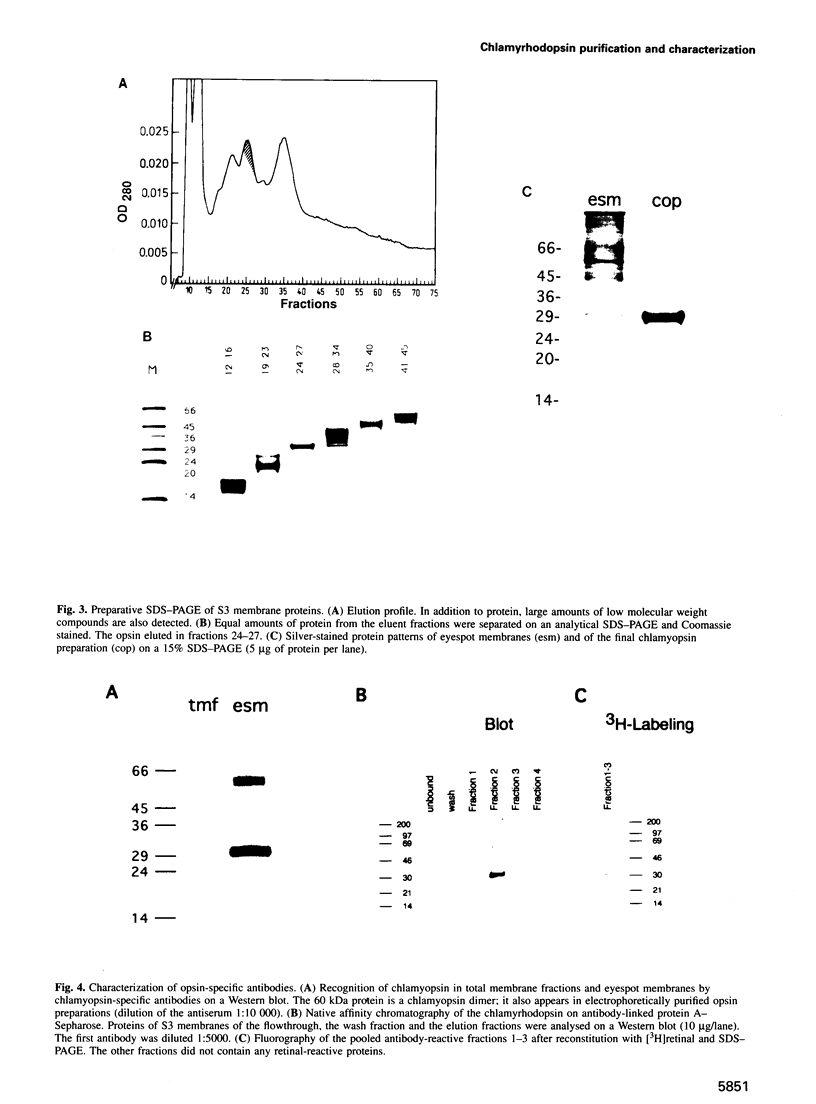
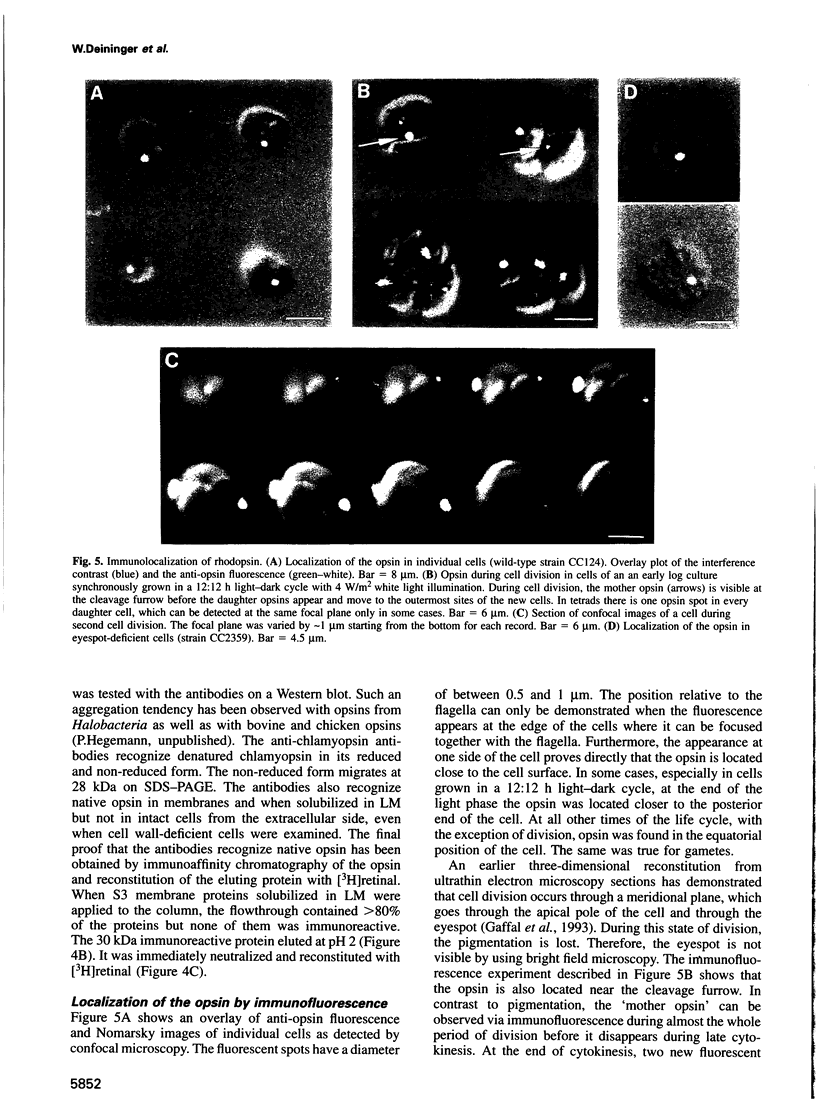
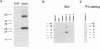Abstract
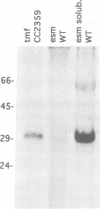
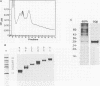
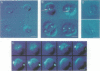
In order to find optimal light conditions for photosynthetic growth, the green alga Chlamydomonas uses a visual system. An optical device, a rhodopsin photoreceptor and an electrical signal transduction chain that mediates between photoreceptor and flagella comprise this system. Here we present an improved strategy for the preparation of eyespot membranes. These membranes contain a retinal binding protein, which has been proposed to be the apoprotein of the phototaxis receptor. The retinal binding protein, which we named chlamyopsin, was purified and opsin-specific antibodies were raised. Using these antibodies, the opsin was localized in the eyespot region of whole cells during growth and cell division. The opsin cDNA was purified and sequenced. The sequence reveals that chlamyopsin is not a typical seven helix receptor. It shows some homology to invertebrate opsins but not to opsins from halobacteria. It contains many polar and charged residues and might function as a light-gated ion channel complex. It is likely that this lower plant rhodopsin diverged from animal opsins early in opsin evolution.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann M., Hegemann P. In vitro identification of rhodopsin in the green alga Chlamydomonas. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 16;30(15):3692–3697. doi: 10.1021/bi00229a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein M., Beech P. L., Katz S. G., Rosenbaum J. L. A new kinesin-like protein (Klp1) localized to a single microtubule of the Chlamydomonas flagellum. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(6):1313–1326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Bennoun P. Thylakoid membrane polypeptides of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: wild-type and mutant strains deficient in photosystem II reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R. J., Hackett N. R., McCoy J. M., Chao B. H., Kimura K., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. I. Expression of the bacterio-opsin gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9246–9254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettl H. Uber den Teilungsverlauf des Chloroplasten bei Chlamydomonas. Protoplasma. 1976;88(1):75–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01280361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. W., Saranak J., Patel N., Zarilli G., Okabe M., Kline T., Nakanishi K. A rhodopsin is the functional photoreceptor for phototaxis in the unicellular eukaryote Chlamydomonas. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):756–759. doi: 10.1038/311756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. W., Smyth R. D. Light Antennas in phototactic algae. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):572–630. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.572-630.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber H. E., Rosario B. Variation in eyespot ultrastructure in Chlamydomonas reinhardi (ac-31). J Cell Sci. 1974 Aug;15(3):481–494. doi: 10.1242/jcs.15.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner W., Towner P. Invertebrate visual pigments. Photochem Photobiol. 1995 Jul;62(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1995.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara-Nishimura I., Kondo M., Nishimura M., Hara R., Hara T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for rhodopsin of the squid Todarodes pacificus. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 8;317(1-2):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81480-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave P. A., Hamm H. E., Hofmann K. P. Interaction of rhodopsin with the G-protein, transducin. Bioessays. 1993 Jan;15(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariyama T., Ozaki K., Tokunaga F., Tsukahara Y. Primary structure of crayfish visual pigment deduced from cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 11;315(3):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann P., Gärtner W., Uhl R. All-trans retinal constitutes the functional chromophore in Chlamydomonas rhodopsin. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1477–1489. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82183-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes J. A., Dutcher S. K. Cellular asymmetry in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Sci. 1989 Oct;94(Pt 2):273–285. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber A., Smith D. P., Zuker C. S., Paulsen R. Opsin of Calliphora peripheral photoreceptors R1-6. Homology with Drosophila Rh1 and posttranslational processing. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17906–17910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A superfamily of ion channels. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):672–672. doi: 10.1038/345672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal S., Khorana H. G. Structure and function in rhodopsin. 7. Point mutations associated with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Biochemistry. 1994 May 24;33(20):6121–6128. doi: 10.1021/bi00186a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketchum K. A., Joiner W. J., Sellers A. J., Kaczmarek L. K., Goldstein S. A. A new family of outwardly rectifying potassium channel proteins with two pore domains in tandem. Nature. 1995 Aug 24;376(6542):690–695. doi: 10.1038/376690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger P., Hegemann P. Photophobic responses and phototaxis in Chlamydomonas are triggered by a single rhodopsin photoreceptor. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 14;341(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Satir P. Characterization of the eyespot regions of "blind" Chlamydomonas mutants after restoration of photophobic responses. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1994 Nov-Dec;41(6):593–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1994.tb01521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Zacks D. N., Derguini F., Nakanishi K., Spudich J. L. Retinal analog restoration of photophobic responses in a blind Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant. Evidence for an archaebacterial like chromophore in a eukaryotic rhodopsin. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1490–1498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82184-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup O. On the phylogenetic validity of the flagellar apparatus in green algae and other chlorophyll A and B containing plants. Biosystems. 1978 Apr;10(1-2):117–144. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(78)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Zolotarev A. S., Artamonov I. D., Bespalov I. A., Dergachev A. E., Tsuda M. Octopus rhodopsin. Amino acid sequence deduced from cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Chisholm R. L., Conner T. W., Ranum L. P. The two alpha-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi code for slightly different proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2389–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sineshchekov O. A., Litvin F. F., Keszthelyi L. Two components of photoreceptor potential in phototaxis of the flagellated green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Biophys J. 1990 Jan;57(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82504-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L. Protein-protein interaction converts a proton pump into a sensory receptor. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):747–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N., Chiang K. S., Kates J. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid replication in meiosis of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. I. Isotopic transfer experiments with a strain producing eight zoospores. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):47–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towner P., Gärtner W. The primary structure of mantid opsin. Gene. 1994 Jun 10;143(2):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl R., Hegemann P. Probing visual transduction in a plant cell: Optical recording of rhodopsin-induced structural changes from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1295–1302. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82469-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera S., Hussy N., Evans R. J., Adami N., North R. A., Surprenant A., Buell G. A new class of ligand-gated ion channel defined by P2x receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):516–519. doi: 10.1038/371516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. R., Osawa S., Shi W., Dickerson C. D. Effects of carboxyl-terminal truncation on the stability and G protein-coupling activity of bovine rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 21;33(24):7587–7593. doi: 10.1021/bi00190a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacks D. N., Derguini F., Nakanishi K., Spudich J. L. Comparative study of phototactic and photophobic receptor chromophore properties in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):508–518. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81067-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacks D. N., Spudich J. L. Gain setting in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: mechanism of phototaxis and the role of the photophobic response. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1994;29(3):225–230. doi: 10.1002/cm.970290305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]