Abstract
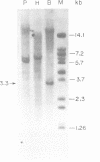
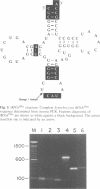
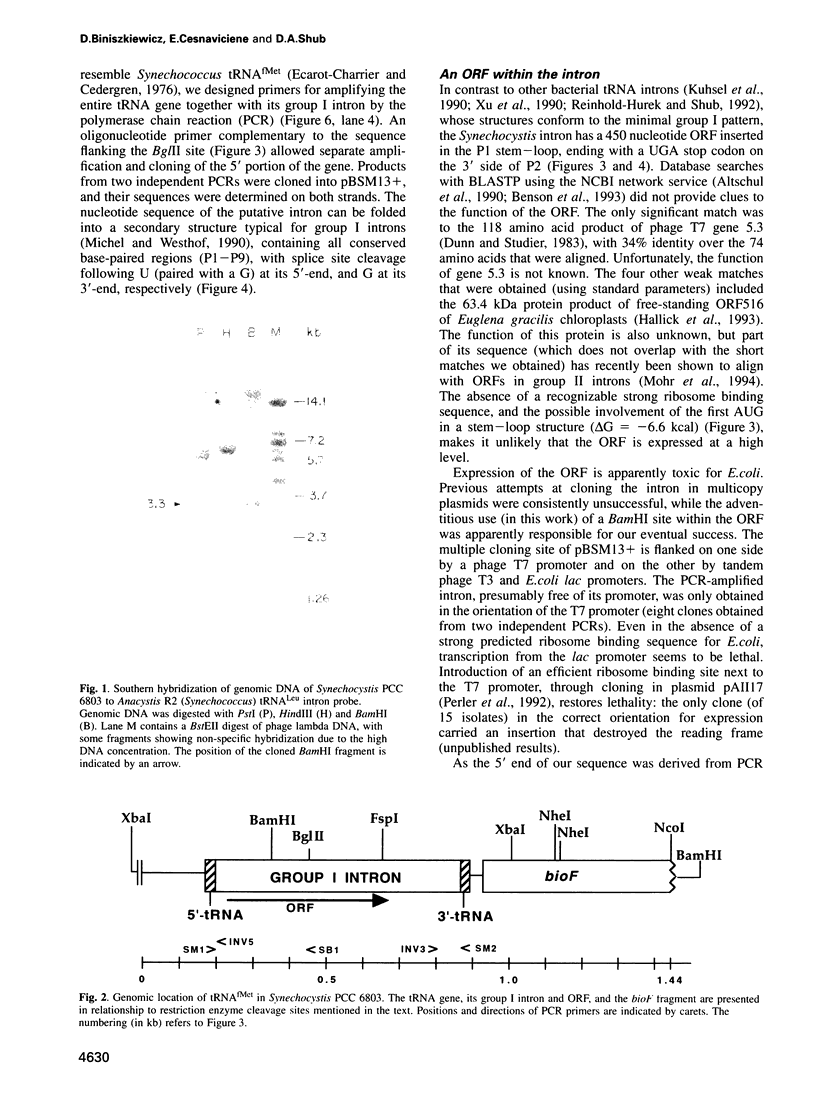
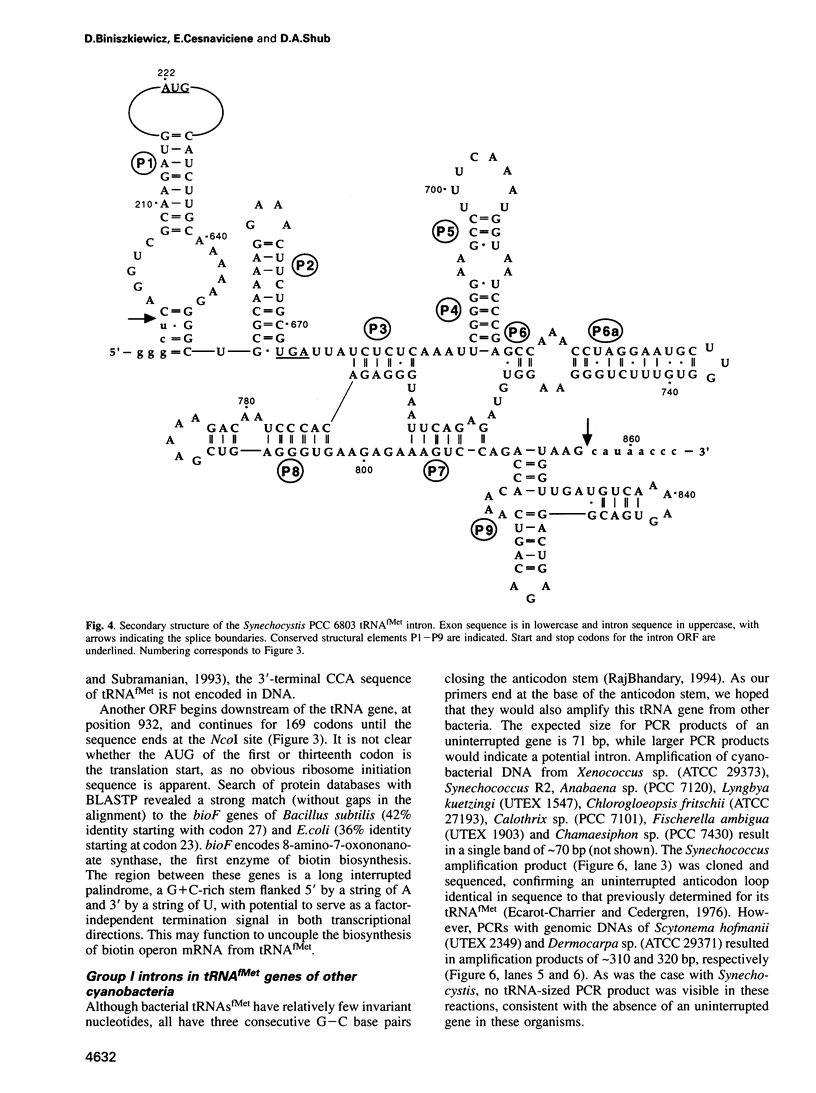
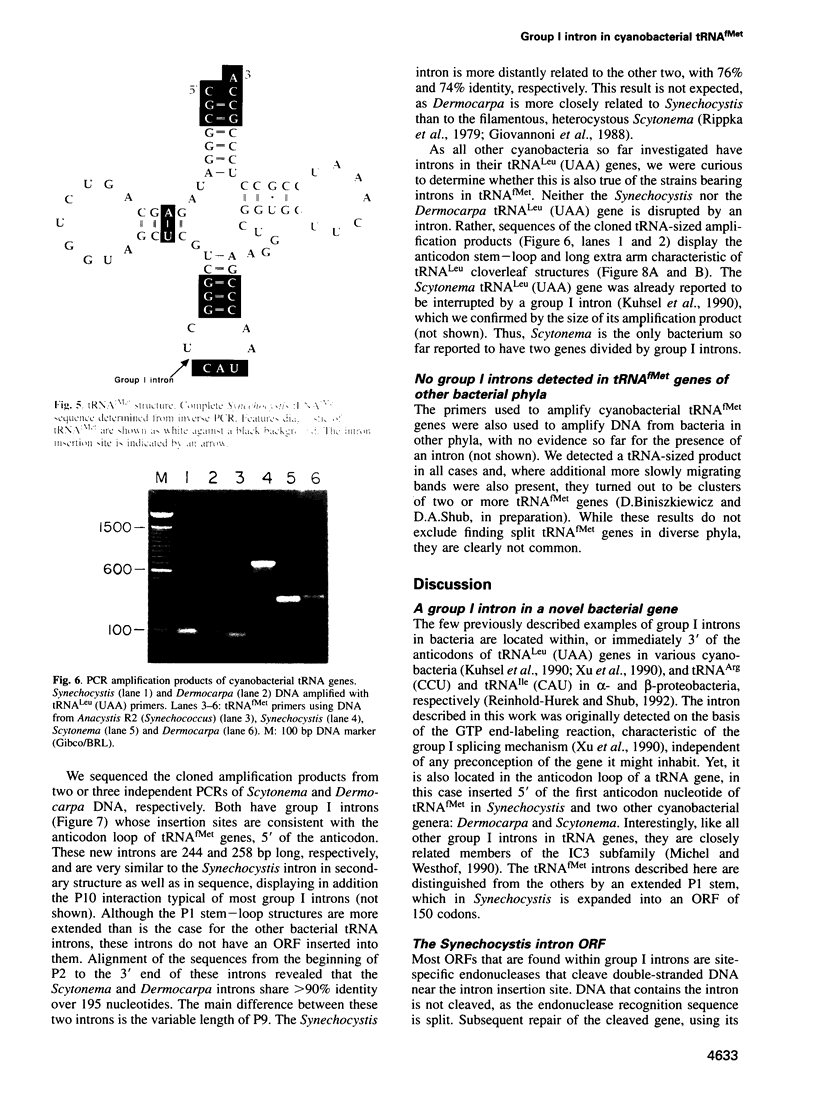
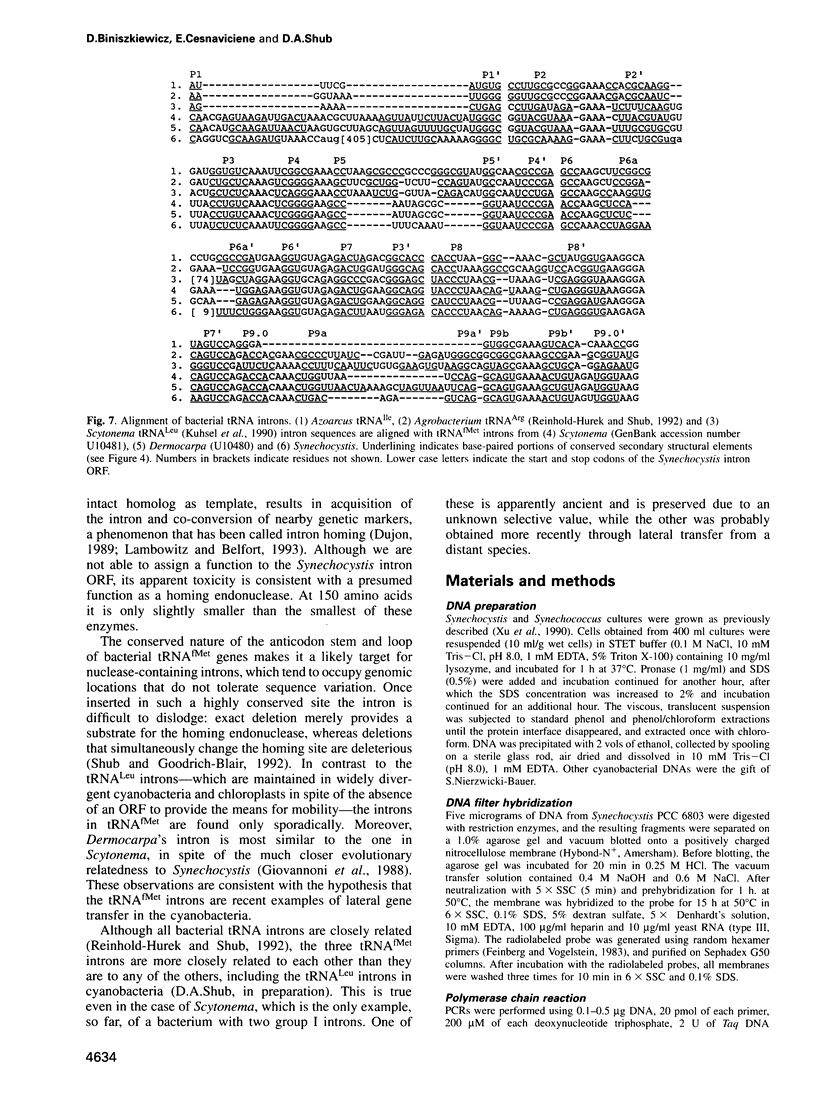
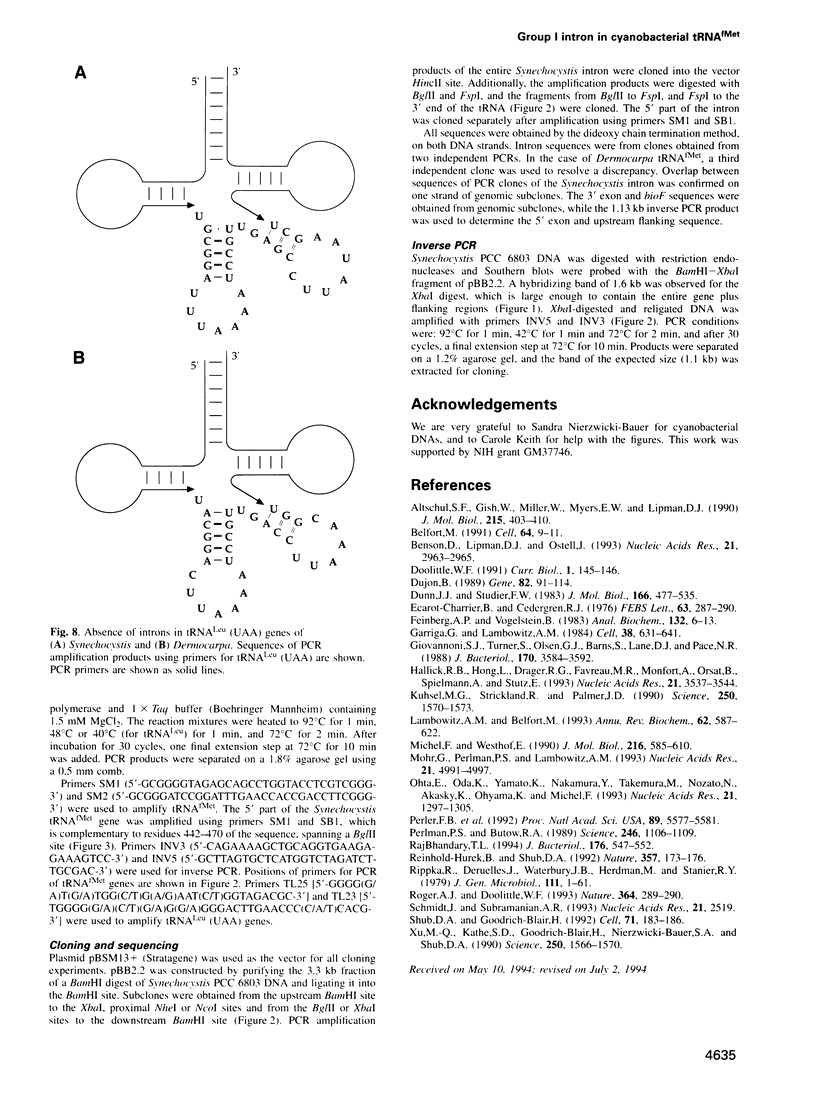
A group I self-splicing intron has been found in the anticodon loop of tRNA(fMet) genes in three cyanobacterial genera: Dermocarpa, Scytonema and Synechocystis; it is absent in nine others. The Synechocystis intron is also interrupted by an open reading frame (ORF) of 150 codons. Of these three bacteria, only Scytonema also contains the group I intron that has previously been reported in tRNA(Leu) (UAA) genes in both cyanobacteria and chloroplasts. The presence of an ORF in the tRNA(fMet) intron, the sporadic distribution of the intron among cyanobacteria and the lack of correlation between relatedness of the intron sequences and the bacteria in which they reside, are all consistent with recent introduction of this intron by lateral transfer.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D., Lipman D. J., Ostell J. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):2963–2965. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.2963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F. The origins of introns. Curr Biol. 1991 Jun;1(3):145–146. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90214-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: facts and mechanistic speculations--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):91–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecarot-Charrier B., Cedergren R. J. The preliminary sequence of tRNA Met F from Anacystis nidulans compared with other initiator tRNAs. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in neurospora mitochondria: self-splicing of a mitochondrial intron in vitro. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Turner S., Olsen G. J., Barns S., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. Evolutionary relationships among cyanobacteria and green chloroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3584–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3584-3592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhsel M. G., Strickland R., Palmer J. D. An ancient group I intron shared by eubacteria and chloroplasts. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.2125748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr G., Perlman P. S., Lambowitz A. M. Evolutionary relationships among group II intron-encoded proteins and identification of a conserved domain that may be related to maturase function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):4991–4997. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta E., Oda K., Yamato K., Nakamura Y., Takemura M., Nozato N., Akashi K., Ohyama K., Michel F. Group I introns in the liverwort mitochondrial genome: the gene coding for subunit 1 of cytochrome oxidase shares five intron positions with its fungal counterparts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1297–1305. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F. B., Comb D. G., Jack W. E., Moran L. S., Qiang B., Kucera R. B., Benner J., Slatko B. E., Nwankwo D. O., Hempstead S. K. Intervening sequences in an Archaea DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5577–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Mobile introns and intron-encoded proteins. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1106–1109. doi: 10.1126/science.2479980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RajBhandary U. L. Initiator transfer RNAs. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(3):547–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.3.547-552.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold-Hurek B., Shub D. A. Self-splicing introns in tRNA genes of widely divergent bacteria. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):173–176. doi: 10.1038/357173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger A. J., Doolittle W. F. Molecular evolution. Why introns-in-pieces? Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):289–290. doi: 10.1038/364289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Subramanian A. R. Sequence of the cyanobacterial tRNA(w) gene in Synechocystis PCC 6803: requirement of enzymatic 3' CCA attachment to the acceptor stem. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2519–2519. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Goodrich-Blair H. Protein introns: a new home for endonucleases. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90345-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M. Q., Kathe S. D., Goodrich-Blair H., Nierzwicki-Bauer S. A., Shub D. A. Bacterial origin of a chloroplast intron: conserved self-splicing group I introns in cyanobacteria. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2125747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]