Abstract
More than 50 genes are required for flagellar formation and function in Salmonella typhimurium. According to the cascade model of flagellar regulon, the flagellar operons are divided into three classes, 1, 2, and 3, with respect to transcriptional hierarchy. FliA is an alternative sigma factor specific for transcription of the class 3 operons, while FlgM is an anti-sigma factor which binds to FliA and prevents its association with RNA polymerase core enzyme. In the present study, we isolated a number of fliA mutants in which the altered FliA proteins become insensitive to inhibition by FlgM. Sequence analysis of their mutation sites revealed that most of them caused the amino acid substitutions in region 4 of the conserved amino acid sequences of sigma factors which lies near the C-terminal end of FliA. Using a set of fliA deletion mutants in a high-expression plasmid, we demonstrated that polypeptides containing the C-terminal portion of FliA could titrate the intracellular FlgM protein resulting in derepression of the class 3 operons. This result indicates that the C-terminal region of FliA contains the FlgM-binding domain. This was confirmed by a chemical cross-linking experiment with FlgM and truncated FliA proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Ochs B., Abel K. J. Tightly regulated tac promoter vectors useful for the expression of unfused and fused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Sep 30;69(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. K., Haldenwang W. G. Bacillus subtilis sigma B is regulated by a binding protein (RsbW) that blocks its association with core RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz D., Hushon J. M., Whitfield H. J., Jr, Roth J., Ames B. N. Procedure for identifying nonsense mutations. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.215-220.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J., Plaskitt K. A., Buttner M. J., Méndez C., Helmann J. D. The developmental fate of S. coelicolor hyphae depends upon a gene product homologous with the motility sigma factor of B. subtilis. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90876-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Amino-terminal amino acids modulate sigma-factor DNA-binding activity. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2446–2455. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., Walter W. A., Record M. T., Jr, Siegele D. A., Gross C. A. Polypeptides containing highly conserved regions of transcription initiation factor sigma 70 exhibit specificity of binding to promoter DNA. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):501–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90174-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan L., Losick R. SpoIIAB is an anti-sigma factor that binds to and inhibits transcription by regulatory protein sigma F from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2325–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillen K. L., Hughes K. T. Molecular characterization of flgM, a gene encoding a negative regulator of flagellin synthesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6453–6459. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6453-6459.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillen K. L., Hughes K. T. Negative regulatory loci coupling flagellin synthesis to flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2301–2310. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2301-2310.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D. Alternative sigma factors and the regulation of flagellar gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2875–2882. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Márquez L. M., Chamberlin M. J. Cloning, sequencing, and disruption of the Bacillus subtilis sigma 28 gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1568–1574. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1568-1574.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K. T., Gillen K. L., Semon M. J., Karlinsey J. E. Sensing structural intermediates in bacterial flagellar assembly by export of a negative regulator. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1277–1280. doi: 10.1126/science.8235660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Protein-protein communication within the transcription apparatus. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2483-2489.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Grimes B., Fujita N., Makino K., Malloch R. A., Hayward R. S., Ishihama A. Role of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in transcription activation. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 14;235(2):405–413. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K. Excretion of the anti-sigma factor through a flagellar substructure couples flagellar gene expression with flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Jun 15;243(6):605–612. doi: 10.1007/BF00279569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T., Komeda Y., Yamaguchi S. Functional homology of fla genes between Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):59–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00267213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T. Role of the FliA-FlgM regulatory system on the transcriptional control of the flagellar regulon and flagellar formation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jun;176(12):3598–3605. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.12.3598-3605.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Nakao T., Iino T. A gene for DNA invertase and an invertible DNA in Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Ohya Y., Iino T. Transcriptional analysis of the flagellar regulon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.741-747.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Ohya Y., Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Operon structure of flagellar genes in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00340172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Okada T., Yokoseki T., Iino T. Sequence analysis of the flgA gene and its adjacent region in Salmonella typhimurium, and identification of another flagellar gene, flgN. Gene. 1994 May 27;143(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90603-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley S. A., Burgess R. R. Characterization of the Escherichia coli transcription factor sigma 70: localization of a region involved in the interaction with core RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7728–7734. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonetto M., Gribskov M., Gross C. A. The sigma 70 family: sequence conservation and evolutionary relationships. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3843–3849. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3843-3849.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
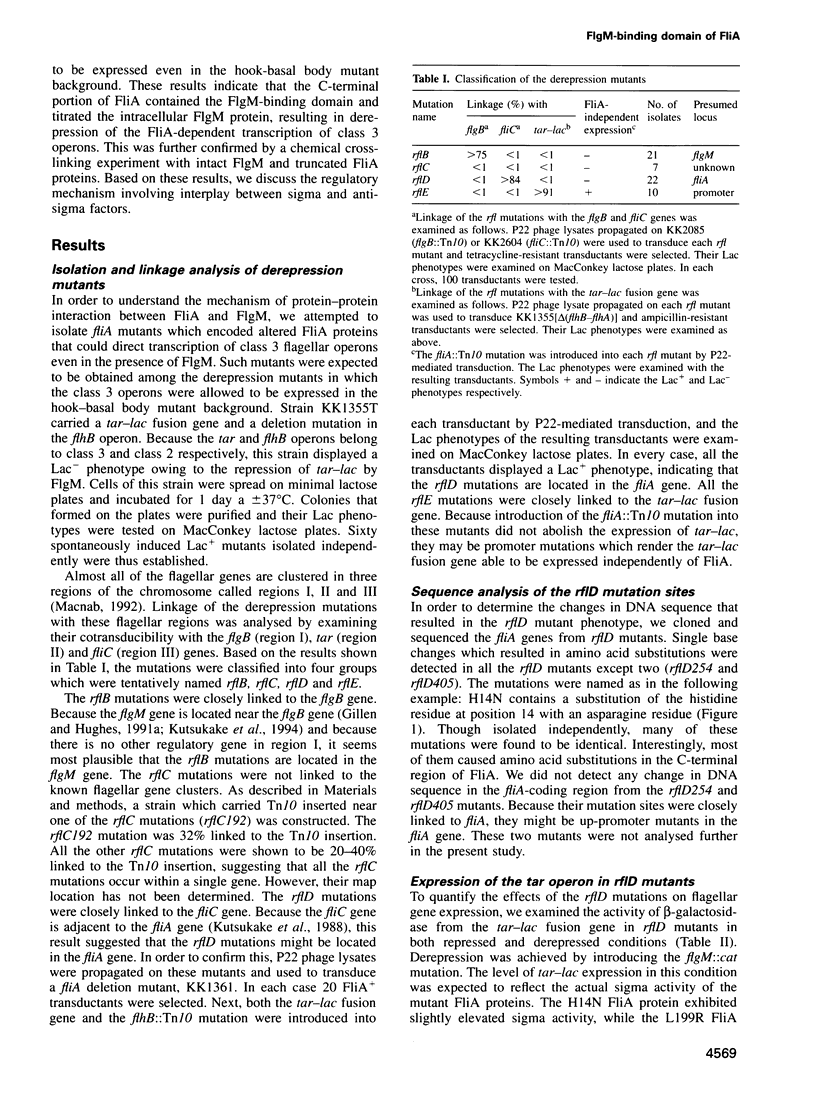
- Macnab R. M. Genetics and biogenesis of bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:131–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Amemura M., Kim S. K., Nakata A., Shinagawa H. Role of the sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase in transcriptional activation by activator protein PhoB in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):149–160. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L. L., Wright M. E. Identification of genes encoding components of the swarmer cell flagellar motor and propeller and a sigma factor controlling differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3361–3371. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3361-3371.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Ames G. F. Evidence for a common mechanism for the insertion of the Tn10 transposon and for the generation of Tn10-stimulated deletions. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 30;166(2):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00285924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi K., Kutsukake K., Suzuki H., Iino T. Gene fliA encodes an alternative sigma factor specific for flagellar operons in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):139–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00261713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi K., Kutsukake K., Suzuki H., Lino T. A novel transcriptional regulation mechanism in the flagellar regulon of Salmonella typhimurium: an antisigma factor inhibits the activity of the flagellum-specific sigma factor, sigma F. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3149–3157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Hu J. C., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Altered promoter recognition by mutant forms of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnbach M. N., Lory S. The fliA (rpoF) gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes an alternative sigma factor required for flagellin synthesis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):459–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Iino T., Horiguchi T., Yamaguchi S. Incomplete flagellar structures in nonflagellate mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):904–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.904-915.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. P., Hartin R. J., Ryu J. Transformation in restriction-deficient Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2561–2567. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]