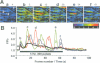
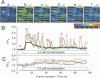
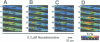
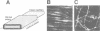Abstract
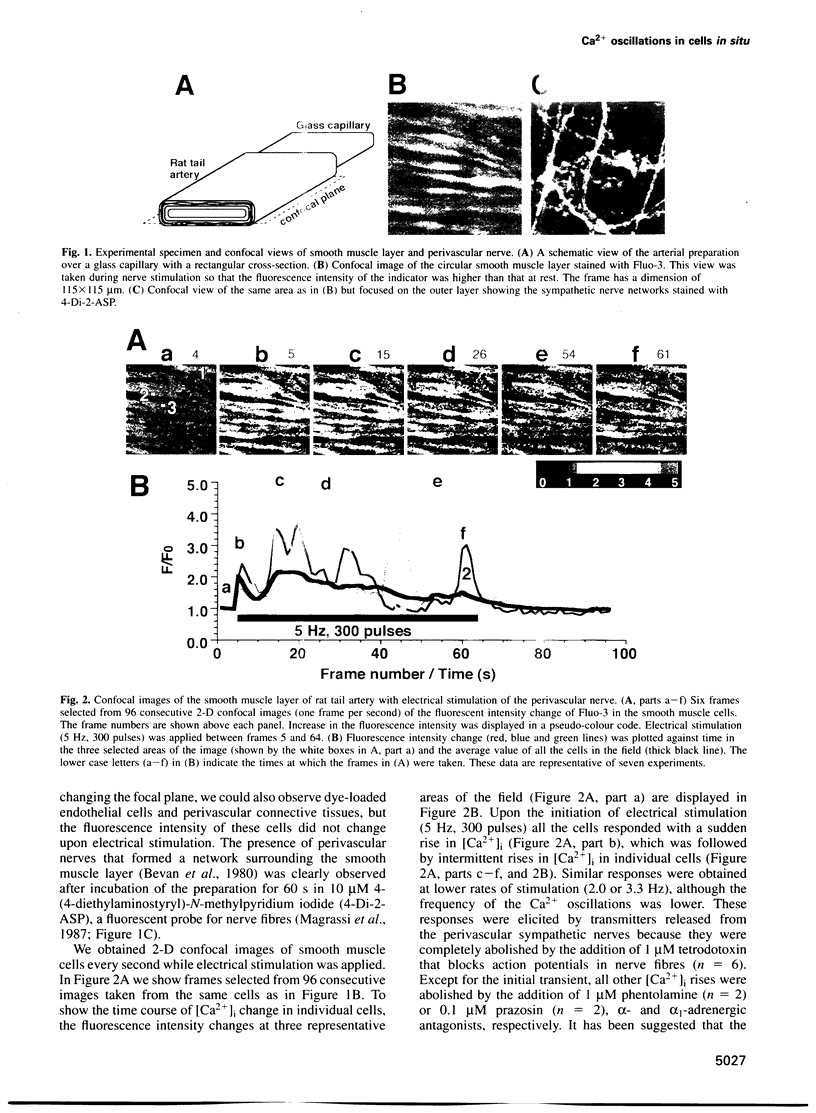
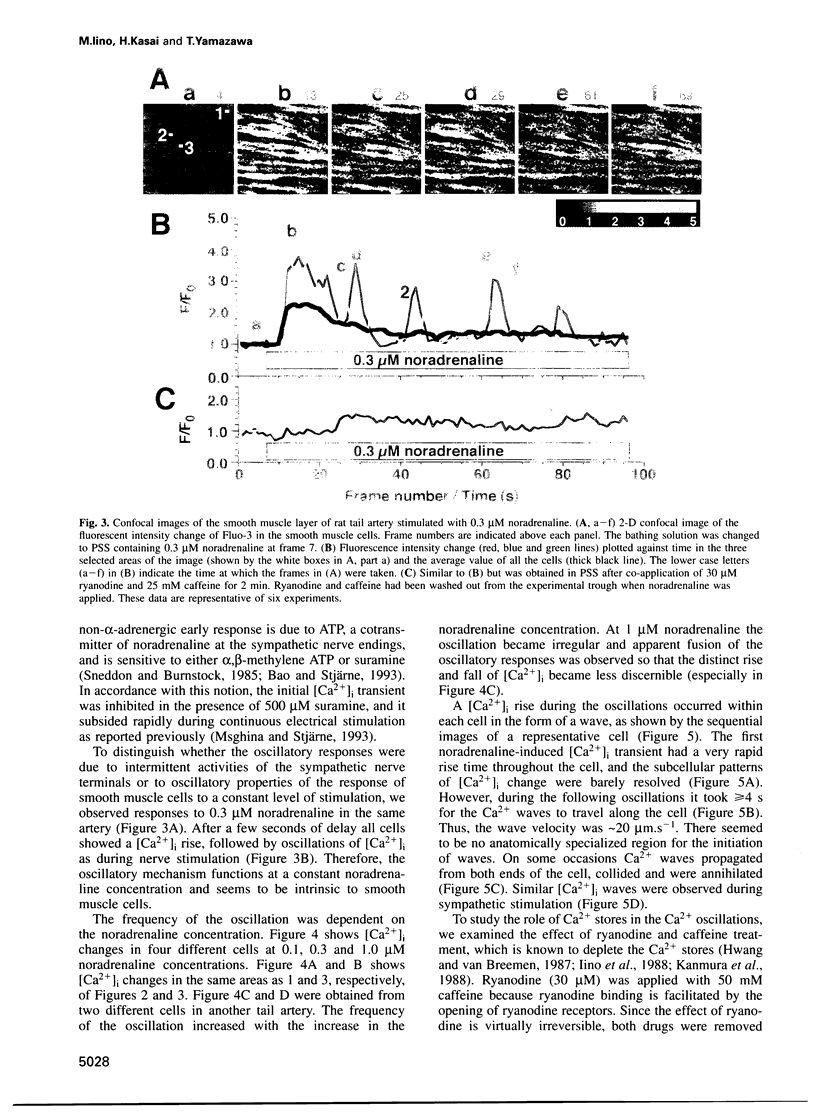
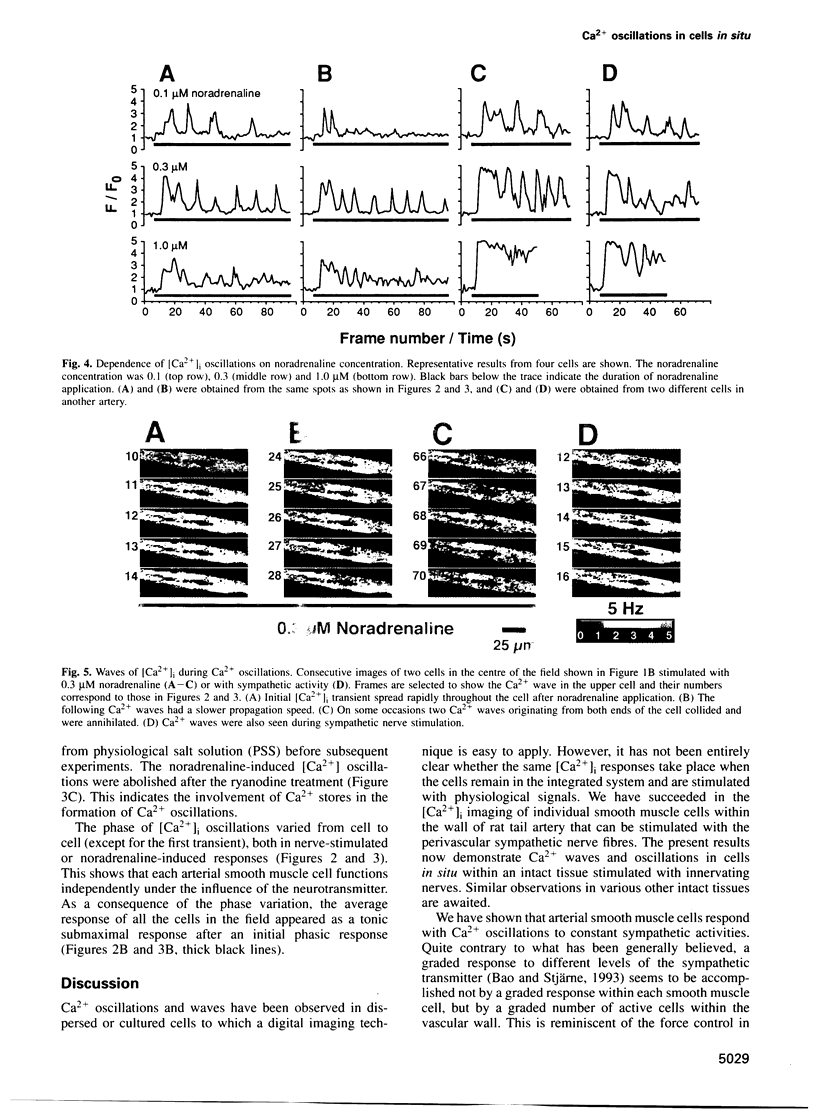
The intermittent rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i oscillation) has been observed in many types of isolated cells, yet it has not been demonstrated whether it plays an essential role during nerve stimulation in situ. We used confocal microscopy to study Ca2+ transients in individual smooth muscle cells in situ within the wall of small arteries stimulated with perivascular sympathetic nerves or noradrenaline. We show here that the sympathetic adrenergic regulation of arterial smooth muscle cells involves the oscillation of [Ca2+]i that propagates within the cell in the form of a wave. Ca2+ release from intracellular stores plays a key role in the oscillation because it is blocked after the store depletion by ryanodine treatment. Ca2+ influx through the plasma membrane sustains the oscillation by replenishing the Ca2+ stores. These results demonstrate the involvement of [Ca2+]i oscillations in the neural regulation of effector cells within the integrated system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bao J. X., Stjärne L. Dual contractile effects of ATP released by field stimulation revealed by effects of alpha,beta-methylene ATP and suramin in rat tail artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1421–1428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Galione A. Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3074–3082. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.2847949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Wier W. G. Agonist-induced [Ca2+]i waves and Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in mammalian vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):H576–H586. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.2.H576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Catecholamine action on smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Mar;39(1):49–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho P., Lechleiter J. D. Increased frequency of calcium waves in Xenopus laevis oocytes that express a calcium-ATPase. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):226–229. doi: 10.1126/science.8385800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine C. E., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Sarcoplasmic reticulum and excitation-contraction coupling in mammalian smooth muscles. J Cell Biol. 1972 Mar;52(3):690–718. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.3.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard S., Clapham D. Acceleration of intracellular calcium waves in Xenopus oocytes by calcium influx. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):229–232. doi: 10.1126/science.8385801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Paranjape S., Tsien R. Y. Generation of calcium oscillations in fibroblasts by positive feedback between calcium and IP3. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1986413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Edwards F. R. Sympathetic neuroeffector transmission in arteries and arterioles. Physiol Rev. 1989 Apr;69(2):546–604. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.2.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. An electrophysiological analysis of the effects of noradrenaline and alpha-receptor antagonists on neuromuscular transmission in mammalian muscular arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):651–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang K. S., van Breemen C. Ryanodine modulation of 45Ca efflux and tension in rabbit aortic smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):343–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00581127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Endo M. Calcium-dependent immediate feedback control of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-induced Ca2+ release. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):76–78. doi: 10.1038/360076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Kobayashi T., Endo M. Use of ryanodine for functional removal of the calcium store in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):417–422. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80730-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Yamazawa T., Miyashita Y., Endo M., Kasai H. Critical intracellular Ca2+ concentration for all-or-none Ca2+ spiking in single smooth muscle cells. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5287–5291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Roles of extrajunctional receptors in the response of guinea-pig mesenteric and rat tail arteries to adrenergic nerves. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:409–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Repetitive spikes in cytoplasmic calcium evoked by histamine in human endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):40–45. doi: 10.1038/335040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F. The path of calcium in cytosolic calcium oscillations: a unifying hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9883–9887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Theler J. M., Capponi A. M., Vallotton M. B. Characterization of oscillations in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration and measurement of cytosolic Na+ concentration changes evoked by angiotensin II and vasopressin in individual rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Use of microfluorometry and digital imaging. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12618–12626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanmura Y., Missiaen L., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Ryanodine reduces the amount of calcium in intracellular stores of smooth-muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Dec;413(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00582525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J. D., Clapham D. E. Molecular mechanisms of intracellular calcium excitability in X. laevis oocytes. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrassi L., Purves D., Lichtman J. W. Fluorescent probes that stain living nerve terminals. J Neurosci. 1987 Apr;7(4):1207–1214. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-04-01207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Calcium spiking. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:153–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic calcium based on rhodamine and fluorescein chromophores. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8171–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msghina M., Stjärne L. Sympathetic transmitter release in rat tail artery and mouse vas deferens: facilitation and depression during high frequency stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1993 May 28;155(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90668-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J., Aalkjaer C. Structure and function of small arteries. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):921–961. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.4.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Patlak J. B., Worley J. F., Standen N. B. Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Hoyland J., Mason W. T., Irvine R. F. Spatial dynamics of intracellular calcium in agonist-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C675–C686. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. C., Petersen O. H., Berridge M. J. The role of endoplasmic reticulum calcium pumps during cytosolic calcium spiking in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22262–22264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Burnstock G. ATP as a co-transmitter in rat tail artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 30;106(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Vascular smooth muscle. I. Normal structure, pathology, biochemistry, and biophysics. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Dec;20(4):197–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Potter B. V., Petersen O. H. Pulsatile intracellular calcium release does not depend on fluctuations in inositol trisphosphate concentration. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):317–320. doi: 10.1038/339317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao X. H., Rand M. J. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists enhance vasoconstrictor responses to alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonists in the rat tail artery by increasing the influx of Ca2+. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):1032–1038. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Y., Parker I. Ca2+ influx modulation of temporal and spatial patterns of inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ liberation in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1994 Apr 1;476(1):17–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]