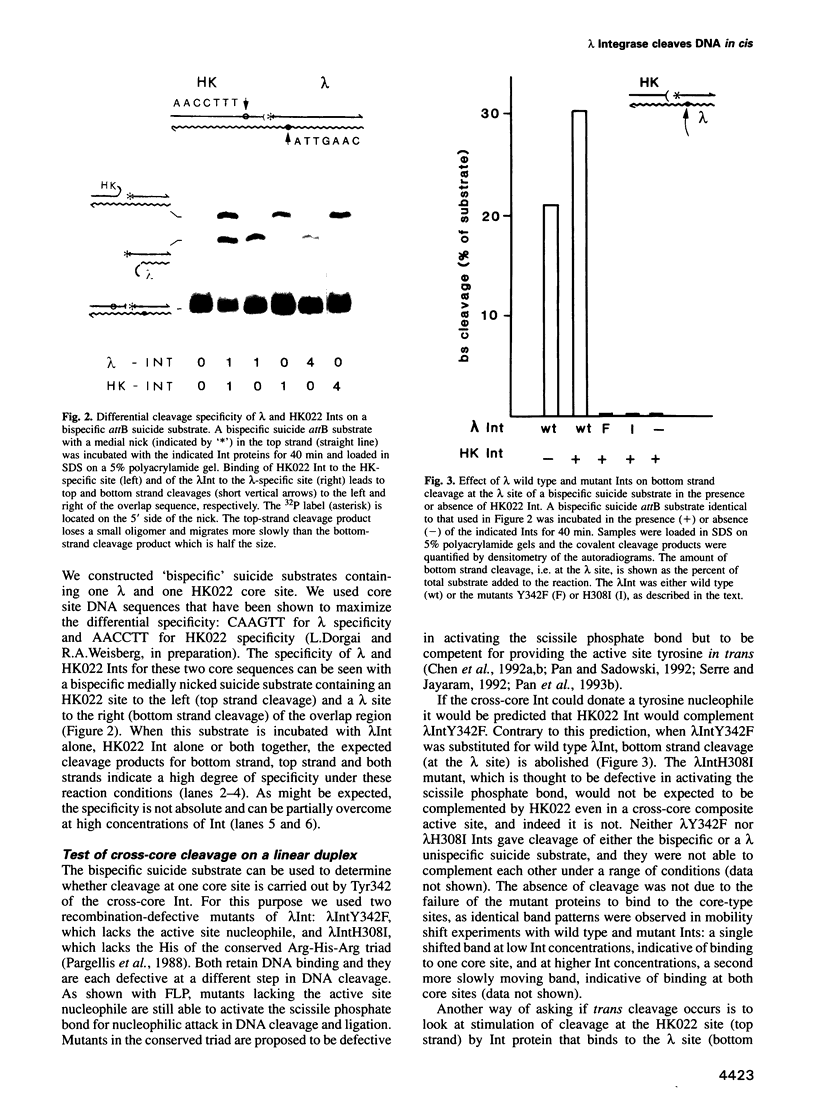
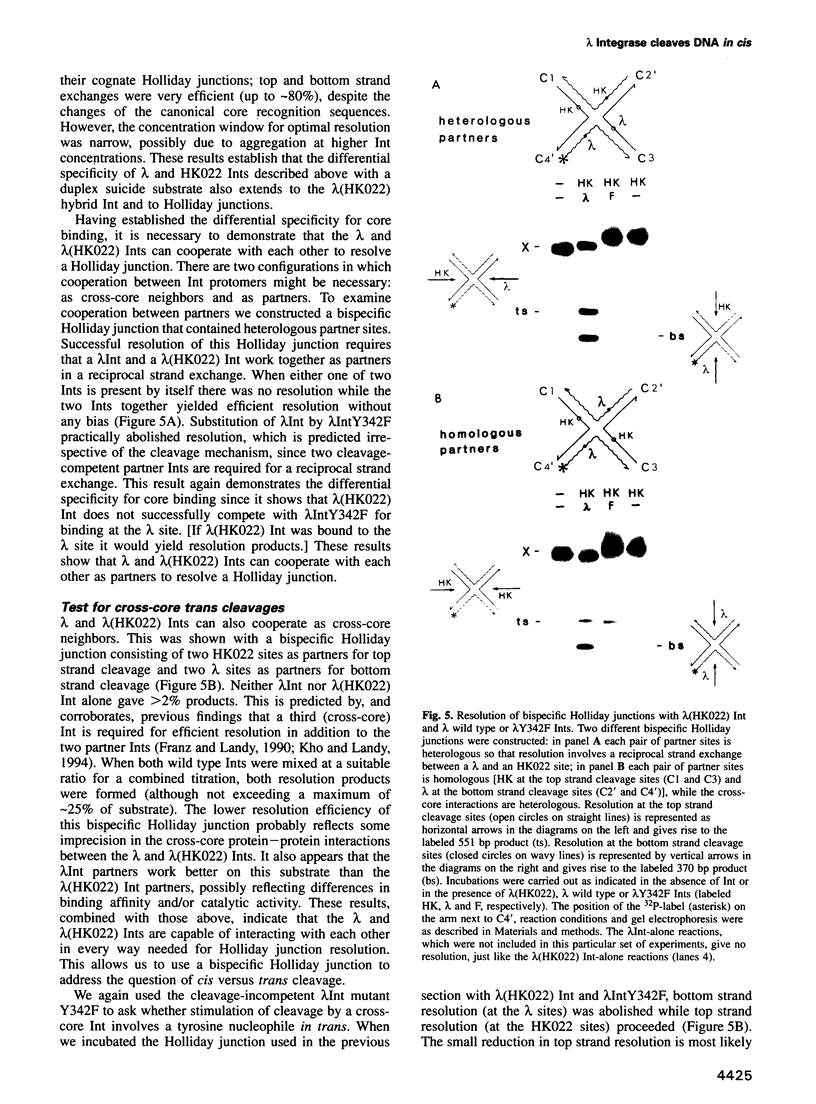
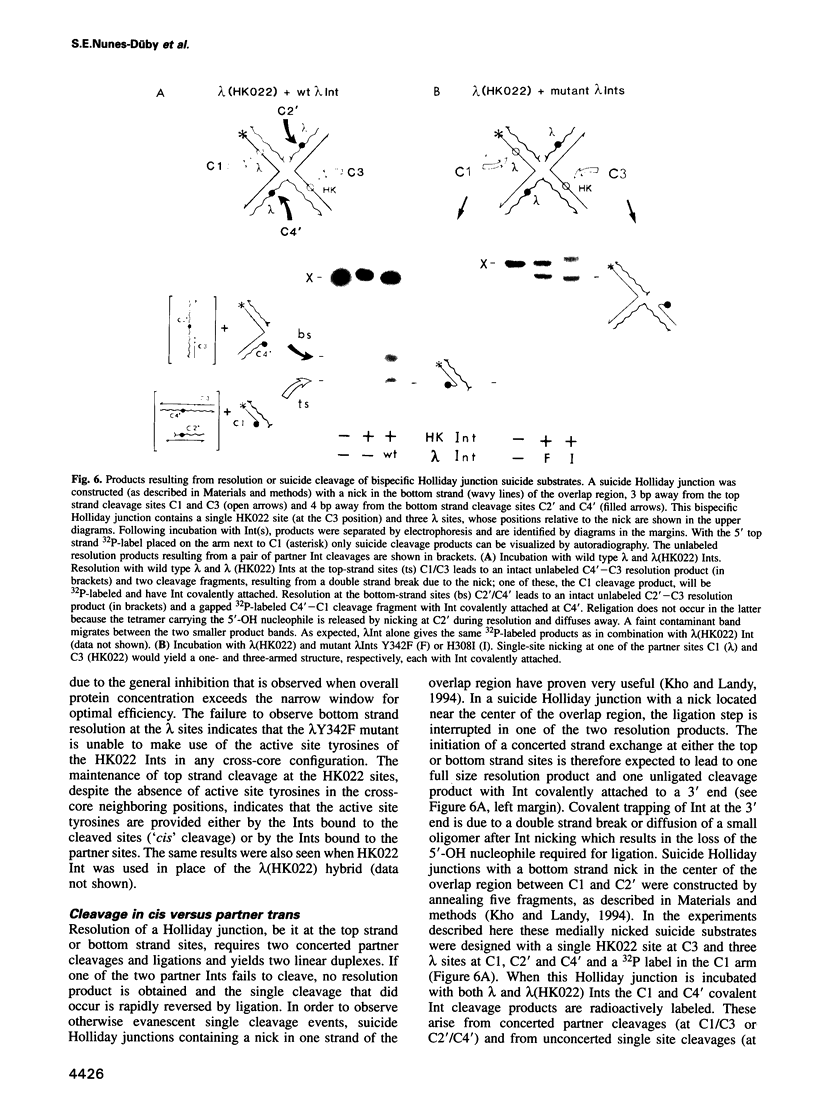
Abstract
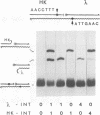
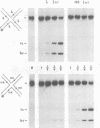
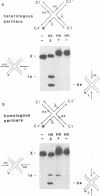
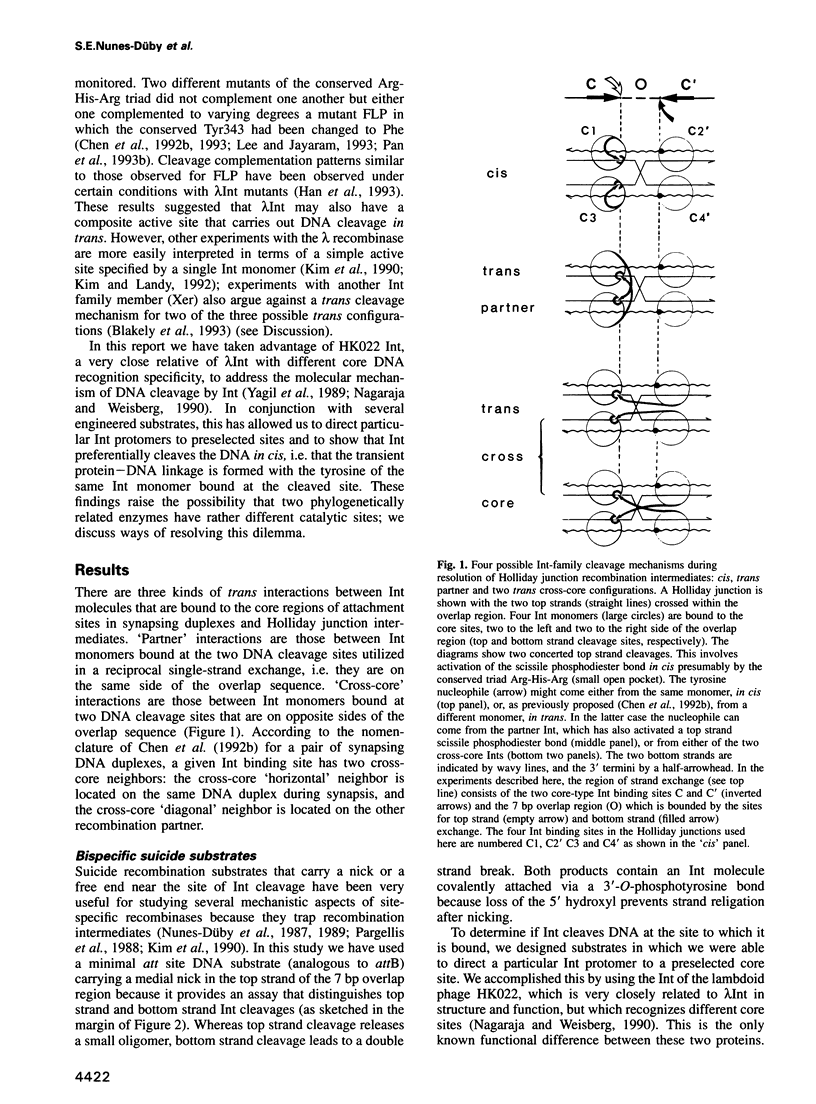
In the Int family of site-specific recombinases, DNA cleavage is accomplished by nucleophilic attack on the activated scissile phosphodiester bond by a specific tyrosine residue. It has been proposed that this tyrosine is contributed by a protomer bound to a site other than the one being cleaved ('trans' cleavage). To test this hypothesis, the difference in DNA binding specificity between closely related integrases (Ints) from phages lambda and HK022 was exploited to direct wild type Ints and cleavage- or activation-defective mutants to particular sites on bispecific substrates. Analysis of Int cleavage at individual sites strongly indicates that DNA cleavage is catalyzed by the Int bound to the cleaved site ('cis' cleavage). This conclusion contrasts with those from previous experiments with two members of the Int family, FLP and lambda Int, that supported the hypothesis of trans cleavage. We suggest explanations for this difference and discuss the implications of the surprising finding that Int-family recombinases appear capable of both cis and trans mechanisms of DNA cleavage.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K. E., Hoess R. H. Evidence for a second conserved arginine residue in the integrase family of recombination proteins. Protein Eng. 1992 Jan;5(1):87–91. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely G., May G., McCulloch R., Arciszewska L. K., Burke M., Lovett S. T., Sherratt D. J. Two related recombinases are required for site-specific recombination at dif and cer in E. coli K12. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):351–361. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80076-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. W., Evans B. R., Yang S. H., Araki H., Oshima Y., Jayaram M. Functional analysis of box I mutations in yeast site-specific recombinases Flp and R: pairwise complementation with recombinase variants lacking the active-site tyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3757–3765. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. W., Lee J., Jayaram M. DNA cleavage in trans by the active site tyrosine during Flp recombination: switching protein partners before exchanging strands. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90228-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. W., Yang S. H., Jayaram M. Tests for the fractional active-site model in Flp site-specific recombination. Assembly of a functional recombination complex in half-site and full-site strand transfer. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14417–14425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colloms S. D., Sykora P., Szatmari G., Sherratt D. J. Recombination at ColE1 cer requires the Escherichia coli xerC gene product, a member of the lambda integrase family of site-specific recombinases. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6973–6980. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6973-6980.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L. The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:77–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. E., Sadowski P. D. Resolution of synthetic chi structures by the FLP site-specific recombinase. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):522–533. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Convergent evolution: the need to be explicit. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans B. R., Chen J. W., Parsons R. L., Bauer T. K., Teplow D. B., Jayaram M. Identification of the active site tyrosine of Flp recombinase. Possible relevance of its location to the mechanism of recombination. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18504–18510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz B., Landy A. Interactions between lambda Int molecules bound to sites in the region of strand exchange are required for efficient Holliday junction resolution. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 20;215(4):523–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen H., Sadowski P. D. Mutagenesis of a conserved region of the gene encoding the FLP recombinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A role for arginine 191 in binding and ligation. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90924-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Sadowski P. D. The FLP recombinase of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2 microns plasmid attaches covalently to DNA via a phosphotyrosyl linkage. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3274–3279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Y. W., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. Complementation of bacteriophage lambda integrase mutants: evidence for an intersubunit active site. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4577–4584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R., Wierzbicki A., Abremski K. Isolation and characterization of intermediates in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6840–6844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeltsch A., Alves J., Wolfes H., Maass G., Pingoud A. Substrate-assisted catalysis in the cleavage of DNA by the EcoRI and EcoRV restriction enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8499–8503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kho S. H., Landy A. Dissecting the resolution reaction of lambda integrase using suicide Holliday junction substrates. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2714–2724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06562.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. Nicking-closing activity associated with bacteriophage lambda int gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3760–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Landy A. Lambda Int protein bridges between higher order complexes at two distant chromosomal loci attL and attR. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):198–203. doi: 10.1126/science.1533056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Moitoso de Vargas L., Nunes-Düby S. E., Landy A. Mapping of a higher order protein-DNA complex: two kinds of long-range interactions in lambda attL. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball A. S., Lee J., Jayaram M., Tullius T. D. Sequence-specific cleavage of DNA via nucleophilic attack of hydrogen peroxide, assisted by Flp recombinase. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4698–4701. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Homology-dependent interactions in phage lambda site-specific recombination. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):346–348. doi: 10.1038/329346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A. Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:913–949. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A. Mechanistic and structural complexity in the site-specific recombination pathways of Int and FLP. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Oct;3(5):699–707. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Jayaram M. Mechanism of site-specific recombination. Logic of assembling recombinase catalytic site from fractional active sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17564–17570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Leon L., Huang L. C., Umlauf S. W., Cox M. M., Inman R. B. Holliday intermediates and reaction by-products in FLP protein-promoted site-specific recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3784–3796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Leon L., Inman R. B., Cox M. M. Characterization of Holliday structures in FLP protein-promoted site-specific recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):235–242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Pargellis C. A., Hasan N. M., Bushman E. W., Landy A. Autonomous DNA binding domains of lambda integrase recognize two different sequence families. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):923–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja R., Weisberg R. A. Specificity determinants in the attachment sites of bacteriophages HK022 and lambda. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6540–6550. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6540-6550.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Half-att site substrates reveal the homology independence and minimal protein requirements for productive synapsis in lambda excisive recombination. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90881-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan G., Luetke K., Juby C. D., Brousseau R., Sadowski P. Ligation of synthetic activated DNA substrates by site-specific recombinases and topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3683–3689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan G., Luetke K., Sadowski P. D. Mechanism of cleavage and ligation by FLP recombinase: classification of mutations in FLP protein by in vitro complementation analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3167–3175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan G., Sadowski P. D. Ligation activity of FLP recombinase. The strand ligation activity of a site-specific recombinase using an activated DNA substrate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12397–12399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Schröder W., Lanka E. Concerted action of three distinct domains in the DNA cleaving-joining reaction catalyzed by relaxase (TraI) of conjugative plasmid RP4. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2782–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargellis C. A., Nunes-Düby S. E., de Vargas L. M., Landy A. Suicide recombination substrates yield covalent lambda integrase-DNA complexes and lead to identification of the active site tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7678–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Prasad P. V., Harshey R. M., Jayaram M. Step-arrest mutants of FLP recombinase: implications for the catalytic mechanism of DNA recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3303–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X. H., Inman R. B., Cox M. M. Protein-based asymmetry and protein-protein interactions in FLP recombinase-mediated site-specific recombination. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21779–21788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. D. Site-specific genetic recombination: hops, flips, and flops. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):760–767. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8392474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serre M. C., Jayaram M. Half-site strand transfer by step-arrest mutants of yeast site-specific recombinase Flp. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):643–649. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90391-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serre M. C., Zheng L., Jayaram M. DNA splicing by an active site mutant of Flp recombinase. Possible catalytic cooperativity between the inactive protein and its DNA substrate. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):455–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. M., Boocock M. R., Sherratt D. J. Catalysis by site-specific recombinases. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):432–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask D. K., DiDonato J. A., Muller M. T. Rapid detection and isolation of covalent DNA/protein complexes: application to topoisomerase I and II. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):671–676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil E., Dolev S., Oberto J., Kislev N., Ramaiah N., Weisberg R. A. Determinants of site-specific recombination in the lambdoid coliphage HK022. An evolutionary change in specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):695–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]