Abstract
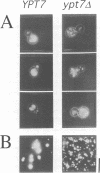
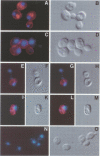
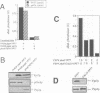
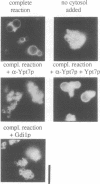
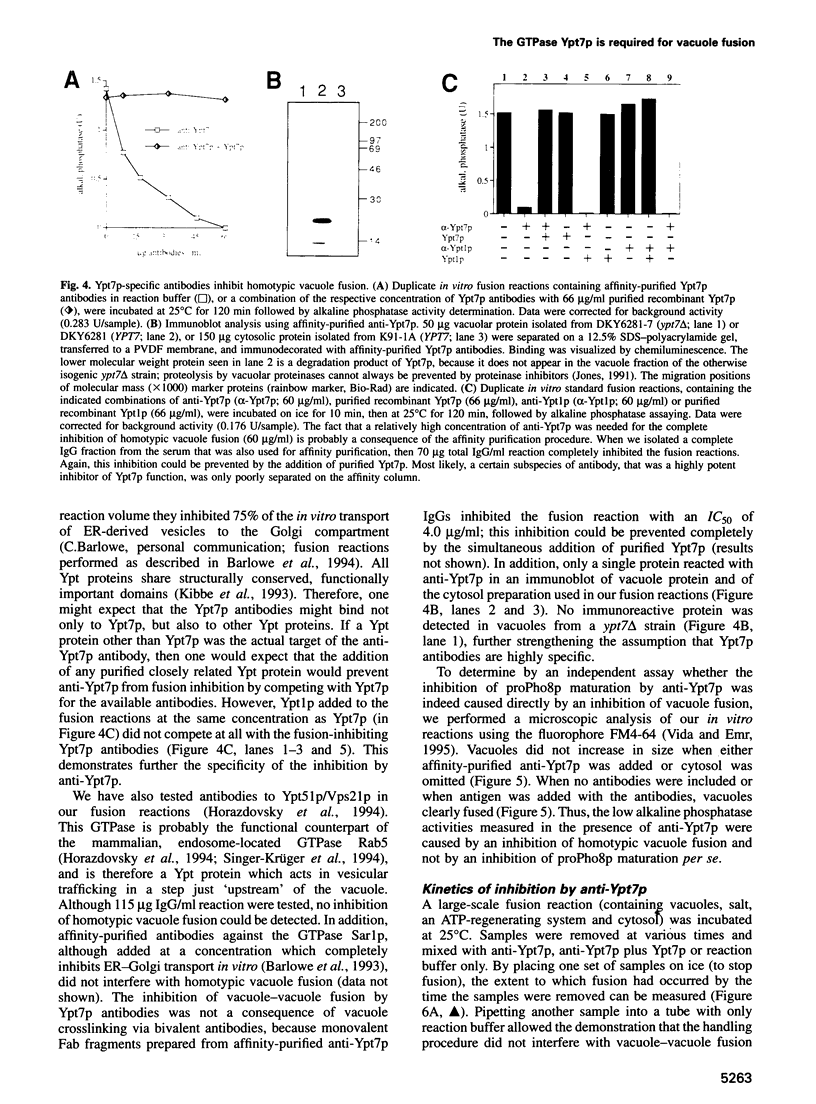
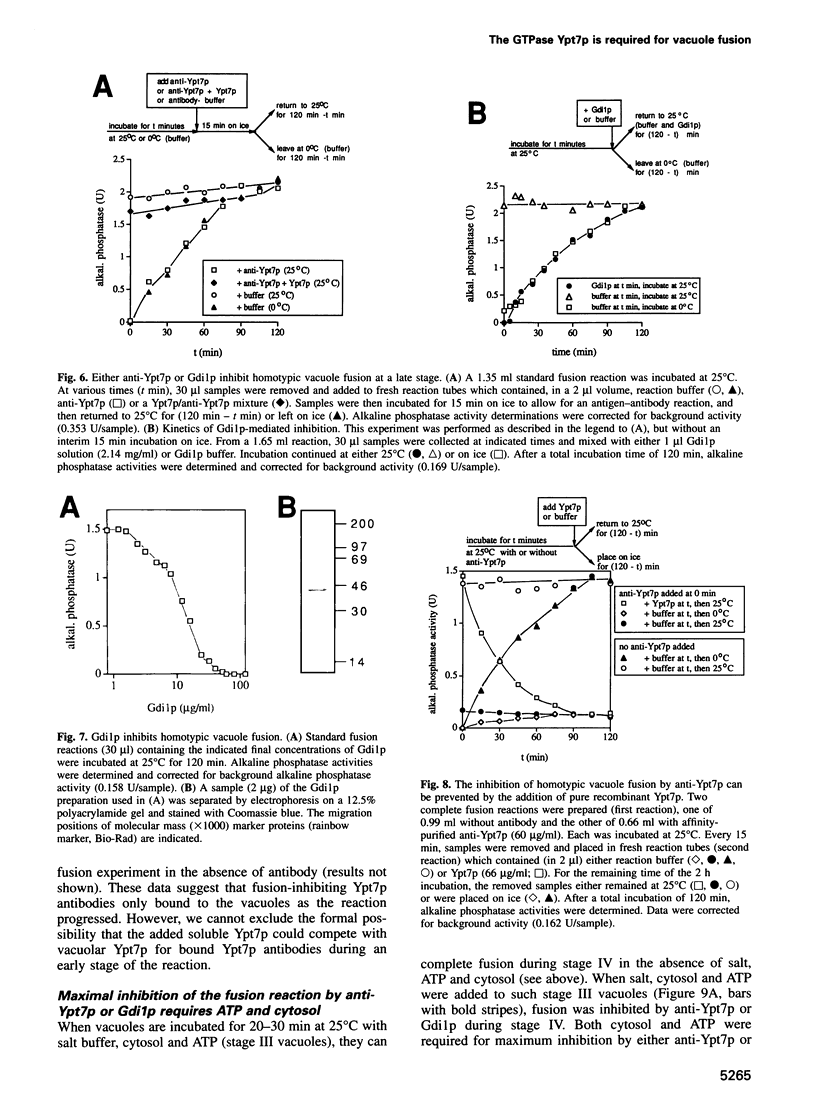
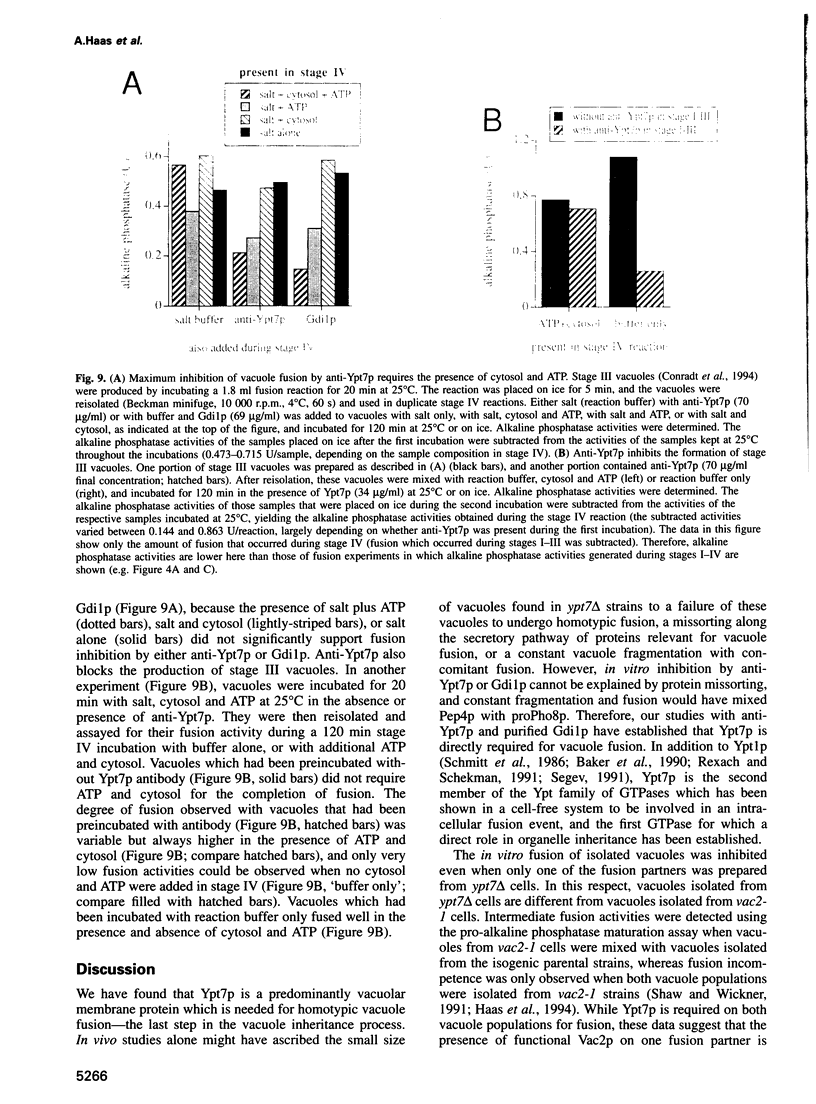
In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, vacuoles are inherited by the projection of vesicles and tubules from the mother-cell vacuole into the growing daughter cell during the S phase. These vesicles then fuse and form the daughter-cell organelle. We have described previously in vitro reactions of the formation of vacuole-derived segregation structures and of vacuole-vacuole fusion. Homotypic vacuole fusion requires cytosol, ATP and a physiological temperature, and is sensitive to GTPase inhibitors. These reactions are divisible into early stages which require ATP and cytosol, and late stages which require neither. Here, we report that Ypt7p, a ras-like GTPase implicated previously in endocytosis in yeast, is largely localized to the vacuole and is required on both partners during the in vitro vacuole fusion reaction. The in vitro fusion reaction is inhibited either by Gdi1p, which extracts the GDP-bound form of ras-like GTPases from membranes, or by antibodies specific for Ypt7p. The presence of anti-Ypt7p during the early stages of the reaction inhibits the development of cytosol- and ATP-independent intermediates. Although cytosol and ATP are no longer needed for the late stage of vacuole inheritance in vitro, the inhibition of this late stage by anti-Ypt7p or Gdi1p requires the continued presence of ATP and cytosol. Ypt7p is the first GTPase for which a direct role in organelle inheritance has been established.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki S., Kikuchi A., Hata Y., Isomura M., Takai Y. Regulation of reversible binding of smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein, to synaptic plasma membranes and vesicles by its specific regulatory protein, GDP dissociation inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13007–13015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon R. A., Salminen A., Ruohola H., Novick P., Ferro-Novick S. The GTP-binding protein Ypt1 is required for transport in vitro: the Golgi apparatus is defective in ypt1 mutants. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D., Wuestehube L., Schekman R., Botstein D., Segev N. GTP-binding Ypt1 protein and Ca2+ function independently in a cell-free protein transport reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Johnson L. M., Emr S. D. Isolation of yeast mutants defective in protein targeting to the vacuole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9075–9079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlowe C., Orci L., Yeung T., Hosobuchi M., Hamamoto S., Salama N., Rexach M. F., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):895–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlowe C., d'Enfert C., Schekman R. Purification and characterization of SAR1p, a small GTP-binding protein required for transport vesicle formation from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):873–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennwald P., Kearns B., Champion K., Keränen S., Bankaitis V., Novick P. Sec9 is a SNAP-25-like component of a yeast SNARE complex that may be the effector of Sec4 function in exocytosis. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci C., Parton R. G., Mather I. H., Stunnenberg H., Simons K., Hoflack B., Zerial M. The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):715–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90306-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradt B., Haas A., Wickner W. Determination of four biochemically distinct, sequential stages during vacuole inheritance in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):99–110. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradt B., Shaw J., Vida T., Emr S., Wickner W. In vitro reactions of vacuole inheritance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1469–1479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Y. P., Storrie B. Animal cell lysosomes rapidly exchange membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirac-Svejstrup A. B., Soldati T., Shapiro A. D., Pfeffer S. R. Rab-GDI presents functional Rab9 to the intracellular transport machinery and contributes selectivity to Rab9 membrane recruitment. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15427–15430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elazar Z., Mayer T., Rothman J. E. Removal of Rab GTP-binding proteins from Golgi membranes by GDP dissociation inhibitor inhibits inter-cisternal transport in the Golgi stacks. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):794–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Novick S., Novick P. The role of GTP-binding proteins in transport along the exocytic pathway. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:575–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Stahl B., Walch-Solimena C., Takei K., Daniels L., Khoklatchev A., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Localization of Rab5 to synaptic vesicles identifies endosomal intermediate in synaptic vesicle recycling pathway. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;65(2):319–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett M. D., Kabcenell A. K., Zahner J. E., Kaibuchi K., Sasaki T., Takai Y., Cheney C. M., Novick P. J. Interaction of Sec4 with GDI proteins from bovine brain, Drosophila melanogaster and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Conservation of GDI membrane dissociation activity. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 4;331(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80343-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett M. D., Zahner J. E., Cheney C. M., Novick P. J. GDI1 encodes a GDP dissociation inhibitor that plays an essential role in the yeast secretory pathway. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1718–1728. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes de Mesquita D. S., ten Hoopen R., Woldringh C. L. Vacuolar segregation to the bud of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: an analysis of morphology and timing in the cell cycle. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2447–2454. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Chavrier P., Zerial M., Gruenberg J. rab5 controls early endosome fusion in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90316-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Clague M. J. Regulation of intracellular membrane transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):593–599. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90077-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A., Conradt B., Wickner W. G-protein ligands inhibit in vitro reactions of vacuole inheritance. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):87–97. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horazdovsky B. F., Busch G. R., Emr S. D. VPS21 encodes a rab5-like GTP binding protein that is required for the sorting of yeast vacuolar proteins. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1297–1309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Tackling the protease problem in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:428–453. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94034-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. D., Schliwa M., Drubin D. G. Video microscopy of organelle inheritance and motility in budding yeast. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;25(2):129–142. doi: 10.1002/cm.970250203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge O., Dascher C., Orci L., Rowe T., Amherdt M., Plutner H., Ravazzola M., Tanigawa G., Rothman J. E., Balch W. E. Sar1 promotes vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum but not Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):51–65. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Stahl P. D. Structure-function relationship of the small GTPase rab5. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24475–24480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J. P., Stone S., Jiang Y., Lyons P., Ferro-Novick S. Ypt1p implicated in v-SNARE activation. Nature. 1994 Dec 15;372(6507):698–701. doi: 10.1038/372698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi D., Soldati T., Riederer M. A., Goda Y., Zerial M., Pfeffer S. R. Rab9 functions in transport between late endosomes and the trans Golgi network. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):677–682. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujumdar R. B., Ernst L. A., Mujumdar S. R., Waggoner A. S. Cyanine dye labeling reagents containing isothiocyanate groups. Cytometry. 1989 Jan;10(1):11–19. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson T. A., Weisman L. S., Payne G. S., Wickner W. T. A truncated form of the Pho80 cyclin redirects the Pho85 kinase to disrupt vacuole inheritance in S. cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(4):835–845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.4.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Brennwald P. Friends and family: the role of the Rab GTPases in vesicular traffic. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):597–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90478-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuoffer C., Balch W. E. GTPases: multifunctional molecular switches regulating vesicular traffic. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:949–990. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter F., Nuoffer C., Pind S. N., Balch W. E. Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor is essential for Rab1 function in budding from the endoplasmic reticulum and transport through the Golgi stack. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(6):1393–1406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.6.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. Rab GTPases: master regulators of membrane trafficking. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):522–526. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutner H., Cox A. D., Pind S., Khosravi-Far R., Bourne J. R., Schwaninger R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):31–43. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Wuestehube L. J., Schekman R. Vesicle-mediated protein sorting. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:471–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S., Horstmann H., Gordon S., Griffiths G. Immunocytochemical characterization of the endocytic and phagolysosomal compartments in peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):95–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond C. K., Howald-Stevenson I., Vater C. A., Stevens T. H. Morphological classification of the yeast vacuolar protein sorting mutants: evidence for a prevacuolar compartment in class E vps mutants. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1389–1402. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond C. K., Roberts C. J., Moore K. E., Howald I., Stevens T. H. Biogenesis of the vacuole in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;139:59–120. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Kikuchi A., Takai Y., Wollheim C. B. The small GTP-binding proteins in the cytosol of insulin-secreting cells are complexed to GDP dissociation inhibitor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17512–17519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M. F., Schekman R. W. Distinct biochemical requirements for the budding, targeting, and fusion of ER-derived transport vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):219–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezman H. Yeast endocytosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;3(8):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Raymond C. K., Yamashiro C. T., Stevens T. H. Methods for studying the yeast vacuole. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:644–661. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94047-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kaibuchi K., Kabcenell A. K., Novick P. J., Takai Y. A mammalian inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (GDP dissociation inhibitor) for smg p25A is active on the yeast SEC4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2909–2912. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmöller F., Riezman H. Involvement of Ypt7p, a small GTPase, in traffic from late endosome to the vacuole in yeast. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):823–830. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaninger R., Plutner H., Bokoch G. M., Balch W. E. Multiple GTP-binding proteins regulate vesicular transport from the ER to Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1077–1096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N. Mediation of the attachment or fusion step in vesicular transport by the GTP-binding Ypt1 protein. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1553–1556. doi: 10.1126/science.1904626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. M., Wickner W. T. vac2: a yeast mutant which distinguishes vacuole segregation from Golgi-to-vacuole protein targeting. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1741–1748. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Krüger B., Stenmark H., Düsterhöft A., Philippsen P., Yoo J. S., Gallwitz D., Zerial M. Role of three rab5-like GTPases, Ypt51p, Ypt52p, and Ypt53p, in the endocytic and vacuolar protein sorting pathways of yeast. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):283–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati T., Riederer M. A., Pfeffer S. R. Rab GDI: a solubilizing and recycling factor for rab9 protein. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Apr;4(4):425–434. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.4.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati T., Shapiro A. D., Svejstrup A. B., Pfeffer S. R. Membrane targeting of the small GTPase Rab9 is accompanied by nucleotide exchange. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):76–78. doi: 10.1038/369076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack J. H., Emr S. D. Genetic and biochemical studies of protein sorting to the yeast vacuole. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90134-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl B., von Mollard G. F., Walch-Solimena C., Jahn R. GTP cleavage by the small GTP-binding protein Rab3A is associated with exocytosis of synaptic vesicles induced by alpha-latrotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24770–24776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søgaard M., Tani K., Ye R. R., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Kirchhausen T., Rothman J. E., Söllner T. A rab protein is required for the assembly of SNARE complexes in the docking of transport vesicles. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich O., Horiuchi H., Bucci C., Zerial M. Membrane association of Rab5 mediated by GDP-dissociation inhibitor and accompanied by GDP/GTP exchange. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):157–160. doi: 10.1038/368157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich O., Stenmark H., Alexandrov K., Huber L. A., Kaibuchi K., Sasaki T., Takai Y., Zerial M. Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor as a general regulator for the membrane association of rab proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18143–18150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vida T. A., Emr S. D. A new vital stain for visualizing vacuolar membrane dynamics and endocytosis in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):779–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P., Hengst L., Gallwitz D. Ypt proteins in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:369–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. S., Bacallao R., Wickner W. Multiple methods of visualizing the yeast vacuole permit evaluation of its morphology and inheritance during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1539–1547. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. S., Emr S. D., Wickner W. T. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that block intervacuole vesicular traffic and vacuole division and segregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1076–1080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. S., Wickner W. Intervacuole exchange in the yeast zygote: a new pathway in organelle communication. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):589–591. doi: 10.1126/science.3041591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. S., Wickner W. Molecular characterization of VAC1, a gene required for vacuole inheritance and vacuole protein sorting. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):618–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichmann H., Hengst L., Gallwitz D. Endocytosis in yeast: evidence for the involvement of a small GTP-binding protein (Ypt7p). Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1131–1142. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]