Abstract
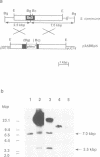
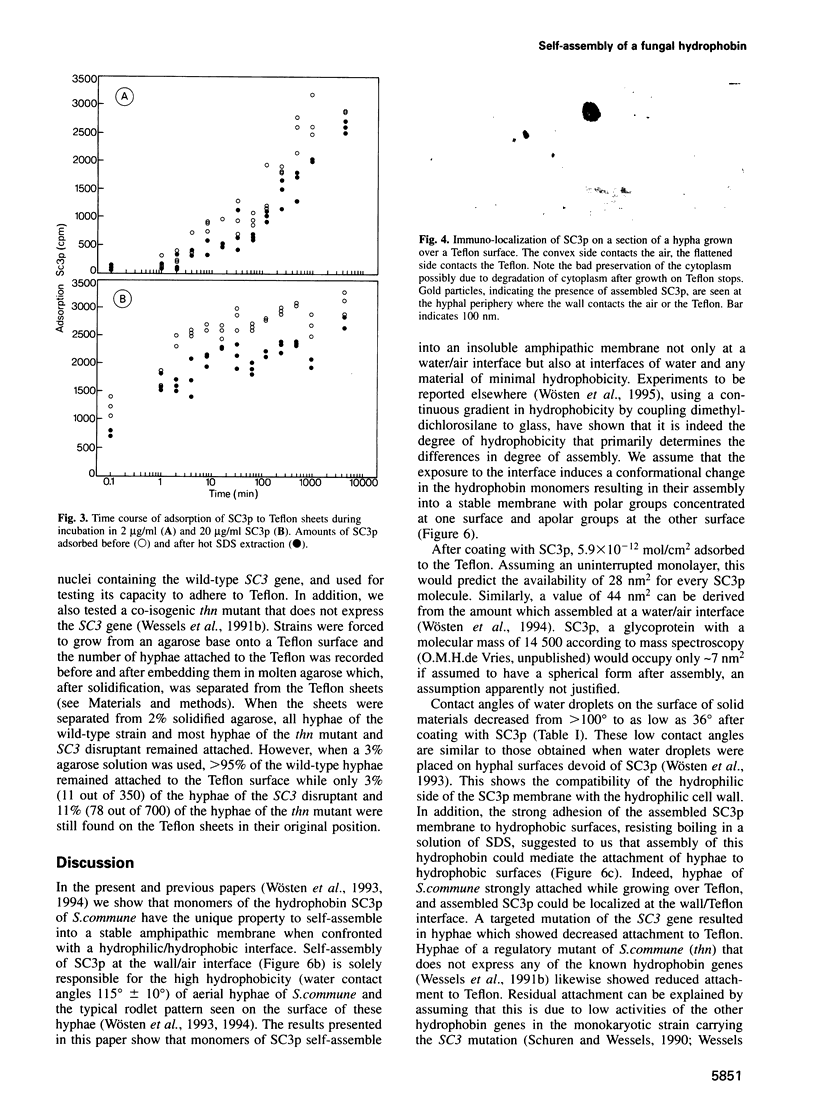
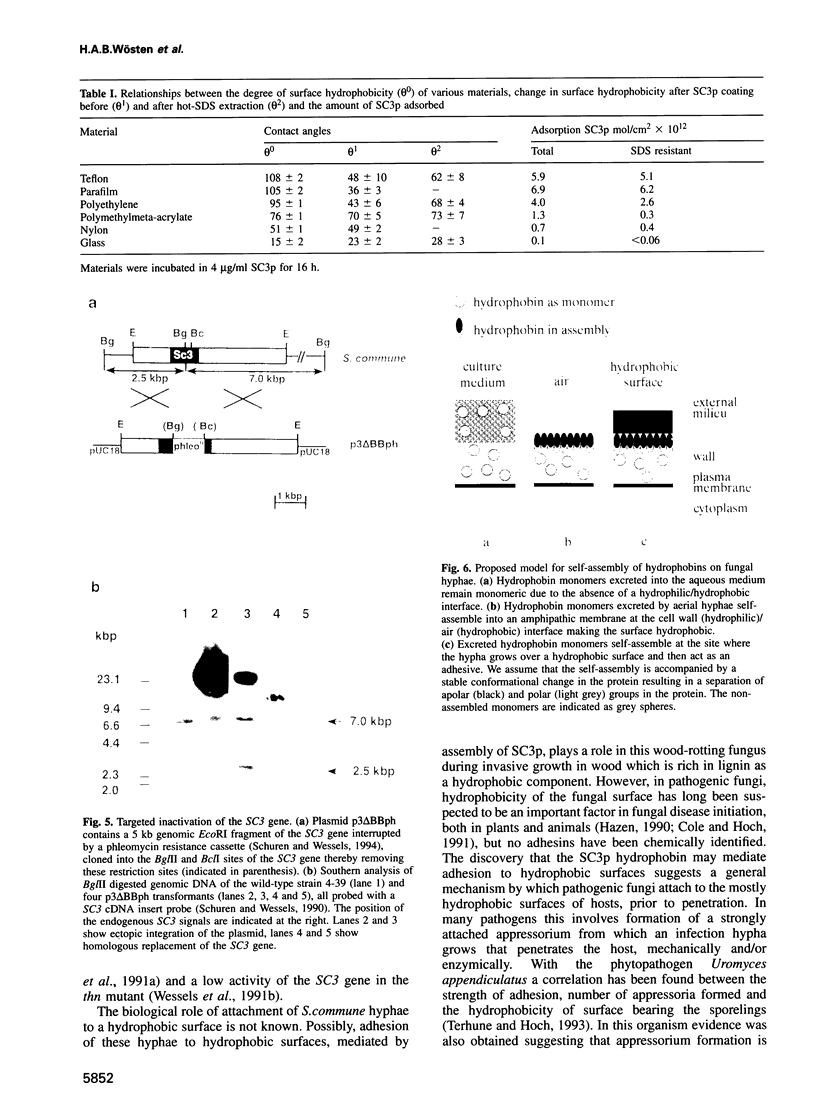
The SC3p hydrophobin of Schizophyllum commune is a small hydrophobic protein (100-101 amino acids with eight cysteine residues) that self-assembles at a water/air interface and coats aerial hyphae with an SDS-insoluble protein membrane, at the outer side highly hydrophobic and with a typical rodlet pattern. SC3p monomers in water also self-assemble at the interfaces between water and oils or hydrophobic solids. These materials are then coated with a 10 nm thick SDS-insoluble assemblage of SC3p making their surfaces hydrophilic. Hyphae of S. commune growing on a Teflon surface became firmly attached and SC3p was shown to be present between the fungal cell wall and the Teflon. Decreased attachment of hyphae to Teflon was observed in strains not expressing SC3, i.e. a strain containing a targeted mutation in this gene and a regulatory mutant thn. These findings indicate that hydrophobins, in addition to forming hydrophobic wall coatings, play a role in adherence of fungal hyphae to hydrophobic surfaces.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell-Pedersen D., Dunlap J. C., Loros J. J. The Neurospora circadian clock-controlled gene, ccg-2, is allelic to eas and encodes a fungal hydrophobin required for formation of the conidial rodlet layer. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2382–2394. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dons J. J., de Vries O. M., Wessels J. G. Characterization of the genome of the basidiomycete Schizophyllum commune. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 20;563(1):100–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauter F. R., Russo V. E., Yanofsky C. Developmental and light regulation of eas, the structural gene for the rodlet protein of Neurospora. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2373–2381. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuren F. H., Harmsen M. C., Wessels J. G. A homologous gene-reporter system for the basidiomycete Schizophyllum commune based on internally deleted homologous genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(1-2):91–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00279535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuren F. H., Wessels J. G. Highly-efficient transformation of the homobasidiomycete Schizophyllum commune to phleomycin resistance. Curr Genet. 1994 Aug;26(2):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00313808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuren F. H., Wessels J. G. Two genes specifically expressed in fruiting dikaryons of Schizophyllum commune: homologies with a gene not regulated by mating-type genes. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90180-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Leger R. J., Staples R. C., Roberts D. W. Cloning and regulatory analysis of starvation-stress gene, ssgA, encoding a hydrophobin-like protein from the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. Gene. 1992 Oct 12;120(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90019-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer M. A., Dean R. A., Sewall T. C., Timberlake W. E. Rodletless, a new Aspergillus developmental mutant induced by directed gene inactivation. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1161–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot N. J., Ebbole D. J., Hamer J. E. Identification and characterization of MPG1, a gene involved in pathogenicity from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell. 1993 Nov;5(11):1575–1590. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.11.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels J. G., de Vries O. M., Asgeirsdóttir S. A., Springer J. The thn mutation of Schizophyllum commune, which suppresses formation of aerial hyphae, affects expression of the Sc3 hydrophobin gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2439–2445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels JGH., De Vries OMH., Asgeirsdottir S. A., Schuren FHJ. Hydrophobin Genes Involved in Formation of Aerial Hyphae and Fruit Bodies in Schizophyllum. Plant Cell. 1991 Aug;3(8):793–799. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.8.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosten HAB., De Vries OMH., Wessels JGH. Interfacial Self-Assembly of a Fungal Hydrophobin into a Hydrophobic Rodlet Layer. Plant Cell. 1993 Nov;5(11):1567–1574. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.11.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wösten H. A., Asgeirsdóttir S. A., Krook J. H., Drenth J. H., Wessels J. G. The fungal hydrophobin Sc3p self-assembles at the surface of aerial hyphae as a protein membrane constituting the hydrophobic rodlet layer. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;63(1):122–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. L., Stumpf M. A., Hoch H. C., Kung C. A mechanosensitive channel in whole cells and in membrane patches of the fungus Uromyces. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.1716786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]