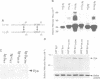
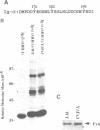
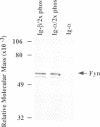
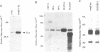Abstract
The B cell antigen receptor complex (BCR) is composed of membrane Ig and heterodimers of Ig-alpha and Ig-beta/gamma. Recent findings indicate that Ig-alpha associates with Src-family kinases, including Fyn and Lyn, via an approximately 26 amino acid motif termed ARH1. Studies reported here (i) define two mechanisms whereby this motif binds Fyn and (ii) reveal an important functional consequence of binding, i.e. kinase activation. Mutational analysis indicates that specific low-affinity binding is determined by a short sequence, -DCSM-, in the motif and is not dependent on motif tyrosine residues. In contrast, the doubly tyrosine phosphorylated motif binds independently of DCSM and with high affinity. Importantly, this binding leads to Fyn activation. Taken together with studies which map low-affinity binding of Fyn or Lyn to the kinase's N-terminal unique region and high-affinity binding to the kinase's SH2 domain, these results suggest a mechanism of BCR activation in which the non-phosphorylated resting receptor is associated with Src-family kinases and, upon stimulation, tyrosine phosphorylation of Ig-alpha leads to reorientation and activation of receptor-associated kinases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alber G., Kim K. M., Weiser P., Riesterer C., Carsetti R., Reth M. Molecular mimicry of the antigen receptor signalling motif by transmembrane proteins of the Epstein-Barr virus and the bovine leukaemia virus. Curr Biol. 1993 Jun 1;3(6):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90196-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the vav proto-oncogene product in activated B cells. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1196–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Campbell K. S. Membrane immunoglobulin and its accomplices: new lessons from an old receptor. FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3207–3217. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Morrison D. C., Chien M. M., Lehmann K. R. Modeling of T cell contact-dependent B cell activation. IL-4 and antigen receptor ligation primes quiescent B cells to mobilize calcium in response to Ia cross-linking. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2075–2082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C. Signal transduction by T- and B-cell antigen receptors: converging structures and concepts. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(3):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90074-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. S., Hager E. J., Friedrich R. J., Cambier J. C. IgM antigen receptor complex contains phosphoprotein products of B29 and mb-1 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Association between B-lymphocyte membrane immunoglobulin and multiple members of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2315–2321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Park D. J., Rhee S. G., Fearon D. T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C induced by membrane immunoglobulin in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2745–2749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casillas A., Hanekom C., Williams K., Katz R., Nel A. E. Stimulation of B-cells via the membrane immunoglobulin receptor or with phorbol myristate 13-acetate induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of a 42-kDa microtubule-associated protein-2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19088–19094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Iwashima M., Turck C. W., Weiss A. ZAP-70: a 70 kd protein-tyrosine kinase that associates with the TCR zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90598-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
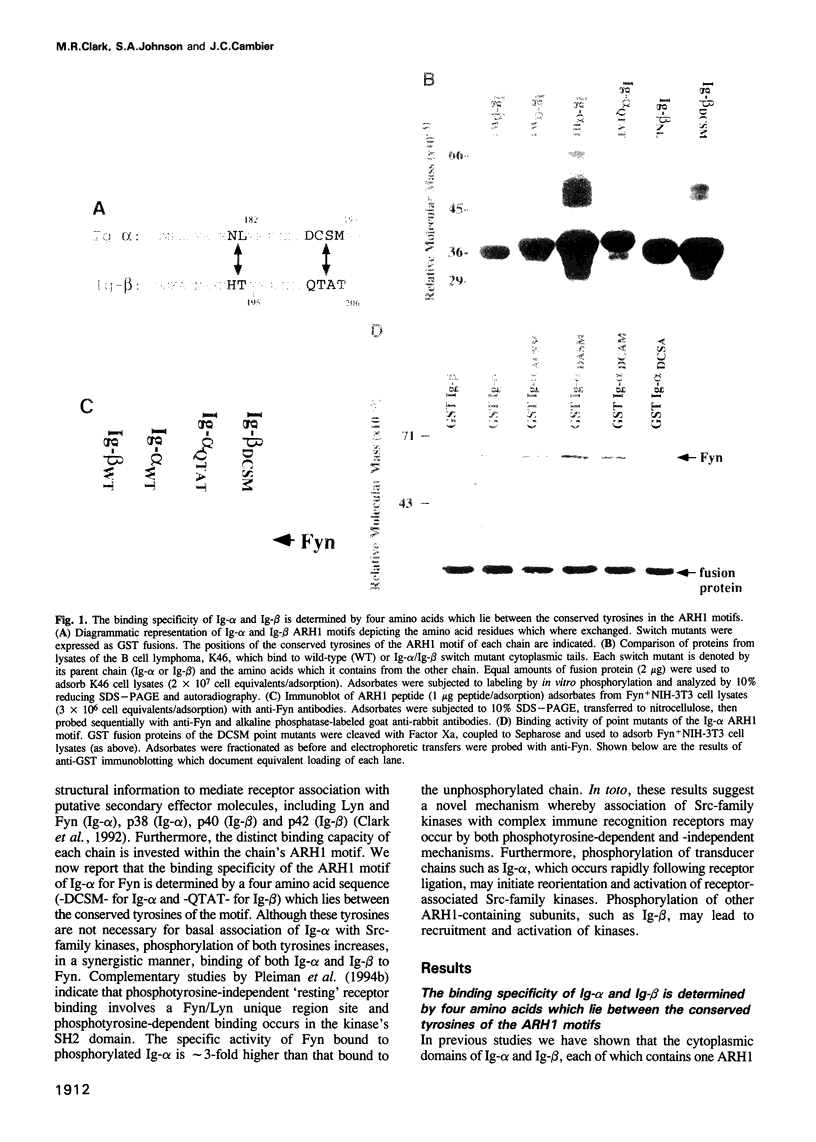
- Clark M. R., Campbell K. S., Kazlauskas A., Johnson S. A., Hertz M., Potter T. A., Pleiman C., Cambier J. C. The B cell antigen receptor complex: association of Ig-alpha and Ig-beta with distinct cytoplasmic effectors. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):123–126. doi: 10.1126/science.1439759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall K. M., McHugh J. C., Altman A. Predominant expression and activation-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 2 in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5660–5664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Howell B. The when and how of Src regulation. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1051–1054. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90634-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettehadieh E., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Hess-Bienz D., Watts J., Shastri N., Aebersold R. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinases by p56lck. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.1311128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Crowley M. T., Martin G. A., McCormick F., DeFranco A. L. Targets of B lymphocyte antigen receptor signal transduction include the p21ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and two GAP-associated proteins. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):377–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Involvement of a guanine-nucleotide-binding component in membrane IgM-stimulated phosphoinositide breakdown. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3604–3613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Matsuuchi L., Kelly R. B., DeFranco A. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of components of the B-cell antigen receptors following receptor crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3436–3440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood A. E., Cambier J. C. B cell antigen receptor cross-linking triggers rapid protein kinase C independent activation of p21ras1. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4513–4522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hombach J., Lottspeich F., Reth M. Identification of the genes encoding the IgM-alpha and Ig-beta components of the IgM antigen receptor complex by amino-terminal sequencing. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2795–2799. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving B. A., Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Kawakami Y., Aaronson S. A., Robbins K. C. Acquisition of transforming properties by FYN, a normal SRC-related human gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
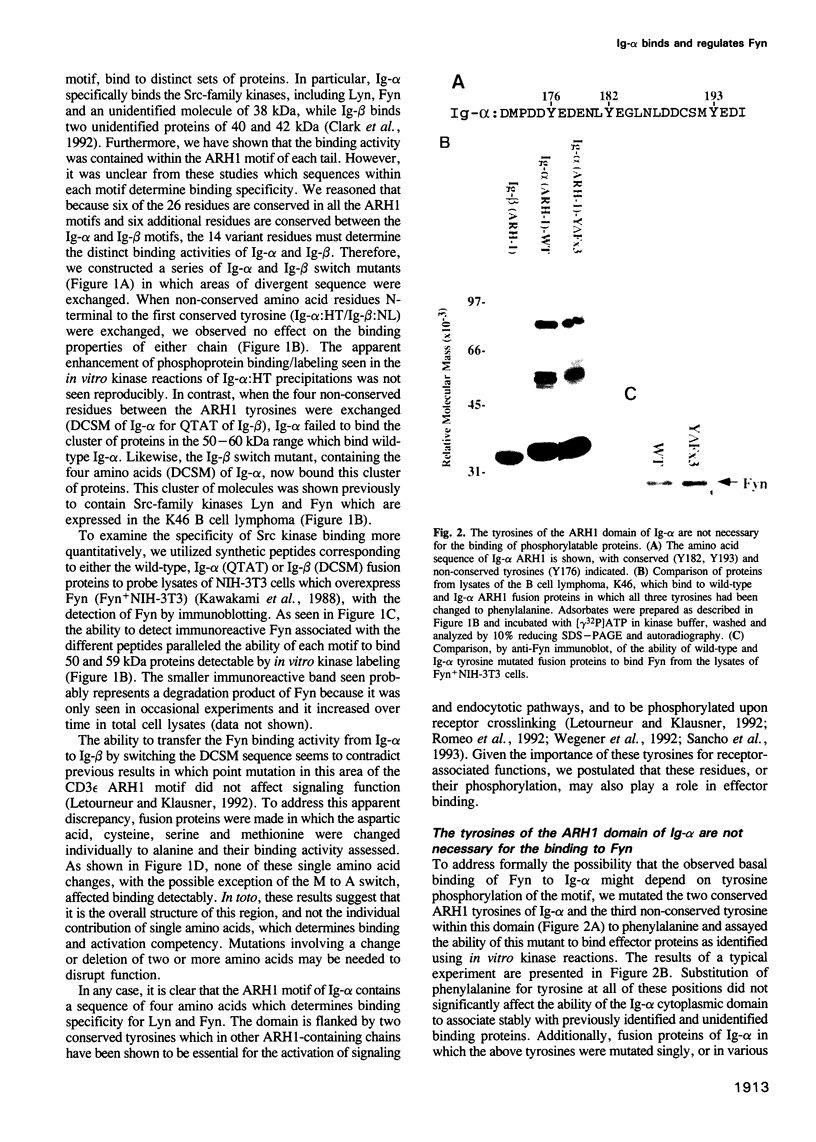
- Keegan A. D., Paul W. E. Multichain immune recognition receptors: similarities in structure and signaling pathways. Immunol Today. 1992 Feb;13(2):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90136-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G. Rhodopsin, photoreceptor of the rod cell. An emerging pattern for structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. M., Alber G., Weiser P., Reth M. Differential signaling through the Ig-alpha and Ig-beta components of the B cell antigen receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):911–916. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G. Role of G-proteins in receptor signalling in T and B cells. Semin Immunol. 1990 Mar;2(2):151–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolanus W., Romeo C., Seed B. Lineage-independent activation of immune system effector function by myeloid Fc receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4861–4868. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. A., Chan V. W., Datta S. K., DeFranco A. L. B-cell antigen receptor motifs have redundant signalling capabilities and bind the tyrosine kinases PTK72, Lyn and Fyn. Curr Biol. 1993 Oct 1;3(10):645–657. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90062-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince C., Draves K. E., Ledbetter J. A., Torres R. M., Clark E. A. Characterization of molecular components associated with surface immunoglobulin M in human B lymphocytes: presence of tyrosine and serine/threonine protein kinases. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Aug;22(8):2093–2099. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. T-cell and basophil activation through the cytoplasmic tail of T-cell-receptor zeta family proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8905–8909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lhoták V., Greer P., Letwin K., Pawson T. Characterization of elk, a brain-specific receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2496–2502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Justement L. B. The MB-1/B29 heterodimer couples the B cell antigen receptor to multiple src family protein tyrosine kinases. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1548–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Brodeur S. R., Gish G., Songyang Z., Cantley L. C., Laudano A. P., Pawson T. Regulation of c-Src tyrosine kinase activity by the Src SH2 domain. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1119–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura J., Matsuo T., Kubota E., Kimoto M., Sakaguchi N. Signal transmission through the B cell-specific MB-1 molecule at the pre-B cell stage. Int Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(2):117–126. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. C., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of the proto-oncogene p60c-src by point mutations in the SH2 domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2855–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier J. P., Raabe T., Henkemeyer M., Dickson B., Mbamalu G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Hafen E., Pawson T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90170-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padeh S., Levitzki A., Gazit A., Mills G. B., Roifman C. M. Activation of phospholipase C in human B cells is dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1114–1118. doi: 10.1172/JCI115074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
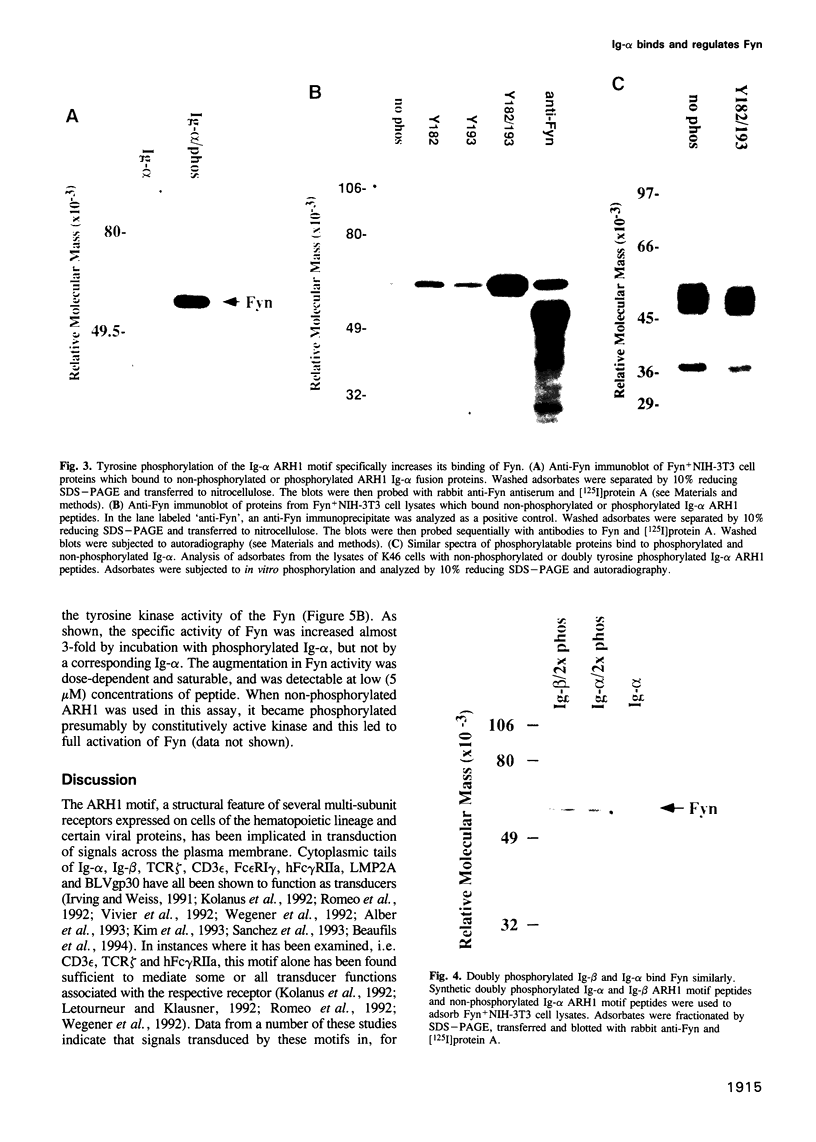
- Pleiman C. M., Clark M. R., Gauen L. K., Winitz S., Coggeshall K. M., Johnson G. L., Shaw A. S., Cambier J. C. Mapping of sites on the Src family protein tyrosine kinases p55blk, p59fyn, and p56lyn which interact with the effector molecules phospholipase C-gamma 2, microtubule-associated protein kinase, GTPase-activating protein, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5877–5887. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):383–384. doi: 10.1038/338383b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Hombach J., Wienands J., Campbell K. S., Chien N., Justement L. B., Cambier J. C. The B-cell antigen receptor complex. Immunol Today. 1991 Jun;12(6):196–201. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90053-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo C., Amiot M., Seed B. Sequence requirements for induction of cytolysis by the T cell antigen/Fc receptor zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):889–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottapel R., Reedijk M., Williams D. E., Lyman S. D., Anderson D. M., Pawson T., Bernstein A. The Steel/W transduction pathway: kit autophosphorylation and its association with a unique subset of cytoplasmic signaling proteins is induced by the Steel factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3043–3051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez M., Misulovin Z., Burkhardt A. L., Mahajan S., Costa T., Franke R., Bolen J. B., Nussenzweig M. Signal transduction by immunoglobulin is mediated through Ig alpha and Ig beta. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1049–1055. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Franco R., Chatila T., Hall C., Terhorst C. The T cell receptor associated CD3-epsilon protein is phosphorylated upon T cell activation in the two tyrosine residues of a conserved signal transduction motif. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1636–1642. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieh M., Bolen J. B., Weiss A. CD45 specifically modulates binding of Lck to a phosphopeptide encompassing the negative regulatory tyrosine of Lck. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):315–321. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Weiss A. The CD3 chains of the T cell antigen receptor associate with the ZAP-70 tyrosine kinase and are tyrosine phosphorylated after receptor stimulation. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1523–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timson Gauen L. K., Kong A. N., Samelson L. E., Shaw A. S. p59fyn tyrosine kinase associates with multiple T-cell receptor subunits through its unique amino-terminal domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5438–5446. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkitaraman A. R., Williams G. T., Dariavach P., Neuberger M. S. The B-cell antigen receptor of the five immunoglobulin classes. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):777–781. doi: 10.1038/352777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., Rochet N., Ackerly M., Petrini J., Levine H., Daley J., Anderson P. Signaling function of reconstituted CD16: zeta: gamma receptor complex isoforms. Int Immunol. 1992 Nov;4(11):1313–1323. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.11.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wange R. L., Malek S. N., Desiderio S., Samelson L. E. Tandem SH2 domains of ZAP-70 bind to T cell antigen receptor zeta and CD3 epsilon from activated Jurkat T cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19797–19801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener A. M., Letourneur F., Hoeveler A., Brocker T., Luton F., Malissen B. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex is composed of at least two autonomous transduction modules. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90208-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90221-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Taniguchi T., Yang C., Yasue S., Saito H., Yamamura H. Association with B-cell-antigen receptor with protein-tyrosine kinase p72syk and activation by engagement of membrane IgM. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):455–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Fukui Y., Wongsasant B., Kinoshita Y., Ichimori Y., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Activation of Src-like protein-tyrosine kinase Lyn and its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase upon B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1118–1122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]