Abstract
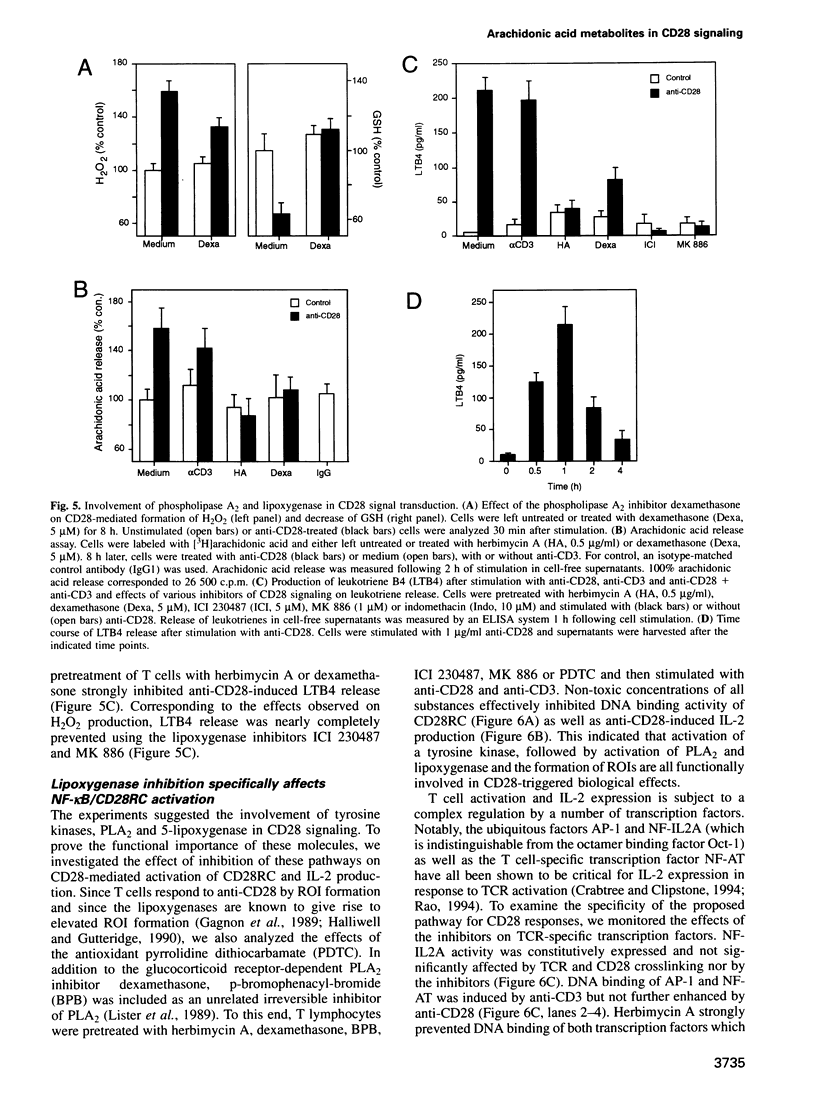
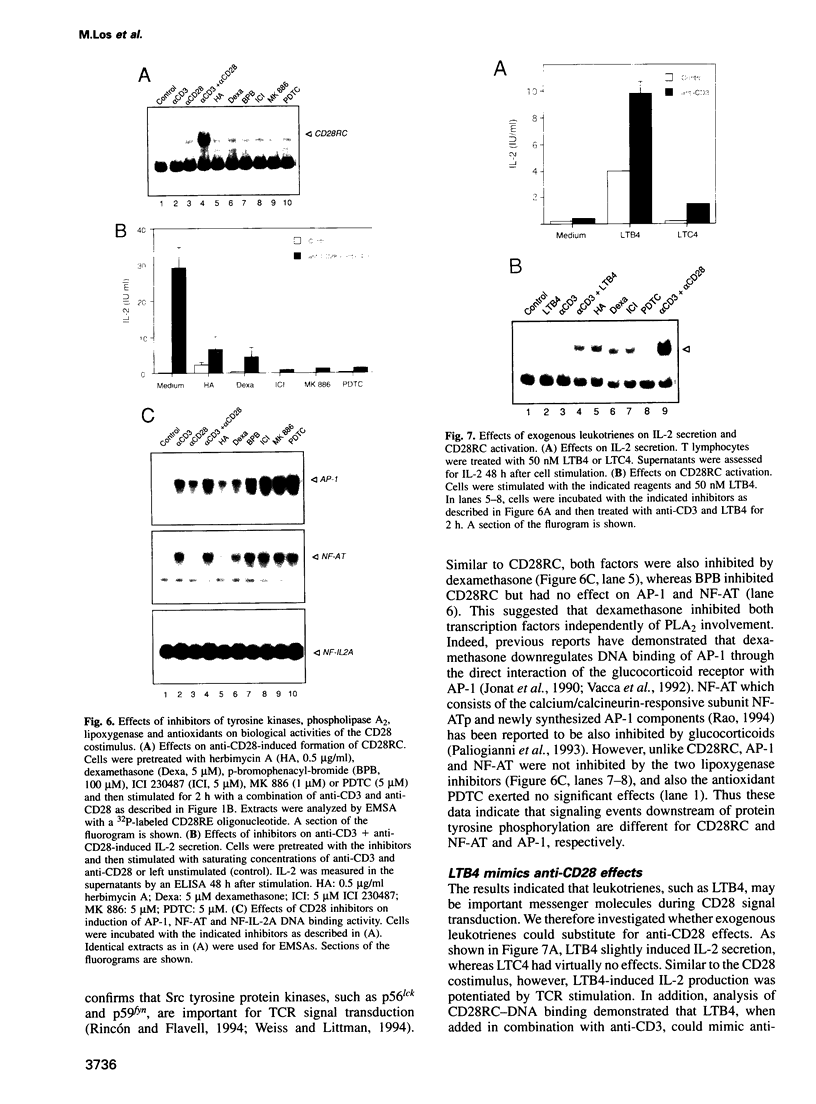
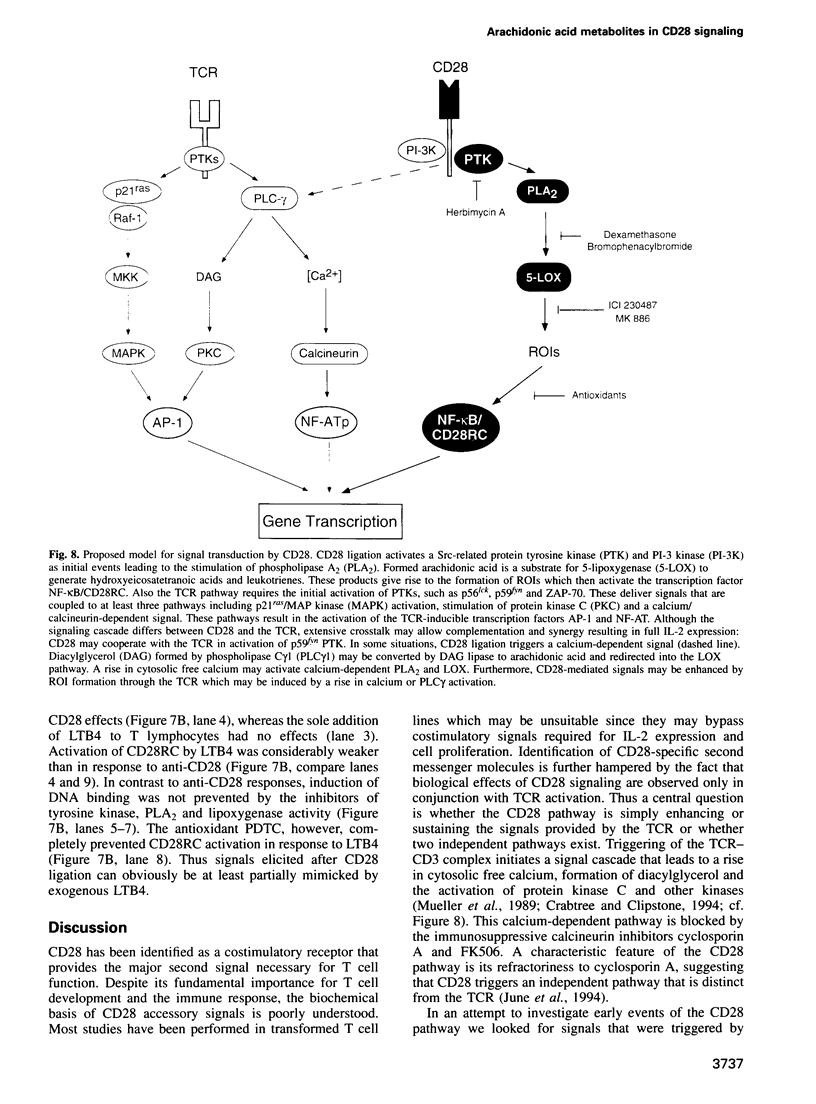
Activation of the CD28 surface receptor provides a major costimulatory signal for T cell activation resulting in enhanced production of interleukin-2 (IL-2) and cell proliferation. In primary T lymphocytes we show that CD28 ligation leads to the rapid intracellular formation of reactive oxygen intermediates (ROIs) which are required for CD28-mediated activation of the NF-kappa B/CD28-responsive complex and IL-2 expression. Delineation of the CD28 signaling cascade was found to involve protein tyrosine kinase activity, followed by the activation of phospholipase A2 and 5-lipoxygenase. Our data suggest that lipoxygenase metabolites activate ROI formation which then induce IL-2 expression via NF-kappa B activation. These findings should be useful for therapeutic strategies and the development of immunosuppressants targeting the CD28 costimulatory pathway.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorndahl J. M., Sung S. S., Hansen J. A., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation: differential response to anti-CD28 as compared to anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):881–887. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brach M. A., de Vos S., Arnold C., Gruss H. J., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Leukotriene B4 transcriptionally activates interleukin-6 expression involving NK-chi B and NF-IL6. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2705–2711. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdan C., Martin Y., Brailly H., Courcoul M., Flavetta S., Costello R., Mawas C., Birg F., Olive D. IL-1 alpha is produced by T lymphocytes activated via the CD2 plus CD28 pathways. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):560–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerdan C., Martin Y., Courcoul M., Brailly H., Mawas C., Birg F., Olive D. Prolonged IL-2 receptor alpha/CD25 expression after T cell activation via the adhesion molecules CD2 and CD28. Demonstration of combined transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2255–2261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
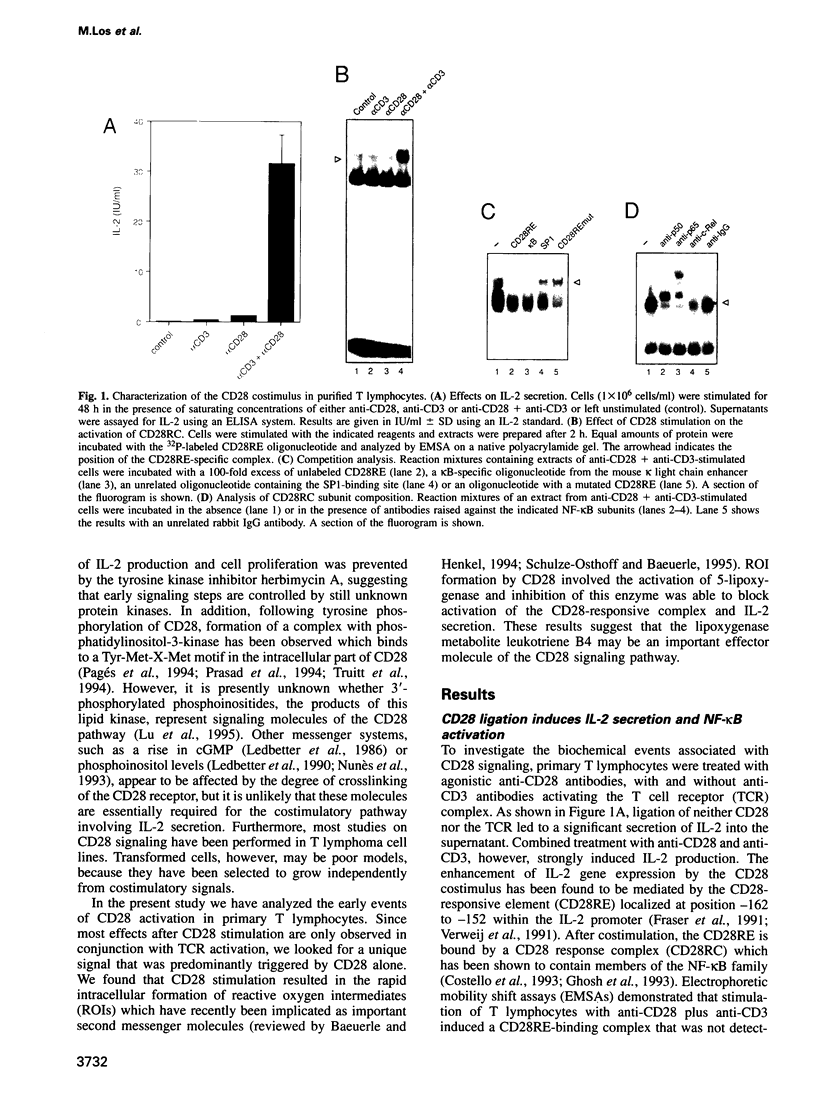
- Costello R., Lipcey C., Algarté M., Cerdan C., Baeuerle P. A., Olive D., Imbert J. Activation of primary human T-lymphocytes through CD2 plus CD28 adhesion molecules induces long-term nuclear expression of NF-kappa B. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Apr;4(4):329–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Clipstone N. A. Signal transmission between the plasma membrane and nucleus of T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:1045–1083. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.005145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley G. C., Bird T. G., Bruneau P., Dowell R. I., Edwards P. N., Foster S. J., Girodeau J. M., McMillan R. M., Walker E. R., Waterson D. Structure and activity relationships leading to the discovery of ICI D2138, a selective, potent and orally active inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. J Lipid Mediat. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(1-3):249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Gresser M., Young R. N. 5-Lipoxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:383–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz B., Nordby E. C., Bren G., Steffan N., Paya C. V., Kincaid R. L., Tocci M. J., O'Keefe S. J., O'Neill E. A. Calcineurin acts in synergy with PMA to inactivate I kappa B/MAD3, an inhibitor of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):861–870. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Irving B. A., Crabtree G. R., Weiss A. Regulation of interleukin-2 gene enhancer activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):313–316. doi: 10.1126/science.1846244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnon L., Filion L. G., Dubois C., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Leukotrienes and macrophage activation: augmented cytotoxic activity and enhanced interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor and hydrogen peroxide production. Agents Actions. 1989 Jan;26(1-2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF02126587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P., Tan T. H., Rice N. R., Sica A., Young H. A. The interleukin 2 CD28-responsive complex contains at least three members of the NF kappa B family: c-Rel, p50, and p65. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1696–1700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
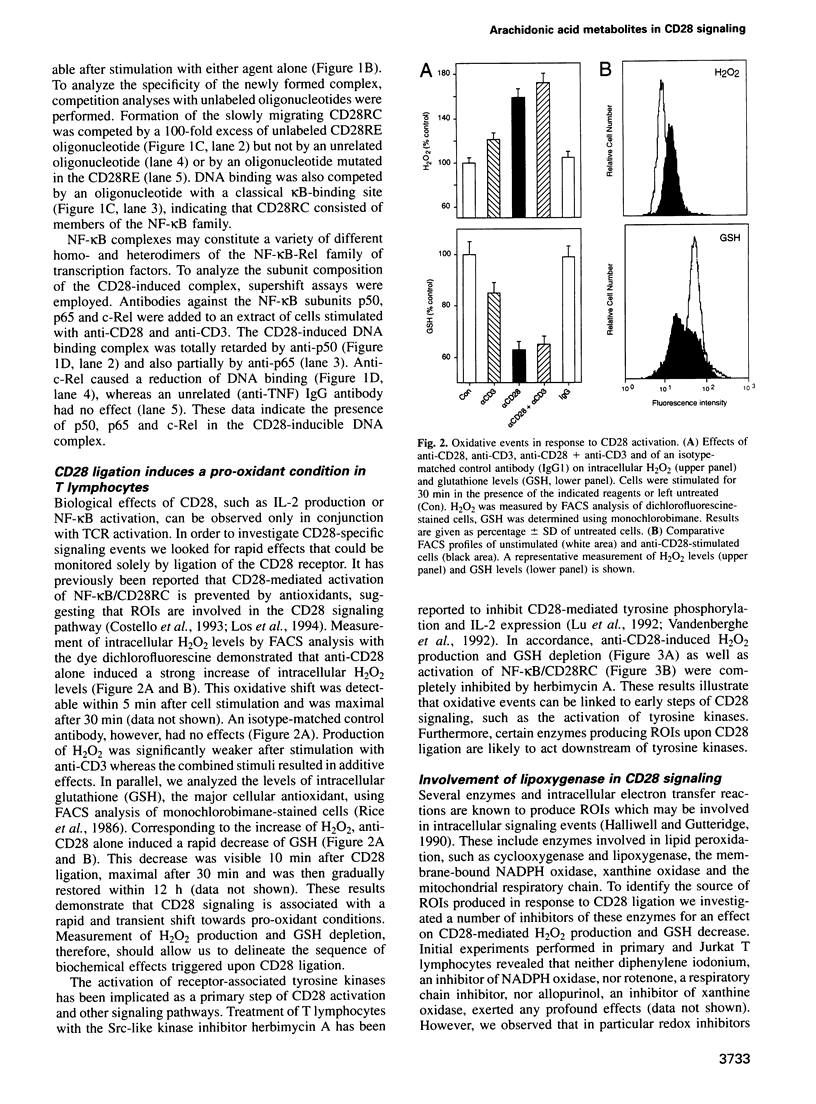
- Guba S. C., Stella G., Turka L. A., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Emerson S. G. Regulation of interleukin 3 gene induction in normal human T cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1701–1706. doi: 10.1172/JCI114352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:1–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86093-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding F. A., McArthur J. G., Gross J. A., Raulet D. H., Allison J. P. CD28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):607–609. doi: 10.1038/356607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchcroft J. E., Bierer B. E. Activation-dependent phosphorylation of the T-lymphocyte surface receptor CD28 and associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo Pastor M., Reif K., Cantrell D. The regulation and function of p21ras during T-cell activation and growth. Immunol Today. 1995 Mar;16(3):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Johnson J. G. Molecules involved in T-cell costimulation. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90054-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Bluestone J. A., Nadler L. M., Thompson C. B. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol Today. 1994 Jul;15(7):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Gillespie M. M., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. T-cell proliferation involving the CD28 pathway is associated with cyclosporine-resistant interleukin 2 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4472–4481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
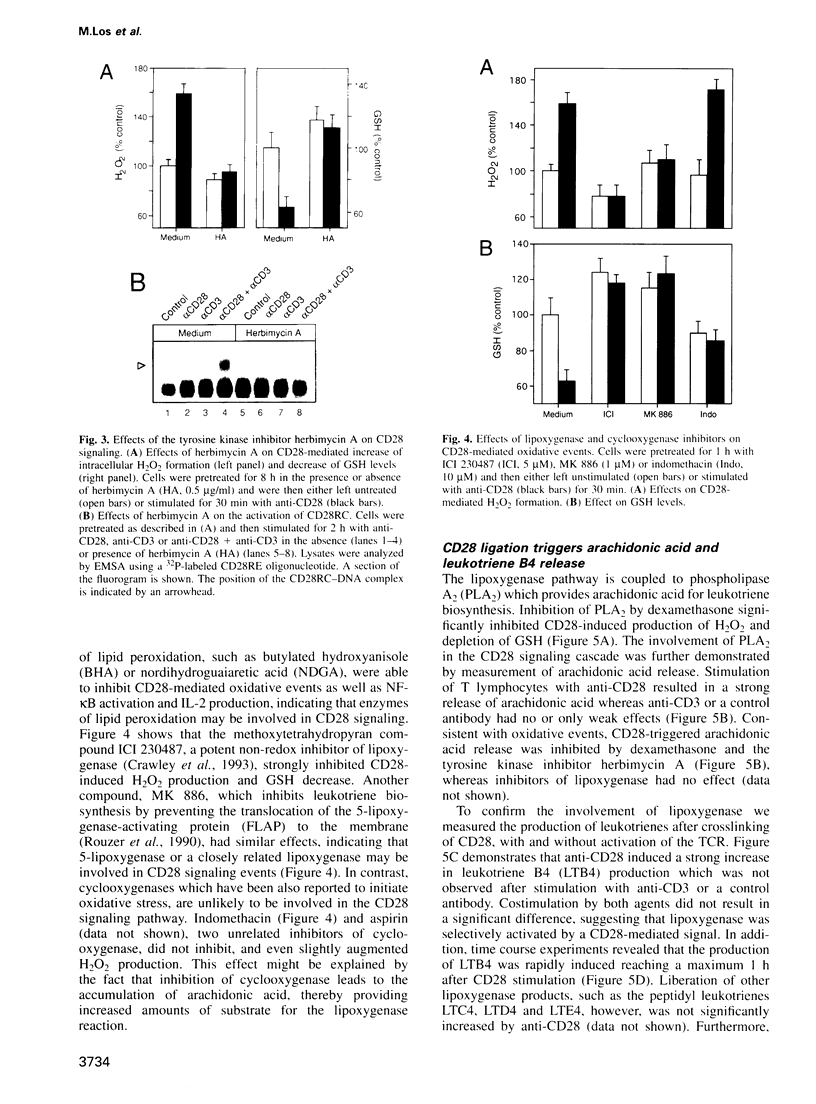
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Linsley P. S., Thompson C. B. Role of the CD28 receptor in T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1990 Jun;11(6):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90085-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Imboden J. B., Schieven G. L., Grosmaire L. S., Rabinovitch P. S., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B., June C. H. CD28 ligation in T-cell activation: evidence for two signal transduction pathways. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1531–1539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Parsons M., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Rabinovitch P. S., June C. H. Antibody binding to CD5 (Tp67) and Tp44 T cell surface molecules: effects on cyclic nucleotides, cytoplasmic free calcium, and cAMP-mediated suppression. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3299–3305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstein T., June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Stella G., Thompson C. B. Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):339–343. doi: 10.1126/science.2540528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Brady W., Urnes M., Grosmaire L. S., Damle N. K., Ledbetter J. A. CTLA-4 is a second receptor for the B cell activation antigen B7. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):561–569. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A. The role of the CD28 receptor during T cell responses to antigen. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:191–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister M. D., Glaser K. B., Ulevitch R. J., Dennis E. A. Inhibition studies on the membrane-associated phospholipase A2 in vitro and prostaglandin E2 production in vivo of the macrophage-like P388D1 cell. Effects of manoalide, 7,7-dimethyl-5,8-eicosadienoic acid, and p-bromophenacyl bromide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8520–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Los M., Dröge W., Schulze-Osthoff K. Inhibition of activation of transcription factor AP-1 by CD28 signalling in human T-cells. Biochem J. 1994 Aug 15;302(Pt 1):119–123. doi: 10.1042/bj3020119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Granelli-Piperno A., Bjorndahl J. M., Phillips C. A., Trevillyan J. M. CD28-induced T cell activation. Evidence for a protein-tyrosine kinase signal transduction pathway. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Phillips C. A., Trevillyan J. M. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is not essential for CD28 costimulatory activity in Jurkat T cells: studies with a selective inhibitor, wortmannin. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Feb;25(2):533–537. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Ledbetter J. A., Morishita Y., June C. H., Beatty P. G., Hansen J. A. A 44 kilodalton cell surface homodimer regulates interleukin 2 production by activated human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3282–3287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2005–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihm S., Ennen J., Pessara U., Kurth R., Dröge W. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication and NF-kappa B activity by cysteine and cysteine derivatives. AIDS. 1991 May;5(5):497–503. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199105000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes J., Klasen S., Franco M. D., Lipcey C., Mawas C., Bagnasco M., Olive D. Signalling through CD28 T-cell activation pathway involves an inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C activity. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 1;293(Pt 3):835–842. doi: 10.1042/bj2930835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunès J. A., Collette Y., Truneh A., Olive D., Cantrell D. A. The role of p21ras in CD28 signal transduction: triggering of CD28 with antibodies, but not the ligand B7-1, activates p21ras. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):1067–1076. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès F., Ragueneau M., Rottapel R., Truneh A., Nunes J., Imbert J., Olive D. Binding of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase to CD28 is required for T-cell signalling. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):327–329. doi: 10.1038/369327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliogianni F., Raptis A., Ahuja S. S., Najjar S. M., Boumpas D. T. Negative transcriptional regulation of human interleukin 2 (IL-2) gene by glucocorticoids through interference with nuclear transcription factors AP-1 and NF-AT. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1481–1489. doi: 10.1172/JCI116353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. V., Cai Y. C., Raab M., Duckworth B., Cantley L., Shoelson S. E., Rudd C. E. T-cell antigen CD28 interacts with the lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by a cytoplasmic Tyr(P)-Met-Xaa-Met motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punt J. A., Osborne B. A., Takahama Y., Sharrow S. O., Singer A. Negative selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes by T cell receptor-induced apoptosis requires a costimulatory signal that can be provided by CD28. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):709–713. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A. NF-ATp: a transcription factor required for the co-ordinate induction of several cytokine genes. Immunol Today. 1994 Jun;15(6):274–281. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. C., Bump E. A., Shrieve D. C., Lee W., Kovacs M. Quantitative analysis of cellular glutathione by flow cytometry utilizing monochlorobimane: some applications to radiation and drug resistance in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6105–6110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincón M., Flavell R. A. AP-1 transcriptional activity requires both T-cell receptor-mediated and co-stimulatory signals in primary T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4370–4381. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M., Stanková J. Leukotriene B4 enhances interleukin-6 (IL-6) production and IL-6 messenger RNA accumulation in human monocytes in vitro: transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):1004–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M., Thivierge M., Gagnon N., Lacasse C., Stankova J. Differential regulation of cytokine and cytokine receptor genes by PAF, LTB4 and PGE2. J Lipid Mediat. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(1-3):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Morton H. E., Gillard J. W. MK886, a potent and specific leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitor blocks and reverses the membrane association of 5-lipoxygenase in ionophore-challenged leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1436–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royall J. A., Ischiropoulos H. Evaluation of 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin and dihydrorhodamine 123 as fluorescent probes for intracellular H2O2 in cultured endothelial cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 May;302(2):348–355. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Dahlén S. E., Lindgren J. A., Rouzer C. A., Serhan C. N. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1171–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.2820055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk H., Klein M., Erdbrügger W., Dröge W., Schulze-Osthoff K. Distinct effects of thioredoxin and antioxidants on the activation of transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1672–1676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Beyaert R., Vandevoorde V., Haegeman G., Fiers W. Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3095–3104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanková J., Dupuis G., Gagnon N., Thivierge M., Turcotte S., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Priming of human monocytes with leukotriene B4 enhances their sensitivity in IL-2-driven tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional up-regulation of IL-2 receptors. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):4041–4051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su B., Jacinto E., Hibi M., Kallunki T., Karin M., Ben-Neriah Y. JNK is involved in signal integration during costimulation of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):727–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Lindsten T., Ledbetter J. A., Kunkel S. L., Young H. A., Emerson S. G., Leiden J. M., June C. H. CD28 activation pathway regulates the production of multiple T-cell-derived lymphokines/cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truitt K. E., Hicks C. M., Imboden J. B. Stimulation of CD28 triggers an association between CD28 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in Jurkat T cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):1071–1076. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Fukazawa H. Use and selectivity of herbimycin A as inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:370–379. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacca A., Felli M. P., Farina A. R., Martinotti S., Maroder M., Screpanti I., Meco D., Petrangeli E., Frati L., Gulino A. Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated suppression of the interleukin 2 gene expression through impairment of the cooperativity between nuclear factor of activated T cells and AP-1 enhancer elements. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):637–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lier R. A., Brouwer M., De Groot E. D., Kramer I., Aarden L. A., Verhoeven A. J. T cell receptor/CD3 and CD28 use distinct intracellular signaling pathways. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1775–1778. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberghe P., Freeman G. J., Nadler L. M., Fletcher M. C., Kamoun M., Turka L. A., Ledbetter J. A., Thompson C. B., June C. H. Antibody and B7/BB1-mediated ligation of the CD28 receptor induces tyrosine phosphorylation in human T cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):951–960. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij C. L., Geerts M., Aarden L. A. Activation of interleukin-2 gene transcription via the T-cell surface molecule CD28 is mediated through an NF-kB-like response element. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14179–14182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Littman D. R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]