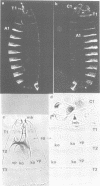
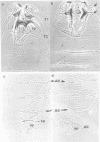
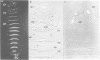
Abstract
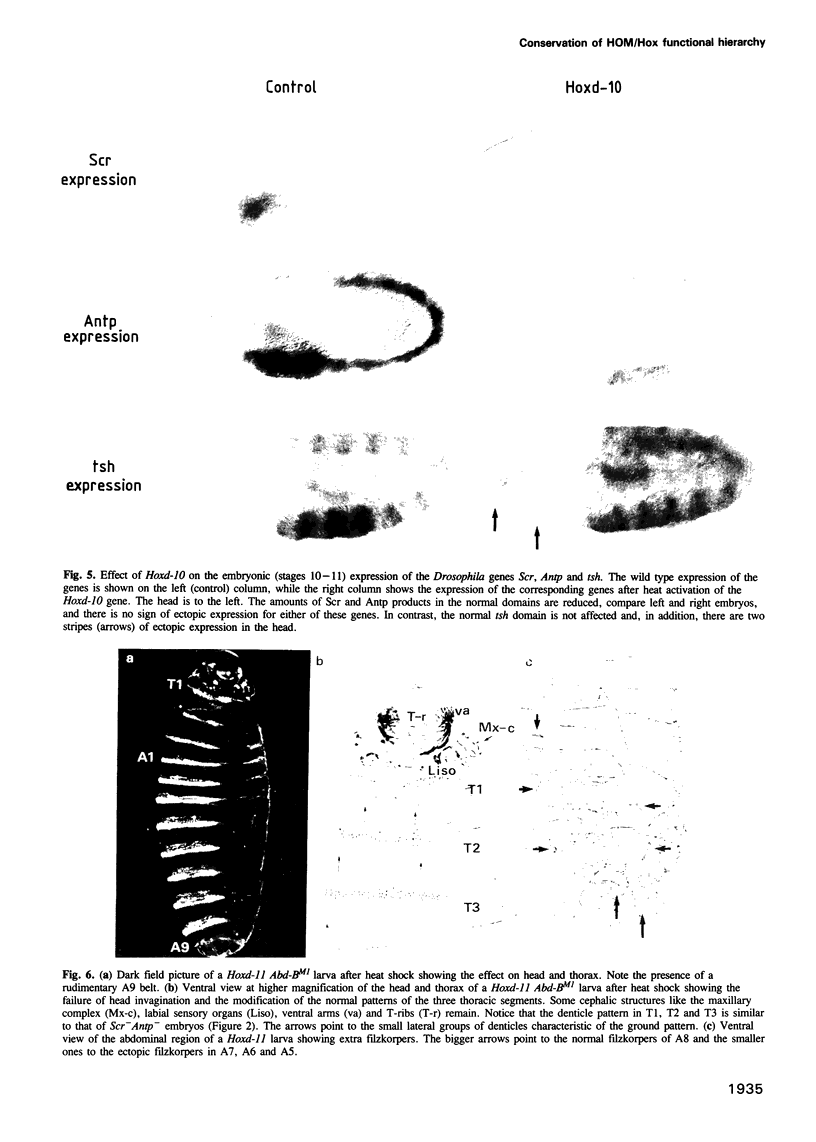
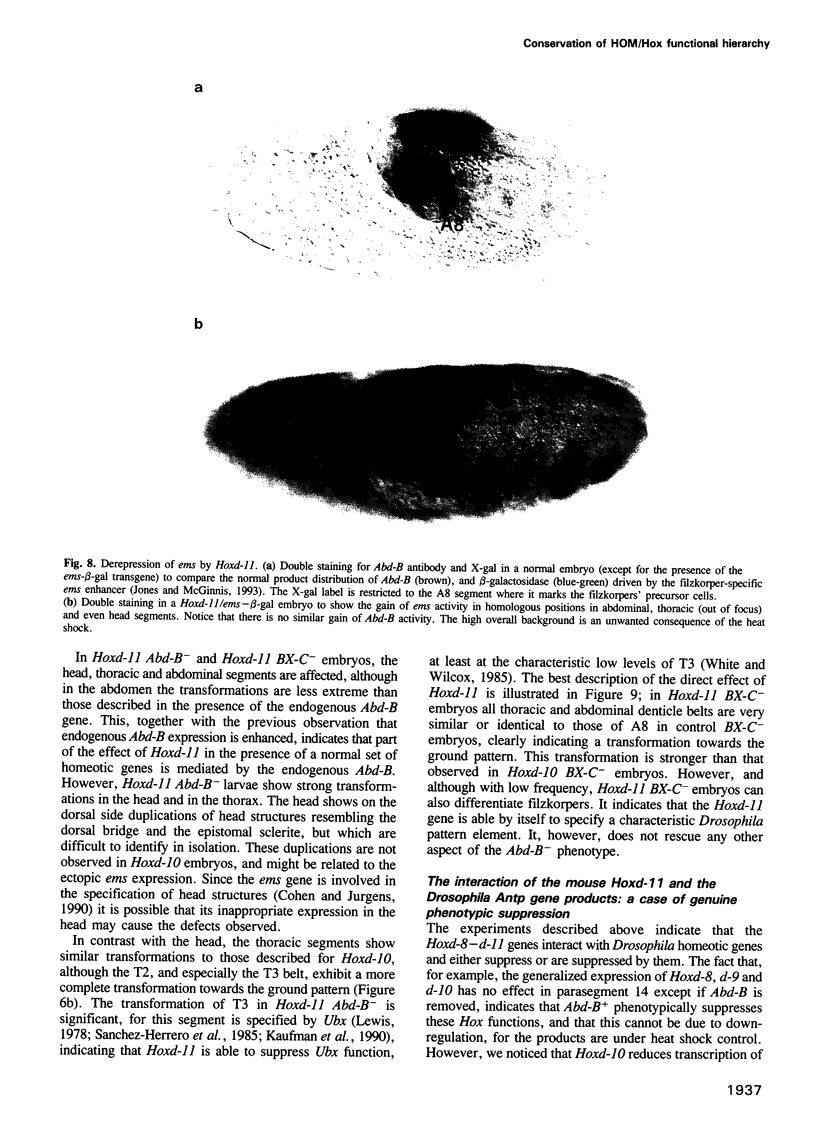
We have generated several transgenic Drosophila strains containing different mouse Hox genes under heat shock control and studied how their generalized expression affects Drosophila larval patterns. We find that they have spatially restricted effects which correlate with their genetic order and expression pattern in the mouse; as they are expressed more posteriorly in the mouse, they have more extensive effects in Drosophila. The generalized expressions of Hoxd-8 and d-9 modify Drosophila anterior head segment(s), but have no effect in the rest of the body. Hoxd-10 expression affects head and thorax, but not the abdomen. Finally, Hoxd-11 alters head, thorax not the abdomen. Finally, Hoxd-11 alters head, thorax and abdomen. The developmental effect of the Hox genes consists of a homeotic transformation of the affected segment(s), which exhibit a 'ground' pattern similar to that obtained in the absence of homeotic information, suggesting that Hox genes are able to inactivate Drosophila homeotic genes, but do not specify a pattern of their own. A partial exception is Hoxd-11 which, even though it has a general suppressing effect, can also activate the resident Abdominal-B and empty spiracles genes in ectopic positions. Our results strongly suggest a general conservation of the functional hierarchy of homeotic genes that correlates with genetic order and expression patterns.
Full text
PDF

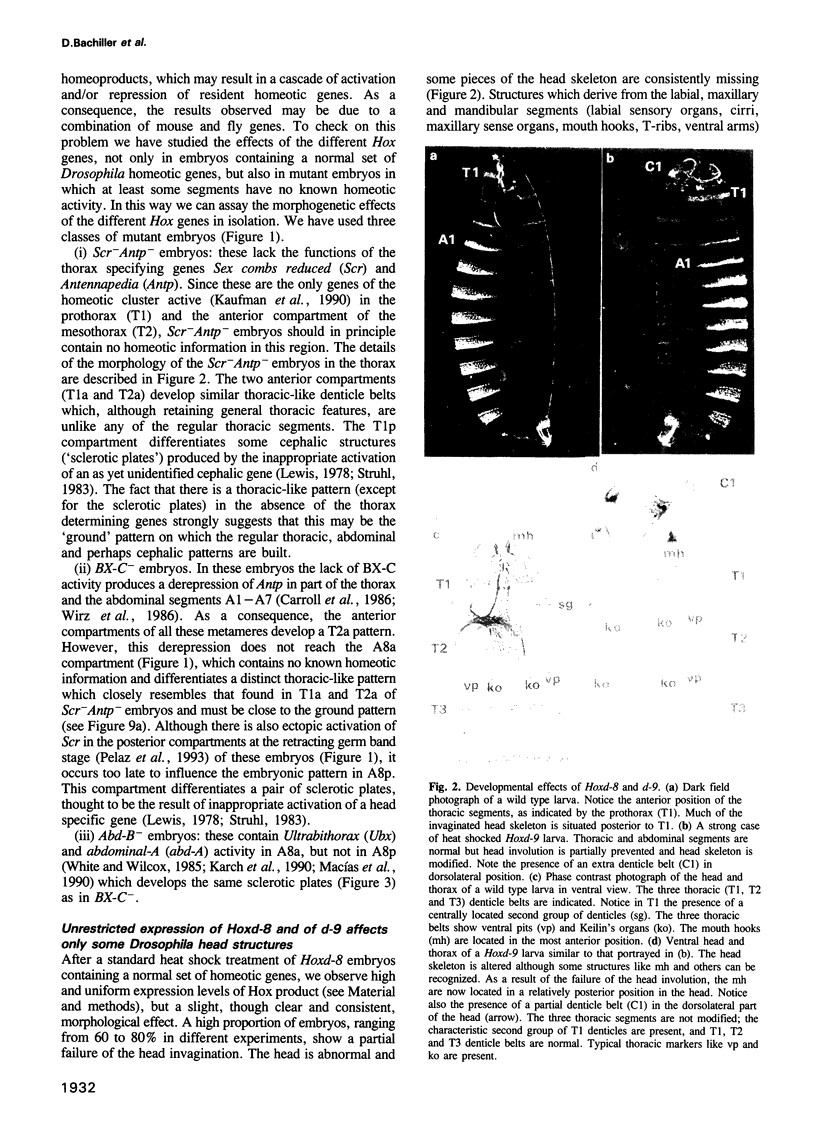

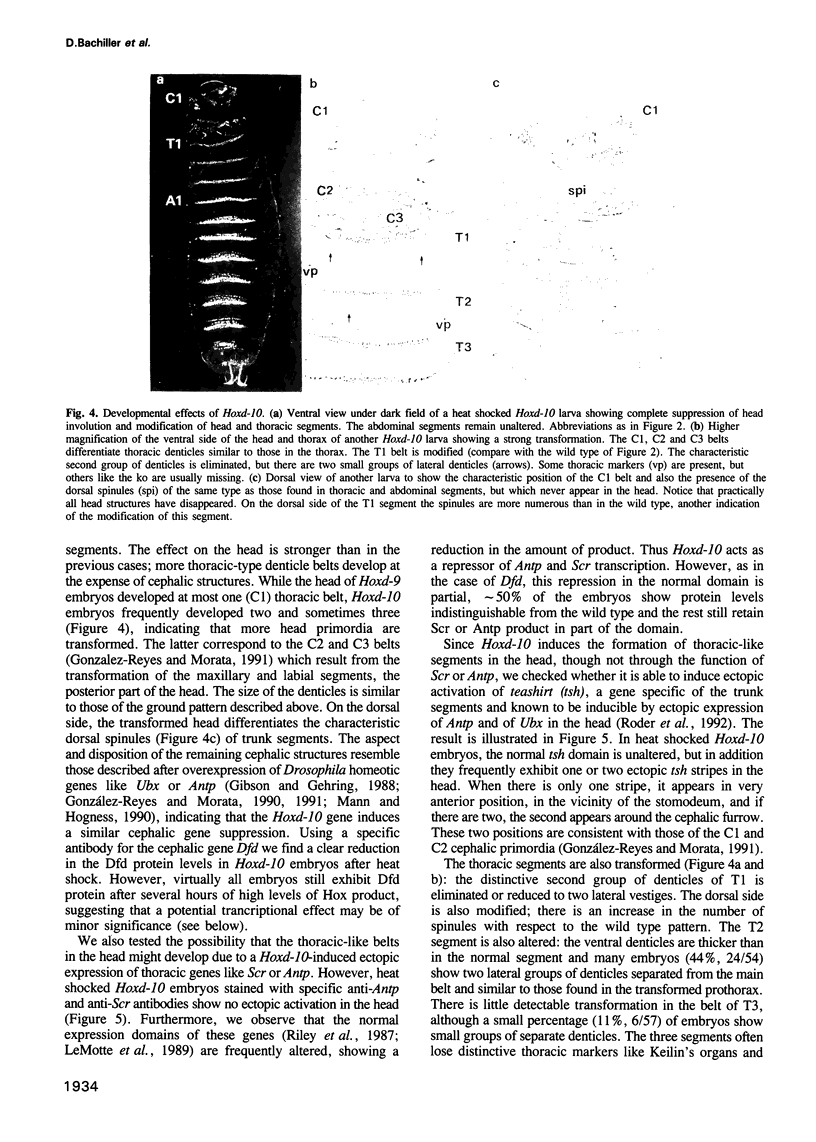





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. Hox and HOM: homologous gene clusters in insects and vertebrates. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90909-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awgulewitsch A., Jacobs D. Deformed autoregulatory element from Drosophila functions in a conserved manner in transgenic mice. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):341–344. doi: 10.1038/358341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Laymon R. A., McCutcheon M. A., Riley P. D., Scott M. P. The localization and regulation of Antennapedia protein expression in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J., Sánchez-Herrero E., Busturia A., Morata G. Double and triple mutant combinations of bithorax complex of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3103–3109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J., Sánchez-Herrero E., Morata G. Identification and characterization of a parasegment specific regulatory element of the abdominal-B gene of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90627-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celniker S. E., Keelan D. J., Lewis E. B. The molecular genetics of the bithorax complex of Drosophila: characterization of the products of the Abdominal-B domain. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1424–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisaka O., Capecchi M. R. Regionally restricted developmental defects resulting from targeted disruption of the mouse homeobox gene hox-1.5. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):473–479. doi: 10.1038/350473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Jürgens G. Mediation of Drosophila head development by gap-like segmentation genes. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):482–485. doi: 10.1038/346482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton D., Chadwick R., McGinnis W. Expression and embryonic function of empty spiracles: a Drosophila homeo box gene with two patterning functions on the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1940–1956. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorenzi M., Bienz M. Expression of Abdominal-B homeoproteins in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1990 Feb;108(2):323–329. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Dollé P. The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1497–1505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D. Patterning in the vertebrate limb. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Aug;1(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D. The vertebrate limb: a model system to study the Hox/HOM gene network during development and evolution. Bioessays. 1992 Jun;14(6):375–384. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano L., Röder L., Coré N., Alexandre E., Vola C., Jacq B., Kerridge S. The gene teashirt is required for the development of Drosophila embryonic trunk segments and encodes a protein with widely spaced zinc finger motifs. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):63–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90209-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Reyes A., Macías A., Morata G. Autocatalysis and phenotypic expression of Drosophila homeotic gene Deformed: its dependence on polarity and homeotic gene function. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):1059–1068. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Reyes A., Morata G. Organization of the Drosophila head as revealed by the ectopic expression of the Ultrabithorax product. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Reyes A., Morata G. The developmental effect of overexpressing a Ubx product in Drosophila embryos is dependent on its interactions with other homeotic products. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90533-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Reyes A., Urquia N., Gehring W. J., Struhl G., Morata G. Are cross-regulatory interactions between homoeotic genes functionally significant? Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):78–80. doi: 10.1038/344078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Gehring W. J. Regulation of Antennapedia transcript distribution by the bithorax complex in Drosophila. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):287–289. doi: 10.1038/307287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Falkenstein H., Dollé P., Renucci A., Duboule D. Murine genes related to the Drosophila AbdB homeotic genes are sequentially expressed during development of the posterior part of the body. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2279–2289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07764.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., McGinnis W. The regulation of empty spiracles by Abdominal-B mediates an abdominal segment identity function. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):229–240. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch F., Bender W., Weiffenbach B. abdA expression in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1573–1587. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman T. C., Seeger M. A., Olsen G. Molecular and genetic organization of the antennapedia gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Adv Genet. 1990;27:309–362. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Saffman E. E., Kornfeld K., Hogness D. S. Transcriptional activation and repression by Ultrabithorax proteins in cultured Drosophila cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1031–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamka M. L., Boulet A. M., Sakonju S. Ectopic expression of UBX and ABD-B proteins during Drosophila embryogenesis: competition, not a functional hierarchy, explains phenotypic suppression. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):841–854. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMotte P. K., Kuroiwa A., Fessler L. I., Gehring W. J. The homeotic gene Sex Combs Reduced of Drosophila: gene structure and embryonic expression. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):219–227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. B. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):565–570. doi: 10.1038/276565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin T., Dierich A., LeMeur M., Mark M., Chambon P. Disruption of the Hox-1.6 homeobox gene results in defects in a region corresponding to its rostral domain of expression. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1105–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90034-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias A., Casanova J., Morata G. Expression and regulation of the abd-A gene of Drosophila. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1197–1207. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malicki J., Cianetti L. C., Peschle C., McGinnis W. A human HOX4B regulatory element provides head-specific expression in Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):345–347. doi: 10.1038/358345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R. S., Hogness D. S. Functional dissection of Ultrabithorax proteins in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):597–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90663-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis N., Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Human Hox-4.2 and Drosophila deformed encode similar regulatory specificities in Drosophila embryos and larvae. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90500-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins M. C., Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. cis-acting DNA sequence requirements for P-element transposition. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):729–738. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelaz S., Urquía N., Morata G. Normal and ectopic domains of the homeotic gene Sex combs reduced of Drosophila. Development. 1993 Mar;117(3):917–923. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.3.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley P. D., Carroll S. B., Scott M. P. The expression and regulation of Sex combs reduced protein in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):716–730. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röder L., Vola C., Kerridge S. The role of the teashirt gene in trunk segmental identity in Drosophila. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):1017–1033. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P. Vertebrate homeobox gene nomenclature. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G. Role of the esc+ gene product in ensuring the selective expression of segment-specific homeotic genes in Drosophila. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983 Aug;76:297–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., White R. A. Regulation of the Ultrabithorax gene of Drosophila by other bithorax complex genes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Herrero E., Vernós I., Marco R., Morata G. Genetic organization of Drosophila bithorax complex. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):108–113. doi: 10.1038/313108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Wilcox M. Distribution of Ultrabithorax proteins in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2035–2043. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirz J., Fessler L. I., Gehring W. J. Localization of the Antennapedia protein in Drosophila embryos and imaginal discs. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3327–3334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zappavigna V., Renucci A., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Urier G., Peschle C., Duboule D. HOX4 genes encode transcription factors with potential auto- and cross-regulatory capacities. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4177–4187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J. J., Lazzarini R. A., Pick L. The mouse Hox-1.3 gene is functionally equivalent to the Drosophila Sex combs reduced gene. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):343–354. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]