Abstract
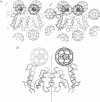
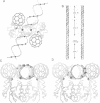
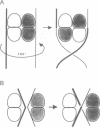
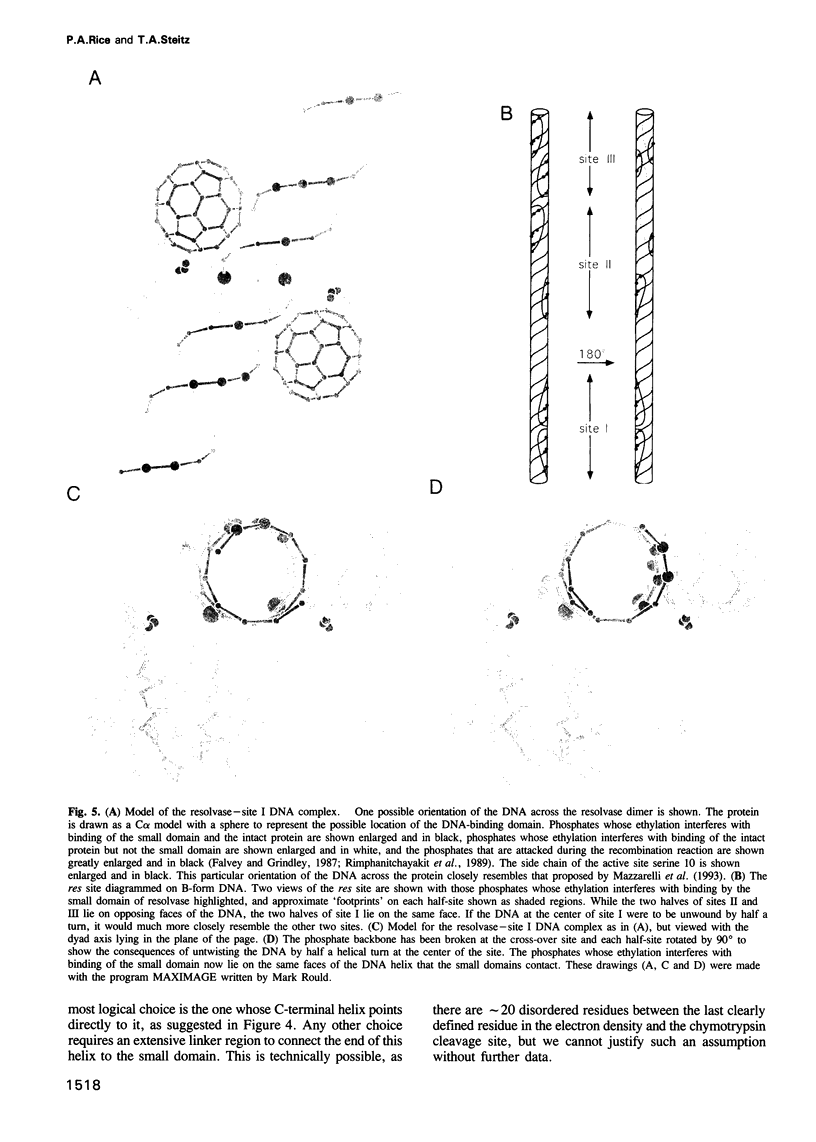
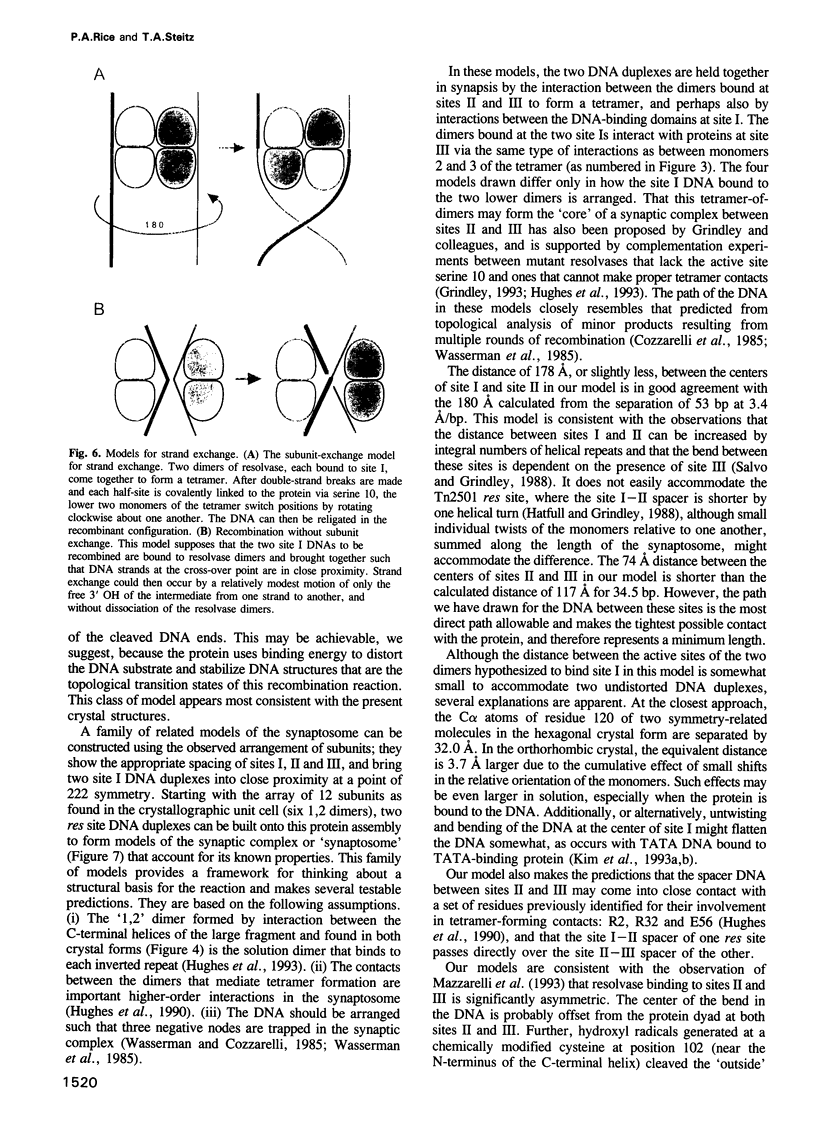
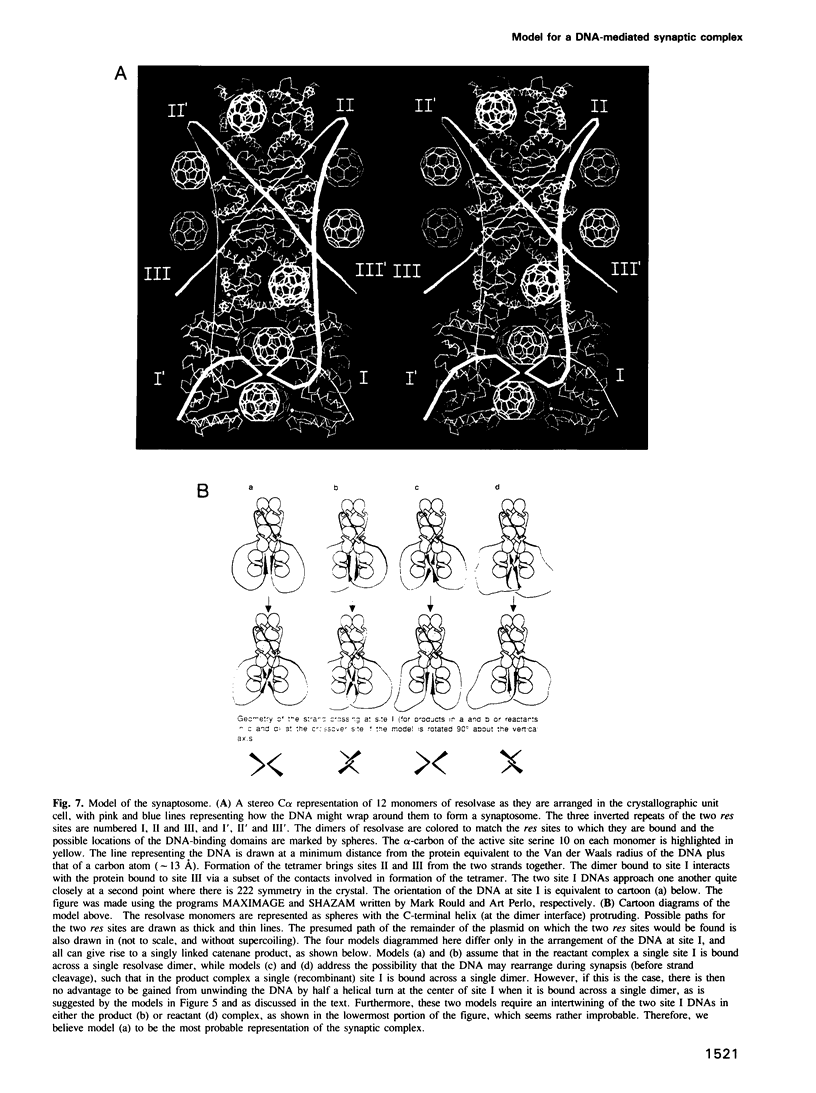
The packing arrangement of the 12 subunits of intact gamma delta resolvase in the unit cell of a hexagonal crystal form suggests a model for site-specific recombination that involves a DNA-mediated synaptic intermediate. The crystal structure has been determined by molecular replacement and partially refined at 2.8/3.5 A resolution. Although the small DNA-binding domain is disordered in these crystals, packing considerations show that only a small region of space in the crystal could accommodate a domain of its size. A family of related models for a synaptic complex between two DNA duplexes and 12 monomers that are arranged as situated in the crystal is consistent with the known topology of the complex and the distances between the three resolvase dimer-binding sites per DNA; further, these models place the two DNA recombination sites in contact with each other between two resolvase dimers, implying that strand exchange is accomplished through direct DNA-DNA interaction. A major role postulated, then, for the resolvase protein assembly is to stabilize a res DNA structure that is close to the topological transition state of the reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Grindley N. D., Templeton N. S., Steitz T. A. Cleavage of the site-specific recombination protein gamma delta resolvase: the smaller of two fragments binds DNA specifically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2001–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Murthy H. M., Steitz T. A. Preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the putative catalytic domain of gamma delta resolvase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15934–15935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Krasnow M. A., Gerrard S. P., White J. H. A topological treatment of recombination and topoisomerases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:383–400. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L. The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:77–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey E., Grindley N. D. Contacts between gamma delta resolvase and the gamma delta res site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):815–821. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham K. S., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the DNA binding domain of gamma delta-resolvase characterized by affinity cleaving. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16534–16540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D. Analysis of a nucleoprotein complex: the synaptosome of gamma delta resolvase. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):738–740. doi: 10.1126/science.8235593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Lauth M. R., Wells R. G., Wityk R. J., Salvo J. J., Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: identification of three binding sites for resolvase at the res sites of gamma delta and Tn3. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Reed R. R. Transpositional recombination in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:863–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffter P., Bickle T. A. Enhancer-independent mutants of the Cin recombinase have a relaxed topological specificity. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3991–3996. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin R. Multiwire area X-ray diffractometers. Methods Enzymol. 1985;114:416–452. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)14029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D. Analysis of gamma delta resolvase mutants in vitro: evidence for an interaction between serine-10 of resolvase and site I of res. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Noble S. M., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase induces an unusual DNA structure at the recombinational crossover point. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90760-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
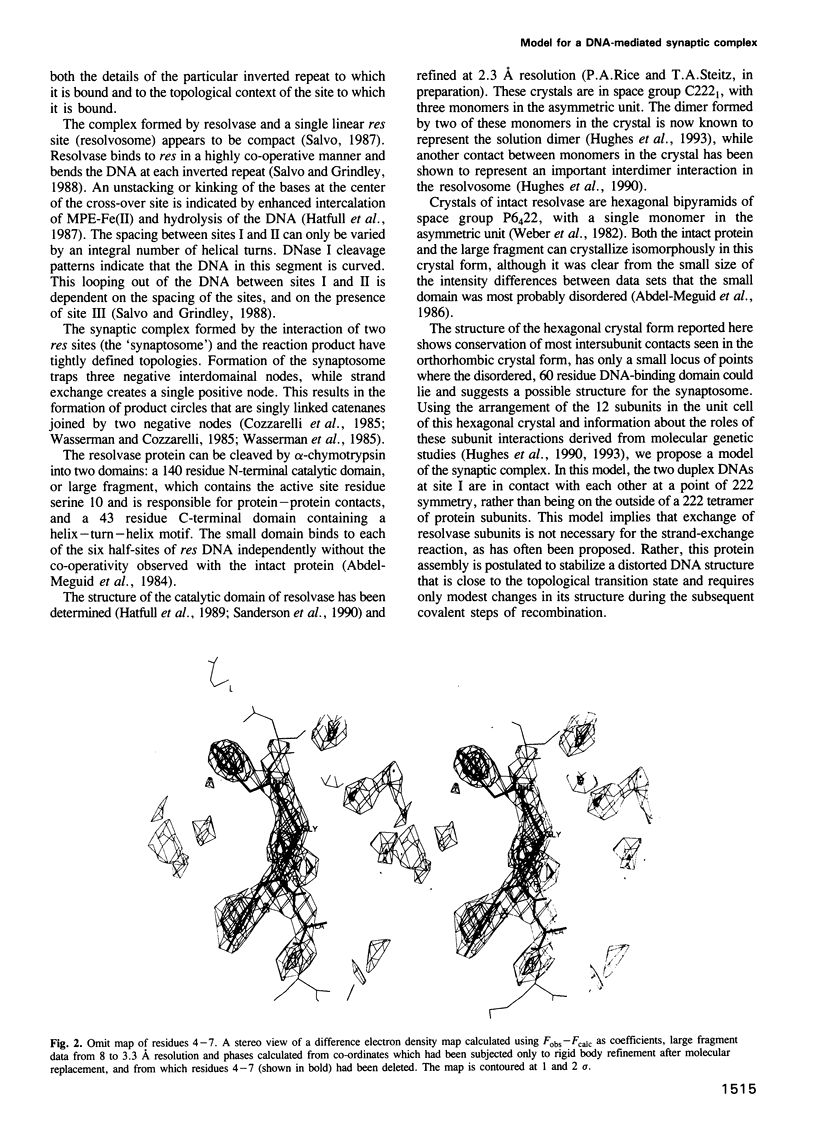
- Hatfull G. F., Sanderson M. R., Freemont P. S., Raccuia P. R., Grindley N. D., Steitz T. A. Preparation of heavy-atom derivatives using site-directed mutagenesis. Introduction of cysteine residues into gamma delta resolvase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):661–667. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heichman K. A., Johnson R. C. The Hin invertasome: protein-mediated joining of distant recombination sites at the enhancer. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2166334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
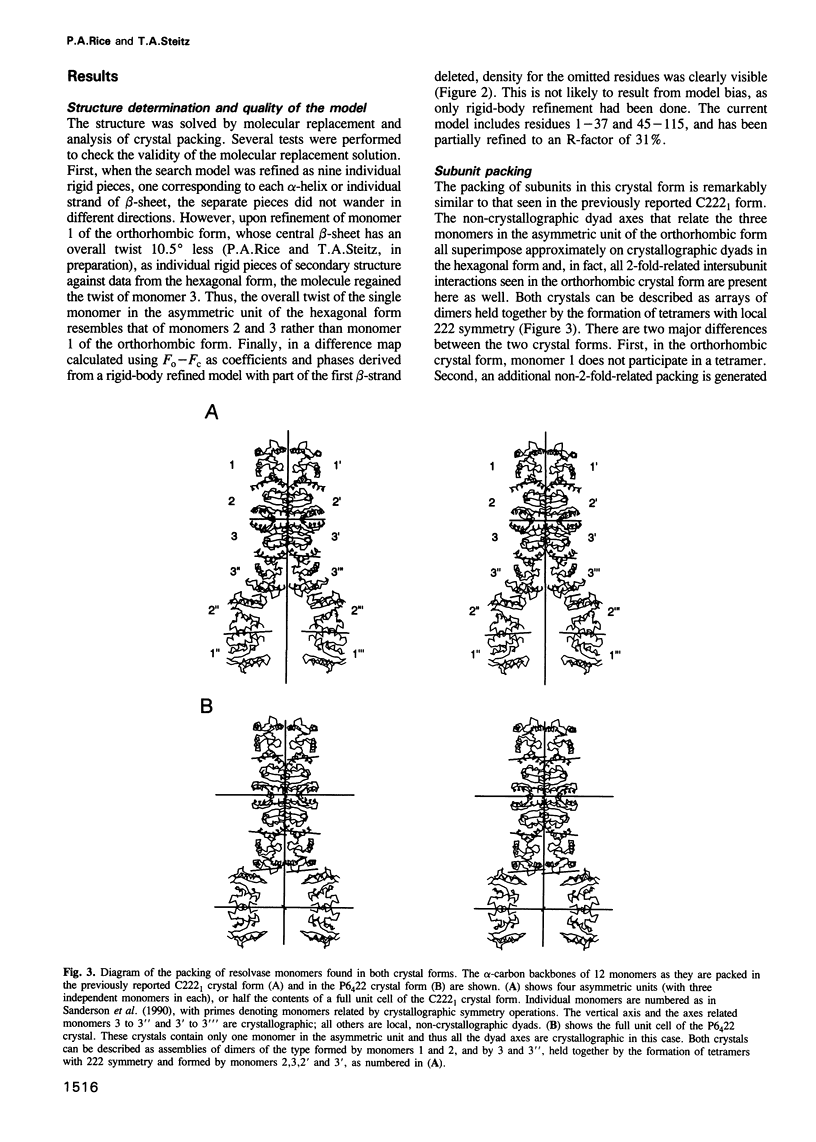
- Hughes R. E., Hatfull G. F., Rice P., Steitz T. A., Grindley N. D. Cooperativity mutants of the gamma delta resolvase identify an essential interdimer interaction. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1331–1338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90428-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. E., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A., Grindley N. D. Protein-protein interactions directing resolvase site-specific recombination: a structure-function analysis. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1447–1458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaar R., Klippel A., Shekhtman E., Dungan J. M., Kahmann R., Cozzarelli N. R. Processive recombination by the phage Mu Gin system: implications for the mechanisms of DNA strand exchange, DNA site alignment, and enhancer action. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90372-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
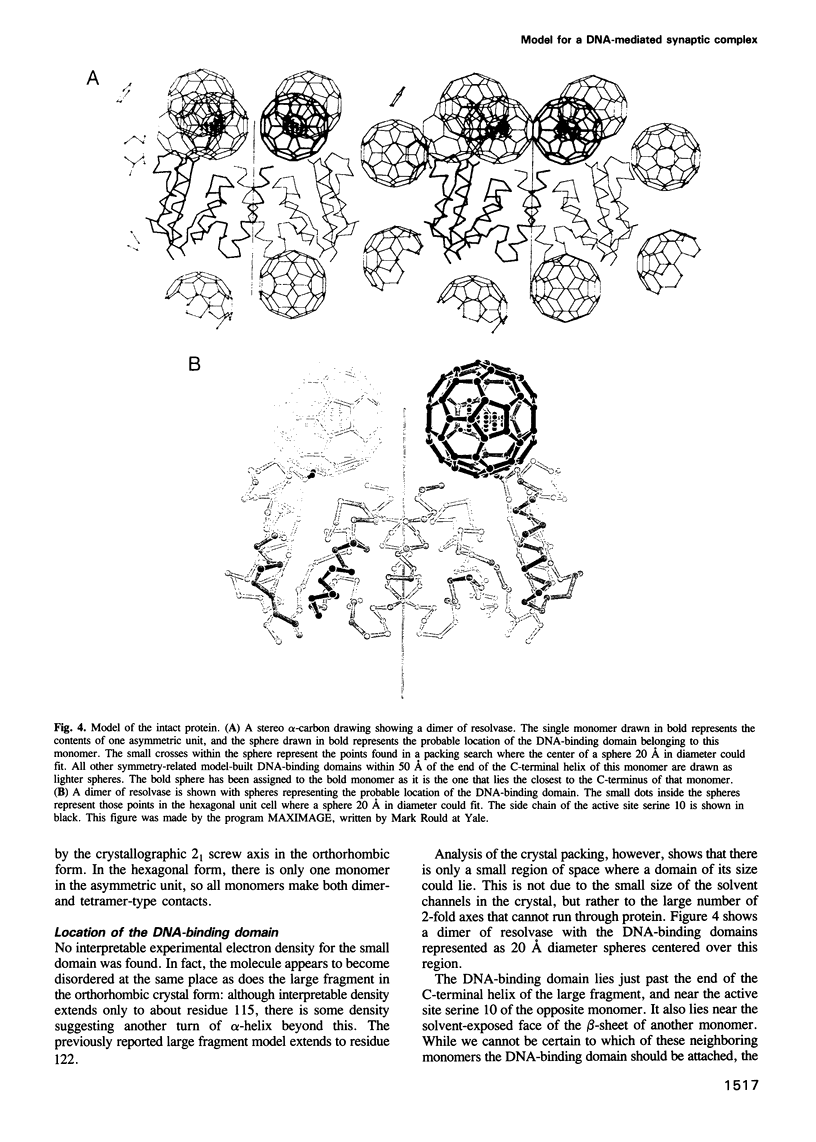
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Cloppenborg K., Kahmann R. Isolation and characterization of unusual gin mutants. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3983–3989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Kanaar R., Kahmann R., Cozzarelli N. R. Analysis of strand exchange and DNA binding of enhancer-independent Gin recombinase mutants. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1047–1057. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05746.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific relaxation and recombination by the Tn3 resolvase: recognition of the DNA path between oriented res sites. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1313–1324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A. Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:913–949. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarelli J. M., Ermácora M. R., Fox R. O., Grindley N. D. Mapping interactions between the catalytic domain of resolvase and its DNA substrate using cysteine-coupled EDTA-iron. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):2979–2986. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Grindley N. D. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination in vitro: DNA cleavage and protein-DNA linkage at the recombination site. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Moser C. D. Resolvase-mediated recombination intermediates contain a serine residue covalently linked to DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:245–249. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimphanitchayakit V., Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D. The 43 residue DNA binding domain of gamma delta resolvase binds adjacent major and minor grooves of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1035–1050. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase bends the res site into a recombinogenic complex. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3609–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson M. R., Freemont P. S., Rice P. A., Goldman A., Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D., Steitz T. A. The crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the site-specific recombination enzyme gamma delta resolvase at 2.7 A resolution. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1323–1329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90427-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. M., Sherratt D. J., Boocock M. R. Site-specific recombination by Tn3 resolvase: topological changes in the forward and reverse reactions. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. The structure of the E. coli recA protein monomer and polymer. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):318–325. doi: 10.1038/355318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Determination of the stereostructure of the product of Tn3 resolvase by a general method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1079–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A., Dungan J. M., Cozzarelli N. R. Discovery of a predicted DNA knot substantiates a model for site-specific recombination. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):171–174. doi: 10.1126/science.2990045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Ollis D. L., Bebrin W. R., Abdel-Meguid S. S., Steitz T. A. Crystallization of resolvase, a repressor that also catalyzes site-specific DNA recombination. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):689–690. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90508-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Grindley N. D. Analysis of the gamma delta res site. Sites required for site-specific recombination and gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):667–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]