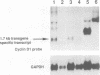
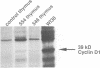
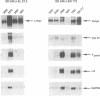
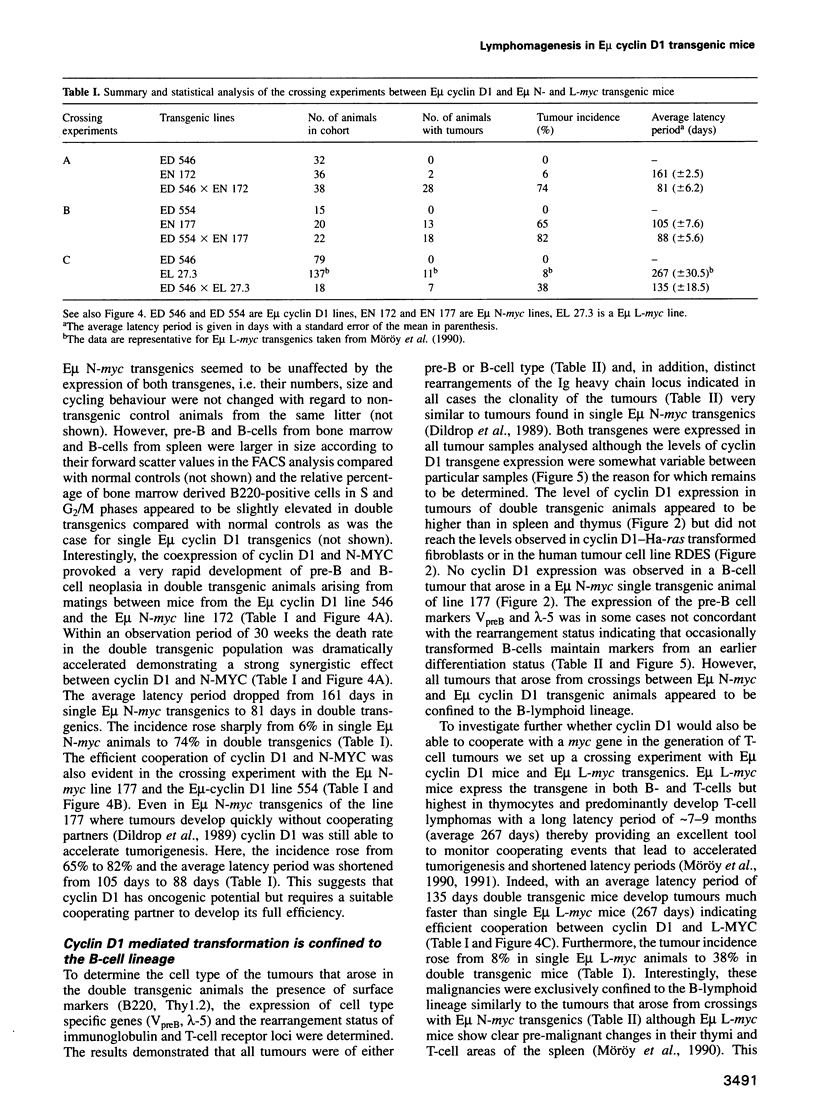
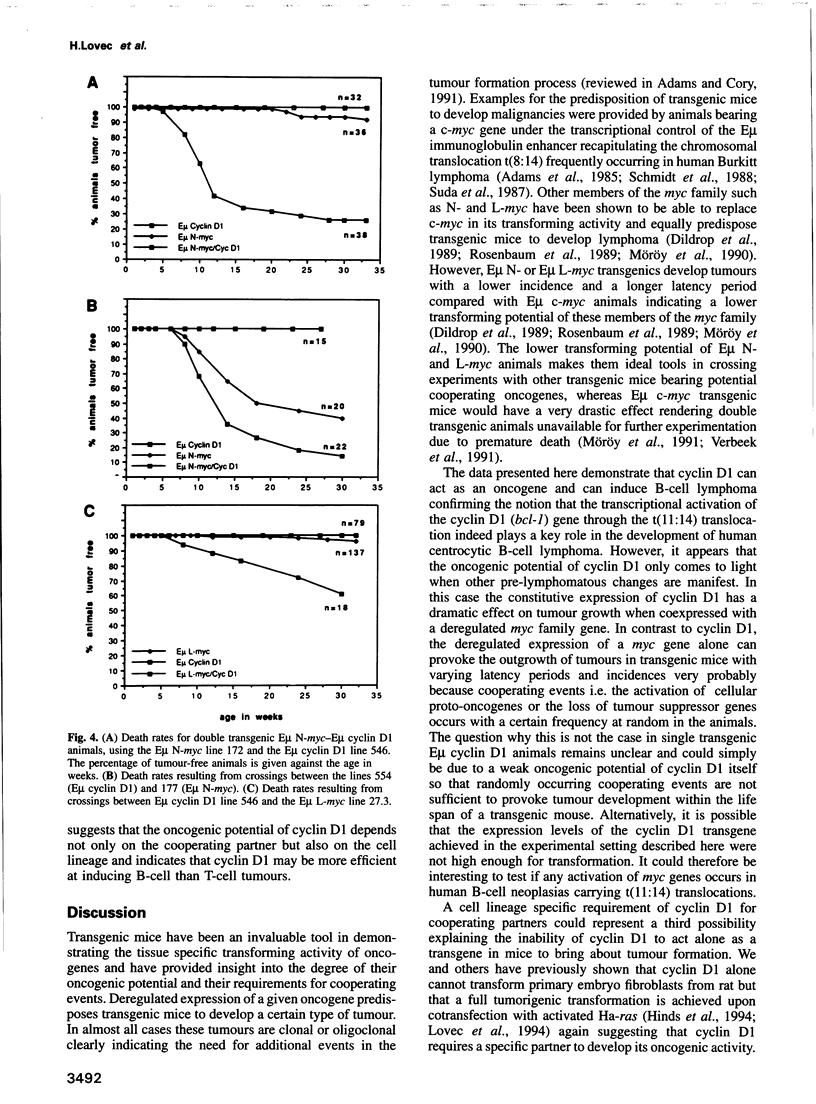
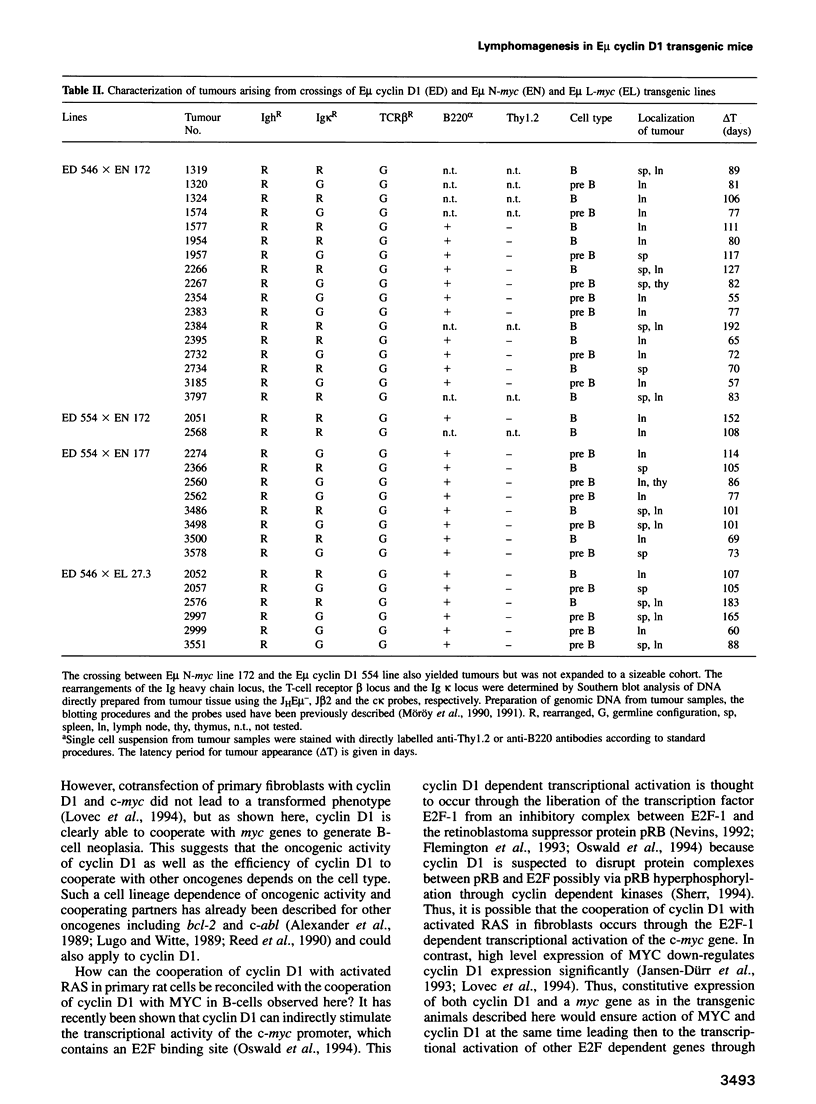
Abstract
The chromosomal translocation t(11:14) is associated with human lymphoid neoplasia affecting centrocytic B-cells of intermediate differentiation. As a consequence the cyclin D1 (bcl-1) gene is juxtaposed to the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer E mu. To show that transcriptional activation of cyclin D1 is causally involved in the generation of B-cell neoplasia we have generated transgenic mice that carry a cyclin D1 gene under the transcriptional control of the E mu element. E mu cyclin D1 transgenic mice show only very subtle alterations in the cycling behaviour of B-cell populations in the bone marrow compared with normal mice and do not develop lymphoid tumours. However, E mu-directed coexpression of cyclin D1 and N-MYC or L-MYC in double transgenic mice reveals a strong cooperative effect between MYC and cyclin D1 provoking the rapid development of clonal pre-B and B-cell lymphomas. Interestingly, crossing of cyclin D1 transgenic mice with E mu L-myc transgenics that express their transgene in both B- and T-cells but predominantly develop T-cell tumours leads in double transgenics exclusively to B-cell neoplasia. The data presented here demonstrate that transcriptional activation of cyclin D1 can oncogenically transform B-cells in concert with a myc gene. They establish cyclin D1 as a proto-oncogene whose activity appears to depend on a specific cell type as well as on a specific cooperating partner and link disturbances in the regulation of cell cycle progression to the development of human malignancies.
Full text
PDF

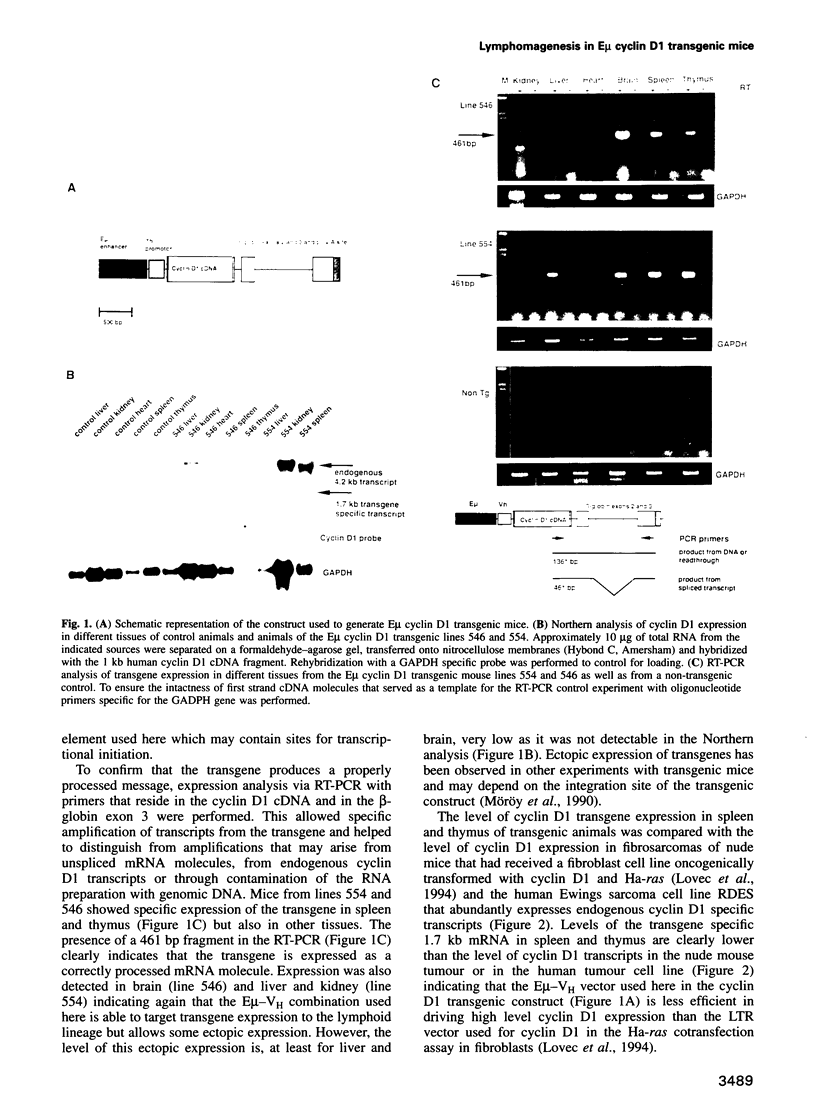



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Cory S. Transgenic models for haemopoietic malignancies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):9–31. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. M., Harris A. W., Pinkert C. A., Corcoran L. M., Alexander W. S., Cory S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):533–538. doi: 10.1038/318533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander W. S., Adams J. M., Cory S. Oncogene cooperation in lymphocyte transformation: malignant conversion of E mu-myc transgenic pre-B cells in vitro is enhanced by v-H-ras or v-raf but not v-abl. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A. B., Fischer S. M., Robles A. I., Rinchik E. M., Conti C. J. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in mouse skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1127–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley M. F., Sweeney K. J., Hamilton J. A., Sini R. L., Manning D. L., Nicholson R. I., deFazio A., Watts C. K., Musgrove E. A., Sutherland R. L. Expression and amplification of cyclin genes in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2127–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildrop R., Ma A., Zimmerman K., Hsu E., Tesfaye A., DePinho R., Alt F. W. IgH enhancer-mediated deregulation of N-myc gene expression in transgenic mice: generation of lymphoid neoplasias that lack c-myc expression. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1121–1128. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdy S. F., Hinds P. W., Louie K., Reed S. I., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Physical interaction of the retinoblastoma protein with human D cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):499–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90137-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Buchkovich K., Whyte P., Harlow E. The cellular 107K protein that binds to adenovirus E1A also associates with the large T antigens of SV40 and JC virus. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90839-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Ludlow J. W., Marsilio E., DeCaprio J. A., Millikan R. C., Cheng S. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. An N-terminal transformation-governing sequence of SV40 large T antigen contributes to the binding of both p110Rb and a second cellular protein, p120. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E. K., Speck S. H., Kaelin W. G., Jr E2F-1-mediated transactivation is inhibited by complex formation with the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6914–6918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Bernard O. Sequences of the joining region genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains and their role in generation of antibody diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):509–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Wu L., Wu F., Carbonaro-Hall D. A., Harper J. W., Warburton D. Two potentially oncogenic cyclins, cyclin A and cyclin D1, share common properties of subunit configuration, tyrosine phosphorylation and physical association with the Rb protein. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1377–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Z., Jankowski M., Tremblay P., Jiang X., Milatovich A., Francke U., Jolicoeur P. The Vin-1 gene, identified by provirus insertional mutagenesis, is the cyclin D2. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Dowdy S. F., Eaton E. N., Arnold A., Weinberg R. A. Function of a human cyclin gene as an oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):709–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Braking the cycle. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):839–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Dürr P., Meichle A., Steiner P., Pagano M., Finke K., Botz J., Wessbecher J., Draetta G., Eilers M. Differential modulation of cyclin gene expression by MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Kahn S. M., Zhou P., Zhang Y. J., Cacace A. M., Infante A. S., Doi S., Santella R. M., Weinstein I. B. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in rat fibroblasts causes abnormalities in growth control, cell cycle progression and gene expression. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3447–3457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyomarsi K., Pardee A. B. Redundant cyclin overexpression and gene amplification in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammie G. A., Fantl V., Smith R., Schuuring E., Brookes S., Michalides R., Dickson C., Arnold A., Peters G. D11S287, a putative oncogene on chromosome 11q13, is amplified and expressed in squamous cell and mammary carcinomas and linked to BCL-1. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Rosenberg N., Alt F., Baltimore D. Continuing kappa-gene rearrangement in a cell line transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovec H., Sewing A., Lucibello F. C., Müller R., Möröy T. Oncogenic activity of cyclin D1 revealed through cooperation with Ha-ras: link between cell cycle control and malignant transformation. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):323–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugo T. G., Witte O. N. The BCR-ABL oncogene transforms Rat-1 cells and cooperates with v-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1263–1270. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma A., Fisher P., Dildrop R., Oltz E., Rathbun G., Achacoso P., Stall A., Alt F. W. Surface IgM mediated regulation of RAG gene expression in E mu-N-myc B cell lines. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2727–2734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros L. J., Van Krieken J. H., Jaffe E. S., Raffeld M. Association of bcl-1 rearrangements with lymphocytic lymphoma of intermediate differentiation. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2086–2090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker T. C., Grimaldi J. C., O'Rourke R., Louie E., Juliusson G., Einhorn S. An additional breakpoint region in the BCL-1 locus associated with the t(11;14)(q13;q32) translocation of B-lymphocytic malignancy. Blood. 1989 Oct;74(5):1801–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Fisher P., Guidos C., Ma A., Zimmerman K., Tesfaye A., DePinho R., Weissman I., Alt F. W. IgH enhancer deregulated expression of L-myc: abnormal T lymphocyte development and T cell lymphomagenesis. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3659–3666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07577.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Verbeek S., Ma A., Achacoso P., Berns A., Alt F. E mu N- and E mu L-myc cooperate with E mu pim-1 to generate lymphoid tumors at high frequency in double-transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1941–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Mumberg D., Lucibello F. C. Signals and genes in the control of cell-cycle progression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Aug 23;1155(2):151–179. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90003-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmero I., Holder A., Sinclair A. J., Dickson C., Peters G. Cyclins D1 and D2 are differentially expressed in human B-lymphoid cell lines. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):1049–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., Coleclough C., Seidman J. G., Leder P., Tonegawa S., Matthyssens G., Weigert M. Transcription of mouse kappa chain genes: implications for allelic exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1937–1941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pircher H., Mak T. W., Lang R., Ballhausen W., Rüedi E., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M., Bürki K. T cell tolerance to Mlsa encoded antigens in T cell receptor V beta 8.1 chain transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):719–727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffeld M., Jaffe E. S. bcl-1, t(11;14), and mantle cell-derived lymphomas. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):259–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Haldar S., Croce C. M., Cuddy M. P. Complementation by BCL2 and C-HA-RAS oncogenes in malignant transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4370–4374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum H., Webb E., Adams J. M., Cory S., Harris A. W. N-myc transgene promotes B lymphoid proliferation, elicits lymphomas and reveals cross-regulation with c-myc. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):749–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C. L., Motokura T., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. Coding sequence of the overexpressed transcript of the putative oncogene PRAD1/cyclin D1 in two primary human tumors. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):519–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. V., Pattengale P. K., Weir L., Leder P. Transgenic mice bearing the human c-myc gene activated by an immunoglobulin enhancer: a pre-B-cell lymphoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6047–6051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuuring E., Verhoeven E., Mooi W. J., Michalides R. J. Identification and cloning of two overexpressed genes, U21B31/PRAD1 and EMS1, within the amplified chromosome 11q13 region in human carcinomas. Oncogene. 1992 Feb;7(2):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto M., Yamamoto K., Iida S., Akao Y., Utsumi K. R., Kubonishi I., Miyoshi I., Ohtsuki T., Yawata Y., Namba M. Gene rearrangement and overexpression of PRAD1 in lymphoid malignancy with t(11;14)(q13;q32) translocation. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewing A., Bürger C., Brüsselbach S., Schalk C., Lucibello F. C., Müller R. Human cyclin D1 encodes a labile nuclear protein whose synthesis is directly induced by growth factors and suppressed by cyclic AMP. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):545–555. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. The ins and outs of RB: coupling gene expression to the cell cycle clock. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;4(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda Y., Aizawa S., Hirai S., Inoue T., Furuta Y., Suzuki M., Hirohashi S., Ikawa Y. Driven by the same Ig enhancer and SV40 T promoter ras induced lung adenomatous tumors, myc induced pre-B cell lymphomas and SV40 large T gene a variety of tumors in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4055–4065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Jaffe E., Cossman J., Gorham J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Clustering of breakpoints on chromosome 11 in human B-cell neoplasms with the t(11;14) chromosome translocation. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):340–343. doi: 10.1038/315340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek S., van Lohuizen M., van der Valk M., Domen J., Kraal G., Berns A. Mice bearing the E mu-myc and E mu-pim-1 transgenes develop pre-B-cell leukemia prenatally. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1176–1179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Chenivesse X., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Hepatitis B virus integration in a cyclin A gene in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):555–557. doi: 10.1038/343555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Sugiyama H., Axelson H., Panda C. K., Babonits M., Ma A., Steinberg J. M., Alt F. W., Klein G., Wiener F. Functional homology between N-myc and c-myc in murine plasmacytomagenesis: plasmacytoma development in N-myc transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1241–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers D. A., Harvey R. C., Faust J. B., Melnyk O., Carey K., Meeker T. C. Characterization of a candidate bcl-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4846–4853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Beach D. Population explosion in the cyclin family. Curr Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90193-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Nisen P. D., Tesfaye A., Kohl N. E., Goldfarb M. P., Alt F. W. N-myc can cooperate with ras to transform normal cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K., Alt F. W. Expression and function of myc family genes. Crit Rev Oncog. 1990;2(1):75–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]