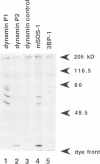
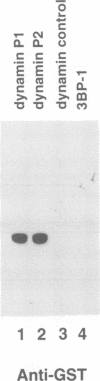
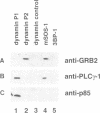
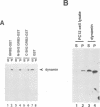
Abstract
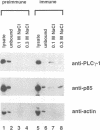
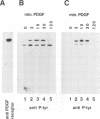
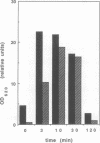
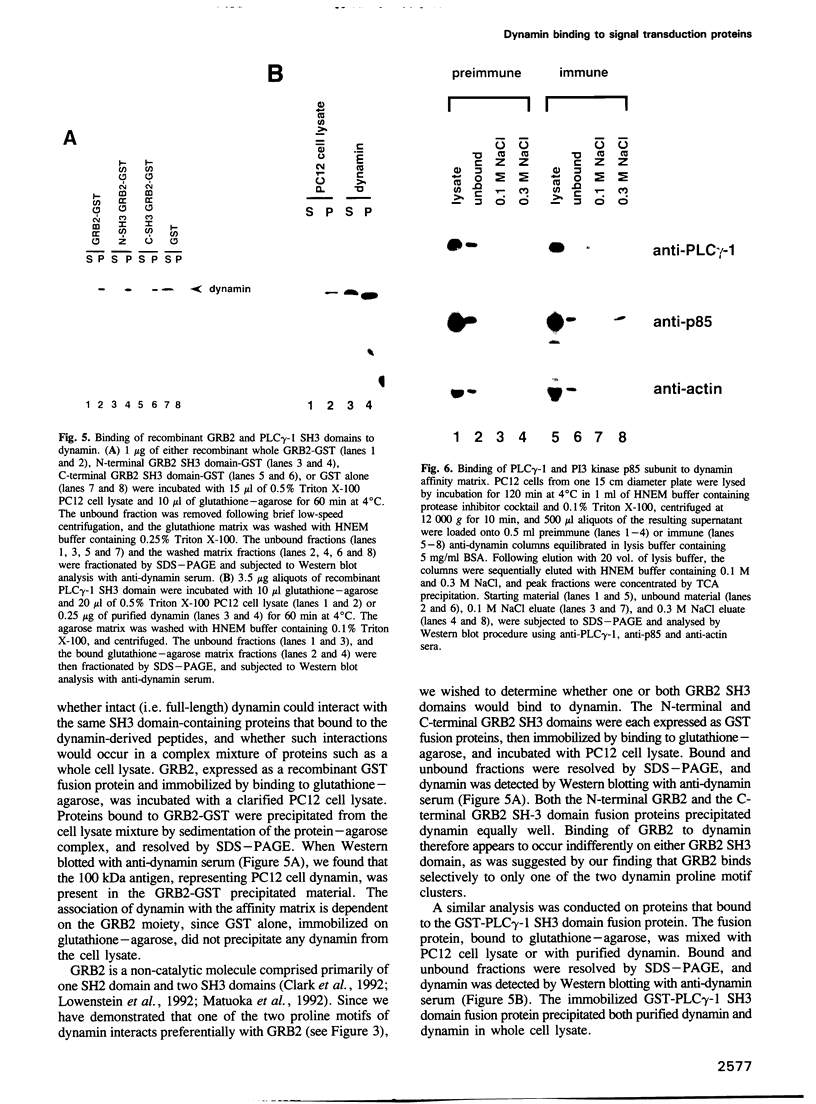
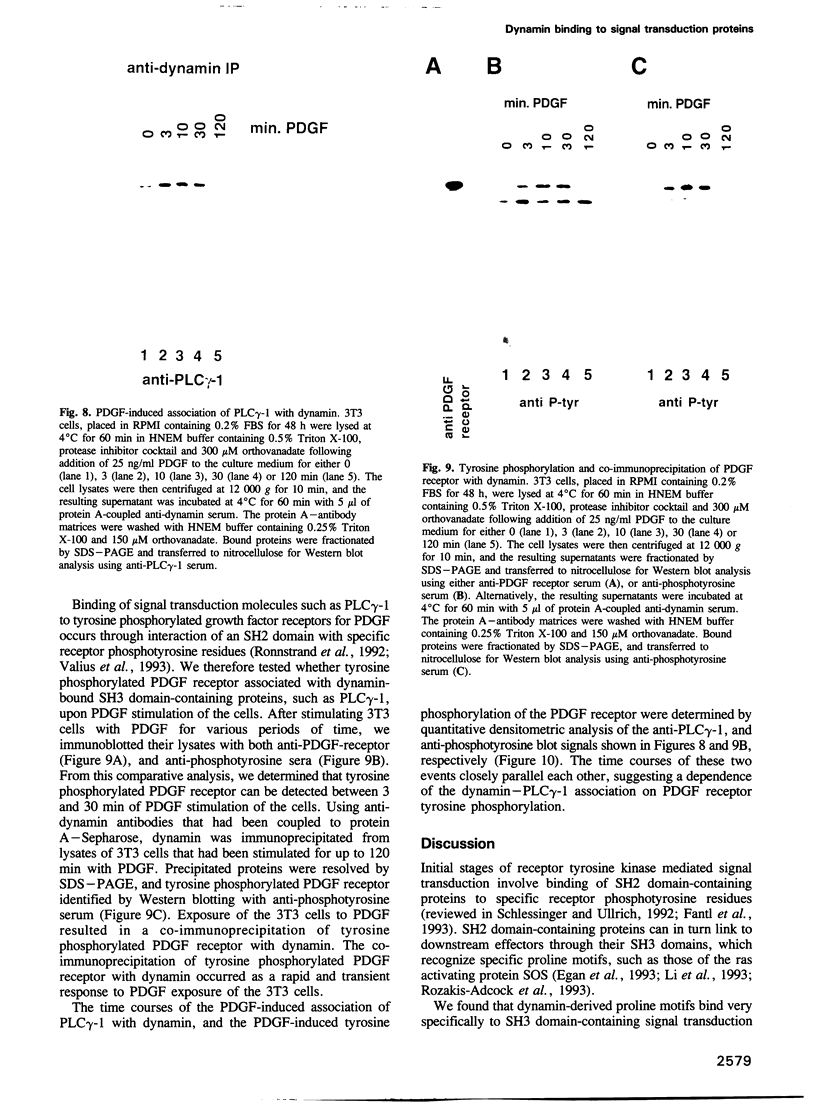
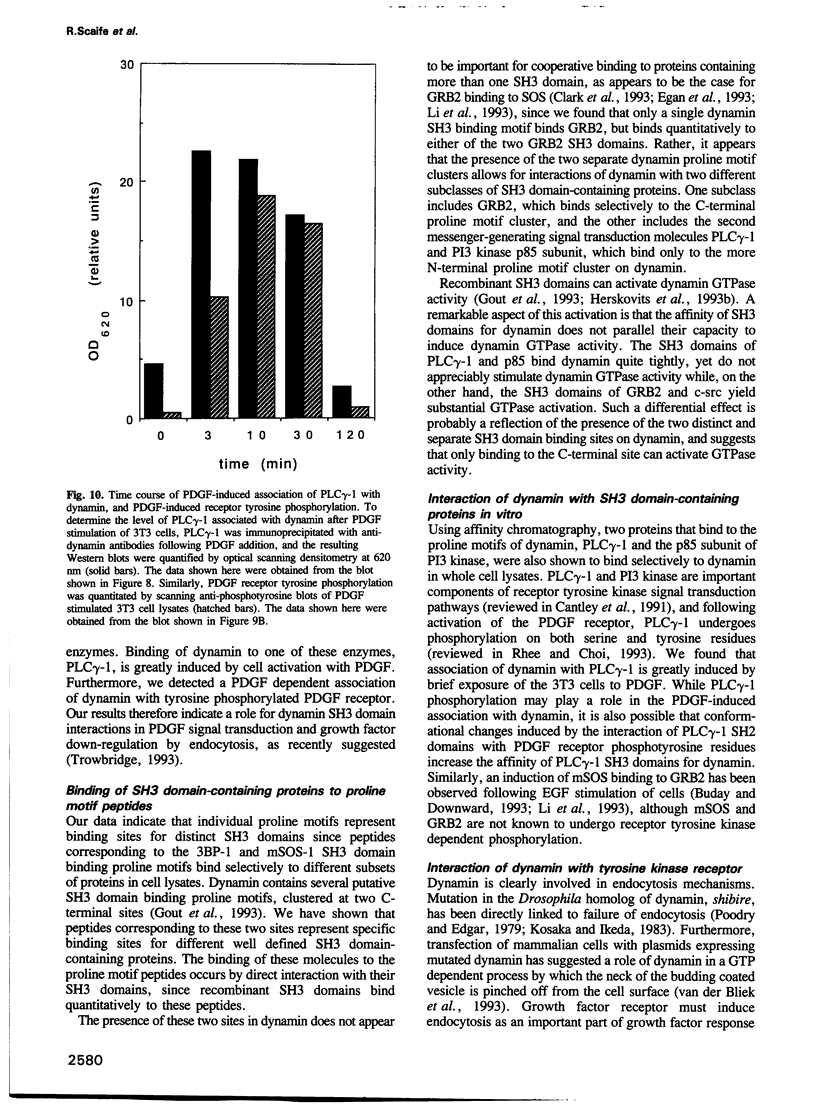
Dynamin, a 100 kDa GTPase, is critical for endocytosis, synaptic transmission and neurogenesis. Endocytosis accompanies receptor processing and plays an essential role in attenuating receptor tyrosine kinase signal transduction. Dynamin has been demonstrated to be involved in the endocytic processing at the cell surface and may play a general role in coupling receptor activation to endocytosis. Src homology (SH) domain dependent protein-protein interactions are important to tyrosine kinase receptor signal transduction. The C-terminus of dynamin contains two clusters of SH3 domain binding proline motifs; these motifs may interact with known SH3 domain proteins during tyrosine kinase receptor activation. We demonstrate here that SH3 domain-containing signal transduction proteins, such as phospholipase C gamma-1 (PLC gamma-1), do indeed bind to dynamin in a growth factor inducible manner. The induction of PLC gamma-1 binding to dynamin occurs within minutes of the addition of platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) to cells. Binding of these signal transduction proteins to dynamin involves specific sorting to individual proline motif clusters and appears to be responsible for co-immunoprecipitation of tyrosine phosphorylated PDGF receptors with dynamin following PDGF stimulation of mammalian cells. The binding of dynamin to SH3 domain-containing proteins may therefore be important for formation of the protein complex required for the endocytic processing of activated tyrosine kinase receptors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti P., Mayer B. J., Thiel G., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein that binds to the SH3 region of Abl and is similar to Bcr and GAP-rho. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.1379745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. G., Stern M. J., Horvitz H. R. C. elegans cell-signalling gene sem-5 encodes a protein with SH2 and SH3 domains. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):340–344. doi: 10.1038/356340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook T. A., Urrutia R., McNiven M. A. Identification of dynamin 2, an isoform ubiquitously expressed in rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):644–648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T. Signalling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:453–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gout I., Dhand R., Hiles I. D., Fry M. J., Panayotou G., Das P., Truong O., Totty N. F., Hsuan J., Booker G. W. The GTPase dynamin binds to and is activated by a subset of SH3 domains. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskovits J. S., Burgess C. C., Obar R. A., Vallee R. B. Effects of mutant rat dynamin on endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):565–578. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskovits J. S., Shpetner H. S., Burgess C. C., Vallee R. B. Microtubules and Src homology 3 domains stimulate the dynamin GTPase via its C-terminal domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11468–11472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Ozawa S., Hagiwara S. Synaptic transmission reversibly conditioned by single-gene mutation in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1976 Feb 12;259(5543):489–491. doi: 10.1038/259489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly M., Kazlauskas A., Fay F. S., Corvera S. Disruption of PDGF receptor trafficking by mutation of its PI-3 kinase binding sites. Science. 1994 Feb 4;263(5147):684–687. doi: 10.1126/science.8303278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. T., Wu C. F. Reversible blockage of neurite development and growth cone formation in neuronal cultures of a temperature-sensitive mutant of Drosophila. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3245–3255. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03245.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Ikeda K. Reversible blockage of membrane retrieval and endocytosis in the garland cell of the temperature-sensitive mutant of Drosophila melanogaster, shibirets1. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):499–507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Nakata T., Noda Y., Sato-Yoshitake R., Hirokawa N. Interaction of dynamin with microtubules: its structure and GTPase activity investigated by using highly purified dynamin. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1181–1194. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Nakata T., Noda Y., Sato-Yoshitake R., Hirokawa N. Interaction of dynamin with microtubules: its structure and GTPase activity investigated by using highly purified dynamin. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1181–1194. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuoka K., Shibata M., Yamakawa A., Takenawa T. Cloning of ASH, a ubiquitous protein composed of one Src homology region (SH) 2 and two SH3 domains, from human and rat cDNA libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9015–9019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T., Takemura R., Hirokawa N. A novel member of the dynamin family of GTP-binding proteins is expressed specifically in the testis. J Cell Sci. 1993 May;105(Pt 1):1–5. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obar R. A., Collins C. A., Hammarback J. A., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. Molecular cloning of the microtubule-associated mechanochemical enzyme dynamin reveals homology with a new family of GTP-binding proteins. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):256–261. doi: 10.1038/347256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier J. P., Raabe T., Henkemeyer M., Dickson B., Mbamalu G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Hafen E., Pawson T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90170-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poodry C. A., Edgar L. Reversible alteration in the neuromuscular junctions of Drosophila melanogaster bearing a temperature-sensitive mutation, shibire. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):520–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., Fernley R., Wade J., Pawson T., Bowtell D. The SH2 and SH3 domains of mammalian Grb2 couple the EGF receptor to the Ras activator mSos1. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):83–85. doi: 10.1038/363083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnstrand L., Mori S., Arridsson A. K., Eriksson A., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Identification of two C-terminal autophosphorylation sites in the PDGF beta-receptor: involvement in the interaction with phospholipase C-gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3911–3919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaife R., Margolis R. L. Biochemical and immunochemical analysis of rat brain dynamin interaction with microtubules and organelles in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3023–3033. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. Dynamin is a GTPase stimulated to high levels of activity by microtubules. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):733–735. doi: 10.1038/355733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi O., Benzer S. Neurophysiological defects in temperature-sensitive paralytic mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3253–3257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Dodson G. S., Rubin G. M. An SH3-SH2-SH3 protein is required for p21Ras1 activation and binds to sevenless and Sos proteins in vitro. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90169-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S. Dynamin, SH3 domains and endocytosis. Curr Biol. 1993 Nov 1;3(11):773–775. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90028-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Bazenet C., Kazlauskas A. Tyrosines 1021 and 1009 are phosphorylation sites in the carboxy terminus of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit and are required for binding of phospholipase C gamma and a 64-kilodalton protein, respectively. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):133–143. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Welsh J. B., Lazar C. S., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Ligand-induced transformation by a noninternalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):962–964. doi: 10.1126/science.2305263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bliek A. M., Redelmeier T. E., Damke H., Tisdale E. J., Meyerowitz E. M., Schmid S. L. Mutations in human dynamin block an intermediate stage in coated vesicle formation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):553–563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]