Abstract
The ProW protein, located in the inner membrane of Escherichia coli, has a very unusual topology with a 100-residue-long N-terminal tail protruding into the periplasmic space. We have studied the mechanism of membrane translocation of the periplasmic tail by analysing ProW-PhoA and ProW-Lep fusion proteins, both in wild-type cells and in cells with an impaired sec machinery. Our results show that the translocation efficiency is not affected by treatments that compromise the SecA and SecY functions, but that translocation is completely blocked by dissipation of the proton motive force or by the introduction of extra positively charged residues into the N-terminal tail. This suggests that the sec machinery can act properly only on domains located on the C-terminal side of a translocation signal, and that the N-terminal tail is driven through the membrane by a mechanism that involves the proton motive force.
Full text
PDF
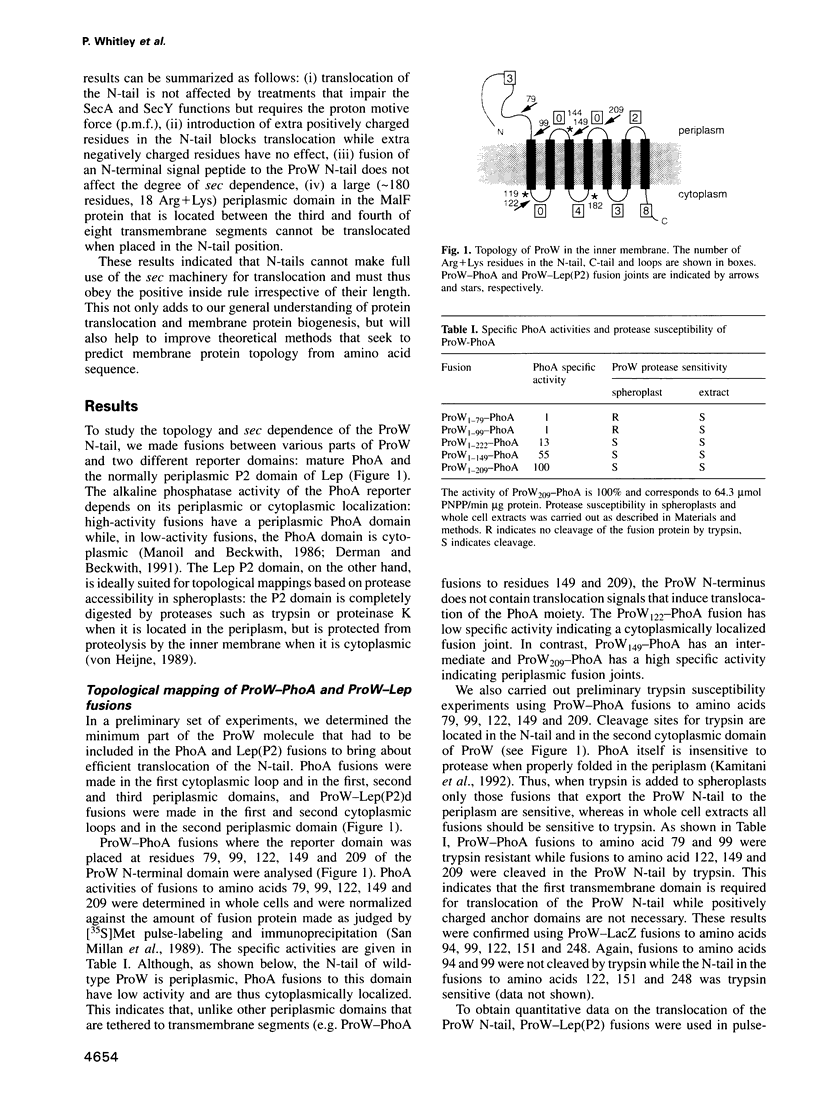






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson H., von Heijne G. Membrane protein topology: effects of delta mu H+ on the translocation of charged residues explain the 'positive inside' rule. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2267–2272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson H., von Heijne G. Sec dependent and sec independent assembly of E. coli inner membrane proteins: the topological rules depend on chain length. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):683–691. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T., Jacq A., Brickman E., Beckwith J., Taura T., Ueguchi C., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Characterization of cold-sensitive secY mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7005–7010. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7005-7010.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Randall L. L. The requirement for energy during export of beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli is fulfilled by the total protonmotive force. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):895–900. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. The role of charged amino acids in the localization of secreted and membrane proteins. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90378-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Determinants of membrane protein topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao G., Dalbey R. E. Translocation of N-terminal tails across the plasma membrane. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4662–4669. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Hanson A. D. Prokaryotic osmoregulation: genetics and physiology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:569–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Wickner W. Leader peptidase of Escherichia coli: critical role of a small domain in membrane assembly. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):783–787. doi: 10.1126/science.3544218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C. J., Bole D. G., Quay S. C., Oxender D. L. Role for membrane potential in the secretion of protein into the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5396–5400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase fails to acquire disulfide bonds when retained in the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7719–7722. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7719-7722.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmann M., Beckwith J. Proper insertion of a complex membrane protein in the absence of its amino-terminal export signal. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16530–16533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., Schwarz H., Degen M., Henning U. A lower size limit exists for export of fragments of an outer membrane protein (OmpA) of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):771–775. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Green G. N., Boyd D., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of the membrane insertion and topology of MalF, a cytoplasmic membrane protein of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):501–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90539-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafvelin G., von Heijne G. Topological "frustration" in multispanning E. coli inner membrane proteins. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowrishankar J. Nucleotide sequence of the osmoregulatory proU operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1923–1931. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1923-1931.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessey E. S., Hashemzadeh-Bonehi L., Hunt L. A., Broome-Smith J. K. Assembly of eukaryotic class III (N-out, C-in) membrane proteins into the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 27;331(1-2):159–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80317-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S., Lee J. H., Ray D. S. High-level expression of M13 gene II protein from an inducible polycistronic messenger RNA. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani S., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Identification and characterization of an Escherichia coli gene required for the formation of correctly folded alkaline phosphatase, a periplasmic enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):57–62. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A. Alterations in the extracellular domain of M13 procoat protein make its membrane insertion dependent on secA and secY. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):267–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Evidence for specificity at an early step in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):267–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.267-274.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. I., Kuhn A., Dalbey R. E. Distinct domains of an oligotopic membrane protein are Sec-dependent and Sec-independent for membrane insertion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):938–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Chang J. A., Simoni R. D. A topological analysis of subunit alpha from Escherichia coli F1F0-ATP synthase predicts eight transmembrane segments. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10541–10550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C. Analysis of membrane protein topology using alkaline phosphatase and beta-galactosidase gene fusions. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;34:61–75. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61676-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern K., Beckwith J. Membrane insertion of the Escherichia coli MalF protein in cells with impaired secretion machinery. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20870–20876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern K., Ehrmann M., Beckwith J. Decoding signals for membrane protein assembly using alkaline phosphatase fusions. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2773–2782. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Cabelli R. J., Dolan K. M., Jarosik G. P. Azide-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli alter the SecA protein, an azide-sensitive component of the protein export machinery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Werner P. K., Müller M. Insertion of proteins into bacterial membranes: mechanism, characteristics, and comparisons with the eucaryotic process. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):333–366. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.333-366.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Yamada M., Suda K., Erni B., Rak B., Lengeler J., Stewart G. C., Waygood E. B., Rapoport G. Bacterial proteins with N-terminal leader sequences resembling mitochondrial targeting sequences of eukaryotes. Biochimie. 1988 Dec;70(12):1743–1748. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Millan J. L., Boyd D., Dalbey R., Wickner W., Beckwith J. Use of phoA fusions to study the topology of the Escherichia coli inner membrane protein leader peptidase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5536–5541. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5536-5541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. G., Rollo E. E., Grodberg J., Oliver D. B. Nucleotide sequence of the secA gene and secA(Ts) mutations preventing protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3404–3414. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3404-3414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. M., Cannon J. G., Bassford P. J., Jr Regions of maltose-binding protein that influence SecB-dependent and SecA-dependent export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6988–6995. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6988-6995.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxler B., Beckwith J. Assembly of a hetero-oligomeric membrane protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10852–10856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Rice M., Wickner W. Effects of two sec genes on protein assembly into the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1836–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Chang Y. Y., Daniels G. A., Wu L. F., Tomich J. M., Yamada M., Saier M. H., Jr Insertion of the mannitol permease into the membrane of Escherichia coli. Possible involvement of an N-terminal amphiphilic sequence. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17863–17871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Wickner W. Energetics and intermediates of the assembly of Protein OmpA into the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3920–3925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Control of topology and mode of assembly of a polytopic membrane protein by positively charged residues. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):456–458. doi: 10.1038/341456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Gavel Y. Topogenic signals in integral membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):671–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane protein structure prediction. Hydrophobicity analysis and the positive-inside rule. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90934-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]