Abstract
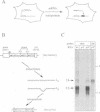
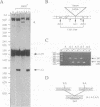
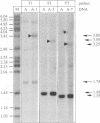
Using a sensitive assay for detection of reverse transcription events, we demonstrate that human HeLa cells can 'retropose', i.e. reverse transcribe and integrate, the mRNA of a naive reporter gene, at a low but detectable frequency. Furthermore, we show that the retroposed copies have all the hallmarks of the processed pseudogenes naturally found in the mammalian genome: they lack intron and 5' promoter sequence, they have acquired a 3' poly(A) tail, and they are flanked by short repeats (< 15 bp) of target DNA sequence. These results demonstrate that human cells possess an endogenous reverse transcription activity, which is not restricted to transcripts of transposable elements, and which is likely to be involved in the formation, still ongoing, of a large fraction of the eukaryotic genome.
Full text
PDF
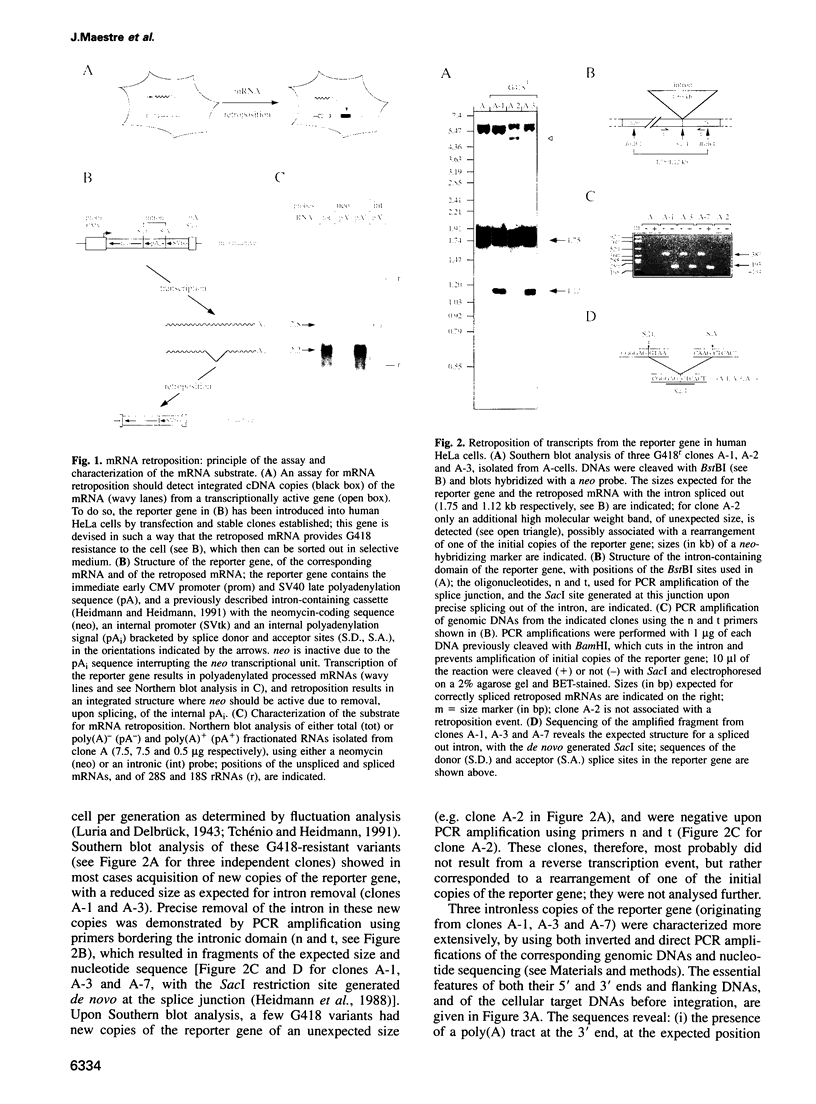



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr L. K., Strathern J. N. A role for reverse transcripts in gene conversion. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):170–173. doi: 10.1038/361170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr L. K., Strathern J. N., Garfinkel D. J. RNA-mediated recombination in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski B. A., Feng Q., Mathias S. L., Sassaman D. M., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boeke J. D. An in vivo assay for the reverse transcriptase of human retrotransposon L1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4485–4492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornburg R., Temin H. M. cDNA genes formed after infection with retroviral vector particles lack the hallmarks of natural processed pseudogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. P., Palmiter R. D. Retrotransposition of a mouse L1 element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8792–8795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Fiers W. Evidence for 'splicing' of SV40 16S mRNA. Nature. 1978 May 4;273(5657):70–73. doi: 10.1038/273070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Heidmann T. Retrotransposition of a mouse IAP sequence tagged with an indicator gene. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90217-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Heidmann O., Nicolas J. F. An indicator gene to demonstrate intracellular transposition of defective retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2219–2223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S., Gassama M. P., Heidmann T. Retrotransposition of the Drosophila LINE I element can induce deletion in the target DNA: a simple model also accounting for the variability of the normally observed target site duplications. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 15;202(1):111–119. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S., Heidmann T. An indicator gene for detection of germline retrotransposition in transgenic Drosophila demonstrates RNA-mediated transposition of the LINE I element. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1927–1937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K. The intracisternal A-particle gene family: structure and functional aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:183–276. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine K. L., Steiner B., Johnson K., Aronoff R., Quinton T. J., Linial M. L. Unusual features of integrated cDNAs generated by infection with genome-free retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1891–1900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L. LINEs. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Dec;1(4):505–508. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarrey J. R., Thomas K. Human testis-specific PGK gene lacks introns and possesses characteristics of a processed gene. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):501–505. doi: 10.1038/326501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita N., Nishio H., Kitoh Y., Ishikawa Y., Ishikawa Y., Minami R., Nakamura H., Matsuo M. Insertion of a 5' truncated L1 element into the 3' end of exon 44 of the dystrophin gene resulted in skipping of the exon during splicing in a case of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):1862–1867. doi: 10.1172/JCI116402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélisson A., Finnegan D. J., Bucheton A. Evidence for retrotransposition of the I factor, a LINE element of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4907–4910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Leclercq L., Göbel E., Saedler H. Cin4, an insert altering the structure of the A1 gene in Zea mays, exhibits properties of nonviral retrotransposons. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3873–3880. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal-Bendirdjian E., Heidmann T. Evidence for a reverse transcription intermediate for a marked line transposon in tumoral rat cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):863–870. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91270-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Schon E., Henderson A., Karathanasis S. K., Cate R., Zeitlin S., Chirgwin J., Efstratiadis A. RNA-mediated gene duplication: the rat preproinsulin I gene is a functional retroposon. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2090–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchenio T., Heidmann T. Defective retroviruses can disperse in the human genome by intracellular transposition. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2113–2118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2113-2118.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchénio T., Segal-Bendirdjian E., Heidmann T. Generation of processed pseudogenes in murine cells. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1487–1497. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Mizutani S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1211–1213. doi: 10.1038/2261211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F. Processed pseudogenes: characteristics and evolution. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:253–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]