms and mechanisms. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Dec;16(12):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90197-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEnery M. W., Snowman A. M., Sharp A. H., Adams M. E., Snyder S. H. Purified omega-conotoxin GVIA receptor of rat brain resembles a dihydropyridine-sensitive L-type calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11095–11099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):46–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2432656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Receptor-mediated regulation of calcium channels and neurotransmitter release. FASEB J. 1990 Dec;4(15):3291–3299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Adams M. E., Bean B. P. P-type calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90223-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Friedrich T., Kim M. S., Mikami A., Nakai J., Ruth P., Bosse E., Hofmann F., Flockerzi V., Furuichi T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a brain calcium channel. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):398–402. doi: 10.1038/350398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundiña-Weilenmann C., Chang C. F., Gutierrez L. M., Hosey M. M. Demonstration of the phosphorylation of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in chick skeletal muscle and the resultant activation of the channels after reconstitution. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4067–4073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. H., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M. L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels mediate synaptic activation of immediate early genes. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):625–635. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90375-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastainczyk W., Röhrkasten A., Sieber M., Rudolph C., Schächtele C., Marmè D., Hofmann F. Phosphorylation of the purified receptor for calcium channel blockers by cAMP kinase and protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Nov 16;169(1):137–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niidome T., Kim M. S., Friedrich T., Mori Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel calcium channel from rabbit brain. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 10;308(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81038-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoki K., Florio V., Catterall W. A. Activation of purified calcium channels by stoichiometric protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6816–6820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callahan C. M., Hosey M. M. Multiple phosphorylation sites in the 165-kilodalton peptide associated with dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6071–6077. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenmund C., Carr D. W., Bergeson S. E., Nilaver G., Scott J. D., Westbrook G. L. Anchoring of protein kinase A is required for modulation of AMPA/kainate receptors on hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):853–856. doi: 10.1038/368853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman E. I., De Jongh K. S., Florio V., Lai Y., Catterall W. A. Specific phosphorylation of a COOH-terminal site on the full-length form of the alpha 1 subunit of the skeletal muscle calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16100–16105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Zhang J. F., Mori Y., Adams M. E., Tsien R. W. Distinctive biophysical and pharmacological properties of class A (BI) calcium channel alpha 1 subunits. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90185-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculptoreanu A., Rotman E., Takahashi M., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Voltage-dependent potentiation of the activity of cardiac L-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunits due to phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10135–10139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculptoreanu A., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Voltage-dependent potentiation of L-type Ca2+ channels due to phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):240–243. doi: 10.1038/364240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Chen L., Seino M., Blondel O., Takeda J., Johnson J. H., Bell G. I. Cloning of the alpha 1 subunit of a voltage-dependent calcium channel expressed in pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):584–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Rat brain expresses a heterogeneous family of calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Tomlinson W. J., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M. Distinct calcium channels are generated by alternative splicing and are differentially expressed in the mammalian CNS. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soong T. W., Stea A., Hodson C. D., Dubel S. J., Vincent S. R., Snutch T. P. Structure and functional expression of a member of the low voltage-activated calcium channel family. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1133–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.8388125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr T. V., Prystay W., Snutch T. P. Primary structure of a calcium channel that is highly expressed in the rat cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5621–5625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Tomlinson W. J., Soong T. W., Bourinet E., Dubel S. J., Vincent S. R., Snutch T. P. Localization and functional properties of a rat brain alpha 1A calcium channel reflect similarities to neuronal Q- and P-type channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10576–10580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striessnig J., Glossmann H., Catterall W. A. Identification of a phenylalkylamine binding region within the alpha 1 subunit of skeletal muscle Ca2+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9108–9112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surmeier D. J., Bargas J., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Modulation of calcium currents by a D1 dopaminergic protein kinase/phosphatase cascade in rat neostriatal neurons. Neuron. 1995 Feb;14(2):385–397. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Catterall W. A. Identification of an alpha subunit of dihydropyridine-sensitive brain calcium channels. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):88–91. doi: 10.1126/science.2436296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Seagar M. J., Jones J. F., Reber B. F., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Momiyama A. Different types of calcium channels mediate central synaptic transmission. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):156–158. doi: 10.1038/366156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A. Molecular diversity of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90595-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Adams M. E., Dunlap K. Multiple Ca2+ channel types coexist to regulate synaptosomal neurotransmitter release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9518–9522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisskopf M. G., Castillo P. E., Zalutsky R. A., Nicoll R. A. Mediation of hippocampal mossy fiber long-term potentiation by cyclic AMP. Science. 1994 Sep 23;265(5180):1878–1882. doi: 10.1126/science.7916482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek R. E., Hell J. W., Warner C., Dubel S. J., Snutch T. P., Catterall W. A. Biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of an N-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1099–1115. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90069-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler D. B., Randall A., Tsien R. W. Roles of N-type and Q-type Ca2+ channels in supporting hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):107–111. doi: 10.1126/science.7832825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Brust P. F., Feldman D. H., Patthi S., Simerson S., Maroufi A., McCue A. F., Veliçelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive human N-type calcium channel. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):389–395. doi: 10.1126/science.1321501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Feldman D. H., McCue A. F., Brenner R., Velicelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunits of a novel human neuronal calcium channel subtype. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90109-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witcher D. R., De Waard M., Sakamoto J., Franzini-Armstrong C., Pragnell M., Kahl S. D., Campbell K. P. Subunit identification and reconstitution of the N-type Ca2+ channel complex purified from brain. Science. 1993 Jul 23;261(5120):486–489. doi: 10.1126/science.8392754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie D. J., Manabe T., Nicoll R. A. A rise in postsynaptic Ca2+ potentiates miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents and AMPA responses in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ffrench-Mullen J. M. Cortisol inhibition of calcium currents in guinea pig hippocampal CA1 neurons via G-protein-coupled activation of protein kinase C. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 2):903–911. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00903.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]