Abstract
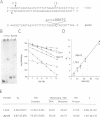
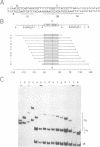
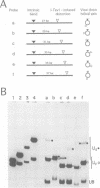
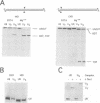
I-TevI, the intron-encoded endonuclease from the thymidylate synthase (td) gene of bacteriophage T4, binds its DNA substrate across the minor groove in a sequence-tolerant fashion. We demonstrate here that the 28 kDa I-TevI binds the extensive 37 bp td homing site as a monomer and significantly distorts its substrate. In situ cleavage assays and phasing analyses indicate that upon nicking the bottom strand of the td homing site, I-TevI induces a directed bend of 38 degrees towards the major groove near the cleavage site. Formation of the bent I-TevI-DNA complex is proposed to promote top-strand cleavage of the homing site. Furthermore, reductions in the degree of distortion and in the efficiency of binding base-substitution variants of the td homing site indicate that sequences flanking the cleavage site contribute to the I-TevI-induced conformational change. These results, combined with genetic, physical and computer-modeling studies, form the basis of a model, wherein I-TevI acts as a hinged monomer to induce a distortion that widens the minor groove, facilitating access to the top-strand cleavage site. The model is compatible with both unmodified DNA and glucosylated hydroxymethylcytosine-containing DNA, as exists in the T-even phages.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avitahl N., Calame K. The C/EBP family of proteins distorts DNA upon binding but does not introduce a large directed bend. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 23;269(38):23553–23562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aymami J., Coll M., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Wang A. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of nicked DNA: a substrate for DNA repair enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2526–2530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M. Phage T4 introns: self-splicing and mobility. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:363–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S. M., Aubrey M., Belfort M. A site-specific endonuclease and co-conversion of flanking exons associated with the mobile td intron of phage T4. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S. M., Bryk M., Belfort M. I-TevI, the endonuclease encoded by the mobile td intron, recognizes binding and cleavage domains on its DNA target. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7719–7723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S., Clyman J., Belfort M. Intron mobility in phage T4 is dependent upon a distinctive class of endonucleases and independent of DNA sequences encoding the intron core: mechanistic and evolutionary implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3763–3770. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryk M., Belisle M., Mueller J. E., Belfort M. Selection of a remote cleavage site by I-tevI, the td intron-encoded endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1995 Mar 24;247(2):197–210. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryk M., Quirk S. M., Mueller J. E., Loizos N., Lawrence C., Belfort M. The td intron endonuclease I-TevI makes extensive sequence-tolerant contacts across the minor groove of its DNA target. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2141–2149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05862.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Maley G., Pedersen-Lane J., Wang A. M., Maley F. Characterization of the restriction site of a prokaryotic intron-encoded endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3574–3578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyman J., Belfort M. Trans and cis requirements for intron mobility in a prokaryotic system. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1269–1279. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON K. A. STARCH-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS--APPLICATION TO THE CLASSIFICATION OF PITUITARY PROTEINS AND POLYPEPTIDES. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL1002. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J. A., Johnson R. C., Dickerson R. E. Hin recombinase bound to DNA: the origin of specificity in major and minor groove interactions. Science. 1994 Jan 21;263(5145):348–355. doi: 10.1126/science.8278807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick K. E., Gonzalez L., Jr, Harrison C. J., Nelson H. C. Yeast heat shock transcription factor contains a flexible linker between the DNA-binding and trimerization domains. Implications for DNA binding by trimeric proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12475–12481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence determinants of CAP-induced bending and protein binding affinity. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):824–829. doi: 10.1038/333824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S. E., Goodall A. J. Modes of DNA cleavage by the EcoRV restriction endonuclease. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1771–1777. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Yun E., Crothers D. M. Detection of localized DNA flexibility. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):163–166. doi: 10.1038/368163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. DNA bending by Fos and Jun: the flexible hinge model. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1210–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.1957173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. Y., Weiss M. A. The SRY high-mobility-group box recognizes DNA by partial intercalation in the minor groove: a topological mechanism of sequence specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11990–11994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm J. D., Rould M. A., Aurora R., Herr W., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of the Oct-1 POU domain bound to an octamer site: DNA recognition with tethered DNA-binding modules. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam E., Fack F., Ménissier-de Murcia J., Cognet J. A., Barbin A., Sarantoglou V., Révet B., Delain E., de Murcia G. Conformational analysis of a 139 base-pair DNA fragment containing a single-stranded break and its interaction with human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 21;235(3):1062–1071. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Frisch H. L. Why does the electrophoretic mobility of DNA in gels vary with the length of the molecule? Biopolymers. 1982 May;21(5):995–997. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Chandrasegaran S. Alteration of the cleavage distance of Fok I restriction endonuclease by insertion mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2764–2768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Wu L. P., Chandrasegaran S. Functional domains in Fok I restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin O. J. Mobility of DNA in gel electrophoresis. Biopolymers. 1982 Nov;21(11):2315–2316. doi: 10.1002/bip.360211116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. B., Cooper J. P., Hagerman P. J. Electrophoretic evidence that single-stranded regions of one or more nucleotides dramatically increase the flexibility of DNA. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 22;33(7):1797–1803. doi: 10.1021/bi00173a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard K., May G. E. An EMSA-based method for determining the molecular weight of a protein--DNA complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3335–3336. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieters J. M., Mans R. M., van den Elst H., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Altona C. Conformational and thermodynamic consequences of the introduction of a nick in duplexed DNA fragments: an NMR study augmented by biochemical experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4551–4565. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. A., Nash H. A. Bending of the bacteriophage lambda attachment site by Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase bends the res site into a recombinogenic complex. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3609–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayre M. H., Geiduschek E. P. Effects of mutations at amino acid 61 in the arm of TF1 on its DNA-binding properties. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 20;216(4):819–833. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(99)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider G. J., Sayre M. H., Geiduschek E. P. DNA-bending properties of TF1. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):777–794. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80175-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka T. E., Hayes J. J., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. DNA binding specificity of the Mu Ner protein. Biochemistry. 1995 Mar 7;34(9):2946–2955. doi: 10.1021/bi00009a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Lahm A., Oefner C. Structure refined to 2A of a nicked DNA octanucleotide complex with DNase I. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):464–468. doi: 10.1038/332464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Yagi N. Stereochemical basis of DNA bending by transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Jun 25;23(12):2083–2091. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.12.2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. D., Halford S. E. Discrimination between DNA sequences by the EcoRV restriction endonuclease. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6198–6207. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. H., Huth J. R., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Molecular basis of human 46X,Y sex reversal revealed from the three-dimensional solution structure of the human SRY-DNA complex. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):705–714. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. W., Appelt K., Wilson K. S., Tanaka I. A protein structural motif that bends DNA. Proteins. 1989;5(4):281–288. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers B. E., Dunbar J. C. The endonuclease isoschizomers, SmaI and XmaI, bend DNA in opposite orientations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 11;21(11):2571–2577. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.11.2571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Catabolite activator protein-induced DNA bending in transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90562-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]