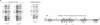Abstract
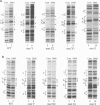
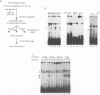
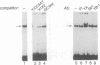
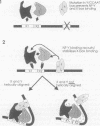
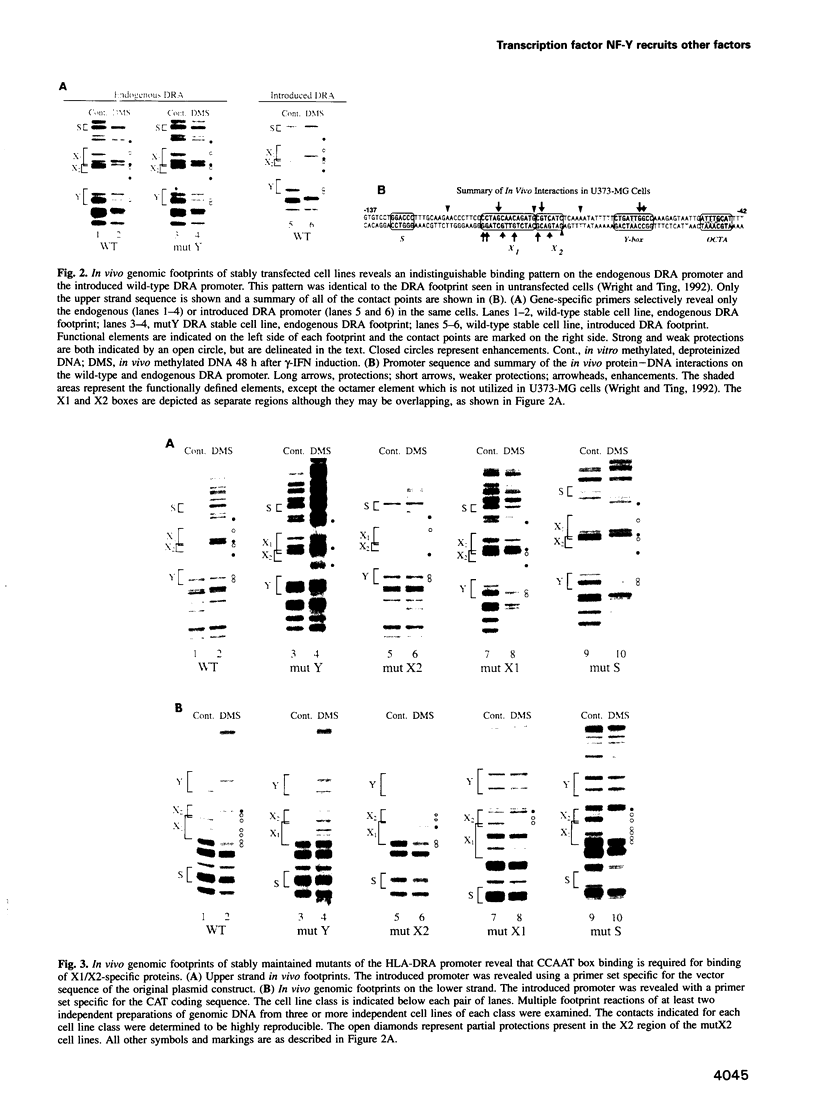
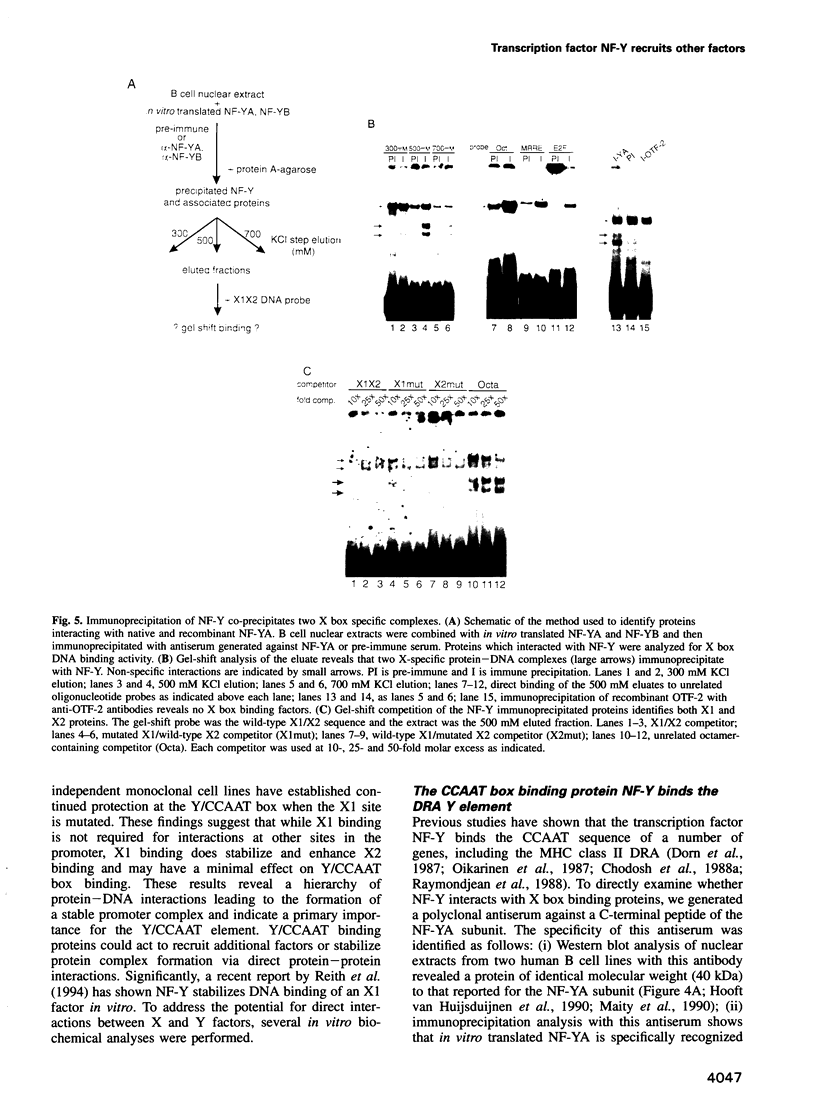
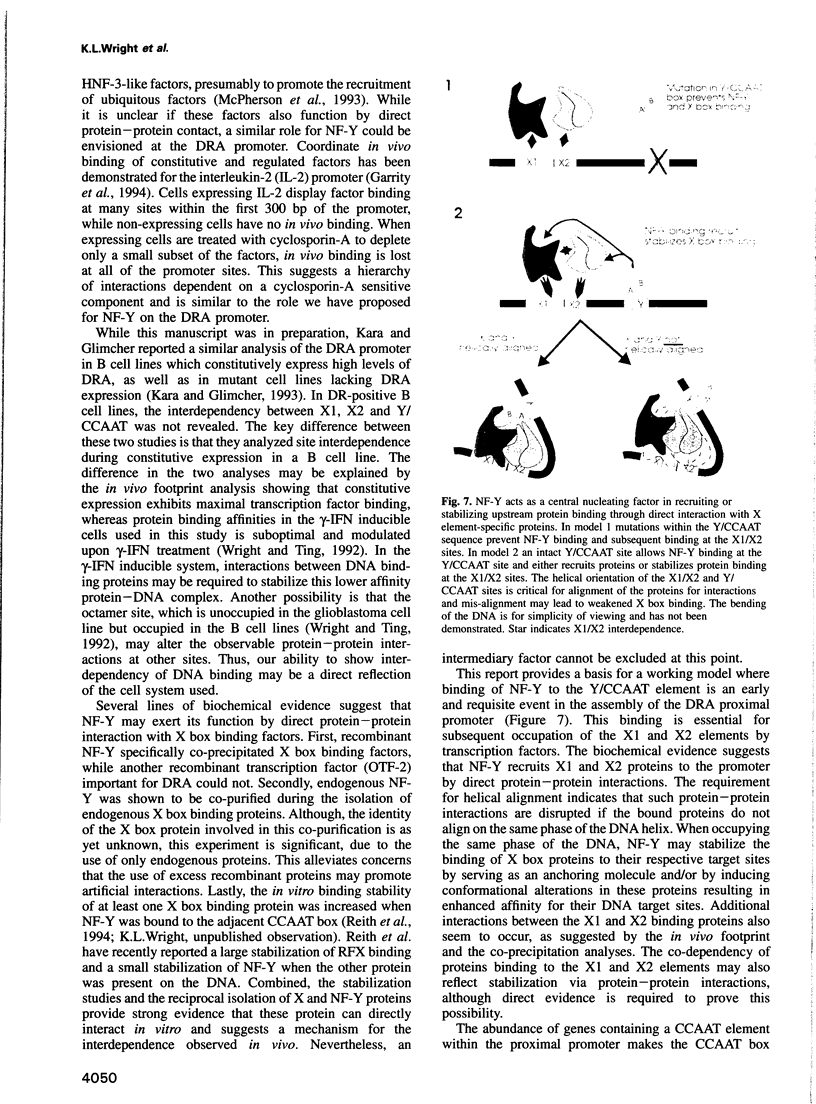
NF-Y binds a CCAAT motif found in many eukaryotic polymerase II-dependent promoters. In the HLA-DRA promoter it has been demonstrated that stereo-specific alignment between this motif and the upstream elements X1 and X2 is required for activation. To study the underlying mechanism for this requirement, a panel of transfected cell lines that maintained integrated, wild-type and mutant promoters were analyzed by in vivo genomic footprinting. Cell lines harboring a mutated CCAAT element exhibited a loss of interactions at the CCAAT site, as expected, and no transcriptional activity. Most importantly, mutation of the CCAAT sequence nearly abolished in vivo binding at the X1 and X2 sites, while mutations of X1 and X2 had little effect on CCAAT box binding. However, X1 and X2 binding was interdependent. In vitro, X1 binding activities are known to be stabilized by NF-Y binding. Interaction between NF-Y and X box binding proteins was demonstrated by reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation in the absence of DNA and co-affinity purification in the presence of DNA. Collectively, these studies indicate that occupancy of the CCAAT element represents an early event affecting other protein-DNA interactions and suggest that NF-Y stabilizes and interacts with X box factors to mediate this function. These findings may represent a common theme among promoters containing a CCAAT element.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G., Peterlin B. M. NF-X2 that binds to the DRA X2-box is activator protein 1. Expression cloning of c-Jun. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3456–3462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Delmas V., Perry R. P. A novel upstream element compensates for an ineffectual octamer motif in an immunoglobulin V kappa promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3109–3117. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basta P. V., Sherman P. A., Ting J. P. Identification of an interferon-gamma response region 5' of the human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen DR alpha chain gene which is active in human glioblastoma multiforme lines. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1275–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Gloss B., Schmid W., Strähle U., Schütz G. In vivo protein-DNA interactions in a glucocorticoid response element require the presence of the hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):686–688. doi: 10.1038/324686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Mathis D. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class-II genes: X, Y and other letters of the alphabet. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:681–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max associate in vivo. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–80. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P. Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr K. D., Richard-Foy H. Glucocorticoids locally disrupt an array of positioned nucleosomes on the rat tyrosine aminotransferase promoter in hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9300–9304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Olesen J., Hahn S., Baldwin A. S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. A yeast and a human CCAAT-binding protein have heterologous subunits that are functionally interchangeable. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90484-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy B., Green M. R. Eukaryotic activators function during multiple steps of preinitiation complex assembly. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):531–536. doi: 10.1038/366531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Resar L. M., Kato G. J., Fearon E. R. Intracellular leucine zipper interactions suggest c-Myc hetero-oligomerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):954–962. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilition S. L., Frederickson R. M., Taylor C. Y., Miyamoto N. G. Transcription factor binding and spacing constraints in the human beta-actin proximal promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6913–6922. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demczuk S., Harbers M., Vennström B. Identification and analysis of all components of a gel retardation assay by combination with immunoblotting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2574–2578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Finkel T., Gillison M. L., Kennedy S. P., Casella J. F., Tomaselli G. F., Morrow J. S., Van Dang C. Karyoplasmic interaction selection strategy: a general strategy to detect protein-protein interactions in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7958–7962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Tsuchiya H., Chuhjo T., Akizawa T., Seiki M. Interaction of HTLV-1 Tax1 with p67SRF causes the aberrant induction of cellular immediate early genes through CArG boxes. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2066–2076. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity P. A., Chen D., Rothenberg E. V., Wold B. J. Interleukin-2 transcription is regulated in vivo at the level of coordinated binding of both constitutive and regulated factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2159–2169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Kara C. J. Sequences and factors: a guide to MHC class-II transcription. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:13–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gégonne A., Bosselut R., Bailly R. A., Ghysdael J. Synergistic activation of the HTLV1 LTR Ets-responsive region by transcription factors Ets1 and Sp1. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey C., Jackson S. M., Siddiqui S. K., Gutierrez-Hartmann A. Structure-function analysis of the rat prolactin promoter: phasing requirements of proximal cell-specific elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;5(6):836–843. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-6-836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. TBP, a universal eukaryotic transcription factor? Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1291–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Weinzierl R. O., Gill G., Chen J. L., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of Drosophila TAF110 reveal properties expected of coactivators. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Li X. Y., Black D., Matthes H., Benoist C., Mathis D. Co-evolution from yeast to mouse: cDNA cloning of the two NF-Y (CP-1/CBF) subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3119–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson L., Pettersson U. Cooperative interactions between transcription factors Sp1 and OTF-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4732–4736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Glimcher L. H. In vivo footprinting of MHC class II genes: bare promoters in the bare lymphocyte syndrome. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.1902592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Glimcher L. H. Promoter accessibility within the environment of the MHC is affected in class II-deficient combined immunodeficiency. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):187–193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Finn P. W., Davidon R., Nabavi N., Zeleznik-Le N. J., Ting J. P., Glimcher L. H. A new member of the leucine zipper class of proteins that binds to the HLA DR alpha promoter. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1581–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Glimcher L. H. Distinct cloned class II MHC DNA binding proteins recognize the X box transcription element. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.3140376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maity S. N., Golumbek P. T., Karsenty G., de Crombrugghe B. Selective activation of transcription by a novel CCAAT binding factor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):582–585. doi: 10.1126/science.3399893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maity S. N., Vuorio T., de Crombrugghe B. The B subunit of a rat heteromeric CCAAT-binding transcription factor shows a striking sequence identity with the yeast Hap2 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5378–5382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani R., Pessara U., Tronche F., Li X. Y., Knapp A. M., Pasquali J. L., Benoist C., Mathis D. Monoclonal antibodies to NF-Y define its function in MHC class II and albumin gene transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3315–3322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson C. E., Shim E. Y., Friedman D. S., Zaret K. S. An active tissue-specific enhancer and bound transcription factors existing in a precisely positioned nucleosomal array. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80079-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milos P. M., Zaret K. S. A ubiquitous factor is required for C/EBP-related proteins to form stable transcription complexes on an albumin promoter segment in vitro. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):991–1004. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H., Panek R. B., Benveniste E. N., Ting J. P. Usage of primary cells to delineate IFN-gamma-responsive DNA elements in the HLA-DRA promoter and to identify a novel IFN-gamma-enhanced nuclear factor. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3643–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen J., Hatamochi A., de Crombrugghe B. Separate binding sites for nuclear factor 1 and a CCAAT DNA binding factor in the mouse alpha 2(I) collagen promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11064–11070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. J., Liou H. C., Davidon R., Strominger J. L., Glimcher L. H. Human X-box-binding protein 1 is required for the transcription of a subset of human class II major histocompatibility genes and forms a heterodimer with c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4309–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Sollner-Webb B. Half helical turn spacing changes convert a frog into a mouse rDNA promoter: a distant upstream domain determines the helix face of the initiation site. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):52–62. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlin B. M., Andersson G., Lötscher E., Tsang S. Transcriptional regulation of HLA class-II genes. Immunol Res. 1990;9(3):164–177. doi: 10.1007/BF02918176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Tanguay R. L., Steigerwald S. D., Riggs A. D. In vivo footprint and methylation analysis by PCR-aided genomic sequencing: comparison of active and inactive X chromosomal DNA at the CpG island and promoter of human PGK-1. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1277–1287. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Herrero-Sanchez C., Kobr M., Silacci P., Berte C., Barras E., Fey S., Mach B. MHC class II regulatory factor RFX has a novel DNA-binding domain and a functionally independent dimerization domain. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1528–1540. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Siegrist C. A., Durand B., Barras E., Mach B. Function of major histocompatibility complex class II promoters requires cooperative binding between factors RFX and NF-Y. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. The complexities of eukaryotic transcription initiation: regulation of preinitiation complex assembly. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90164-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Moore T. L., Brown A. M., Ting J. P. Class II box consensus sequences in the HLA-DR alpha gene: transcriptional function and interaction with nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. Upstream DNA sequences required for tissue-specific expression of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J. P., Baldwin A. S. Regulation of MHC gene expression. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama T., Becker P. B., Wu C. ATP-dependent nucleosome disruption at a heat-shock promoter mediated by binding of GAGA transcription factor. Nature. 1994 Feb 10;367(6463):525–532. doi: 10.1038/367525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilen B. J., Cogswell J. P., Ting J. P. Stereospecific alignment of the X and Y elements is required for major histocompatibility complex class II DRA promoter function. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2406–2415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilen B. J., Penta J. F., Ting J. P. Structural constraints within a trimeric transcriptional regulatory region. Constitutive and interferon-gamma-inducible expression of the HLA-DRA gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23728–23734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waibel F., Filipowicz W. RNA-polymerase specificity of transcription of Arabidopsis U snRNA genes determined by promoter element spacing. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):199–202. doi: 10.1038/346199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K. L., Ting J. P. In vivo footprint analysis of the HLA-DRA gene promoter: cell-specific interaction at the octamer site and up-regulation of X box binding by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7601–7605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Berk A. Constraints on spacing between transcription factor binding sites in a simple adenovirus promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):403–411. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J., Mueller C., Schibler U. A ubiquitous CCAAT factor is required for efficient in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):865–874. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90341-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Perisic O., Lis J. T. Cooperative binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to arrays of a conserved 5 bp unit. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90242-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeleznik-Le N. J., Azizkhan J. C., Ting J. P. Affinity-purified CCAAT-box-binding protein (YEBP) functionally regulates expression of a human class II major histocompatibility complex gene and the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1873–1877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]