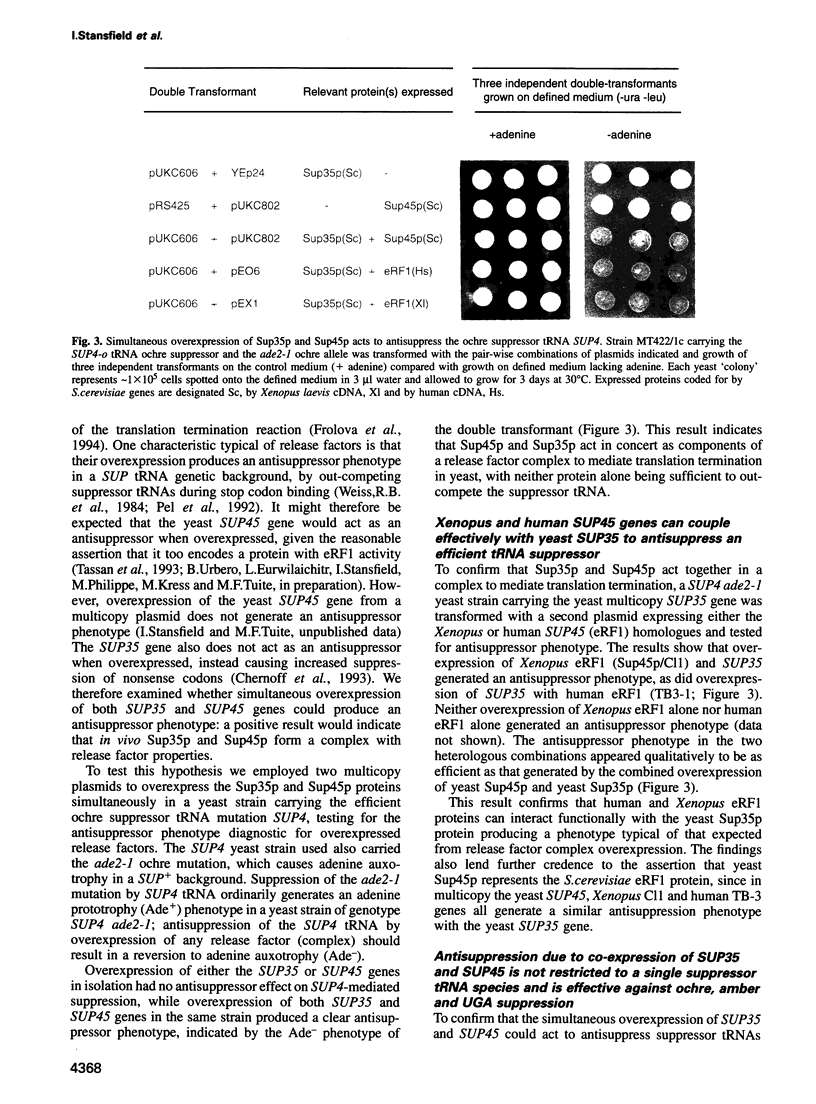
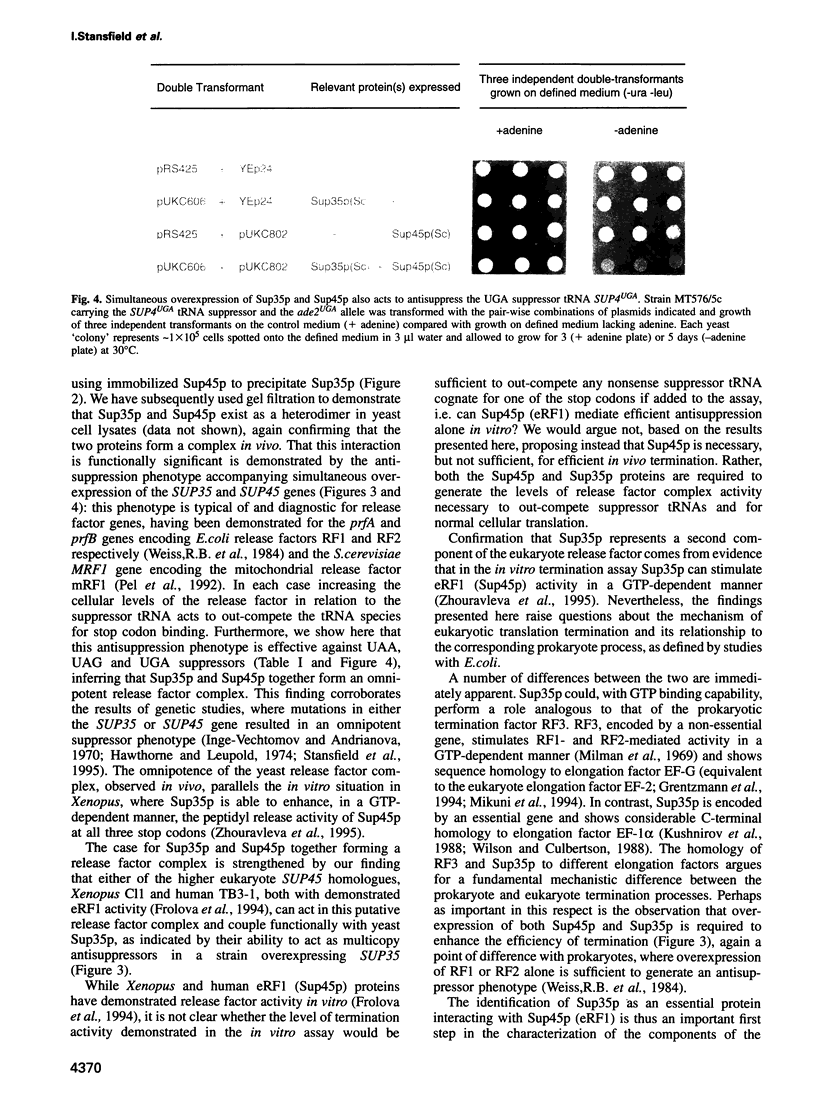
Abstract
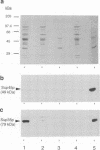
The product of the yeast SUP45 gene (Sup45p) is highly homologous to the Xenopus eukaryote release factor 1 (eRF1), which has release factor activity in vitro. We show, using the two-hybrid system, that in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sup45p and the product of the SUP35 gene (Sup35p) interact in vivo. The ability of Sup45p C-terminally tagged with (His)6 to specifically precipitate Sup35p from a cell lysate was used to confirm this interaction in vitro. Although overexpression of either the SUP45 or SUP35 genes alone did not reduce the efficiency of codon-specific tRNA nonsense suppression, the simultaneous overexpression of both the SUP35 and SUP45 genes in nonsense suppressor tRNA-containing strains produced an antisuppressor phenotype. These data are consistent with Sup35p and Sup45p forming a complex with release factor properties. Furthermore, overexpression of either Xenopus or human eRF1 (SUP45) genes also resulted in anti-suppression only if that strain was also overexpressing the yeast SUP35 gene. Antisuppression is a characteristic phenotype associated with overexpression of both prokaryote and mitochondrial release factors. We propose that Sup45p and Sup35p interact to form a release factor complex in yeast and that Sup35p, which has GTP binding sequence motifs in its C-terminal domain, provides the GTP hydrolytic activity which is a demonstrated requirement of the eukaryote translation termination reaction.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel P., Chien C. T., Sternglanz R., Fields S. Elimination of false positives that arise in using the two-hybrid system. Biotechniques. 1993 Jun;14(6):920–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D. M., Guarente L. High-efficiency transformation of yeast by electroporation. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:182–187. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:643–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey C. T., Tompkins R., Scolnick E., Caryk T., Nirenberg M. Sequential translation of trinucleotide codons for the initiation and termination of protein synthesis. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):135–138. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff Y. O., Derkach I. L., Inge-Vechtomov S. G. Multicopy SUP35 gene induces de-novo appearance of psi-like factors in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1993 Sep;24(3):268–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00351802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Sikorski R. S., Dante M., Shero J. H., Hieter P. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. Cytoplasmic inheritance. Prion-like factors in yeast. Curr Biol. 1994 Aug 1;4(8):744–748. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didichenko S. A., Ter-Avanesyan M. D., Smirnov V. N. Ribosome-bound EF-1 alpha-like protein of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jun 15;198(3):705–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel S. M., McCready S. J., Nierras C. R., Cox B. S. The dominant PNM2- mutation which eliminates the psi factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the result of a missense mutation in the SUP35 gene. Genetics. 1994 Jul;137(3):659–670. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowell S. J., Tsang J. S., Mellor J. The centromere and promoter factor 1 of yeast contains a dimerisation domain located carboxy-terminal to the bHLH domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4229–4236. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein D. B., Strausberg S. Heat shock-regulated production of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1625–1633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolova LYu, Dalphin M. E., Justesen J., Powell R. J., Drugeon G., McCaughan K. K., Kisselev L. L., Tate W. P., Haenni A. L. Mammalian polypeptide chain release factor and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase are distinct proteins. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):4013–4019. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolova L., Le Goff X., Rasmussen H. H., Cheperegin S., Drugeon G., Kress M., Arman I., Haenni A. L., Celis J. E., Philippe M. A highly conserved eukaryotic protein family possessing properties of polypeptide chain release factor. Nature. 1994 Dec 15;372(6507):701–703. doi: 10.1038/372701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination with mammalian release factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):99–106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenett H. E., Bounelis P., Fuller G. M. Identification of a human cDNA with high homology to yeast omnipotent suppressor 45. Gene. 1992 Jan 15;110(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90655-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grentzmann G., Brechemier-Baey D., Heurgue V., Mora L., Buckingham R. H. Localization and characterization of the gene encoding release factor RF3 in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5848–5852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne D. C., Leupold U. Suppressors in yeast. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):1–47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb H. J., Maicas E., Friesen J. D. Isolation of the SUP45 omnipotent suppressor gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and characterization of its gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):816–822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima A., Kaji A. Factor-dependent release of ribosomes from messenger RNA. Requirement for two heat-stable factors. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;65(1):43–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90490-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino S., Miyazawa H., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Kikuchi Y., Kikuchi A., Ui M. A human homologue of the yeast GST1 gene codes for a GTP-binding protein and is expressed in a proliferation-dependent manner in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3807–3814. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. S., Prakash L. Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae selectable markers in pUC18 polylinkers. Yeast. 1990 Sep-Oct;6(5):363–366. doi: 10.1002/yea.320060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H., Capecchi M. R. Polypetide chain termination. Purification of the release factors, R1 and R2, from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1055–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Aune K. C., Tate W., Caskey C. T. Characterization of reticulocyte release factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4514–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnirov V. V., Ter-Avanesyan M. D., Didichenko S. A., Smirnov V. N., Chernoff Y. O., Derkach I. L., Novikova O. N., Inge-Vechtomov S. G., Neistat M. A., Tolstorukov I. I. Divergence and conservation of SUP2 (SUP35) gene of yeast Pichia pinus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1990 Nov-Dec;6(6):461–472. doi: 10.1002/yea.320060603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnirov V. V., Ter-Avanesyan M. D., Telckov M. V., Surguchov A. P., Smirnov V. N., Inge-Vechtomov S. G. Nucleotide sequence of the SUP2 (SUP35) gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Craigen W. J., Muzny D. M., Harlow E., Caskey C. T. Cloning and expression of a mammalian peptide chain release factor with sequence similarity to tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3508–3512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikuni O., Ito K., Moffat J., Matsumura K., McCaughan K., Nobukuni T., Tate W., Nakamura Y. Identification of the prfC gene, which encodes peptide-chain-release factor 3 of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5798–5802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Goldstein J., Scolnick E., Caskey T. Peptide chain termination. 3. Stimulation of in vitro termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):183–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pel H. J., Maat C., Rep M., Grivell L. A. The yeast nuclear gene MRF1 encodes a mitochondrial peptide chain release factor and cures several mitochondrial RNA splicing defects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6339–6346. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pure G. A., Robinson G. W., Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. Partial suppression of an ochre mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by multicopy plasmids containing a normal yeast tRNAGln gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E., Tompkins R., Caskey T., Nirenberg M. Release factors differing in specificity for terminator codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):768–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J. M., Liebman S. W. Allosuppressors that enhance the efficiency of omnipotent suppressors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 Mar;115(3):451–460. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfield I., Akhmaloka, Tuite M. F. A mutant allele of the SUP45 (SAL4) gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae shows temperature-dependent allosuppressor and omnipotent suppressor phenotypes. Curr Genet. 1995 Apr;27(5):417–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00311210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfield I., Grant G. M., Akhmaloka, Tuite M. F. Ribosomal association of the yeast SAL4 (SUP45) gene product: implications for its role in translation fidelity and termination. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Dec;6(23):3469–3478. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassan J. P., Le Guellec K., Kress M., Faure M., Camonis J., Jacquet M., Philippe M. In Xenopus laevis, the product of a developmentally regulated mRNA is structurally and functionally homologous to a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in translation fidelity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2815–2821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuite M. F. Genetics. Psi no more for yeast prions. Nature. 1994 Aug 4;370(6488):327–328. doi: 10.1038/370327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuite M. F., McLaughlin C. S. Endogenous read-through of a UGA termination codon in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell-free system: evidence for involvement of both a mitochondrial and a nuclear tRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 May;2(5):490–497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.5.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuite M. F., Stansfield I. Translation. Knowing when to stop. Nature. 1994 Dec 15;372(6507):614–615. doi: 10.1038/372614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Newnam G., Liebman S. W. The yeast translational allosuppressor, SAL6: a new member of the PP1-like phosphatase family with a long serine-rich N-terminal extension. Genetics. 1994 Nov;138(3):597–608. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.3.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Murphy J. P., Gallant J. A. Genetic screen for cloned release factor genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):362–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.362-364.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss W. A., Friedberg E. C. Normal yeast tRNA(CAGGln) can suppress amber codons and is encoded by an essential gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. [URE3] as an altered URE2 protein: evidence for a prion analog in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):566–569. doi: 10.1126/science.7909170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. G., Culbertson M. R. SUF12 suppressor protein of yeast. A fusion protein related to the EF-1 family of elongation factors. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):559–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhouravleva G., Frolova L., Le Goff X., Le Guellec R., Inge-Vechtomov S., Kisselev L., Philippe M. Termination of translation in eukaryotes is governed by two interacting polypeptide chain release factors, eRF1 and eRF3. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 15;14(16):4065–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]