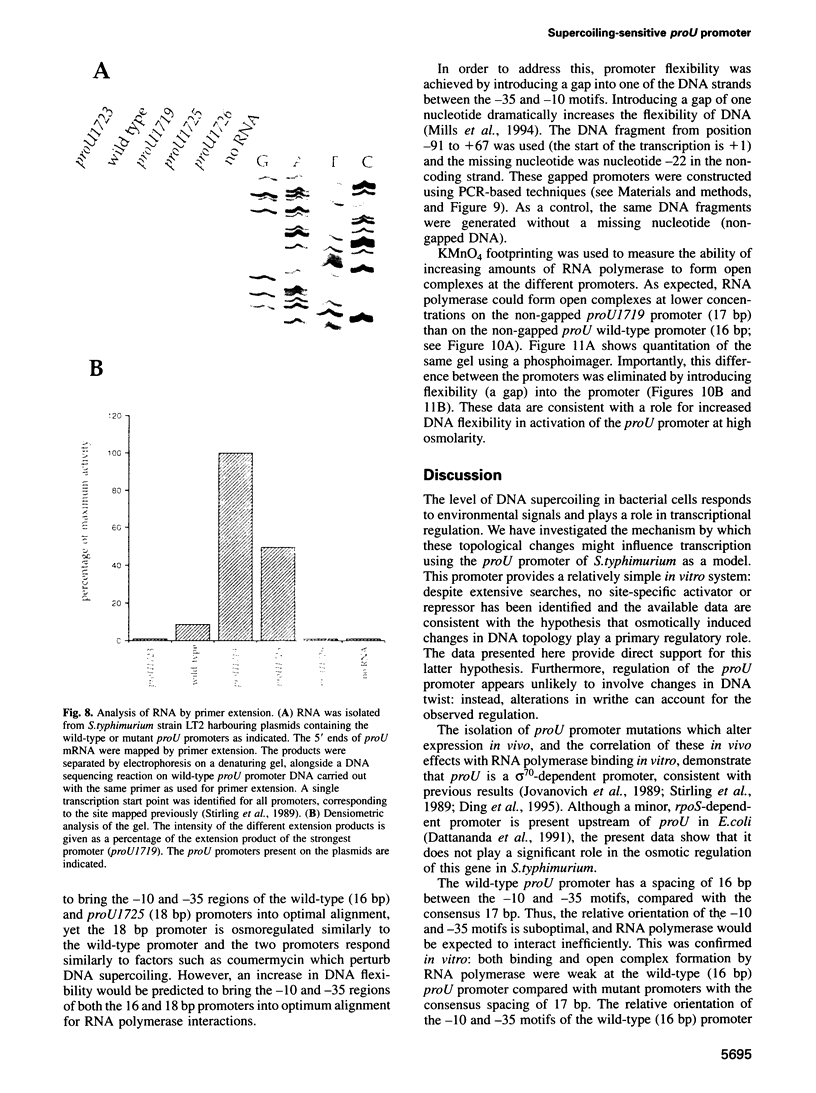
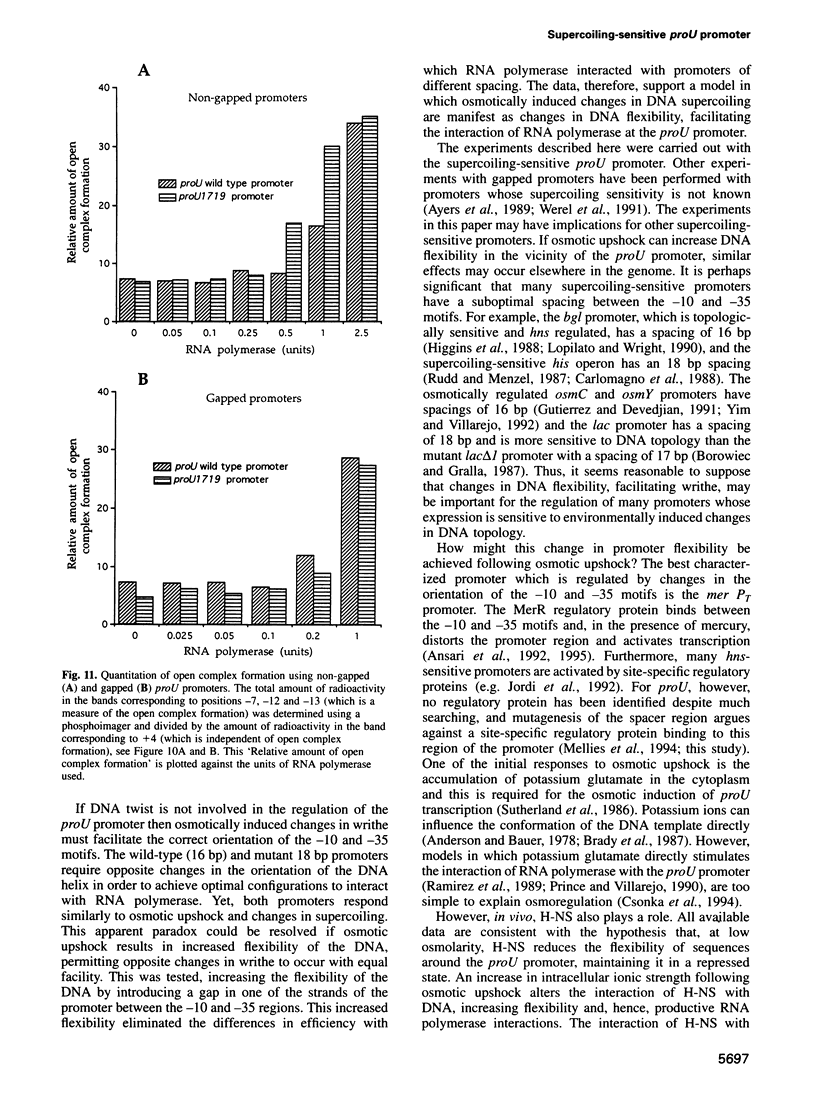
Abstract
Transcription from many bacterial promoters is sensitive to the level of DNA supercoiling. We have investigated the mechanism by which environmentally induced changes in DNA supercoiling might regulate transcription. For the proU promoter of Salmonella typhimurium, osmotically induced changes in DNA topology appear to play a primary regulatory role. Changes in DNA supercoiling (linking number; delta Lk) are partitioned into changes in the winding of the strands of the double helix about themselves (twist; delta Tw) and/or elastic deformations or flexibility of the DNA helix (writhe; delta Wr). Mutations of the proU promoter were isolated in vivo, or generated in vitro, which altered the spacing between the -10 and -35 motifs. Studies on these mutant promoters, both in vivo and in vitro, exclude models in which changes in DNA twist play a regulatory role. Instead, our data suggest that increased DNA flexibility, reflecting the osmotically induced increase in negative supercoiling of DNA, is required for promoter activation.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Bauer W. Supercoiling in closed circular DNA: dependence upon ion type and concentration. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):594–601. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A. Z., Bradner J. E., O'Halloran T. V. DNA-bend modulation in a repressor-to-activator switching mechanism. Nature. 1995 Mar 23;374(6520):371–375. doi: 10.1038/374370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A. Z., Chael M. L., O'Halloran T. V. Allosteric underwinding of DNA is a critical step in positive control of transcription by Hg-MerR. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):87–89. doi: 10.1038/355087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auble D. T., deHaseth P. L. Promoter recognition by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Influence of DNA structure in the spacer separating the -10 and -35 regions. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers D. G., Auble D. T., deHaseth P. L. Promoter recognition by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Role of the spacer DNA in functional complex formation. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):749–756. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.293-300.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke V. L., Gralla J. D. Changes in the linking number of supercoiled DNA accompany growth transitions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4499–4506. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4499-4506.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. All three elements of the lac ps promoter mediate its transcriptional response to DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady G. W., Satkowski M., Foos D., Benham C. J. Environmental influences on DNA superhelicity. The effect of ionic strength on superhelix conformation in solution. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90335-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahms J. G., Dargouge O., Brahms S., Ohara Y., Vagner V. Activation and inhibition of transcription by supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 20;181(4):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairney J., Booth I. R., Higgins C. F. Osmoregulation of gene expression in Salmonella typhimurium: proU encodes an osmotically induced betaine transport system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1224–1232. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1224-1232.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlomagno M. S., Chiariotti L., Alifano P., Nappo A. G., Bruni C. B. Structure and function of the Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli K-12 histidine operons. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):585–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Ikeda T. P., Fletcher S. A., Kustu S. The accumulation of glutamate is necessary for optimal growth of Salmonella typhimurium in media of high osmolality but not induction of the proU operon. J Bacteriol. 1994 Oct;176(20):6324–6333. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.20.6324-6333.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattananda C. S., Rajkumari K., Gowrishankar J. Multiple mechanisms contribute to osmotic inducibility of proU operon expression in Escherichia coli: demonstration of two osmoresponsive promoters and of a negative regulatory element within the first structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7481–7490. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7481-7490.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayn A., Malkhosyan S., Duzhy D., Lyamichev V., Panchenko Y., Mirkin S. Formation of (dA-dT)n cruciforms in Escherichia coli cells under different environmental conditions. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2658–2664. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2658-2664.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding Q., Kusano S., Villarejo M., Ishihama A. Promoter selectivity control of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase by ionic strength: differential recognition of osmoregulated promoters by E sigma D and E sigma S holoenzymes. Mol Microbiol. 1995 May;16(4):649–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Barr G. C., Ni Bhriain N., Higgins C. F. DNA supercoiling and the anaerobic and growth phase regulation of tonB gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2816–2826. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2816-2826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Ni Bhriain N., Higgins C. F. DNA supercoiling and environmental regulation of virulence gene expression in Shigella flexneri. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):789–792. doi: 10.1038/344789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druger-Liotta J., Prange V. J., Overdier D. G., Csonka L. N. Selection of mutations that alter the osmotic control of transcription of the Salmonella typhimurium proU operon. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2449–2459. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2449-2459.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap V. J., Csonka L. N. Osmotic regulation of L-proline transport in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):296–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.296-304.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Drlica K. Regulation of bacterial DNA supercoiling: plasmid linking numbers vary with growth temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4046–4050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowrishankar J. Identification of osmoresponsive genes in Escherichia coli: evidence for participation of potassium and proline transport systems in osmoregulation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):434–445. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.434-445.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Devedjian J. C. Osmotic induction of gene osmC expression in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):959–973. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90366-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton J. C., Santos D. S., Seirafi A., Hulton C. S., Pavitt G. D., Higgins C. F. Expression and mutational analysis of the nucleoid-associated protein H-NS of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(16):2327–2337. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh L. S., Rouviere-Yaniv J., Drlica K. Bacterial DNA supercoiling and [ATP]/[ADP] ratio: changes associated with salt shock. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3914–3917. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3914-3917.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton C. S., Seirafi A., Hinton J. C., Sidebotham J. M., Waddell L., Pavitt G. D., Owen-Hughes T., Spassky A., Buc H., Higgins C. F. Histone-like protein H1 (H-NS), DNA supercoiling, and gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90458-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordi B. J., Dagberg B., de Haan L. A., Hamers A. M., van der Zeijst B. A., Gaastra W., Uhlin B. E. The positive regulator CfaD overcomes the repression mediated by histone-like protein H-NS (H1) in the CFA/I fimbrial operon of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2627–2632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovich S. B., Record M. T., Jr, Burgess R. R. In an Escherichia coli coupled transcription-translation system, expression of the osmoregulated gene proU is stimulated at elevated potassium concentrations and by an extract from cells grown at high osmolality. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7821–7825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landt O., Grunert H. P., Hahn U. A general method for rapid site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90351-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucht J. M., Bremer E. Characterization of mutations affecting the osmoregulated proU promoter of Escherichia coli and identification of 5' sequences required for high-level expression. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):801–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.801-809.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucht J. M., Dersch P., Kempf B., Bremer E. Interactions of the nucleoid-associated DNA-binding protein H-NS with the regulatory region of the osmotically controlled proU operon of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6578–6578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manna D., Gowrishankar J. Evidence for involvement of proteins HU and RpoS in transcription of the osmoresponsive proU operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Sep;176(17):5378–5384. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.17.5378-5384.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Dersch P., Haardt M., Middendorf A., Bremer E. The osmZ (bglY) gene encodes the DNA-binding protein H-NS (H1a), a component of the Escherichia coli K12 nucleoid. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00259454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Faatz E., Villarejo M., Bremer E. Binding protein dependent transport of glycine betaine and its osmotic regulation in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00430432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellies J., Brems R., Villarejo M. The Escherichia coli proU promoter element and its contribution to osmotically signaled transcription activation. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jun;176(12):3638–3645. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.12.3638-3645.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. B., Cooper J. P., Hagerman P. J. Electrophoretic evidence that single-stranded regions of one or more nucleotides dramatically increase the flexibility of DNA. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 22;33(7):1797–1803. doi: 10.1021/bi00173a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni Bhriain N., Dorman C. J., Higgins C. F. An overlap between osmotic and anaerobic stress responses: a potential role for DNA supercoiling in the coordinate regulation of gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):933–942. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overdier D. G., Csonka L. N. A transcriptional silencer downstream of the promoter in the osmotically controlled proU operon of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3140–3144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Hughes T. A., Pavitt G. D., Santos D. S., Sidebotham J. M., Hulton C. S., Hinton J. C., Higgins C. F. The chromatin-associated protein H-NS interacts with curved DNA to influence DNA topology and gene expression. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90354-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince W. S., Villarejo M. R. Osmotic control of proU transcription is mediated through direct action of potassium glutamate on the transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17673–17679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and prokaryotic transcription. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez R. M., Prince W. S., Bremer E., Villarejo M. In vitro reconstitution of osmoregulated expression of proU of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K. E., Menzel R. his operons of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium are regulated by DNA supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):517–521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling D. A., Hulton C. S., Waddell L., Park S. F., Stewart G. S., Booth I. R., Higgins C. F. Molecular characterization of the proU loci of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli encoding osmoregulated glycine betaine transport systems. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1025–1038. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland L., Cairney J., Elmore M. J., Booth I. R., Higgins C. F. Osmotic regulation of transcription: induction of the proU betaine transport gene is dependent on accumulation of intracellular potassium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):805–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.805-814.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita S., Sato M., Toba M., Masahashi W., Hashimoto-Gotoh T. High-copy-number and low-copy-number plasmid vectors for lacZ alpha-complementation and chloramphenicol- or kanamycin-resistance selection. Gene. 1987;61(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thein S. L., Hinton J. A simple and rapid method of direct sequencing using Dynabeads. Br J Haematol. 1991 Sep;79(1):113–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb08016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Yoshikawa M., Sasakawa C. Thermoregulation of virB transcription in Shigella flexneri by sensing of changes in local DNA superhelicity. J Bacteriol. 1995 Feb;177(4):1094–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.4.1094-1097.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper A. E., Owen-Hughes T. A., Ussery D. W., Santos D. S., Ferguson D. J., Sidebotham J. M., Hinton J. C., Higgins C. F. The chromatin-associated protein H-NS alters DNA topology in vitro. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):258–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueguchi C., Mizuno T. The Escherichia coli nucleoid protein H-NS functions directly as a transcriptional repressor. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1039–1046. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Syvanen M. DNA twist as a transcriptional sensor for environmental changes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1861–1866. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werel W., Schickor P., Heumann H. Flexibility of the DNA enhances promoter affinity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2589–2594. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yim H. H., Villarejo M. osmY, a new hyperosmotically inducible gene, encodes a periplasmic protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3637–3644. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3637-3644.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]