Abstract
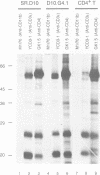
Recent observations suggest that the tyrosine kinase p56lck is involved in the transduction of transmembrane signals through the antigen specific T cell receptor (TCR) in CD4+ T cells. By means of in vitro kinase assays, we have found that p56lck coprecipitated with the TCR from lysates of a murine CD4+ T cell line in the absence of TCR-mediated stimuli. Analysis of CD4- mutants and CD4-transfected cells shows that p56lck-TCR association occurred only when CD4 was present. The functional importance of CD4:p56lck-TCR association was demonstrated by low activating potential of rare clonotypic antibodies which did not coprecipitate CD4:p56lck, as well as by total or partial loss of anti-TCR or antigen induced stimulation in CD4- cells, which could be recovered by CD4 transfection. Complementation assays using different anti-TCR antibodies suggest that cross linking of TCR-p56lck:CD4 plus structural changes in the complex are needed for efficient transduction of activating signals through the TCR in these cells.
Full text
PDF

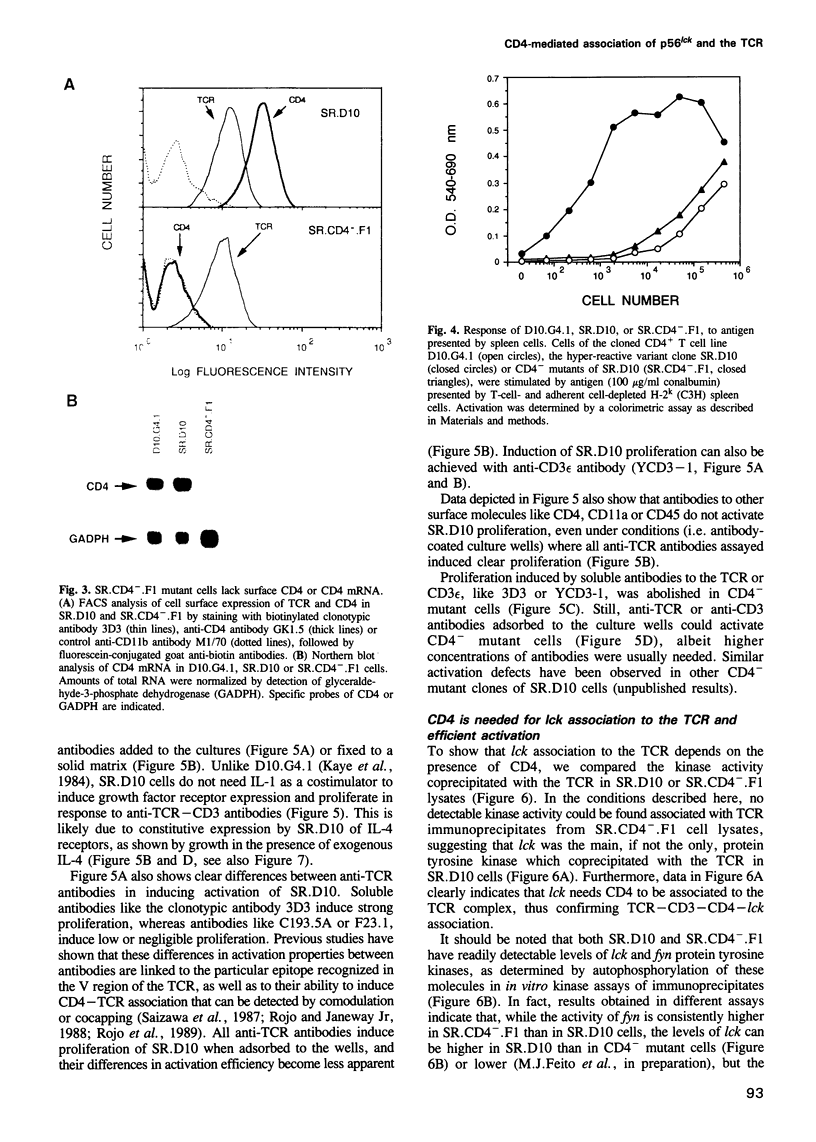
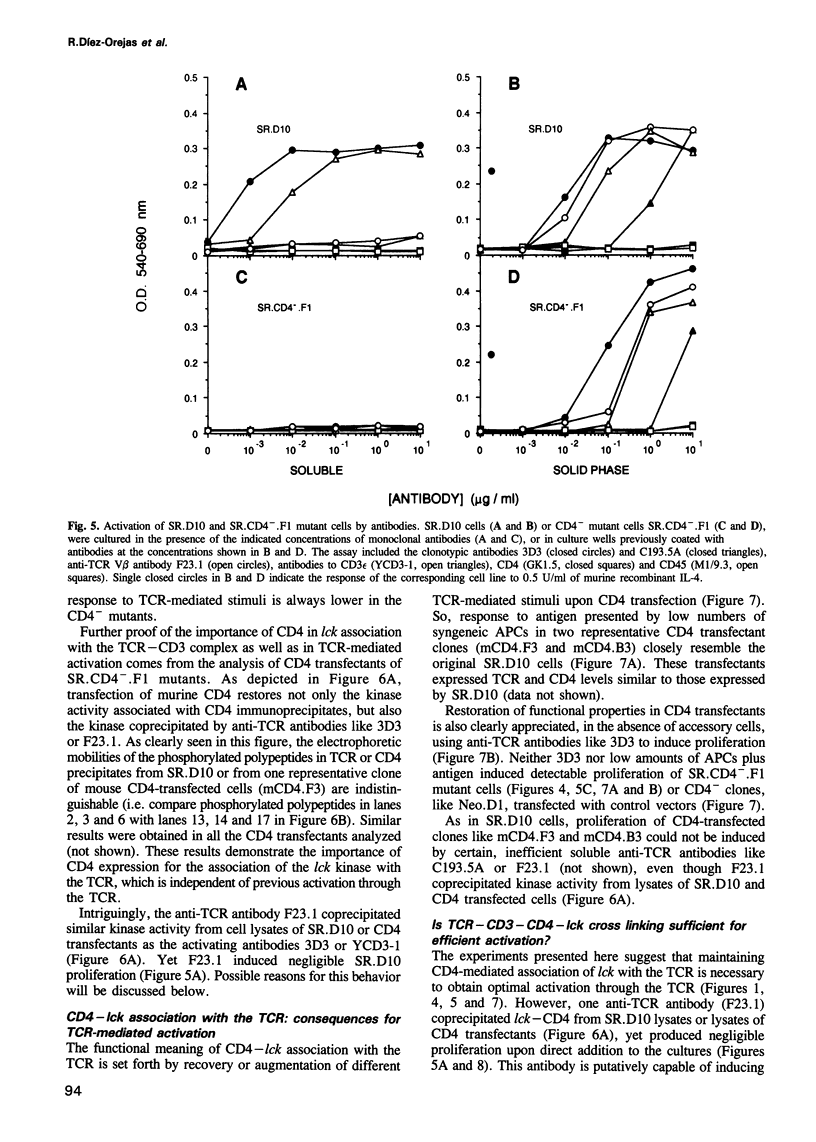
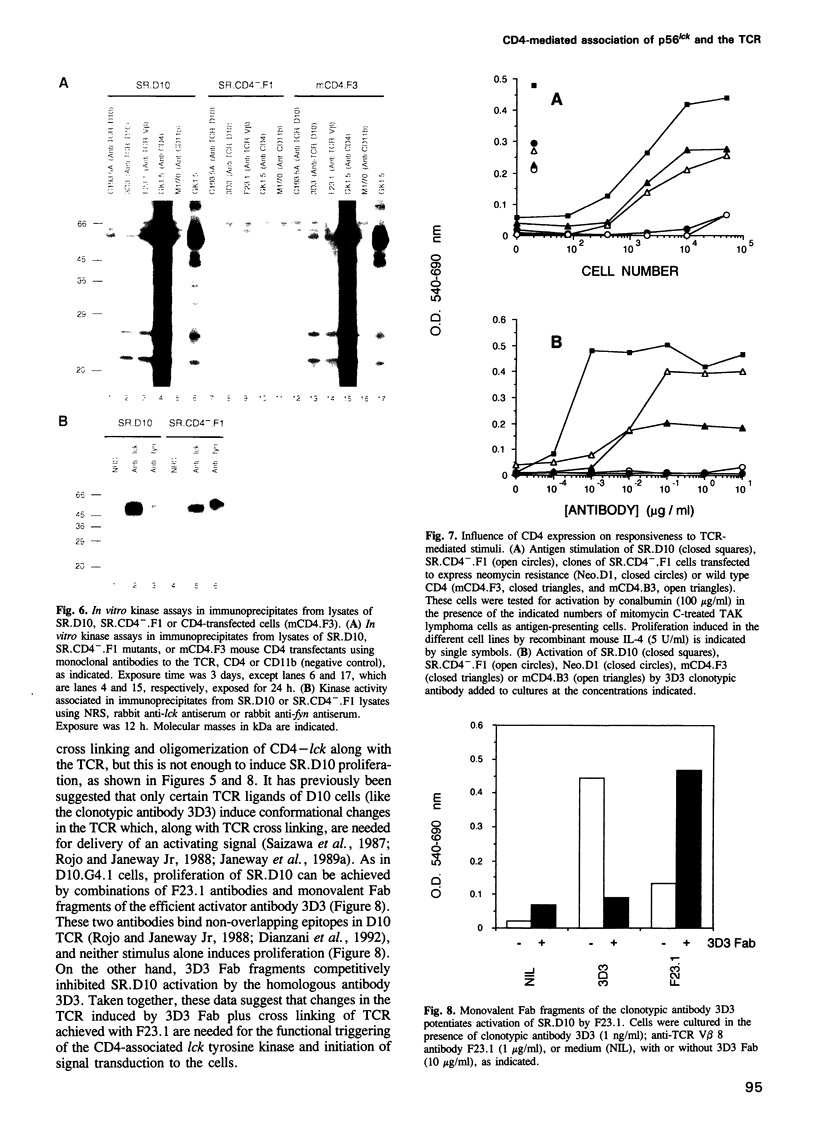




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Blue M. L., Schlossman S. F. Comodulation of CD3 and CD4. Evidence for a specific association between CD4 and approximately 5% of the CD3:T cell receptor complexes on helper T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1732–1737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyers A. D., Spruyt L. L., Williams A. F. Molecular associations between the T-lymphocyte antigen receptor complex and the surface antigens CD2, CD4, or CD8 and CD5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2945–2949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buerstedde J. M., Pease L. R., Bell M. P., Nilson A. E., Buerstedde G., Murphy D., McKean D. J. Identification of an immunodominant region on the I-A beta chain using site-directed mutagenesis and DNA-mediated gene transfer. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):473–487. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess K. E., Odysseos A. D., Zalvan C., Druker B. J., Anderson P., Schlossman S. F., Rudd C. E. Biochemical identification of a direct physical interaction between the CD4:p56lck and Ti(TcR)/CD3 complexes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1663–1668. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrera A. C., Wee S. B., Roberts T. M., Pardoll D. M. Selective association between MHC class I-restricted T cell receptors, CDS, and activated tyrosine kinases on thymocytes undergoing positive selection. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3142–3149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalupny N. J., Ledbetter J. A., Kavathas P. Association of CD8 with p56lck is required for early T cell signalling events. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1201–1207. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L. Surface antigen expression and immunoglobulin gene rearrangement during mouse pre-B cell development. Immunol Rev. 1982;69:5–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T. L., Uniyal S., Shin J., Strominger J. L., Mittler R. S., Burakoff S. J. p56lck association with CD4 is required for the interaction between CD4 and the TCR/CD3 complex and for optimal antigen stimulation. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2159–2162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by a src family protein-tyrosine kinase (p59fyn). Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D., Chow L. M., Fournel M., Veillette A. Differential regulation of T cell antigen responsiveness by isoforms of the src-related tyrosine protein kinase p59fyn. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1483–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani U., Luqman M., Rojo J., Yagi J., Baron J. L., Woods A., Janeway C. A., Jr, Bottomly K. Molecular associations on the T cell surface correlate with immunological memory. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2249–2257. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani U., Shaw A., al-Ramadi B. K., Kubo R. T., Janeway C. A., Jr Physical association of CD4 with the T cell receptor. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):678–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Interaction between CD4 and class II MHC molecules mediates cell adhesion. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):256–259. doi: 10.1038/330256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Jönsson J. I., Falk I., Emmrich F. Effective activation of resting mouse T lymphocytes by cross-linking submitogenic concentrations of the T cell antigen receptor with either Lyt-2 or L3T4. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):643–650. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich F., Kanz L., Eichmann K. Cross-linking of the T cell receptor complex with the subset-specific differentiation antigen stimulates interleukin 2 receptor expression in human CD4 and CD8 T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):529–534. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Mutations of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor that cause a loss of ligand-induced conformational change, subtle changes in kinase activity, and impaired ability to stimulate DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4473–4478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. J., Niklinska B. B., Orloff D. G., Merćep M., Ashwell J. D., Klausner R. D. Structural mutations of the T cell receptor zeta chain and its role in T cell activation. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):174–177. doi: 10.1126/science.2371564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann M., Guttinger M., Amrein K. E., Burn P. Protein tyrosine kinase p59fyn is associated with the T cell receptor-CD3 complex in functional human lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):283–286. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaichenhaus N., Shastri N., Littman D. R., Turner J. M. Requirement for association of p56lck with CD4 in antigen-specific signal transduction in T cells. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90235-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield C., Hiles I., Waterfield M. D., Federwisch M., Wollmer A., Blundell T. L., McDonald N. Epidermal growth factor binding induces a conformational change in the external domain of its receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4115–4123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughn L., Gratton S., Caron L., Sékaly R. P., Veillette A., Julius M. Association of tyrosine kinase p56lck with CD4 inhibits the induction of growth through the alpha beta T-cell receptor. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):328–331. doi: 10.1038/358328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving B. A., Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Carding S., Jones B., Murray J., Portoles P., Rasmussen R., Rojo J., Saizawa K., West J., Bottomly K. CD4+ T cells: specificity and function. Immunol Rev. 1988 Jan;101:39–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Dianzani U., Portoles P., Rath S., Reich E. P., Rojo J., Yagi J., Murphy D. B. Cross-linking and conformational change in T-cell receptors: role in activation and in repertoire selection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 2):657–666. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Haque S., Smith L. A., Saizawa K. The role of the murine L3T4 molecule in T cell activation: differential effects of anti-L3T4 on activation by monoclonal anti-receptor antibodies. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987;3(2):121–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Rojo J., Saizawa K., Dianzani U., Portoles P., Tite J., Haque S., Jones B. The co-receptor function of murine CD4. Immunol Rev. 1989 Jun;109:77–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr The T cell receptor as a multicomponent signalling machine: CD4/CD8 coreceptors and CD45 in T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:645–674. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Functional activities of antibodies against brain-associated T cell antigens. I. Induction of T cell proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jul;11(7):584–592. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Samelson L. E. Increases in tyrosine phosphorylation are detectable before phospholipase C activation after T cell receptor stimulation. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1591–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Porcelli S., Tite J., Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Both a monoclonal antibody and antisera specific for determinants unique to individual cloned helper T cell lines can substitute for antigen and antigen-presenting cells in the activation of T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):836–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Singer S. J. Molecular dynamics in the membranes of helper T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luqman M., Greenbaum L., Lu D., Bottomly K. Differential effect of interleukin 1 on naive and memory CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):95–100. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miceli M. C., von Hoegen P., Parnes J. R. Adhesion versus coreceptor function of CD4 and CD8: role of the cytoplasmic tail in coreceptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittler R. S., Goldman S. J., Spitalny G. L., Burakoff S. J. T-cell receptor-CD4 physical association in a murine T-cell hybridoma: induction by antigen receptor ligation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8531–8535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina T. J., Kishihara K., Siderovski D. P., van Ewijk W., Narendran A., Timms E., Wakeham A., Paige C. J., Hartmann K. U., Veillette A. Profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking p56lck. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):161–164. doi: 10.1038/357161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norment A. M., Salter R. D., Parham P., Engelhard V. H., Littman D. R. Cell-cell adhesion mediated by CD8 and MHC class I molecules. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):79–81. doi: 10.1038/336079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Rho H. W., Rhee S. G. CD3 stimulation causes phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 on serine and tyrosine residues in a human T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5453–5456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoles P., Rojo J. M., Janeway C. A., Jr Asymmetry in the recognition of antigen: self class II MHC and non-self class II MHC molecules by the same T-cell receptor. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1989;4(3):129–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoles P., Rojo J., Golby A., Bonneville M., Gromkowski S., Greenbaum L., Janeway C. A., Jr, Murphy D. B., Bottomly K. Monoclonal antibodies to murine CD3 epsilon define distinct epitopes, one of which may interact with CD4 during T cell activation. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4169–4175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo J. M., Janeway C. A., Jr The biologic activity of anti-T cell receptor V region monoclonal antibodies is determined by the epitope recognized. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1081–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo J. M., Saizawa K., Janeway C. A., Jr Physical association of CD4 and the T-cell receptor can be induced by anti-T-cell receptor antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3311–3315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo C., Seed B. Cellular immunity to HIV activated by CD4 fused to T cell or Fc receptor polypeptides. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90327-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saizawa K., Rojo J., Janeway C. A., Jr Evidence for a physical association of CD4 and the CD3:alpha:beta T-cell receptor. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):260–263. doi: 10.1038/328260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Norment A. M., Chen B. P., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Littman D. R., Parham P. Polymorphism in the alpha 3 domain of HLA-A molecules affects binding to CD8. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):345–347. doi: 10.1038/338345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Patel M. D., Weissman A. M., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Antigen activation of murine T cells induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a polypeptide associated with the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1083–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Davignon D., Martz E., Springer T. A. Antigens involved in mouse cytolytic T-lymphocyte (CTL)-mediated killing: functional screening and topographic relationship. Cell Immunol. 1982 Oct;73(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staerz U. D., Rammensee H. G., Benedetto J. D., Bevan M. J. Characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on T cell antigen receptor. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3994–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Weiss A. Genetic evidence for the involvement of the lck tyrosine kinase in signal transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90428-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Kupsch J., Eichmann K., Saizawa M. K. Biochemical evidence of the physical association of the majority of CD3 delta chains with the accessory/co-receptor molecules CD4 and CD8 on nonactivated T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2475–2479. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. T cell subsets and the recognition of MHC class. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:129–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telfer J. C., Rudd C. E. A 32-kD GTP-binding protein associated with the CD4-p56lck and CD8-p56lck T cell receptor complexes. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):439–441. doi: 10.1126/science.1925604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Kaye J., Saizawa K. M., Ming J., Katz M. E., Smith L. A., Janeway C. A., Jr Direct interactions between B and T lymphocytes bearing complementary receptors. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):189–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Sloan A., Janeway C. A., Jr The role of L3T4 in T cell activation: L3T4 may be both an Ia-binding protein and a receptor that transduces a negative signal. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1986;2(4):179–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wange R. L., Kong A. N., Samelson L. E. A tyrosine-phosphorylated 70-kDa protein binds a photoaffinity analogue of ATP and associates with both the zeta chain and CD3 components of the activated T cell antigen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11685–11688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener A. M., Letourneur F., Hoeveler A., Brocker T., Luton F., Malissen B. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex is composed of at least two autonomous transduction modules. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90208-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Koretzky G., Schatzman R. C., Kadlecek T. Functional activation of the T-cell antigen receptor induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5484–5488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigzell H. Specific affinity fractionation of lymphocytes using glass or plastic bead columns. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Yamamoto F., Almoguera C., Perucho M. A method to detect and characterize point mutations in transcribed genes: amplification and overexpression of the mutant c-Ki-ras allele in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]