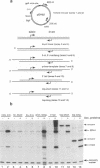
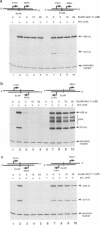
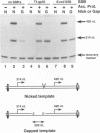
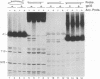
Abstract
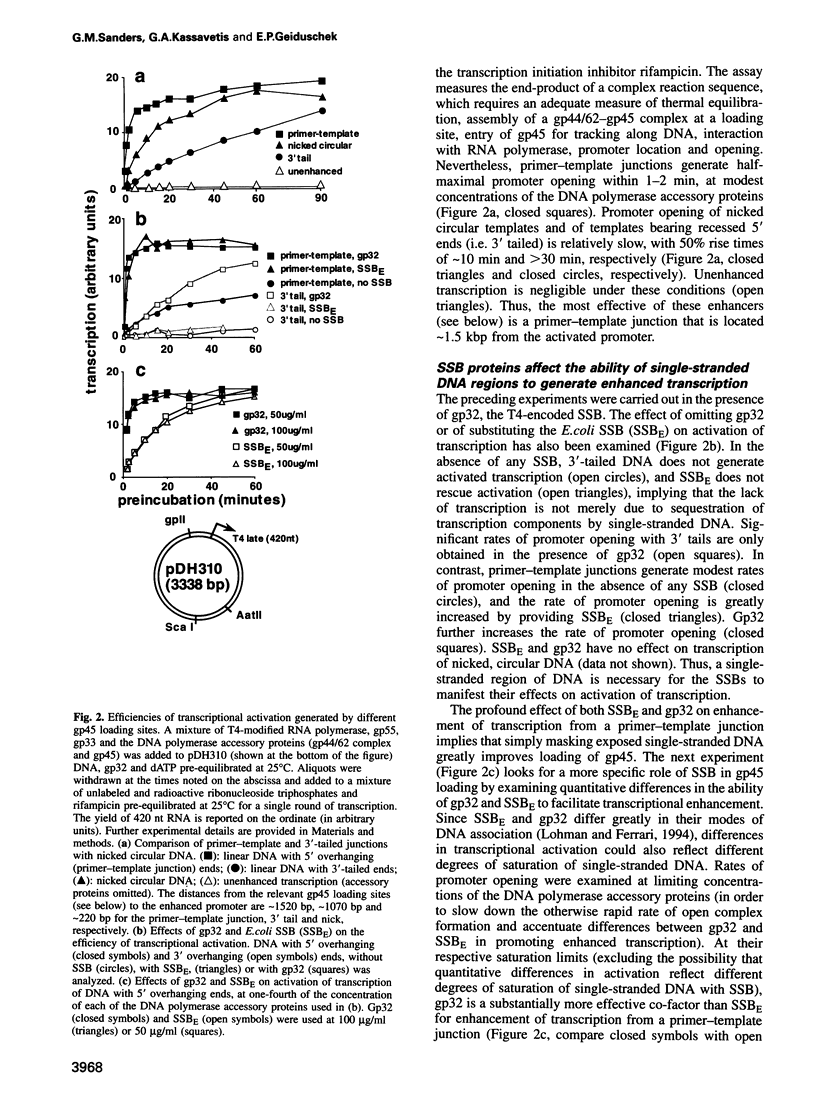
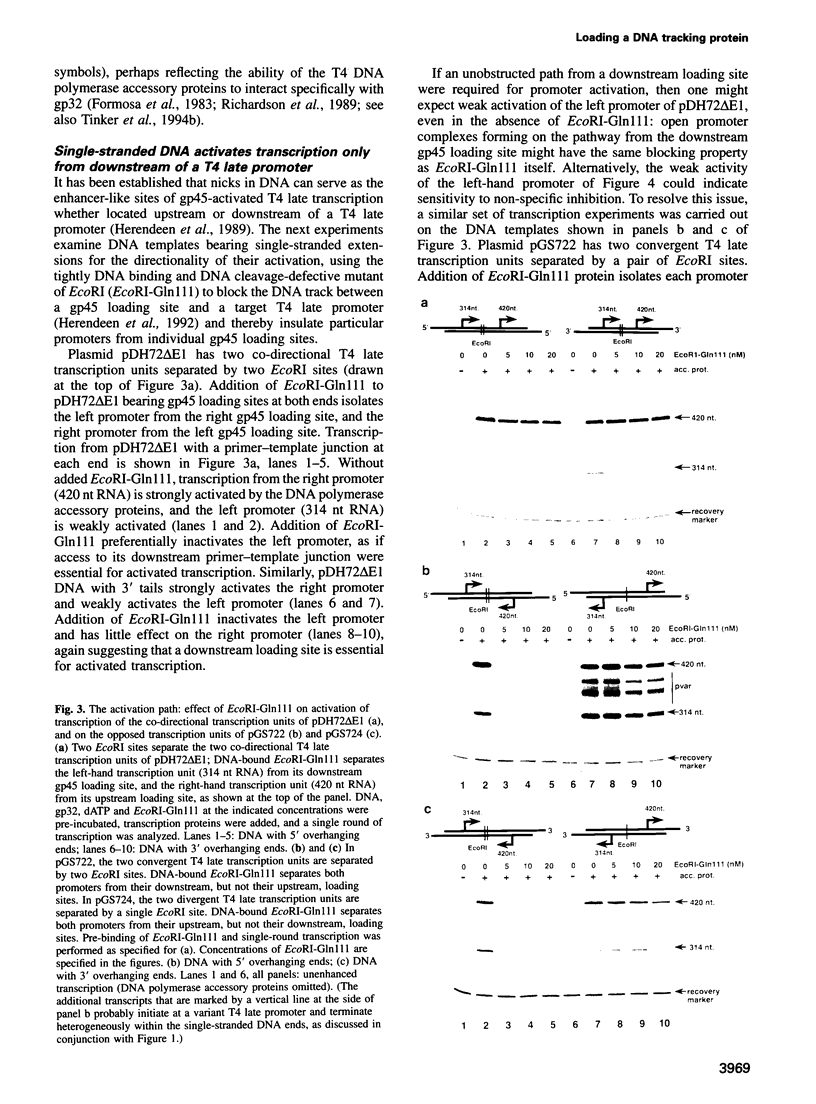
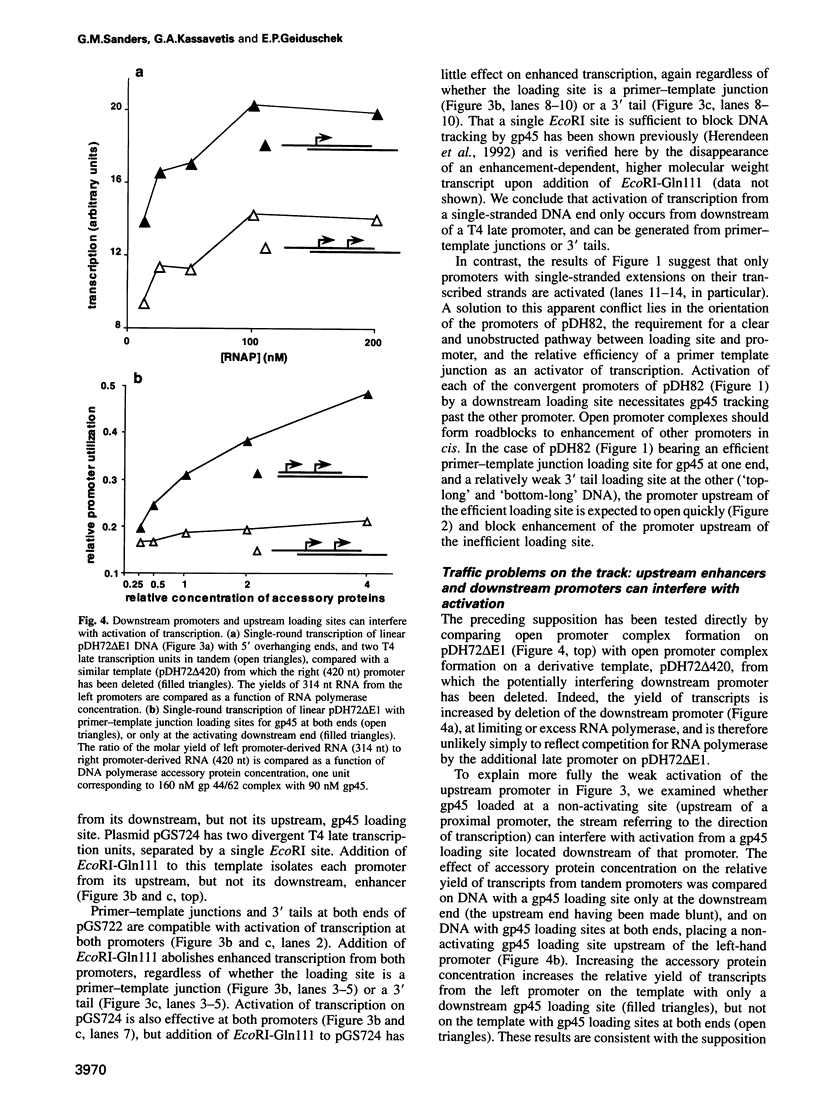
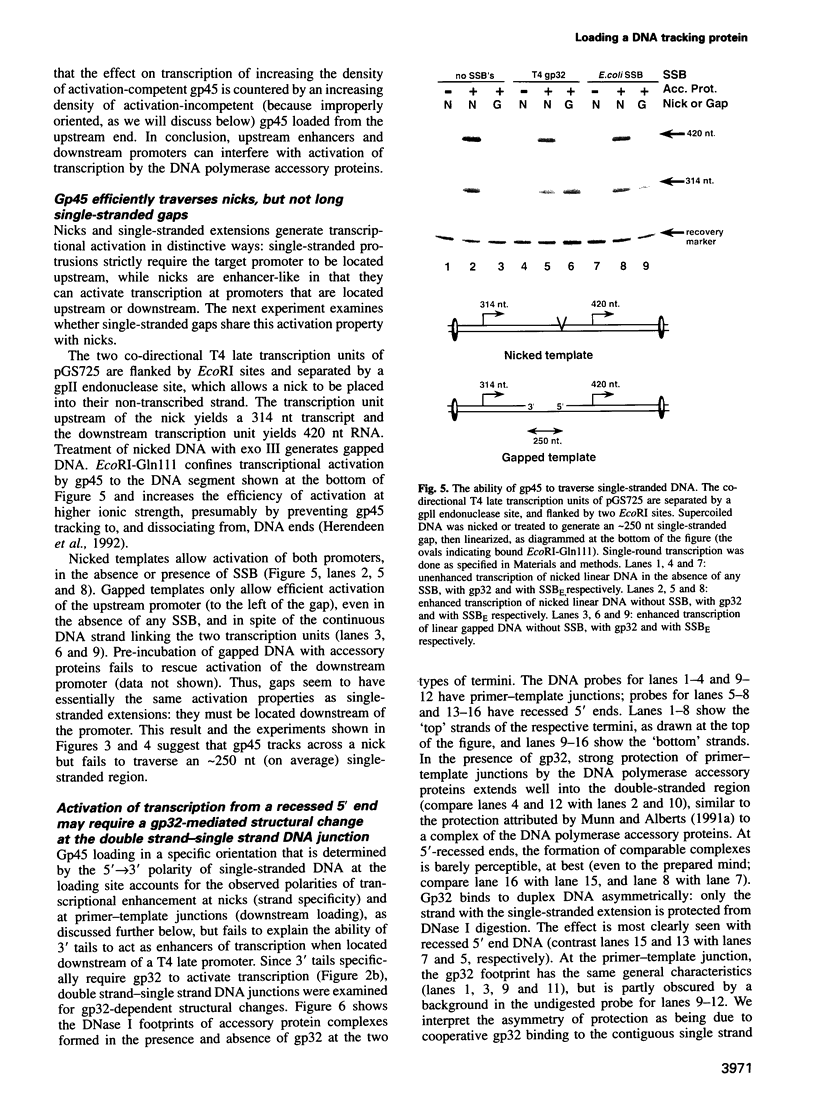
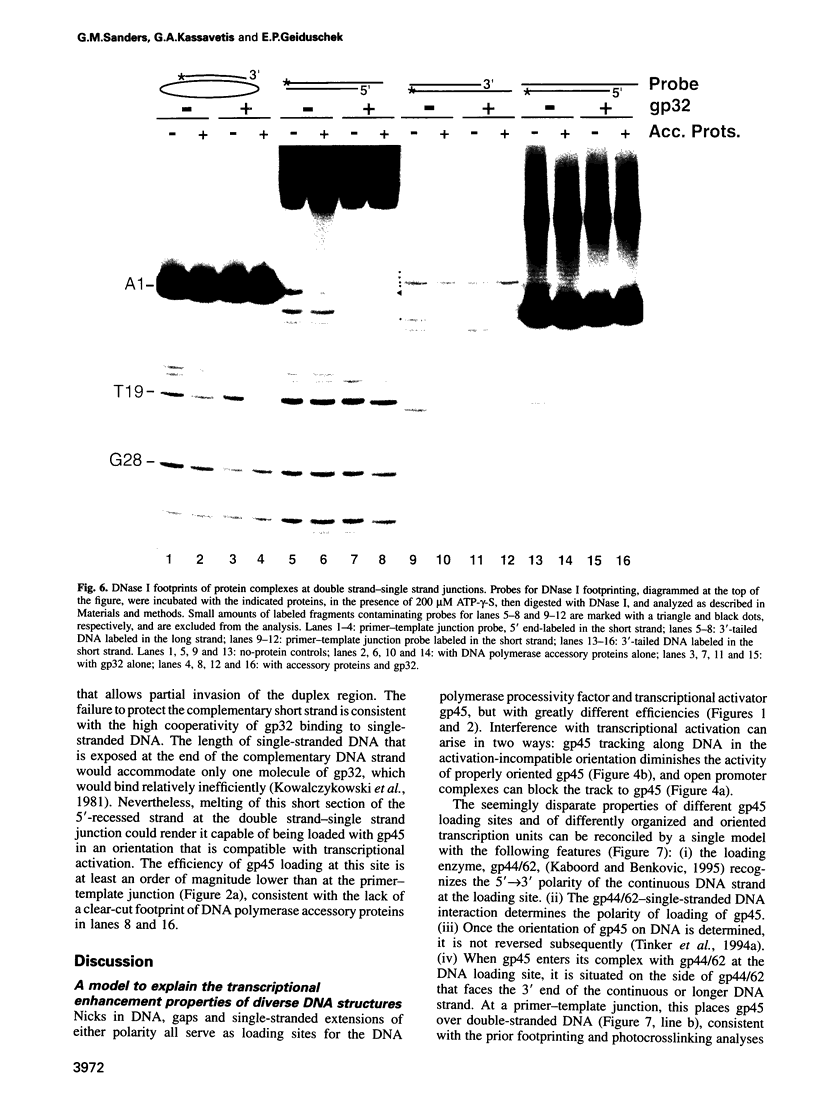
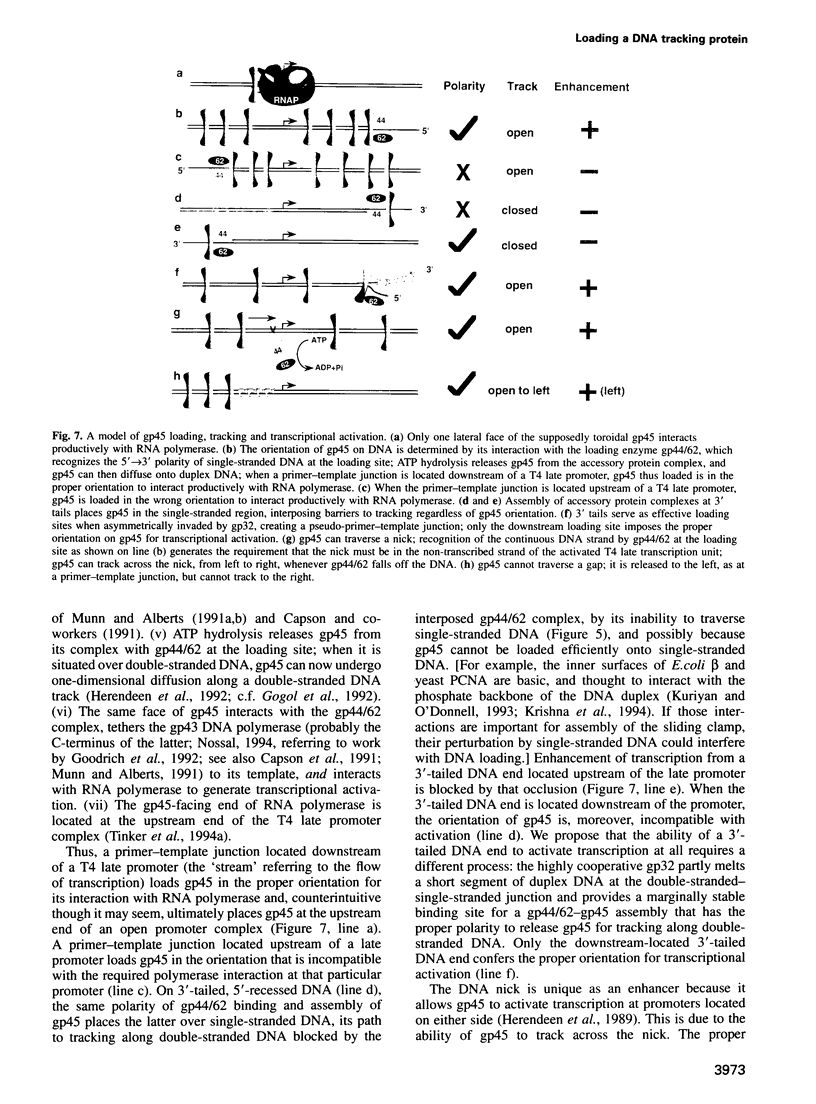
The bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase accessory proteins confer processivity and high speed on replicative DNA chain elongation: the gene 45 protein, gp45, tracks along DNA and serves as the sliding clamp of the viral DNA polymerase; the gene 44/62 protein complex, gp44/62, is an ATP-dependent loading enzyme that mounts gp45 on DNA. Gp45 also activates T4 late transcription. Transcriptional enhancement by gp45 requires a particular orientation that is imposed by gp44/62 at the DNA loading site. Loading and orienting gp45 on DNA, tracking along DNA and interaction with RNA polymerase have been analyzed by measuring transcriptional activation. The efficiency of loading gp45 at different DNA structures and the resulting transcriptional activation have been compared, and sources of interference with transcriptional activation have been examined. All observations are compatible with a mechanism in which the loading enzyme recognizes the polarity of single-stranded DNA and imposes a corresponding polarity of DNA entry on gp45. Primer-template junctions are the most efficient DNA loading sites for gp45 and can generate very rapid opening at promoters that are located at a distance of > 1 kbp. In contrast, gp45 does not track efficiently across single-stranded DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brody E. N., Kassavetis G. A., Ouhammouch M., Sanders G. M., Tinker R. L., Geiduschek E. P. Old phage, new insights: two recently recognized mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in bacteriophage T4 development. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995 Apr 15;128(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Yoder B. L. ATP-independent loading of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen requires DNA ends. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):19923–19926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capson T. L., Benkovic S. J., Nossal N. G. Protein-DNA cross-linking demonstrates stepwise ATP-dependent assembly of T4 DNA polymerase and its accessory proteins on the primer-template. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90159-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formosa T., Burke R. L., Alberts B. M. Affinity purification of bacteriophage T4 proteins essential for DNA replication and genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2442–2446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogol E. P., Young M. C., Kubasek W. L., Jarvis T. C., von Hippel P. H. Cryoelectron microscopic visualization of functional subassemblies of the bacteriophage T4 DNA replication complex. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):395–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen D. R., Kassavetis G. A., Barry J., Alberts B. M., Geiduschek E. P. Enhancement of bacteriophage T4 late transcription by components of the T4 DNA replication apparatus. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):952–958. doi: 10.1126/science.2672335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen D. R., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. A transcriptional enhancer whose function imposes a requirement that proteins track along DNA. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1298–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1598572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen D. R., Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. An RNA polymerase-binding protein that is required for communication between an enhancer and a promoter. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):573–578. doi: 10.1126/science.2185541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis T. C., Paul L. S., Hockensmith J. W., von Hippel P. H. Structural and enzymatic studies of the T4 DNA replication system. II. ATPase properties of the polymerase accessory protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12717–12729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis T. C., Paul L. S., von Hippel P. H. Structural and enzymatic studies of the T4 DNA replication system. I. Physical characterization of the polymerase accessory protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12709–12716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaboord B. F., Benkovic S. J. Accessory proteins function as matchmakers in the assembly of the T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme. Curr Biol. 1995 Feb 1;5(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong X. P., Onrust R., O'Donnell M., Kuriyan J. Three-dimensional structure of the beta subunit of E. coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: a sliding DNA clamp. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90445-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Lonberg N., Newport J. W., von Hippel P. H. Interactions of bacteriophage T4-coded gene 32 protein with nucleic acids. I. Characterization of the binding interactions. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):75–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna T. S., Kong X. P., Gary S., Burgers P. M., Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of the eukaryotic DNA polymerase processivity factor PCNA. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1233–1243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyan J., O'Donnell M. Sliding clamps of DNA polymerases. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):915–925. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Ferrari M. E. Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein: multiple DNA-binding modes and cooperativities. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:527–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn M. M., Alberts B. M. DNA footprinting studies of the complex formed by the T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme at a primer-template junction. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20034–20044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn M. M., Alberts B. M. The T4 DNA polymerase accessory proteins form an ATP-dependent complex on a primer-template junction. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20024–20033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podust L. M., Podust V. N., Sogo J. M., Hübscher U. Mammalian DNA polymerase auxiliary proteins: analysis of replication factor C-catalyzed proliferating cell nuclear antigen loading onto circular double-stranded DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3072–3081. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders G. M., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Use of a macromolecular crowding agent to dissect interactions and define functions in transcriptional activation by a DNA-tracking protein: bacteriophage T4 gene 45 protein and late transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7703–7707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stukenberg P. T., Studwell-Vaughan P. S., O'Donnell M. Mechanism of the sliding beta-clamp of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11328–11334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhl S., Hultman T., Olsson A., Moks T., Uhlén M. Solid phase DNA sequencing using the biotin-avidin system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3025–3038. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker R. L., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Detecting the ability of viral, bacterial and eukaryotic replication proteins to track along DNA. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5330–5337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker R. L., Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Transcriptional activation by a DNA-tracking protein: structural consequences of enhancement at the T4 late promoter. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. C., Reddy M. K., von Hippel P. H. Structure and function of the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8675–8690. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]