Abstract
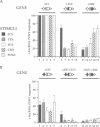
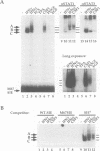
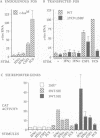
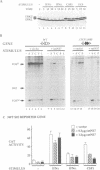
The upstream regulatory region of the c-fos promoter contains two growth factor-regulated promoter elements: the serum response element, which binds a ternary complex comprising serum response factor (SRF) and a ternary complex factor (TCF); and the sis-inducible element (SIE) which binds STAT transcription factors. We used transient transfection of c-fos promoter mutants in NIH 3T3 cells to assess the contributions of these elements to activation by different extracellular stimuli. Colony-stimulating factor-1, platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor activate the c-fos promoter via cooperation of the SIE and the SRE; however, mutants that can bind SRF but not STATs or TCF remain inducible by whole serum. Activation by the SIE is context-dependent: interferons activate STAT DNA binding activity and transcription of SIE reporter genes, but not the c-fos promoter, which requires an additional ras-dependent signal. SRE activation by receptor tyrosine kinases requires TCF binding, and can be mediated by the TCF Elk-1. In contrast, SRE activation following activation of heterotrimeric G proteins by lysophosphatidic acid or aluminium fluoride ion requires SRF but is independent of TCF binding. These results suggest that heterotrimeric G proteins activate a signalling pathway distinct from those that activate the STATs and the TCFs, that controls SRF activity.
Full text
PDF



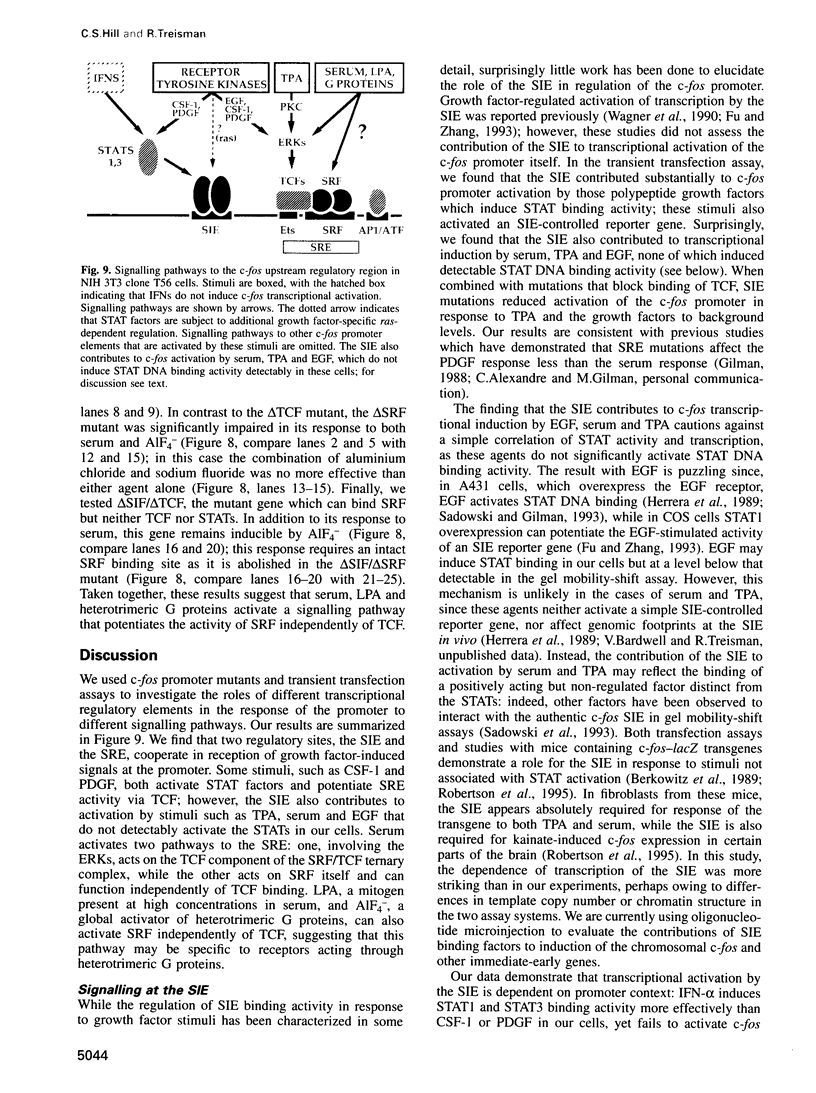



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowitz L. A., Riabowol K. T., Gilman M. Z. Multiple sequence elements of a single functional class are required for cyclic AMP responsiveness of the mouse c-fos promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4272–4281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoride complexes of aluminium or beryllium act on G-proteins as reversibly bound analogues of the gamma phosphate of GTP. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoroaluminates activate transducin-GDP by mimicking the gamma-phosphate of GTP in its binding site. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Treisman R. Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):597–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. An AP1-binding site in the c-fos gene can mediate induction by epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Zhang J. J. Transcription factor p91 interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor and mediates activation of the c-fos gene promoter. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1135–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Kortenjann M., Thomae O., Moomaw C., Slaughter C., Cobb M. H., Shaw P. E. ERK phosphorylation potentiates Elk-1-mediated ternary complex formation and transactivation. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 1;14(5):951–962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z. The c-fos serum response element responds to protein kinase C-dependent and -independent signals but not to cyclic AMP. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):394–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginty D. D., Bonni A., Greenberg M. E. Nerve growth factor activates a Ras-dependent protein kinase that stimulates c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of CREB. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding C. R., Temperley S. M., Fisher F. Multiple transcription factors interact with the adenovirus-2 EII-late promoter: evidence for a novel CCAAT recognition factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7761–7780. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R., Gilman M. Distinct protein targets for signals acting at the c-fos serum response element. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):189–192. doi: 10.1126/science.1898992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Kitchen A. M., Cochran B. H. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1272–1276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
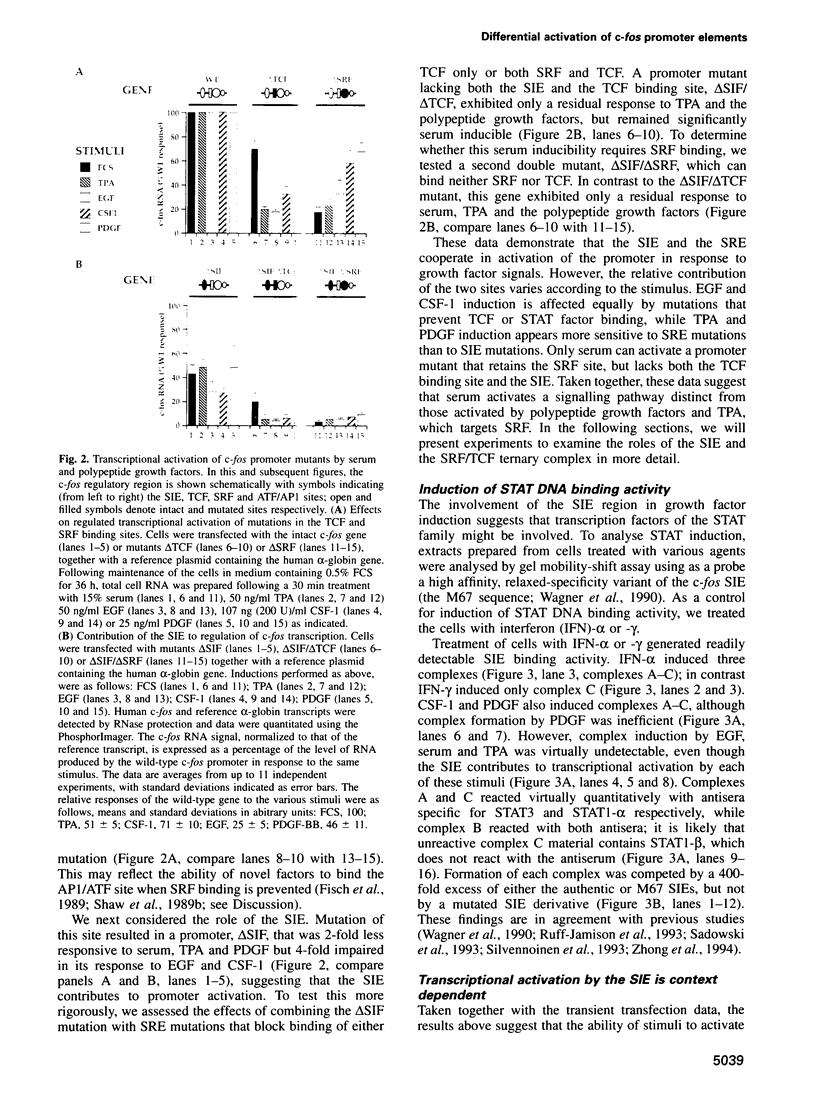
- Hill C. S., Marais R., John S., Wynne J., Dalton S., Treisman R. Functional analysis of a growth factor-responsive transcription factor complex. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90238-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Treisman R. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Wynne J., Treisman R. Serum-regulated transcription by serum response factor (SRF): a novel role for the DNA binding domain. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5421–5432. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Wynne J., Treisman R. The Rho family GTPases RhoA, Rac1, and CDC42Hs regulate transcriptional activation by SRF. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1159–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Rao V. N., Mueller C. G., Reddy E. S., Nordheim A. Ets-related protein Elk-1 is homologous to the c-fos regulatory factor p62TCF. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):531–534. doi: 10.1038/354531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., Hordijk P. L., Moolenaar W. H. Growth factor-like effects of lysophosphatidic acid, a novel lipid mediator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Dec 30;1198(2-3):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(94)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Ernst W. H., Nordheim A. SAP1a is a nuclear target of signaling cascades involving ERKs. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 16;10(6):1209–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
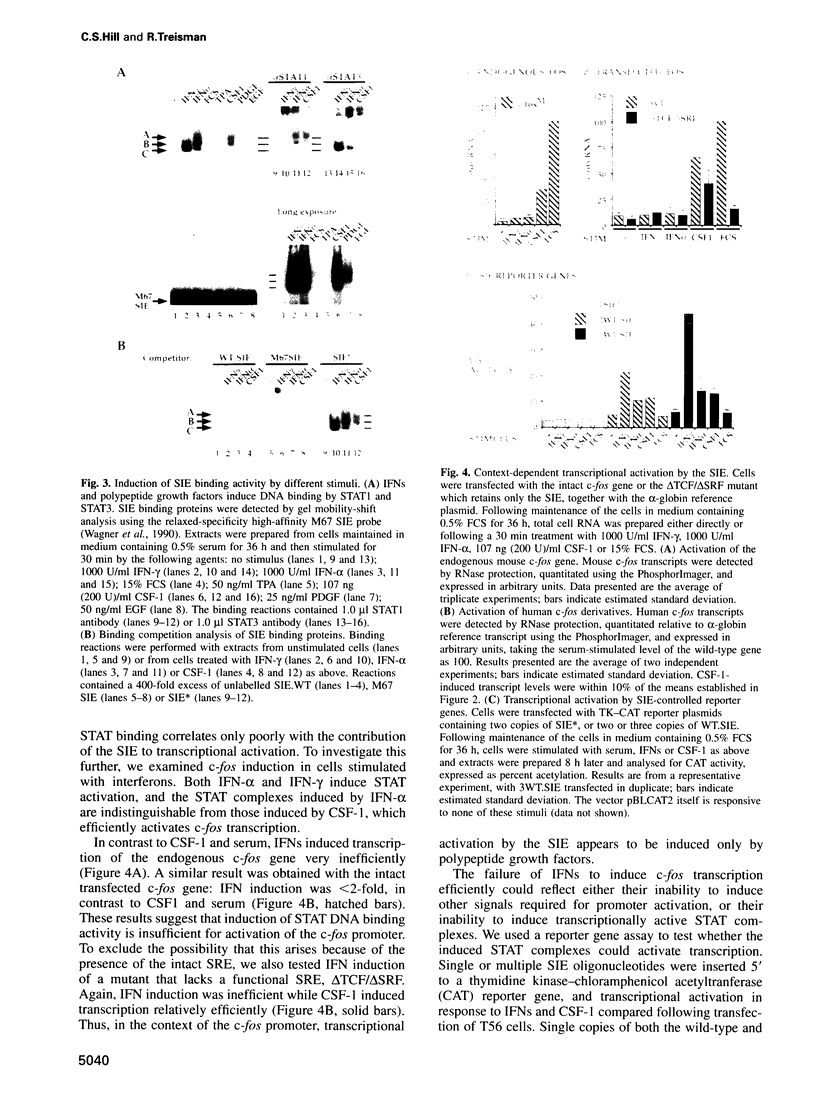
- Janknecht R., Ernst W. H., Pingoud V., Nordheim A. Activation of ternary complex factor Elk-1 by MAP kinases. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5097–5104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen F. E., Prywes R. Two pathways for serum regulation of the c-fos serum response element require specific sequence elements and a minimal domain of serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):5920–5928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.5920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortenjann M., Thomae O., Shaw P. E. Inhibition of v-raf-dependent c-fos expression and transformation by a kinase-defective mutant of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk2. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4815–4824. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H. Cell-type specific multiprotein complex formation over the c-fos serum response element in vivo: ternary complex formation is not required for the induction of c-fos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3607–3611. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütticken C., Coffer P., Yuan J., Schwartz C., Caldenhoven E., Schindler C., Kruijer W., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Interleukin-6-induced serine phosphorylation of transcription factor APRF: evidence for a role in interleukin-6 target gene induction. FEBS Lett. 1995 Feb 27;360(2):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00076-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Zhao Z. S., Lim L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):40–46. doi: 10.1038/367040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90237-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidic acid signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
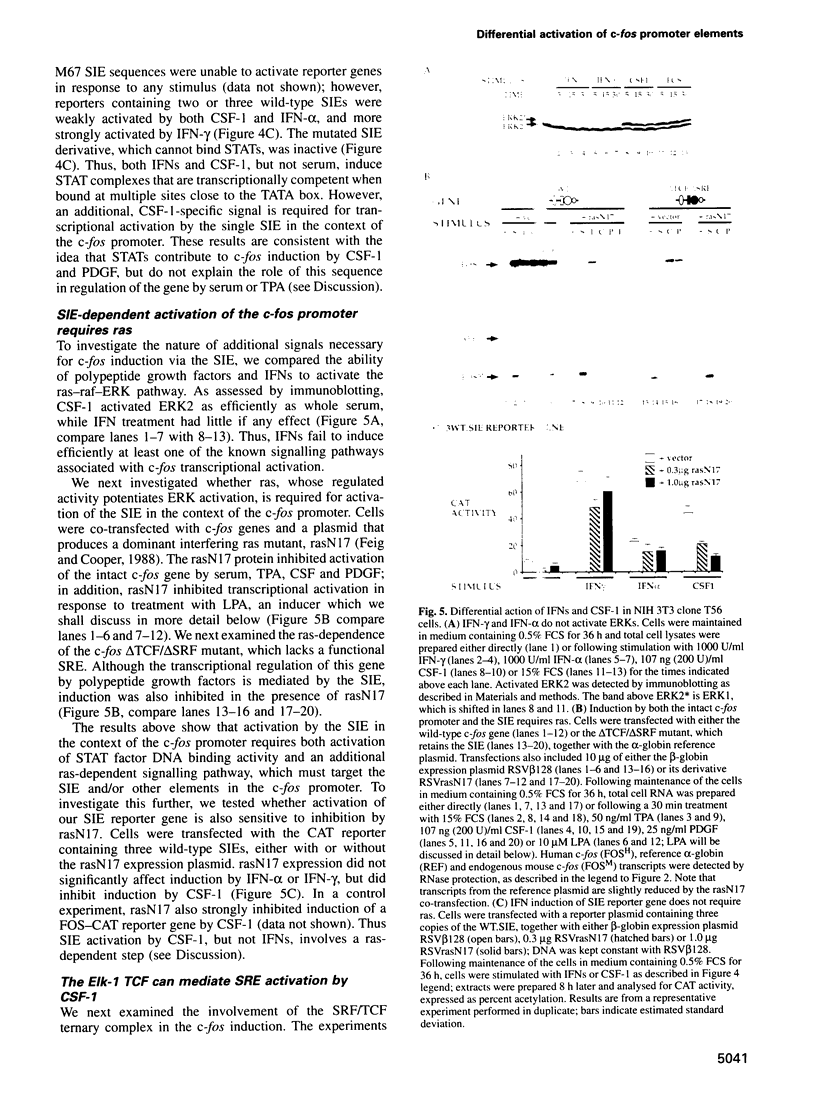
- Perkins L. M., Ramirez F. E., Kumar C. C., Thomson F. J., Clark M. A. Activation of serum response element-regulated genes by lysophosphatidic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):450–452. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Yaniv M. Two different factors bind to the alpha-domain of the polyoma virus enhancer, one of which also interacts with the SV40 and c-fos enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M. A., Rogers A. E., Treisman R. Comparative analysis of the ternary complex factors Elk-1, SAP-1a and SAP-2 (ERP/NET). EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2589–2601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson L. M., Kerppola T. K., Vendrell M., Luk D., Smeyne R. J., Bocchiaro C., Morgan J. I., Curran T. Regulation of c-fos expression in transgenic mice requires multiple interdependent transcription control elements. Neuron. 1995 Feb;14(2):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90282-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Shurtleff S. A., Downing J. R., Sherr C. J. A point mutation at tyrosine-809 in the human colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor impairs mitogenesis without abrogating tyrosine kinase activity, association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, or induction of c-fos and junB genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6738–6742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff-Jamison S., Chen K., Cohen S. Induction by EGF and interferon-gamma of tyrosine phosphorylated DNA binding proteins in mouse liver nuclei. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1733–1736. doi: 10.1126/science.8378774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski H. B., Gilman M. Z. Cell-free activation of a DNA-binding protein by epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):79–83. doi: 10.1038/362079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski H. B., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Gilman M. Z. A common nuclear signal transduction pathway activated by growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1739–1744. doi: 10.1126/science.8397445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Visvader J., Ferland L., Mellon P. L., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene fos transcription through the adenylate cyclase pathway: characterization of a cAMP-responsive element. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1529–1538. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Ferguson B., Sprague G. F., Jr Signal transduction and growth control in yeast. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Frasch S., Nordheim A. Repression of c-fos transcription is mediated through p67SRF bound to the SRE. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2567–2574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Schindler C., Schlessinger J., Levy D. E. Ras-independent growth factor signaling by transcription factor tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1736–1739. doi: 10.1126/science.8378775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Marais R., Wynne J. Spatial flexibility in ternary complexes between SRF and its accessory proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4631–4640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. The SRE: a growth factor responsive transcriptional regulator. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):47–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B. J., Hayes T. E., Hoban C. J., Cochran B. H. The SIF binding element confers sis/PDGF inducibility onto the c-fos promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4477–4484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y. O., Stroke I. L., Fields S. Coupling of cell identity to signal response in yeast: interaction between the alpha 1 and STE12 proteins. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1584–1597. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Blenis J., Li H. C., Schindler C., Chen-Kiang S. Requirement of serine phosphorylation for formation of STAT-promoter complexes. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):1990–1994. doi: 10.1126/science.7701321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.8140422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]