Abstract
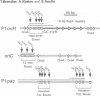
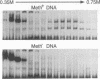
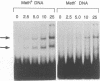
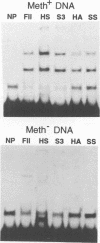
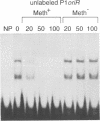
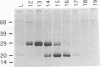
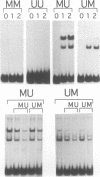
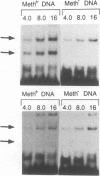
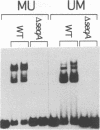
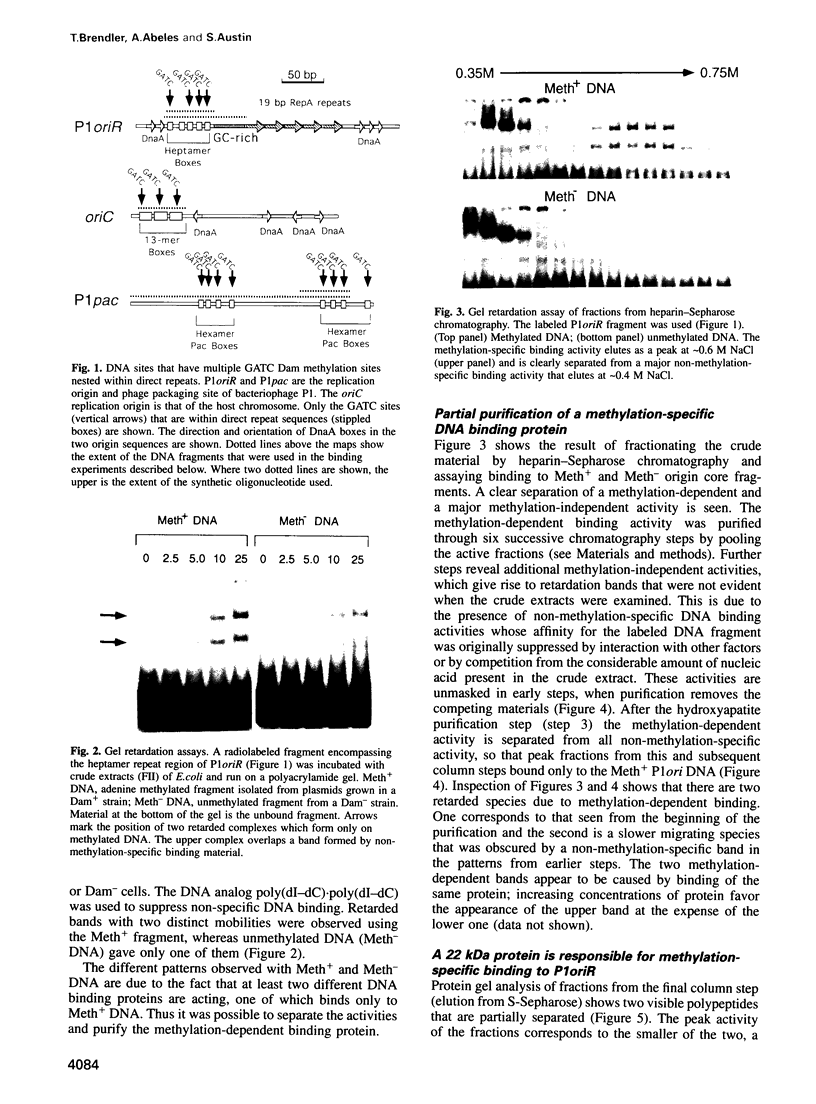
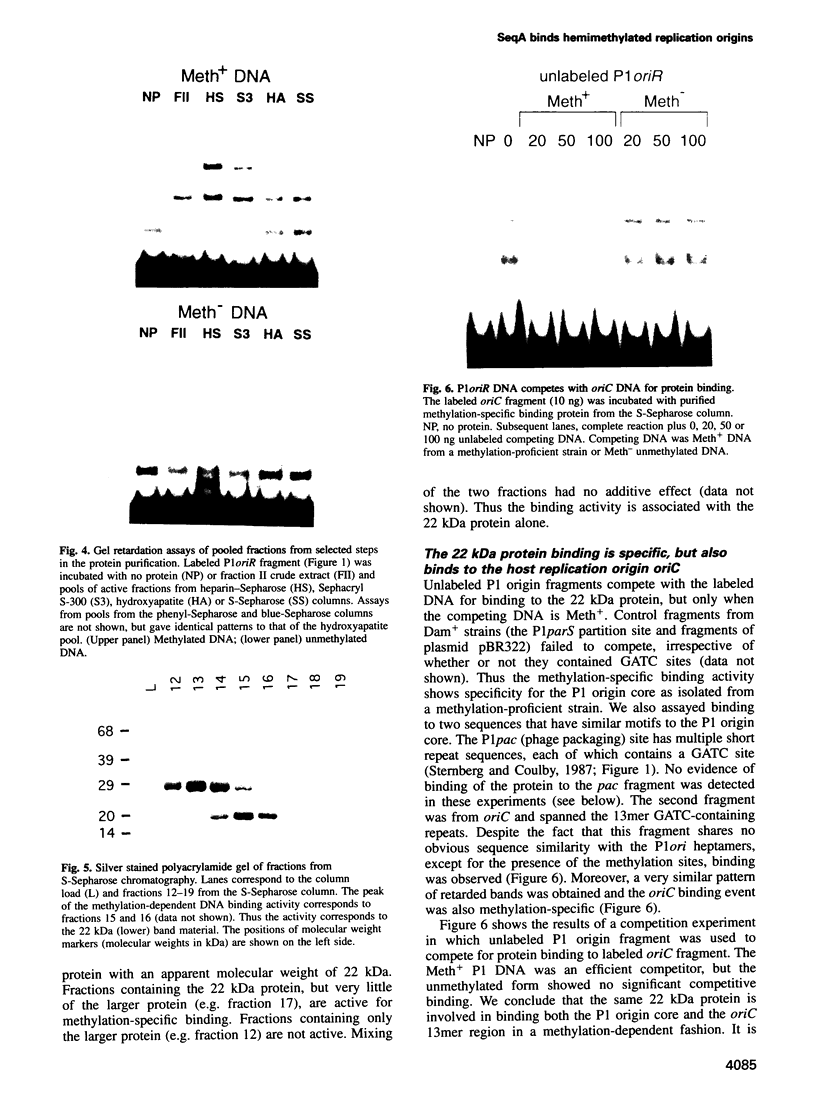
The P1 plasmid replication origin P1oriR is controlled by methylation of four GATC adenine methylation sites within heptamer repeats. A comparable (13mer) region is present in the host origin, oriC. The two origins show comparable responses to methylation; negative control by recognition of hemimethylated DNA (sequestration) and a positive requirement for methylation for efficient function. We have isolated a host protein that recognizes the P1 origin region only when it is isolated from a strain proficient for adenine methylation. The substantially purified 22 kDa protein also binds to the 13mer region of oriC in a methylation-specific fashion. It proved to be the product of the seqA gene that acts in the negative control of oriC by sequestration. We conclude that the role of the SeqA protein in sequestration is to recognize the methylation state of P1oriR and oriC by direct DNA binding. Using synthetic substrates we show that SeqA binds exclusively to the hemimethylated forms of these origins forms that are the immediate products of replication in a methylation-proficient strain. We also show that the protein can recognize sequences with multiple GATC sites, irrespective of the surrounding sequence. The basis for origin specificity is primarily the persistence of hemimethylated forms that are over-represented in the natural. DNA preparations relative to controls.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles A. L., Austin S. J. P1 plasmid replication requires methylated DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3185–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeles A. L., Snyder K. M., Chattoraj D. K. P1 plasmid replication: replicon structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):307–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeles A., Brendler T., Austin S. Evidence of two levels of control of P1 oriR and host oriC replication origins by DNA adenine methylation. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(24):7801–7807. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.24.7801-7807.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker A., Smith D. W. Methylation of GATC sites is required for precise timing between rounds of DNA replication in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5738–5742. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5738-5742.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boye E., Løbner-Olesen A. The role of dam methyltransferase in the control of DNA replication in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):981–989. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90272-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. A model for initiation at origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):743–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendler T., Abeles A., Austin S. Critical sequences in the core of the P1 plasmid replication origin. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):3935–3942. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.3935-3942.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L., Kleckner N. E. coli oriC and the dnaA gene promoter are sequestered from dam methyltransferase following the passage of the chromosomal replication fork. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90271-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D. Effects of the modification of transfer buffer composition and the renaturation of proteins in gels on the recognition of proteins on Western blots by monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):144–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Kaguni J. M., Kornberg A. Enzymatic replication of the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7370–7374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabant P., Newnham P., Taylor D., Couturier M. Isolation and location on the R27 map of two replicons and an incompatibility determinant specific for IncHI1 plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7697–7701. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7697-7701.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang D. S., Kornberg A. Opposed actions of regulatory proteins, DnaA and IciA, in opening the replication origin of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23087–23091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Terawaki Y. Nucleotide sequence of an incompatibility region of mini-Rts1 that contains five direct repeats. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1185–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1185-1191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L. Influence of GATC sequences on Escherichia coli DNA mismatch repair in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1254–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1254-1259.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu M., Campbell J. L., Boye E., Kleckner N. SeqA: a negative modulator of replication initiation in E. coli. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):413–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer M., Beck E., Hansen F. G., Bergmans H. E., Messer W., von Meyenburg K., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence of the origin of replication of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):580–584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer W., Bellekes U., Lother H. Effect of dam methylation on the activity of the E. coli replication origin, oriC. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1327–1332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden G. B., Pratt M. J., Schaechter M. The replicative origin of the E. coli chromosome binds to cell membranes only when hemimethylated. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul D., Lane D., Bergquist P. L. A replication region of the IncHI plasmid, R27, is highly homologous with the RepFIA replicon of F. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Coulby J. Recognition and cleavage of the bacteriophage P1 packaging site (pac). II. Functional limits of pac and location of pac cleavage termini. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90675-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woelker B., Messer W. The structure of the initiation complex at the replication origin, oriC, of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5025–5033. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Cleary J. M., Brusilow W. S., Harding N. E., Smith D. W. Chromosomal replication origin from the marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi functions in Escherichia coli: oriC consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1164–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]