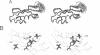Abstract
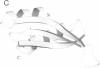
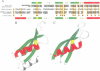
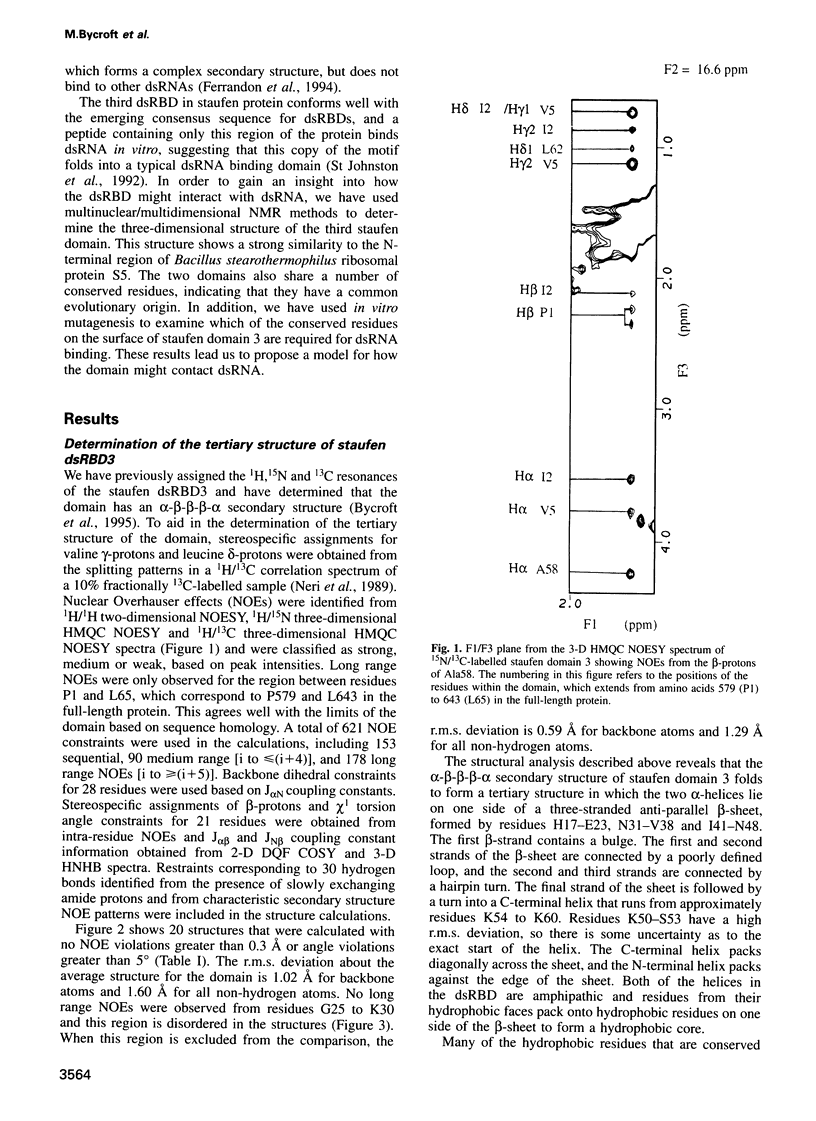
The double-stranded RNA binding domain (dsRBD) is an approximately 65 amino acid motif that is found in a variety of proteins that interact with double-stranded (ds) RNA, such as Escherichia coli RNase III and the dsRNA-dependent kinase, PKR. Drosophila staufen protein contains five copies of this motif, and the third of these binds dsRNA in vitro. Using multinuclear/multidimensional NMR methods, we have determined that staufen dsRBD3 forms a compact protein domain with an alpha-beta-beta-beta-alpha structure in which the two alpha-helices lie on one face of a three-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet. This structure is very similar to that of the N-terminal domain of a prokaryotic ribosomal protein S5. Furthermore, the consensus derived from all known S5p family sequences shares several conserved residues with the dsRBD consensus sequence, indicating that the two domains share a common evolutionary origin. Using in vitro mutagenesis, we have identified several surface residues which are important for the RNA binding of the dsRBD, and these all lie on the same side of the domain. Two residues that are essential for RNA binding, F32 and K50, are also conserved in the S5 protein family, suggesting that the two domains interact with RNA in a similar way.
Full text
PDF
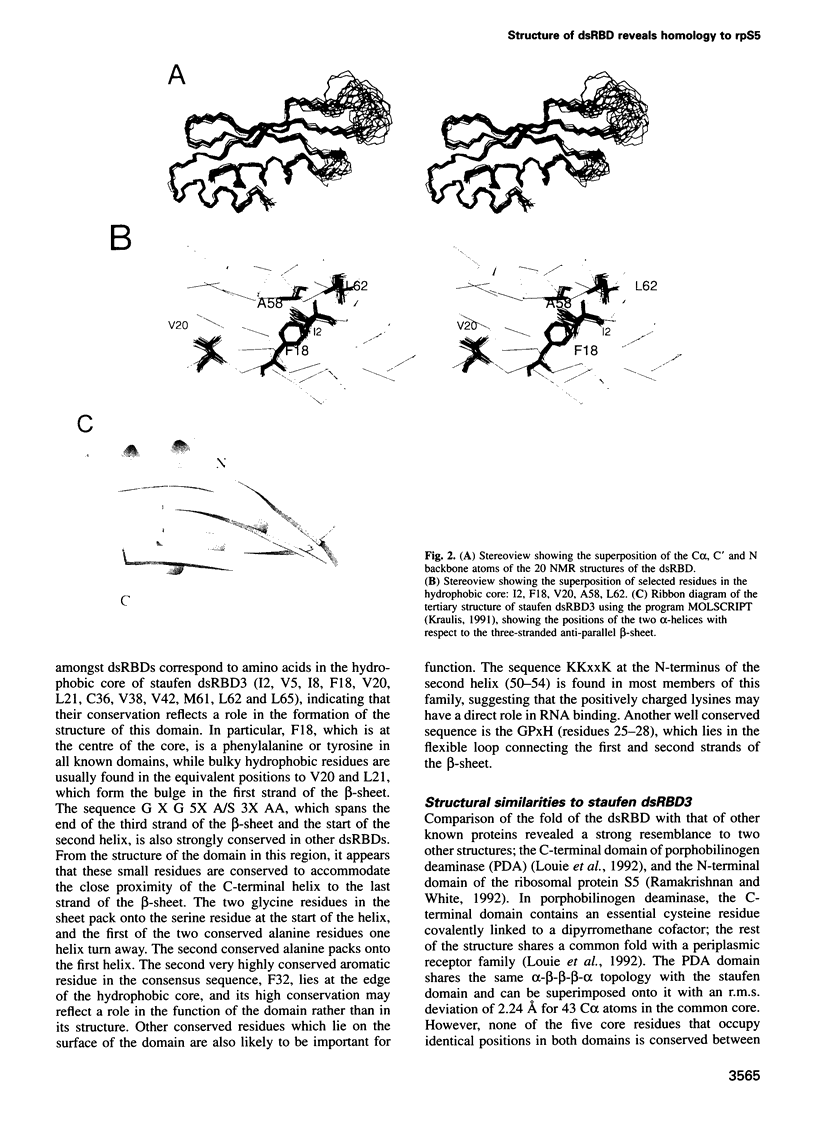





Images in this article
Selected References
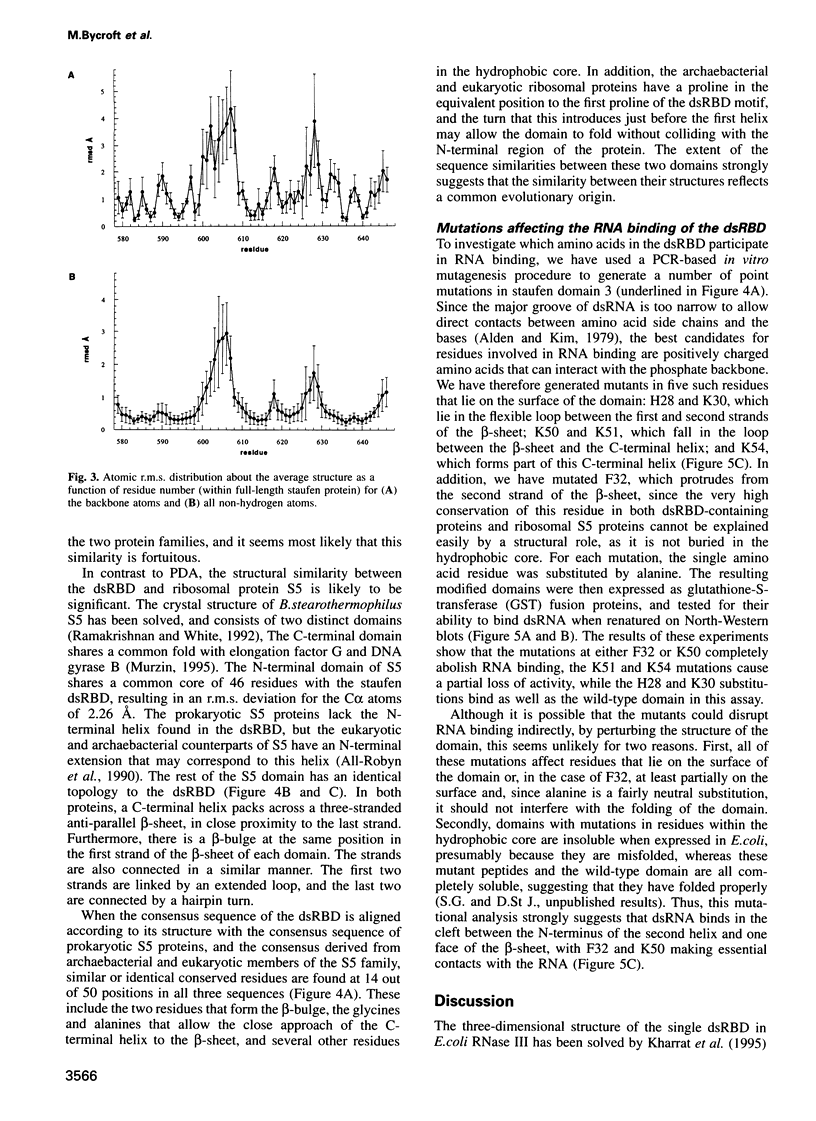
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Mathews M. B., Andersson P., Vennström B., Pettersson U. Structure of genes for virus-associated RNAI and RNAII of adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alden C. J., Kim S. H. Solvent-accessible surfaces of nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):411–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- All-Robyn J. A., Brown N., Otaka E., Liebman S. W. Sequence and functional similarity between a yeast ribosomal protein and the Escherichia coli S5 ram protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6544–6553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H. An unwinding activity that covalently modifies its double-stranded RNA substrate. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1089–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biou V., Yaremchuk A., Tukalo M., Cusack S. The 2.9 A crystal structure of T. thermophilus seryl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Ser). Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1404–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.8128220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birney E., Kumar S., Krainer A. R. Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5803–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R. RNA-protein interactions in the Escherichia coli ribosome. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90134-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):615–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8036511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castiglone Morelli M. A., Stier G., Gibson T., Joseph C., Musco G., Pastore A., Travè G. The KH module has an alpha beta fold. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 23;358(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01422-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dock-Bregeon A. C., Chevrier B., Podjarny A., Johnson J., de Bear J. S., Gough G. R., Gilham P. T., Moras D. Crystallographic structure of an RNA helix: [U(UA)6A]2. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 5;209(3):459–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandon D., Elphick L., Nüsslein-Volhard C., St Johnston D. Staufen protein associates with the 3'UTR of bicoid mRNA to form particles that move in a microtubule-dependent manner. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1221–1232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Thompson J. D. Detection of dsRNA-binding domains in RNA helicase A and Drosophila maleless: implications for monomeric RNA helicases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2552–2556. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Thompson J. D., Heringa J. The KH domain occurs in a diverse set of RNA-binding proteins that include the antiterminator NusA and is probably involved in binding to nucleic acid. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 21;324(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80152-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden B. L., Hoffman D. W., Ramakrishnan V., White S. W. Ribosomal protein S17: characterization of the three-dimensional structure by 1H and 15N NMR. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12812–12820. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good L., Nazar R. N. An improved thermal cycle for two-step PCR-based targeted mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4934–4934. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. R., Manche L., Mathews M. B. Two functionally distinct RNA-binding motifs in the regulatory domain of the protein kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):358–364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Two RNA-binding motifs in the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, DAI. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2478–2490. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. W., Query C. C., Golden B. L., White S. W., Keene J. D. RNA-binding domain of the A protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein analyzed by NMR spectroscopy is structurally similar to ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharrat A., Macias M. J., Gibson T. J., Nilges M., Pastore A. Structure of the dsRNA binding domain of E. coli RNase III. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 17;14(14):3572–3584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Burley S. K. 1.9 A resolution refined structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of TATAAAAG. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Sep;1(9):638–653. doi: 10.1038/nsb0994-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U., Wang Y., Sanford T., Zeng Y., Nishikura K. Molecular cloning of cDNA for double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminase, a candidate enzyme for nuclear RNA editing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11457–11461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladomery M., Sommerville J. Binding of Y-box proteins to RNA: involvement of different protein domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 25;22(25):5582–5589. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.25.5582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl M., Svensson L. A., Liljas A., Sedelnikova S. E., Eliseikina I. A., Fomenkova N. P., Nevskaya N., Nikonov S. V., Garber M. B., Muranova T. A. Crystal structure of the ribosomal protein S6 from Thermus thermophilus. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1249–1254. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ris/pdb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie G. V., Brownlie P. D., Lambert R., Cooper J. B., Blundell T. L., Wood S. P., Warren M. J., Woodcock S. C., Jordan P. M. Structure of porphobilinogen deaminase reveals a flexible multidomain polymerase with a single catalytic site. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):33–39. doi: 10.1038/359033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manche L., Green S. R., Schmedt C., Mathews M. B. Interactions between double-stranded RNA regulators and the protein kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5238–5248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E., Ahnn J., Inouye M. The DNA sequence of the gene (rnc) encoding ribonuclease III of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4677–4685. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. RNA recognition: a family matter? Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):837–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan N. A., Carpick B. W., Hollis B., Toone W. M., Zamanian-Daryoush M., Williams B. R. Mutational analysis of the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) binding domain of the dsRNA-activated protein kinase, PKR. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 10;270(6):2601–2606. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.6.2601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Chong K., Galabru J., Thomas N. S., Kerr I. M., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moras D., Poterszman A. RNA-protein interactions. Diverse modes of recognition. Curr Biol. 1995 Mar 1;5(3):249–251. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T. Nucleic acid-binding properties of the Xenopus oocyte Y box protein mRNP3+4. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13910–13917. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murzin A. G. A ribosomal protein module in EF-G and DNA gyrase. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Jan;2(1):25–26. doi: 10.1038/nsb0195-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri D., Szyperski T., Otting G., Senn H., Wüthrich K. Stereospecific nuclear magnetic resonance assignments of the methyl groups of valine and leucine in the DNA-binding domain of the 434 repressor by biosynthetically directed fractional 13C labeling. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7510–7516. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk K., Feng W., Jiang W., Tejero R., Emerson S. D., Inouye M., Montelione G. T. Solution NMR structure of the major cold shock protein (CspA) from Escherichia coli: identification of a binding epitope for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5114–5118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. A., Krause S., Higuchi M., Hsuan J. J., Totty N. F., Jenny A., Keller W. Cloning of cDNAs encoding mammalian double-stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1389–1397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oubridge C., Ito N., Evans P. R., Teo C. H., Nagai K. Crystal structure at 1.92 A resolution of the RNA-binding domain of the U1A spliceosomal protein complexed with an RNA hairpin. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):432–438. doi: 10.1038/372432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard V., Ersdal-Badju E., Lu A., Bock S. C. A rapid and efficient one-tube PCR-based mutagenesis technique using Pfu DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2587–2591. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polson A. G., Bass B. L. Preferential selection of adenosines for modification by double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminase. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5701–5711. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., White S. W. The structure of ribosomal protein S5 reveals sites of interaction with 16S rRNA. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):768–771. doi: 10.1038/358768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke-Appel J., Jünke N., Stade K., Brimacombe R. The path of mRNA through the Escherichia coli ribosome; site-directed cross-linking of mRNA analogues carrying a photo-reactive label at various points 3' to the decoding site. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2195–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Webster R. E., Zinder N. D. Purification and properties of ribonuclease III from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin H., Jiang W., Inouye M., Heinemann U. Crystal structure of CspA, the major cold shock protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin H., Marahiel M. A., Heinemann U. Universal nucleic acid-binding domain revealed by crystal structure of the B. subtilis major cold-shock protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):164–168. doi: 10.1038/364164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnuchel A., Wiltscheck R., Czisch M., Herrler M., Willimsky G., Graumann P., Marahiel M. A., Holak T. A. Structure in solution of the major cold-shock protein from Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):169–171. doi: 10.1038/364169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweisguth D. C., Chelladurai B. S., Nicholson A. W., Moore P. B. Structural characterization of a ribonuclease III processing signal. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 25;22(4):604–612. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Choi M., Siomi M. C., Nussbaum R. L., Dreyfuss G. Essential role for KH domains in RNA binding: impaired RNA binding by a mutation in the KH domain of FMR1 that causes fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Matunis M. J., Michael W. M., Dreyfuss G. The pre-mRNA binding K protein contains a novel evolutionarily conserved motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1193–1198. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Beuchle D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Staufen, a gene required to localize maternal RNAs in the Drosophila egg. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90138-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Brown N. H., Gall J. G., Jantsch M. A conserved double-stranded RNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10979–10983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Driever W., Berleth T., Richstein S., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Multiple steps in the localization of bicoid RNA to the anterior pole of the Drosophila oocyte. Development. 1989;107 (Suppl):13–19. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.Supplement.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of ribosomal proteins S5, S6, S11, S12, S18 and S21 with 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 20;201(4):683–695. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. RNA-protein interactions in 30S ribosomal subunits: folding and function of 16S rRNA. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):783–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2658053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valegård K., Murray J. B., Stockley P. G., Stonehouse N. J., Liljas L. Crystal structure of an RNA bacteriophage coat protein-operator complex. Nature. 1994 Oct 13;371(6498):623–626. doi: 10.1038/371623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B., Greuer B. The primary structure of protein S5 from the small subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 1;95(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Structural and functional properties of the evolutionarily ancient Y-box family of nucleic acid binding proteins. Bioessays. 1994 Apr;16(4):245–251. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]