Abstract
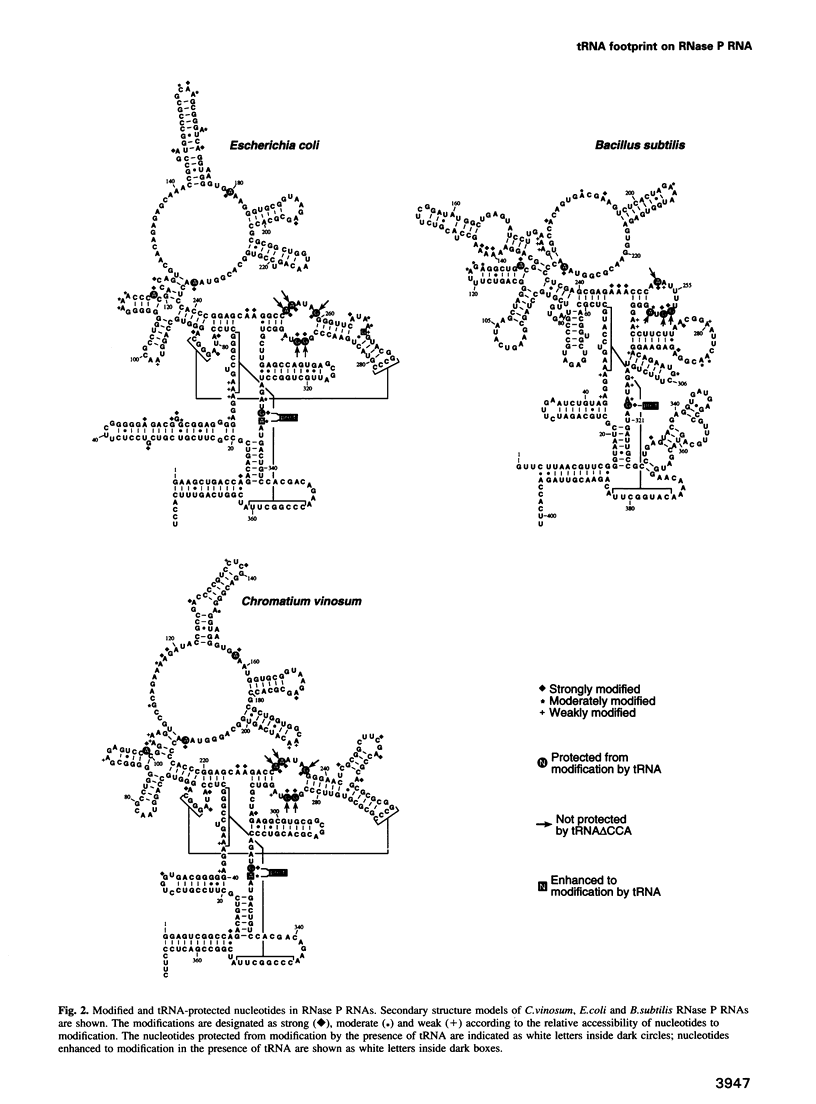
Ribonuclease P RNA is the catalytic moiety of the ribonucleoprotein enzyme that endonucleolytically cleaves precursor sequences from the 5' ends of pre-tRNAs. The bacterial RNase P RNA-tRNA complex was examined with a footprinting approach, utilizing chemical modification to determine RNase P RNA nucleotides that potentially contact tRNA. RNase P RNA was modified with dimethylsulfate or kethoxal in the presence or absence of tRNA, and sites of modification were detected by primer extension. Comparison of the results reveals RNase P bases that are protected from modification upon binding tRNA. Analyses were carried out with RNase P RNAs from three different bacteria: Escherichia coli, Chromatium vinosum and Bacillus subtilis. Discrete bases of these RNAs that lie within conserved, homologous portions of the secondary structures are similarly protected. One protection among all three RNAs was attributed to the precursor segment of pre-tRNA. Experiments using pre-tRNAs containing precursor segments of variable length demonstrate that a precursor segment of only 2-4 nucleotides is sufficient to confer this protection. Deletion of the 3'-terminal CCA sequence of tRNA correlates with loss of protection of a particular loop in the RNase P RNA secondary structure. Analysis of mutant tRNAs containing sequential 3'-terminal deletions suggests a relative orientation of the bound tRNA CCA to that loop.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman S., Kirsebom L., Talbot S. Recent studies of ribonuclease P. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):7–14. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7916700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgin A. B., Pace N. R. Mapping the active site of ribonuclease P RNA using a substrate containing a photoaffinity agent. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4111–4118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darr S. C., Brown J. W., Pace N. R. The varieties of ribonuclease P. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 May;17(5):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darr S. C., Zito K., Smith D., Pace N. R. Contributions of phylogenetically variable structural elements to the function of the ribozyme ribonuclease P. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):328–333. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Vold B. S. Structural requirements for processing of synthetic tRNAHis precursors by the catalytic RNA component of RNase P. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):652–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Structure in solution of M1 RNA, the catalytic subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6327–6334. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Lumelsky N., Altman S. Specific interactions in RNA enzyme-substrate complexes. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1578–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2480641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., McClain W. H., Altman S. Cleavage of tRNA precursors by the RNA subunit of E. coli ribonuclease P (M1 RNA) is influenced by 3'-proximal CCA in the substrates. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90543-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Liu J. S., Pace N. R. The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahle D., Wehmeyer U., Krupp G. Substrate recognition by RNase P and by the catalytic M1 RNA: identification of possible contact points in pre-tRNAs. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1929–1937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A., Altman S. Reaction in vitro of some mutants of RNase P with wild-type and temperature-sensitive substrates. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):837–840. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A., Svärd S. G. Identification of a region within M1 RNA of Escherichia coli RNase P important for the location of the cleavage site on a wild-type tRNA precursor. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jun 5;231(3):594–604. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knap A. K., Wesolowski D., Altman S. Protection from chemical modification of nucleotides in complexes of M1 RNA, the catalytic subunit of RNase P from E coli, and tRNA precursors. Biochimie. 1990 Nov;72(11):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90187-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Model substrates for an RNA enzyme. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):527–530. doi: 10.1126/science.2443980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of tRNA with 23S rRNA in the ribosomal A, P, and E sites. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):585–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Sites of interaction of the CCA end of peptidyl-tRNA with 23S rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3725–3728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. M., Burke D. H., Pace N. R. Circularly permuted tRNAs as specific photoaffinity probes of ribonuclease P RNA structure. Science. 1993 Aug 6;261(5122):762–765. doi: 10.1126/science.7688143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich C., Gardiner K. J., Olsen G. J., Pace B., Marsh T. L., Pace N. R. The RNA component of the Bacillus subtilis RNase P. Sequence, activity, and partial secondary structure. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7888–7893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich C., Olsen G. J., Pace B., Pace N. R. Role of the protein moiety of ribonuclease P, a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):178–181. doi: 10.1126/science.3122322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi H., Shimura Y. Functional domains of the RNA component of ribonuclease P revealed by chemical probing of mutant RNAs. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3817–3821. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03266.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Burgin A. B., Haas E. S., Pace N. R. Influence of metal ions on the ribonuclease P reaction. Distinguishing substrate binding from catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Moazed D., Noller H. F. Structural analysis of RNA using chemical and enzymatic probing monitored by primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:481–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt C. K., Carter B. J., Payne R. C., Hecht S. M. Metal ion and substrate structure dependence of the processing of tRNA precursors by RNase P and M1 RNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22513–22519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh D. S., Green C. J., Pace N. R. The design and catalytic properties of a simplified ribonuclease P RNA. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1569–1571. doi: 10.1126/science.2472671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]