Abstract
Staphylococcal enterotoxins are prototype superantigens characterized by their ability to bind to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules and subsequently activate a large fraction of T-lymphocytes. The crystal structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin type A (SEA), a 27 kDa monomeric protein, was determined to 1.9 A resolution with an R-factor of 19.9% by multiple isomorphous replacement. SEA is a two domain protein composed of a beta-barrel and a beta-grasp motif demonstrating the same general structure as staphylococcal enterotoxins SEB and TSST-1. Unique for SEA, however, is a Zn2+ coordination site involved in MHC class II binding. Four amino acids including Ser1, His187, His225 and Asp227 were found to be involved in direct coordination of the metal ion. SEA is the first Zn2+ binding enterotoxin that has been structurally determined.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahmsén L., Dohlsten M., Segrén S., Björk P., Jonsson E., Kalland T. Characterization of two distinct MHC class II binding sites in the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 3;14(13):2978–2986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acharya K. R., Passalacqua E. F., Jones E. Y., Harlos K., Stuart D. I., Brehm R. D., Tranter H. S. Structural basis of superantigen action inferred from crystal structure of toxic-shock syndrome toxin-1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):94–97. doi: 10.1038/367094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Borst D. W., Regassa L. B. Staphylococcal enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin and streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins: a comparative study of their molecular biology. Chem Immunol. 1992;55:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.34-41.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Heeg H., Edwards C. K., 3rd, Cullen C. M. A mutation at histidine residue 135 of toxic shock syndrome toxin yields an immunogenic protein with minimal toxicity. Infect Immun. 1995 Feb;63(2):509–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.2.509-515.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):33–39. doi: 10.1038/364033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Boswell D. R., Lesk A. M. The outline structure of the T-cell alpha beta receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3745–3755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson D. W. Structural biology of zinc. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;42:281–355. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60538-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Urban R. G., Strominger J. L., Robinson H. Zinc regulates the function of two superantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5507–5511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman D., Van M., Mollick J. A., Highlander S. K., Rich R. R. Mutation of the disulfide loop in staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Consequences for T cell recognition. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3274–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S., Hansen L. K., Hough E. Crystal structures of phosphate, iodide and iodate-inhibited phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus and structural investigations of the binding of reaction products and a substrate analogue. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90938-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. O., Grossman D., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Rich R. R., Betley M. J. Lack of complete correlation between emetic and T-cell-stimulatory activities of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3175–3183. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3175-3183.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. O., Hufnagle W. O., Betley M. J. Staphylococcal enterotoxin type A internal deletion mutants: serological activity and induction of T-cell proliferation. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2059–2068. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2059-2068.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Herrmann T., Buell G., Lando P. A., Segrén S., Schrimsher J., MacDonald H. R., Sjögren H. O., Kalland T. A recombinant C-terminal fragment of staphylococcal enterotoxin A binds to human MHC class II products but does not activate T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4082–4085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Labrecque N., Thibodeau J., Marrack P., Kappler J. W., Sekaly R. P. Identification of the staphylococcal enterotoxin A superantigen binding site in the beta 1 domain of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9954–9958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough E., Hansen L. K., Birknes B., Jynge K., Hansen S., Hordvik A., Little C., Dodson E., Derewenda Z. High-resolution (1.5 A) crystal structure of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):357–360. doi: 10.1038/338357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson K. R., Robinson H., Fraser J. D. Two adjacent residues in staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E determine T cell receptor V beta specificity. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):175–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Brown J. H., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Chi Y. I., Stauffacher C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of a human class II histocompatibility molecule complexed with superantigen. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):711–718. doi: 10.1038/368711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R., Long E. O. Identification of HLA-DR1 beta chain residues critical for binding staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):415–424. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A., Håkansson K., Jonsson B. H., Xue Y. Inhibition and catalysis of carbonic anhydrase. Recent crystallographic analyses. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79502-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollick J. A., Chintagumpala M., Cook R. G., Rich R. R. Staphylococcal exotoxin activation of T cells. Role of exotoxin-MHC class II binding affinity and class II isotype. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollick J. A., McMasters R. L., Grossman D., Rich R. R. Localization of a site on bacterial superantigens that determines T cell receptor beta chain specificity. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):283–293. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad G. S., Earhart C. A., Murray D. L., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M., Ohlendorf D. H. Structure of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 21;32(50):13761–13766. doi: 10.1021/bi00213a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren K., Bannan J. D., Pancholi V., Cheung A. L., Robbins J. C., Fischetti V. A., Zabriskie J. B. Characterization and biological properties of a new staphylococcal exotoxin. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1675–1683. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
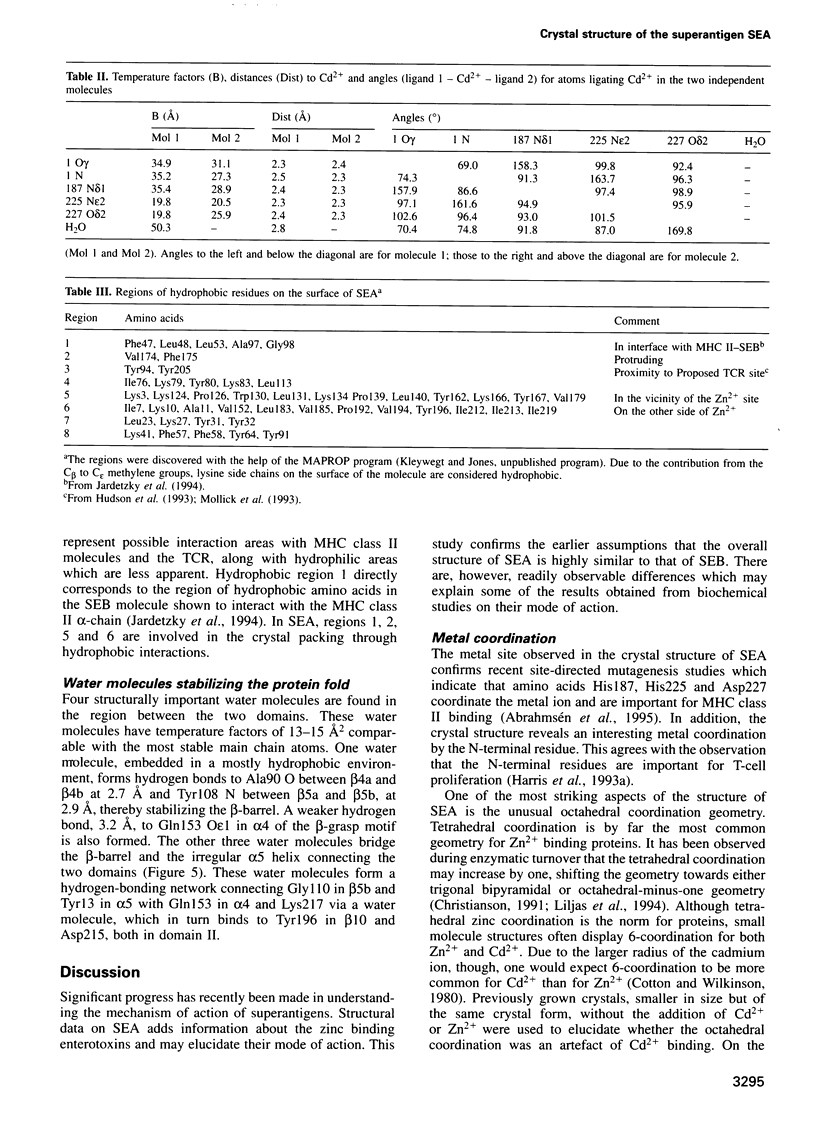
- Saqi M. A., Sayle R. PdbMotif--a tool for the automatic identification and display of motifs in protein structures. Comput Appl Biosci. 1994 Sep;10(5):545–546. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.5.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan S., Furey W., Pletcher J., Sax M. Crystal structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin B, a superantigen. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):801–806. doi: 10.1038/359801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
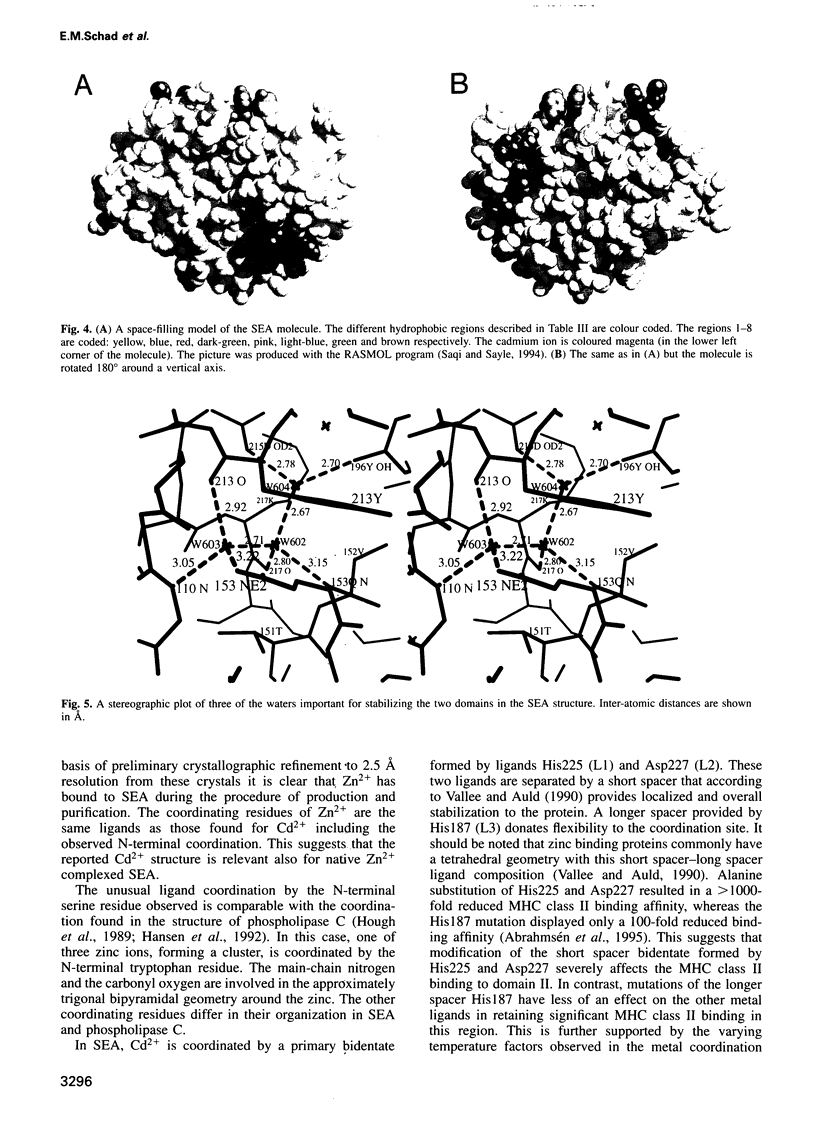
- Vallee B. L., Auld D. S. Active-site zinc ligands and activated H2O of zinc enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]