Abstract
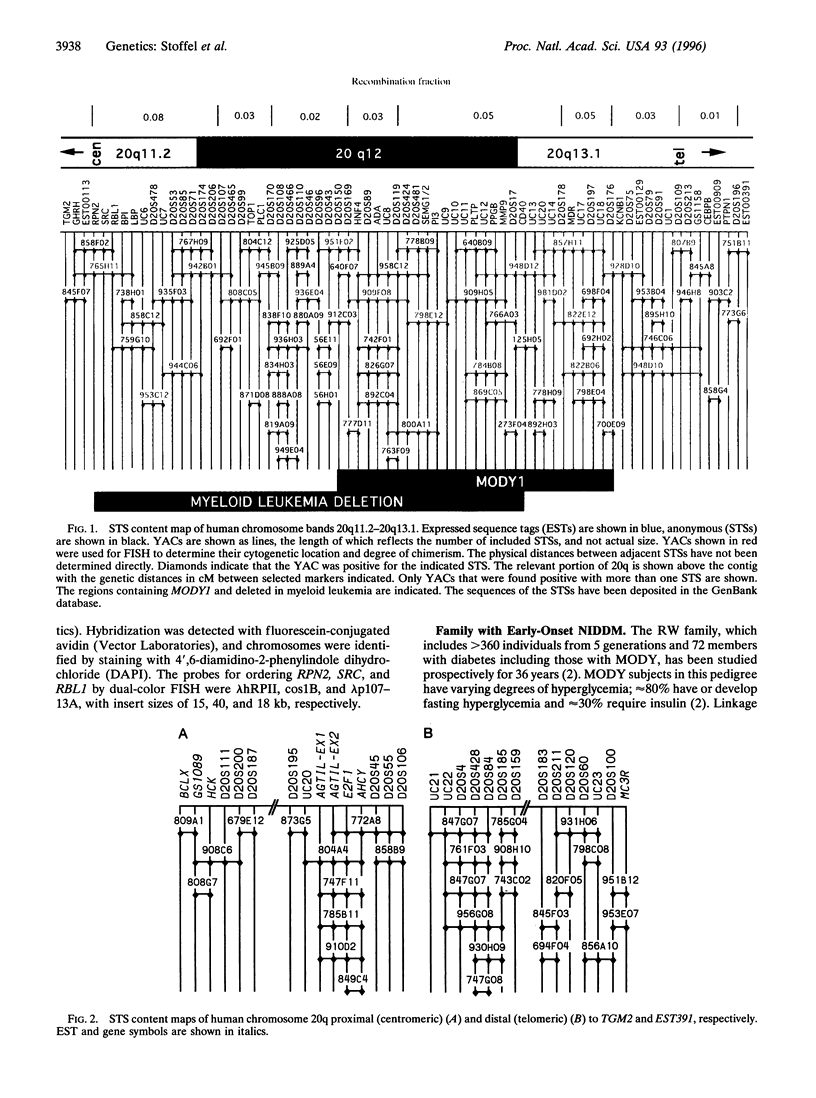
We have generated a physical map of human chromosome bands 20q11.2-20q13.1, a region containing a gene involved in the development of one form of early-onset, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, MODY1, as well as a putative myeloid tumor suppressor gene. The yeast artificial chromosome contig consists of 71 clones onto which 71 markers, including 20 genes, 5 expressed sequence tags, 32 simple tandem repeat DNA polymorphisms, and 14 sequence-tagged sites have been ordered. This region spans about 18 Mb, which represents about 40% of the physical length of 20q. Using this physical map, we have refined the location of MODY1 to a 13-centimorgan interval (approximately equal to 7 Mb) between D20S169 and D20S176. The myeloid tumor suppressor gene was localized to an 18-centimorgan interval (approximately equal to 13 Mb) between RPN2 and D20S17. This physical map will facilitate the isolation of MODY1 and the myeloid tumor suppressor gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsen H. M., Abderrahim H., Cann H. M., Dausset J., Le Paslier D., Cohen D. Construction and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome library containing seven haploid human genome equivalents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4256–4260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijersbergen R. L., Carlée L., Kerkhoven R. M., Bernards R. Regulation of the retinoblastoma protein-related p107 by G1 cyclin complexes. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 1;9(11):1340–1353. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.11.1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Xiang K. S., Newman M. V., Wu S. H., Wright L. G., Fajans S. S., Spielman R. S., Cox N. J. Gene for non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (maturity-onset diabetes of the young subtype) is linked to DNA polymorphism on human chromosome 20q. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1484–1488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlander S. K., Espinosa R., 3rd, Le Beau M. M., Rowley J. D., Díaz M. O. A method for the rapid sequence-independent amplification of microdissected chromosomal material. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1322–1324. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90057-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boise L. H., González-García M., Postema C. E., Ding L., Lindsten T., Turka L. A., Mao X., Nuñez G., Thompson C. B. bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90508-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne M. M., Sturis J., Fajans S. S., Ortiz F. J., Stoltz A., Stoffel M., Smith M. J., Bell G. I., Halter J. B., Polonsky K. S. Altered insulin secretory responses to glucose in subjects with a mutation in the MODY1 gene on chromosome 20. Diabetes. 1995 Jun;44(6):699–704. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.6.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Manova K., Weinstein D. C., Duncan S. A., Plump A. S., Prezioso V. R., Bachvarova R. F., Darnell J. E., Jr Disruption of the HNF-4 gene, expressed in visceral endoderm, leads to cell death in embryonic ectoderm and impaired gastrulation of mouse embryos. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 15;8(20):2466–2477. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.20.2466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov I. M., Le Gall I., Billault A., Ougen P., Soularue P., Guillou S., Rigault P., Bui H., De Tand M. F., Barillot E. Isolation of chromosome 21-specific yeast artificial chromosomes from a total human genome library. Nat Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):222–225. doi: 10.1038/ng0692-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Bonadonna R. C., Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):318–368. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S., Bell G. I., Bowden D. W., Halter J. B., Polonsky K. S. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Life Sci. 1994;55(6):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentile V., Davies P. J., Baldini A. The human tissue transglutaminase gene maps on chromosome 20q12 by in situ fluorescence hybridization. Genomics. 1994 Mar 15;20(2):295–297. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Bhatia K., Magrath I. T., Dang C. V., Dalla-Favera R. Binding and suppression of the Myc transcriptional activation domain by p107. Science. 1994 Apr 8;264(5156):251–254. doi: 10.1126/science.8146655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melis R., Stauffer D., Zhao X., Zhu X. L., Albrecht B., Pongs O., Brothman A., Leppert M. Physical and genetic localization of a Shab subfamily potassium channel (KCNB1) gene to chromosomal region 20q13.2. Genomics. 1995 Jan 1;25(1):285–287. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80138-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintrell N., Lebo R., Varmus H., Bishop J. M., Pettenati M. J., Le Beau M. M., Diaz M. O., Rowley J. D. Identification of a human gene (HCK) that encodes a protein-tyrosine kinase and is expressed in hemopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2267–2275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild C. B., Akots G., Fajans S. S., Bowden D. W. A microsatellite polymorphism associated with the PLC1 (phospholipase C) locus: identification, mapping, and linkage to the MODY locus on chromosome 20. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):560–564. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90125-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roulston D., Espinosa R., 3rd, Stoffel M., Bell G. I., Le Beau M. M. Molecular genetics of myeloid leukemia: identification of the commonly deleted segment of chromosome 20. Blood. 1993 Dec 1;82(11):3424–3429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D., Diaz M. O., Espinosa R., 3rd, Patel Y. D., van Melle E., Ziemin S., Taillon-Miller P., Lichter P., Evans G. A., Kersey J. H. Mapping chromosome band 11q23 in human acute leukemia with biotinylated probes: identification of 11q23 translocation breakpoints with a yeast artificial chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9358–9362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel M., Xiang K. S., Espinosa R., 3rd, Cox N. J., Le Beau M. M., Bell G. I. cDNA sequence and localization of polymorphic human cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene (PCK1) to chromosome 20, band q13.31: PCK1 is not tightly linked to maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jan;2(1):1–4. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera A., Pujol A., Pelegrin M., Bosch F. Transgenic mice overexpressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase develop non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9151–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. D., Ollmann M. M., Kang L., Stoffel M., Bell G. I., Barsh G. S. Structure and function of ASP, the human homolog of the mouse agouti gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Feb;4(2):223–230. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]