Abstract
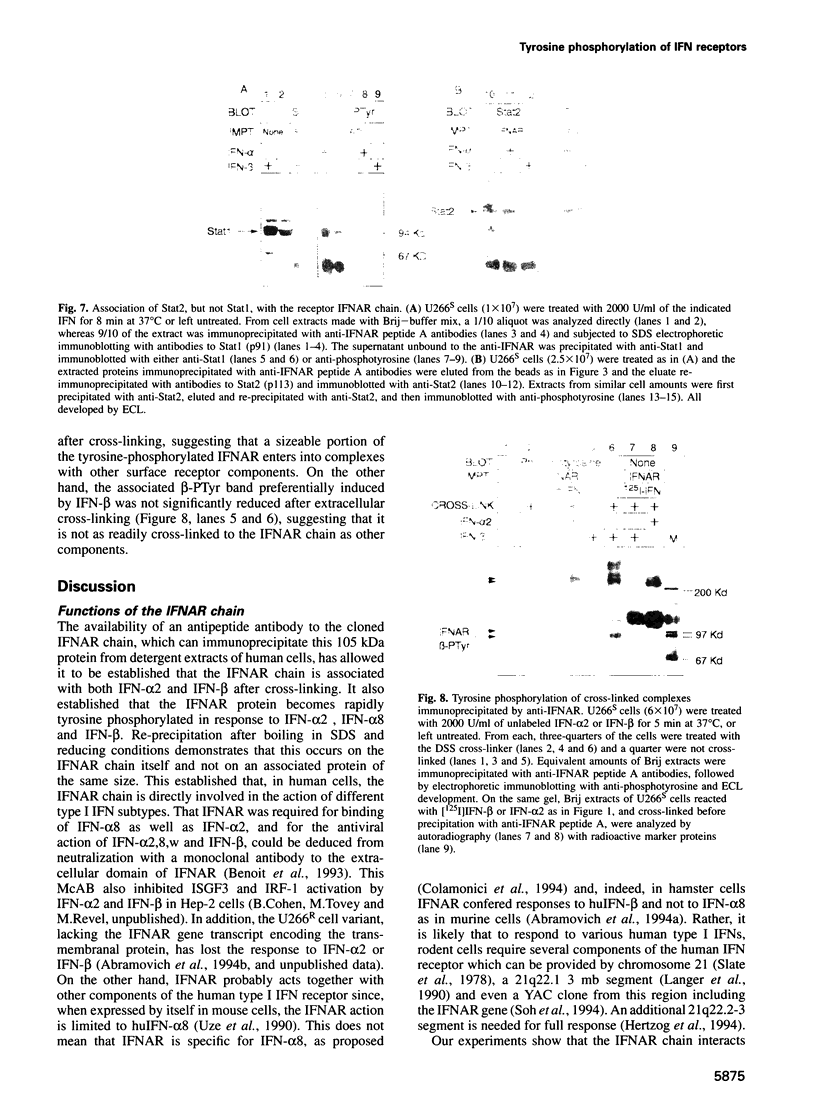
The human interferon alpha-receptor (IFNAR gene product) is a transmembranal protein of 557 amino acids with an intracytoplasmic domain of 100 amino acids containing four tyrosines. Antibodies to a C-terminal peptide (residues 521-536) were developed which efficiently immunoprecipitate the 105 kDa IFNAR protein from detergent extracts of human cells. We show that the IFNAR protein becomes tyrosine phosphorylated within 5 min after treatment of human myeloma U266 cells with IFN-alpha 2, IFN-alpha 8 or IFN-beta. The IFNAR chain interacts with both IFN-alpha 2 and IFN-beta, as demonstrated by cross-linking. Among elements involved in signal transduction by type I IFNs, the tyrosine kinase Tyk2 but not Jak1, and the ISGF3 transcription factor subunit Stat2 (p113) but not Stat1 (p91), are found associated with the IFNAR protein. After IFN-beta treatment for 5 min, a tyrosine-phosphorylated protein of approximately 95 kDa (beta-PTyr) is found bound to IFNAR, but can be dissociated by denaturation. The beta-PTyr protein is present on the cell surface, like IFNAR, as shown by extracellular biotin tagging. The ratio of beta-PTyr to IFNAR tyrosine phosphorylation is much higher with IFN-beta than with IFN-alpha 2 or 8. Both are IFN dependent and abrogated by a monoclonal antibody which blocks IFNAR action. The beta-PTyr component may represent an important difference in the action of IFN-beta as compared with IFN-alpha in their shared receptor system.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovich C., Chebath J., Revel M. The human interferon alpha-receptor protein confers differential responses to human interferon-beta versus interferon-alpha subtypes in mouse and hamster cell transfectants. Cytokine. 1994 Jul;6(4):414–424. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(94)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramovich C., Ratovitski E., Lundgren E., Revel M. Identification of mRNAs encoding two different soluble forms of the human interferon alpha-receptor. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 7;338(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M., Gröbke M., Dreiding P. Various human interferon alpha subclasses cross-react with common receptors: their binding affinities correlate with their specific biological activities. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit P., Maguire D., Plavec I., Kocher H., Tovey M., Meyer F. A monoclonal antibody to recombinant human IFN-alpha receptor inhibits biologic activity of several species of human IFN-alpha, IFN-beta, and IFN-omega. Detection of heterogeneity of the cellular type I IFN receptor. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):707–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Benech P., Hovanessian A., Galabru J., Revel M. Four different forms of interferon-induced 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase identified by immunoblotting in human cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3852–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernajovsky Y., Mory Y., Chen L., Marks Z., Novick D., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Efficient constitutive production of human fibroblast interferon by hamster cells transformed with the IFN-beta 1 gene fused to an SV40 early promoter. DNA. 1984 Aug;3(4):297–308. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., D'Alessandro F., Diaz M. O., Gregory S. A., Neckers L. M., Nordan R. Characterization of three monoclonal antibodies that recognize the interferon alpha 2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7230–7234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Domanski P. Identification of a novel subunit of the type I interferon receptor localized to human chromosome 21. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10895–10899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Pfeffer L. M., D'Alessandro F., Platanias L. C., Gregory S. A., Rosolen A., Nordan R., Cruciani R. A., Diaz M. O. Multichain structure of the IFN-alpha receptor on hematopoietic cells. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2126–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Pfeffer L. M. Structure of the human interferon alpha receptor. Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Nov;52(2):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90010-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Uyttendaele H., Domanski P., Yan H., Krolewski J. J. p135tyk2, an interferon-alpha-activated tyrosine kinase, is physically associated with an interferon-alpha receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3518–3522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores I., Mariano T. M., Pestka S. Human interferon omega (omega) binds to the alpha/beta receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19875–19877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Schindler C., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr The proteins of ISGF-3, the interferon alpha-induced transcriptional activator, define a gene family involved in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7840–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlund A. C., Farrar M. A., Viviano B. L., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced IFN gamma receptor tyrosine phosphorylation couples the receptor to its signal transduction system (p91). EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1591–1600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzog P. J., Hwang S. Y., Holland K. A., Tymms M. J., Iannello R., Kola I. A gene on human chromosome 21 located in the region 21q22.2 to 21q22.3 encodes a factor necessary for signal transduction and antiviral response to type I interferons. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14088–14093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu R., Gan Y., Liu J., Miller D., Zoon K. C. Evidence for multiple binding sites for several components of human lymphoblastoid interferon-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12591–12595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns T. G., Mackay I. R., Callister K. A., Hertzog P. J., Devenish R. J., Linnane A. W. Antiproliferative potencies of interferons on melanoma cell lines and xenografts: higher efficacy of interferon beta. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Aug 5;84(15):1185–1190. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.15.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Rashidbaigi A., Lai L. W., Patterson D., Jones C. Sublocalization on chromosome 21 of human interferon-alpha receptor gene and the gene for an interferon-gamma response protein. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 May;16(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF01233359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutfalla G., Gardiner K., Proudhon D., Vielh E., Uzé G. The structure of the human interferon alpha/beta receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2802–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlin G., Falcoff E., Aguet M. 125I-labelled human interferons alpha, beta and gamma: comparative receptor-binding data. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1149–1152. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Cohen B., Rubinstein M. Soluble interferon-alpha receptor molecules are present in body fluids. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):445–448. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81523-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Cohen B., Rubinstein M. The human interferon alpha/beta receptor: characterization and molecular cloning. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., Schindler C. Early events in signalling by interferons. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):338–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platanias L. C., Colamonici O. R. Interferon alpha induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of its receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24053–24057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platanias L. C., Uddin S., Colamonici O. R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the alpha and beta subunits of the type I interferon receptor. Interferon-beta selectively induces tyrosine phosphorylation of an alpha subunit-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):17761–17764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin A., Sarkar F. H., Dutkowski R., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H., Gupta S. L. Receptors for human alpha and beta interferon but not for gamma interferon are specified by human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Bash D., Ruddle F. H. Antibodies to a cell-surface component coded by human chromosome 21 inhibit action of interferon. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):139–141. doi: 10.1038/260139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum M. G., Yung W. K., Kelleher P. J., Ruzicka F., Steck P. A., Borden E. C. Growth inhibitory effects of interferon-beta but not interferon-alpha on human glioma cells: correlation of receptor binding, 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and protein kinase activity. J Interferon Res. 1990 Apr;10(2):141–151. doi: 10.1089/jir.1990.10.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe M., Princler G. L., Faltynek C. R. Characterization of the human type I interferon receptor by ligand blotting. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slate D. L., Shulman L., Lawrence J. B., Revel M., Ruddle F. H. Presence of human chromosome 21 alone is sufficient for hybrid cell sensitivity to human interferon. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):319–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.319-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soh J., Mariano T. M., Lim J. K., Izotova L., Mirochnitchenko O., Schwartz B., Langer J. A., Pestka S. Expression of a functional human type I interferon receptor in hamster cells: application of functional yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) screening. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):18102–18110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzé G., Lutfalla G., Gresser I. Genetic transfer of a functional human interferon alpha receptor into mouse cells: cloning and expression of its cDNA. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90738-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]