Abstract
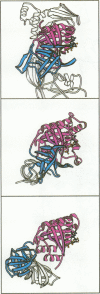
Elongation factor G (EF-G) catalyzes the translocation step of protein synthesis in bacteria, and like the other bacterial elongation factor, EF-Tu--whose structure is already known--it is a member of the GTPase superfamily. We have determined the crystal structure of EF-G--GDP from Thermus thermophilus. It is an elongated molecule whose large, N-terminal domain resembles the G domain of EF-Tu, except for a 90 residue insert, which covers a surface that is involved in nucleotide exchange in EF-Tu and other G proteins. The tertiary structures of the second domains of EF-G and EF-Tu are nearly identical, but the relative placement of the first two domains in EF-G--GDP resembles that seen in EF-Tu--GTP, not EF-Tu--GDP. The remaining three domains of EF-G look like RNA binding domains, and have no counterparts in EF-Tu.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AEvarsson A., Brazhnikov E., Garber M., Zheltonosova J., Chirgadze Y., al-Karadaghi S., Svensson L. A., Liljas A. Three-dimensional structure of the ribosomal translocase: elongation factor G from Thermus thermophilus. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3669–3677. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLENDE J. E., MONRO R., LIPMANN F. RESOLUTION OF THE E. COLI AMINO ACYL SRNA TRANSFER FACTOR INTO TWO COMPLEMENTARY FRACTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1211–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARLINGHAUS R., SHAEFER J., SCHWEET R. MECHANISM OF PEPTIDE BOND FORMATION IN POLYPEPTIDE SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1291–1299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Kawakita M., Nakamura S., Ishikawa K., Kaziro Y. Studies on the polypeptide elongation factors form E. coli. VI. Characterization of sulfhydryl groups in EF-Tu and EF-Ts. J Biochem. 1974 Sep;76(3):523–534. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Ota Y., Arai N., Nakamura S., Henneke C., Oshima T., Kaziro Y. Studies on polypeptide-chain-elongation factors from an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus HB8. 1. Purification and some properties of the purified factors. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):509–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):126–132. doi: 10.1038/365126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Palm P., Creti R., Ceccarelli E., Sanangelantoni A. M., Tiboni O. Early evolutionary relationships among known life forms inferred from elongation factor EF-2/EF-G sequences: phylogenetic coherence and structure of the archaeal domain. J Mol Evol. 1992 May;34(5):396–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00162996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilova L. P., Kostiashkina O. E., Koteliansky V. E., Rutkevitch N. M., Spirin A. S. Factor-free ("non-enzymic") and factor-dependent systems of translation of polyuridylic acid by Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):537–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinblat Y., Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Isolation and characterization of the Drosophila translational elongation factor 2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7303–7314. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillot D., Lavergne J. P., Reboud J. P. Trp221 is involved in the protective effect of elongation factor eEF-2 on the ricin/alpha-sarcin site of the ribosome. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26082–26084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Waterson J., Sopori M. L., Weissman S. M., Lengyel P. Movement of the ribosome along the messenger ribonucleic acid during protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4410–4421. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner T. P., Atmadja J., Nierhaus K. H. Evidence that the G2661 region of 23S rRNA is located at the ribosomal binding sites of both elongation factors. Biochimie. 1987 Sep;69(9):911–923. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y., Lin Y. P., Sharer J. D., March P. E. In vivo selection of conditional-lethal mutations in the gene encoding elongation factor G of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(1):123–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.1.123-129.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Carter M., Miller D. L. The identification of a domain in Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu that interacts with elongation factor Ts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22198–22205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson U., Hughes D. Fusidic acid-resistant mutants define three regions in elongation factor G of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1994 May 27;143(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in polypeptide chain elongation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;505(1):95–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Thirup S., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. Refined structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):721–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90986-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberman R., Antonsson B., Giovanelli R., Guariguata R., Schumann R., Wittinghofer A. A simplified procedure for the isolation of bacterial polypeptide elongation factor EF-Tu. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Robertson J. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):362–364. doi: 10.1038/334362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D., LIPMANN F. Amino acid transfer from aminoacyl-ribonucleic acids to protein on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Apr 15;47:497–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H. Solution of the ribosome riddle: how the ribosome selects the correct aminoacyl-tRNA out of 41 similar contestants. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. Comparison of guanosine triphosphate split and polypeptide synthesis with a purified E. coli system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):212–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M. E., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Kiefhaber T., Ott G., Grillenbeck N. W., Sprinzl M. Interaction of the isolated domain II/III of Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Tu with the nucleotide exchange factor EF-Ts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6889–6893. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUIOCHO F. A., RICHARDS F. M. INTERMOLECULAR CROSS LINKING OF A PROTEIN IN THE CRYSTALLINE STATE: CARBOXYPEPTIDASE-A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:833–839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman N., Bodley J. W. Ribosomes cannot interact simultaneously with elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):686–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Henriksen O., Maxwell E. S. Elongation factor 2. Amino acid sequence at the site of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5088–5093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling-Bartetzko S., Bartetzko A., Nierhaus K. H. Kinetic and thermodynamic parameters for tRNA binding to the ribosome and for the translocation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4703–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin A. S. Ribosomal translocation: facts and models. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:75–114. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Steitz T. A. Structure of the recA protein-ADP complex. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):374–376. doi: 10.1038/355374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thach S. S., Thach R. E. Translocation of messenger RNA and "accommodation" of fMet-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1791–1795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willie G. R., Richman N., Godtfredsen W. P., Bodley J. W. Some characteristics of and structural requirements for the interaction of 24,25-dihydrofusidic acid with ribosome - elongation factor g Complexes. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1713–1718. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G., Glück A., Endo Y. Ribotoxin recognition of ribosomal RNA and a proposal for the mechanism of translocation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):266–269. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90407-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurmbach P., Nierhaus K. H. Isolation of the protein synthesis elongation factors EF-Tu, EF-Ts, and EF-G from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:593–606. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakhnin A. V., Vorozheykina D. P., Matvienko N. I. Nucleotide sequence of the Thermus thermophilus HB8 gene coding for elongation factor G. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8863–8863. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]