Abstract
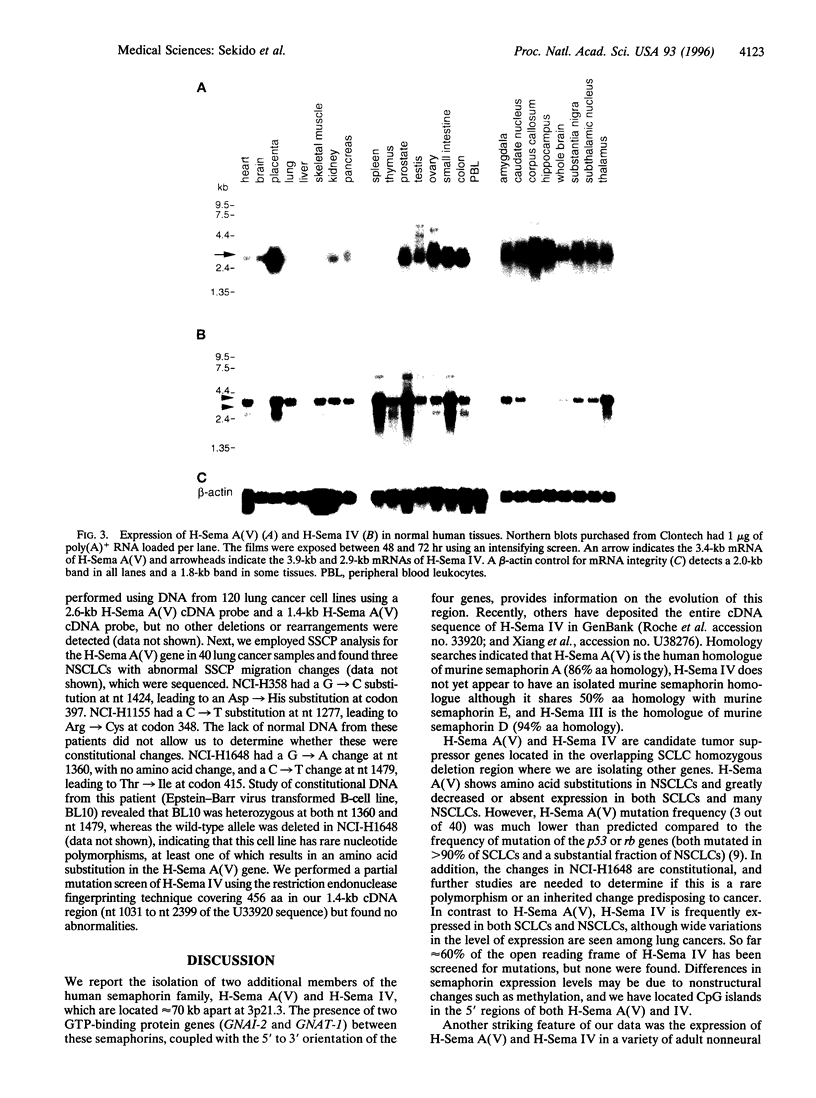
Semaphorins and collapsins make up a family of conserved genes that encode nerve growth cone guidance signals. We have identified two additional members of the human semaphorin family [human semaphorin A(V) and human semaphorin IV] in chromosome region 3p21.3, where several small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cell lines exhibit homozygous deletions indicative of a tumor suppressor gene. Human semaphorin A(V) has 86% amino acid homology with murine semaphorin A, whereas semaphorin IV is most closely related to murine semaphorin E, with 50% homology. These semaphorin genes are approximately 70 kb apart flanking two GTP-binding protein genes, GNAI-2 and GNAT-1. In contrast, other human semaphorin gene sequences (human semaphorin III and homologues of murine semaphorins B and C) are not located on chromosome 3. Human semaphorin A(V) is translated in vitro into a 90-kDa protein, which accumulates at the endoplasmic reticulum. The human semaphorin A(V) (3.4-kb mRNA) and IV (3.9- and 2.9-kb mRNAs) genes are expressed abundantly but differentially in a variety of human neural and nonneural tissues. Human semaphorin A(V) was expressed in only 1 out of 23 SCLCs and 7 out of 16 non-SCLCs, whereas semaphorin IV was expressed in 19 out of 23 SCLCs and 13 out of 16 non-SCLCs. Mutational analysis in semaphorin A(V) revealed mutations (germ line in one case) in 3 of 40 lung cancers. Our data suggest the need to determine the function of human semaphorins A(V) and IV in nonneural tissues and their role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brauch H., Tory K., Kotler F., Gazdar A. F., Pettengill O. S., Johnson B., Graziano S., Winton T., Buys C. H., Sorenson G. D. Molecular mapping of deletion sites in the short arm of chromosome 3 in human lung cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 Jan;1(3):240–246. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower M., Carney D. N., Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. Growth of cell lines and clinical specimens of human non-small cell lung cancer in a serum-free defined medium. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):798–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. N., Gazdar A. F., Bepler G., Guccion J. G., Marangos P. J., Moody T. W., Zweig M. H., Minna J. D. Establishment and identification of small cell lung cancer cell lines having classic and variant features. Cancer Res. 1985 Jun;45(6):2913–2923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carritt B., Kok K., van den Berg A., Osinga J., Pilz A., Hofstra R. M., Davis M. B., van der Veen A. Y., Rabbitts P. H., Gulati K. A gene from human chromosome region 3p21 with reduced expression in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 15;52(6):1536–1541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly M. C., Xiang R. H., Buchhagen D., Hensel C. H., Garcia D. K., Killary A. M., Minna J. D., Naylor S. L. A homozygous deletion on chromosome 3 in a small cell lung cancer cell line correlates with a region of tumor suppressor activity. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1721–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd J., Schuchardt A. Axon guidance: a compelling case for repelling growth cones. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):471–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi K., Takahashi T., Yamakawa K., Ueda R., Sekido Y., Ariyoshi Y., Suyama M., Takagi H., Nakamura Y., Takahashi T. Three distinct regions involved in 3p deletion in human lung cancer. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok K., van den Berg A., Veldhuis P. M., van der Veen A. Y., Franke M., Schoenmakers E. F., Hulsbeek M. M., van der Hout A. H., de Leij L., van de Ven W. A homozygous deletion in a small cell lung cancer cell line involving a 3p21 region with a marked instability in yeast artificial chromosomes. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 1;54(15):4183–4187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodkin A. L., Matthes D. J., Goodman C. S. The semaphorin genes encode a family of transmembrane and secreted growth cone guidance molecules. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1389–1399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90625-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodkin A. L., Matthes D. J., O'Connor T. P., Patel N. H., Admon A., Bentley D., Goodman C. S. Fasciclin IV: sequence, expression, and function during growth cone guidance in the grasshopper embryo. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):831–845. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Yazdani A., Wehnert M., Zhao Z. Y., Lindsay E. A., Bailey J., Coolbaugh M. I., Couch L., Xiong M., Chinault A. C. Isolation of chromosome-specific genes by reciprocal probing of arrayed cDNA and cosmid libraries. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Aug;4(8):1373–1380. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.8.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q., Sommer S. S. Restriction endonuclease fingerprinting (REF): a sensitive method for screening mutations in long, contiguous segments of DNA. Biotechniques. 1995 Mar;18(3):470–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Raible D., Raper J. A. Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80064-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Shepherd I., Li J., Renzi M. J., Chang S., Raper J. A. A family of molecules related to collapsin in the embryonic chick nervous system. Neuron. 1995 Jun;14(6):1131–1140. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magovcevic I., Ang S. L., Seidman J. G., Tolman C. J., Neer E. J., Morton C. C. Regional localization of the human G protein alpha i2 (GNAI2) gene: assignment to 3p21 and a related sequence (GNAI2L) to 12p12-p13. Genomics. 1992 Jan;12(1):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90414-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes D. J., Sink H., Kolodkin A. L., Goodman C. S. Semaphorin II can function as a selective inhibitor of specific synaptic arborizations. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):631–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messersmith E. K., Leonardo E. D., Shatz C. J., Tessier-Lavigne M., Goodman C. S., Kolodkin A. L. Semaphorin III can function as a selective chemorepellent to pattern sensory projections in the spinal cord. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):949–959. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D. The molecular biology of lung cancer pathogenesis. Chest. 1993 Apr;103(4 Suppl):449S–456S. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.4_supplement.449s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Johnson B. E., Minna J. D., Sakaguchi A. Y. Loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 3p markers in small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):451–454. doi: 10.1038/329451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Püschel A. W., Adams R. H., Betz H. Murine semaphorin D/collapsin is a member of a diverse gene family and creates domains inhibitory for axonal extension. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):941–948. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekido Y., Pass H. I., Bader S., Mew D. J., Christman M. F., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) gene is somatically mutated in mesothelioma but not in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1227–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Zabarovsky E. R., Talmadge C., Berglund P., Chan K. W., Pokrovskaya E. S., Kashuba V. I., Zhen D. K., Boldog F., Zabarovskaya V. I. Somatic cell hybrid panel and NotI linking clones for physical mapping of human chromosome 3. Genomics. 1994 Mar 1;20(1):105–113. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei M. H., Latif F., Bader S., Kashuba V., Chen J. Y., Duh F. M., Sekido Y., Lee C. C., Geil L., Kuzmin I. Construction of a 600-kilobase cosmid clone contig and generation of a transcriptional map surrounding the lung cancer tumor suppressor gene (TSG) locus on human chromosome 3p21.3: progress toward the isolation of a lung cancer TSG. Cancer Res. 1996 Apr 1;56(7):1487–1492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L. S., Spiegel A. M., Carter A. D. Cloning and characterization of the human gene for the alpha-subunit of Gi2, a GTP-binding signal transduction protein. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Bunn P. A., Jr, Kao-Shan C. S., Lee E. C., Carney D. N., Gazdar A., Minna J. D. A nonrandom chromosomal abnormality, del 3p(14-23), in human small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1982 Jun;6(2):119–134. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(82)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Kao-Shan C. S., Lee E. C., Bunn P. A., Carney D. N., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. Specific chromosome defect associated with human small-cell lung cancer; deletion 3p(14-23). Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):181–182. doi: 10.1126/science.6274023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Gazdar A., Steinberg S. M., Oie H., Linnoila I., Mulshine J., Nau M., Minna J. D. Nonrandom structural and numerical chromosome changes in non-small-cell lung cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1991 May;3(3):168–188. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870030303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang R. H., Hensel C. H., Garcia D. K., Carlson H. C., Kok K., Daly M. C., Kerbacher K., van den Berg A., Veldhuis P., Buys C. H. Isolation of the human semaphorin III/F gene (SEMA3F) at chromosome 3p21, a region deleted in lung cancer. Genomics. 1996 Feb 15;32(1):39–48. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]