Abstract
In this paper, we consider the problem of the accuracy of estimating the location and other attributes of a moving single molecule whose trajectory is imaged by fluorescence microscopy. As accuracy in parameter estimation is closely related to the Fisher information matrix, we first give a general expression of the Fisher information matrix for the estimated parameters for a single object moving in three-dimensional (3D) space. Explicit Cramér-Rao lower bound (CRLB) expressions are then obtained from the Fisher information matrix for a single object moving in the two-dimensional (2D) focus plane with the object trajectory being either linear or circular. We also investigate how extraneous noise sources, pixelation, parameters of the detection system and parameters of the trajectory affect the limit of the accuracy. The results obtained in this paper provide insights that enable the experimentalists to optimize their experimental setups for tracking single molecules in order to achieve the best possible accuracy. They are also applicable to the general problem of tracking an object using quantum limited detectors.
Index Terms: Cramér-Rao lower bound (CRLB), Fisher information matrix, fluorescence microscopy, limit of the accuracy, moving object, quantum limited imaging, single-molecule microscopy
I. Introduction
In recent years, single-molecule fluorescence microscopy has become an important biological research tool in cell biology, biochemistry and biophysics and is experiencing a rapid growth in its applications [1]–[6]. It provides, for example, quantitative information on the behaviour of molecules in cells, which is seldom available through bulk studies due to averaging effects [7], [8]. One way of gaining new insights into biological and cellular processes is to optically track the molecules as they move over time [9]–[11]. It is therefore important to know the accuracy with which the location and other attributes of a single molecule can be determined with fluorescence microscopy. It has been shown in [12] that the localization accuracy has to be taken into account when analyzing the diffusion behaviour of single molecules, as otherwise noisy measurements of the single molecule locations could be misinterpreted as sub-diffusion. In addition to the noise, the molecular motion during the finite acquisition time also contributes to the localization error [13]. Hence, knowing the limit of the accuracy of the parameters concerned not only helps to validate the results obtained but also provides a means to evaluate and optimize the single-molecule tracking experimental setups and various algorithms used [14].
To obtain the lower bound on the accuracy of parameter estimation, Ober et al. [15] and Ram et al. [16] derived the Cramér-Rao lower bound (CRLB), i.e., the inverse of the Fisher information matrix. The general expression of the Fisher information matrix derived in [16] is applicable to both stationary and moving point sources. They applied their methodology to the case of a stationary point source and performed an extensive investigation on the effect of noise, image function, pixelation, detector size and pixel size on the limits of the accuracy of the parameter estimates [15], [16].
In this paper, we apply the general framework developed in [16] to the case of a moving point source, which is used to model a single molecule here. We express the Fisher information matrix, from which the performance limit that quantifies the capabilities of an optical microscope is determined, in terms of the image function and object trajectory. Explicit CRLB expressions are obtained for a moving single object with the object trajectory being either linear or circular. In the case of a 2D pixelated detector, we show through simulations how extraneous noise sources, pixelation, parameters of the detector system, and parameters of the trajectory affect the performance of an optical microscope. Some of the results obtained are unique to a moving point source as no counterparts exist for a stationary point source. For example, in the case of a linear trajectory, the practical limit of the accuracy for the estimation of the starting location depends not only on the acquisition time, but also on the speed of the moving point source. In the case of a circular trajectory, for certain starting points, there is a noticeable disparity between the limits of the localization accuracy for estimating the coordinates of its center xc and yc when the radius of the circular trajectory is small.
The organization of this paper is as follows. In Section II, we derive an expression of the Fisher information matrix for a nonpixelated detector of infinite size in terms of the image function and object trajectory in 3D space. We then obtain explicit expressions for the fundamental limit of the accuracy of parameter estimation for specific image functions and a single object moving in the two-dimensional (2D) focus plane with the object trajectory being either linear or circular. In Section III, we consider a pixelated detector of finite size and derive the general expression of the Fisher information matrix for two stochastic models when various types of noise are present. We also investigate the effect of extraneous noise sources, pixelation, parameters of the detector system and parameters of the trajectory on the performance of an optical microscope, and provide guidelines for experimentalists to optimize their experimental setups for tracking single molecules in order to achieve the best possible results. Conclusions are presented in Section IV. Proofs are given in the Appendix.
II. General Framework
In a basic optical microscope setup, we consider an object of interest moving in the object space, imaged by a lens system and its image captured by a detector in the detector space. The detector detects photons emitted by the fluorescent-labelled object during a fixed acquisition time. Since this detection process of the emitted photons is inherently a random phenomenon, the recorded image of the object is stochastic in nature.
From the acquired data, using a specific estimation technique such as the maximum likelihood method, we can estimate object attributes such as the location and orientation and in the case of a moving object, its speed, direction of movement, etc. The accuracy of these estimates can be determined by calculating their standard deviations from the true parameter values upon repeated experiments [11], [14], [16], [17]. However, in any estimation problem, it is important to have a benchmark against which the accuracy of the estimate of the desired attribute can be measured. According to the Cramér-Rao inequality [18]–[20], the (co)variance (matrix) of any unbiased estimator θ̂ of an unknown vector parameter θ is bounded from below by the inverse of the Fisher information matrix I(θ), i.e., Cov(θ̂) ≥ I−1(θ). Hence, we can obtain the benchmark, which provides the limit of the accuracy, by taking the square root of the diagonal elements of the inverse of the Fisher information matrix for the underlying random process that characterizes the acquired data. It should be noted that the Fisher information matrix is independent of any estimation technique used and only depends on the statistical nature of the acquired data.
Following [16], the acquired data is modelled as a space-time random process [21] which we will refer to as the image detection process 𝒢. The temporal part describes the time points of the photons detected by the detector and is modelled as a temporal Poisson process with intensity function Λθ. The spatial part describes the spatial coordinates of the arrival location of the detected photons and is modelled as a family of mutually independent random variables {𝒰τ}τ≥t0 with probability densities {fθ,τ}τ≥t0 defined on the detector 𝒞, where τ denotes the time point of a detected photon. The time dependence of the random variables {𝒰τ}τ≥t0 denotes the fact that the spatial distribution of the detected photons can change with time as is the case with a moving object. Although not explicitly denoted as such, the probability densities {fθ,τ}τ≥t0 can also depend on the focus level zθ(τ) and orientation oθ(τ), τ ≥ t0, of the object. Throughout the paper, we let t0 ∈ ℝ and θ ∈ Θ, where Θ denotes the parameter space that is an open subset of ℝn with n being the dimension of θ which consists of the location and other attributes of the moving object that are to be estimated. We assume that the spatial and temporal parts of 𝒢 are mutually independent of each other and that the probability density function fθ,τ satisfies certain regularity conditions that are necessary for the calculation of the Fisher information matrix (see [16] for details).
In the following theorem and throughout this section, we consider the case of a nonpixelated detector of infinite size, i.e., 𝒞 = R2. This idealized detector provides us with the best case scenario where all the photons from the moving object are detected and pixelation does not deteriorate the accuracy of the photon impact measurements. In addition, in this case we assume that there are no extraneous noise sources that negatively influence the quality of the acquired data. Therefore, this scenario allows us to evaluate what is theoretically possible. In Section III we will consider the “practical” scenario that also models the experimental factors that are not considered here. Comparison of the results from the two models provides important insights to what extent the specific experimental settings, such as pixel size, array size and the noise levels adversely affect the quality of the estimates. In the following theorem an expression for the Fisher information matrix is given for data acquired as a space-time random process. It is a slightly simplified version of a more general result presented in [16].
Theorem 1 [16]
Let 𝒢(Λθ, {fθ,τ}τ≥t0, 𝒞) be an image detection process. Assume that the photon distribution rate Λθ(τ), τ ≥ t0, is independent of the parameter vector θ. Then for θ ∈ Θ, the Fisher information matrix I(θ) of 𝒢 for the time interval [t0, t] is given by
In the remainder of the section this result will be used to derive expressions for the Fisher information for the estimation of parameters related to moving objects as observed using highly sensitive microscopy techniques. As the next step of the derivation we make the assumption that the photon distribution profile fθ,τ can be expressed as a scaled and shifted version of the image of the object since in an optical microscope, the image of an object can often be considered to be invariant with respect to shifts in the object location. In the case of a moving object, fθ,τ can then be written as
where qzθ(τ),oθ(τ) denotes an image function, M > 0 denotes the lateral magnification and (xθ(τ), yθ(τ)), τ ≥ t0, denotes the time dependent trajectory of the object. The image function qzθ(τ),oθ(τ), which is dependent on its focus level zθ(τ) and orientation oθ(τ), describes the image of an object on the detector plane at unit lateral magnification when the object is located along the z axis in the object space and is assumed to be normalized such that , τ ≥ t0.
The following theorem provides a more concrete expression for the Fisher information matrix than that given in Theorem 1 by illustrating its dependence on the trajectory of the tracked object.
Theorem 2. (Appendix A)
Let 𝒢(Λ,{fθ,τ}τ≥t0, ℝ2) be an image detection process. For θ ∈ Θ, assume that
-
A1)
there exists an image function qzθ(τ),oθ(τ) such that for M > 0, the photon distribution profile fθ,τ of a moving object is given by fθ,τ (x, y) = 1/M2qzθ(τ), oθ(τ) (x/M − xθ(τ), y/M − yθ(τ)), (x, y) ∈ ℝ2, τ ≥ t0;
-
A2)
|xθ(τ)| and |yθ(τ)| are uniformly bounded for t0 ≤ τ ≤ t;
-
A3)
∂qzθ(τ), oθ(τ)(x/M − xθ(τ), y/M − yθ(τ))/∂p(τ) exists for (x, y) ∈ ℝ2, zθ(τ), oθ(τ) ∈ ℝ, τ ≥ t0 where .
Then for θ ∈ Θ, the Fisher information matrix I(θ) of 𝒢 for the time interval [t0, t] is given by
| (1) |
where
The inner integral
of the Fisher information matrix in Theorem 2 is essentially the same as the spatial integral of the time-invariant case [16]. Thus the time-varying case can be obtained by integrating the time-invariant result over time with weighting functions Vθ(τ) and . The weighting function Vθ(τ) is the derivative of the object trajectory with respect to the parameters concerned. The significance of this theorem is that we can now calculate the Fisher information matrix of the underlying random process that characterizes the acquired data from a moving object by assuming the image function to be stationary in the x – y plane, such that its origin is located along the z axis, i.e., the optical axis of the objective lens. To calculate the Fisher information matrix of an object moving in 3D space, we simply use the derivative of the parametric expressions of the object trajectory and its image at the corresponding locations along the optical axis. This expression can be applied to an arbitrary trajectory in 3D space. Note that the image function used is quite general.
In the following proposition, we consider a 2D time-varying case where the image function qzθ(τ), oθ(τ) does not depend on the focus level zθ(τ) and the orientation oθ(τ) and is simply denoted as q. This leads to a further simplification of the expression for the Fisher information matrix.
Proposition 3. (Appendix B)
Let 𝒢(Λ,{fθ,τ}τ≥t0, ℝ2) be an image detection process. For θ ∈ Θ, assume that
-
A1)there exists a radially symmetric image function q, i.e., q(x, y) = q̃(r2) = q̃(x2 + y2), for a function q̃: ℝ → ℝ, that does not depend on zθ(τ) and oθ(τ) such that for M > 0, the photon distribution profile fθ, τ of a moving object is given by
-
A2)
∂q(x, y)/∂x and ∂q (x, y)/∂y exist for every (x, y) ∈ ℝ2.
Let (xθ(τ), yθ(τ)), τ ≥ t0, denote the time dependent trajectory of the object with respect to its starting location (x0, y0). Then for θ ∈ Θ, the Fisher information matrix I(θ) of 𝒢 for the time interval [t0, t] is given by
| (2) |
The expression of I(θ) in Proposition 3 is now separable in terms of the spatial and temporal integrals, similar to the case of a stationary object [16]. The spatial integral includes the image function and its derivative while the temporal integral includes the photon detection rate and the derivative of the trajectory. Thus, to calculate the Fisher information matrix of an object moving in the 2D focus plane or in a relatively flat structure, we can assume that its trajectory is decoupled from its image. The significance of this expression is that it greatly simplifies the calculation of the Fisher information matrix since it is now simply a product of two entities and hence it can be easily applied to an arbitrary trajectory in the 2D focus plane provided that the image function is radially symmetric. Note that there is a major difference between the expressions of the Fisher information matrix for the time-invariant and the time-varying cases. In the former case, its Fisher information matrix is affected by the image function and the photon detection rate whereas in the latter, other than the image function and the photon detection rate, it is also affected by the parameters of the trajectory to be estimated.
We now illustrate the result in Proposition 3 by considering specific image functions that describe the image of a moving object, more specifically a moving point source. According to optical diffraction theory, when a point source is in focus with respect to the detector, the intensity distribution of the image of the point source is described by the Airy profile. The 2D Gaussian profile, on the other hand, has been widely used to approximate the Airy profile as it is argued that the Gaussian profile provides a good approximation to the Airy profile in the central region and its use simplifies the analysis [17], [22], [23]. As such, we will consider two different image profiles, specifically a Gaussian image profile and an Airy profile, for both the linear and circular trajectories. For both trajectories, we use the expression of I(θ) in Proposition 3 to derive general expressions for the lower bound to the best possible accuracy for the parameters to be estimated. We will also obtain an explicit analytical expression for the lower bound for a special case where the photon detection rate is assumed to be a known constant. Following [16], this lower bound is referred to as the fundamental limit of the accuracy for the particular parameter vector, or in short, the fundamental limit. The term fundamental is used to describe the fact that the model which underlies the expressions for calculating the lower bound does not take into account any deteriorating effects of the acquisition system such as pixelation of the detector and the various noise sources that typically occur in experimental settings. The fundamental limit has practical value as it provides us with a quantity of what is theoretically possible in the absence of deteriorating factors and thus serves as a benchmark for practical cases. Since the fundamental limit only takes into consideration the basic optical and stochastic phenomena that are inherent in any single-molecule experiment, it can easily be used to study the impact of the important optical and physical parameters without being confounded by the influence of extraneous parameters such as noise, detector properties, etc. In particular, comparisons with the practical limits (see Section III) allow us to evaluate by how much the experimental conditions, e.g., detector array size, pixel size, readout noise level, deteriorate the theoretically best possible results.
In the following corollary, we consider the case of a linear trajectory where the object moves from a given initial position (x0, y0) in the direction of movement φ at a constant speed v. We derive the fundamental limits of the estimated parameters for the corresponding time interval [t0, t], and then specialize the results to the case where the photon detection rate of the image detection process is a known constant.
Corollary 4. (Appendix C)
Let 𝒢(Λ,{fθ,τ}τ≥t0, ℝ2) be an image detection process. The parametric expressions for the linear trajectory of the object for the time interval [t0, t] are given by xθ(τ) = x0 + v(τ − t0) cos φ, yθ(τ) = y0 + v(τ − t0) sin φ, t0 ≤ τ ≤ t. For τ ≥ t0 and M > 0, assume that there exists a radially symmetric image function q(x, y) such that fθ,τ(x, y) = 1/M2q(x/M − xθ(τ), y/M − yθ(τ)), (x, y) ∈ ℝ2 with q(x, y) = q̃(r2) = q̃(x2 + y2), for a function q̃: ℝ → ℝ and let .
-
For θ = (x0, y0, φ, v) ∈ Θ, the fundamental limit of the localization accuracy δx0 (δy0) of x0 (y0), the fundamental limits δφ and δv of φ and v are given, respectively, by
(3) where(4) In the case of the 2D Gaussian image function q(x, y) = 1/2πσ2 exp(−(x2 + y2)/2σ2), σ > 0, (x, y) ∈ ℝ2, γ: = 1/σ. As for the Airy image function , (x, y) ∈ ℝ2, γ: = 2πna/λ, where na and λ denote the numerical aperture and emission wavelength respectively and J1 denotes the first order Bessel function of the first kind.
-
If Λ(τ) = Λ0, τ ≥ t0, where Λ0 is a positive constant, then for θ = (x0, y0, φ, v) ∈ Θ, the fundamental limit of the localization accuracy δx0 (δy0) of x0 (y0), the fundamental limits δφ and δv of φ and v are given, respectively, by
(5) where N: = Λ0(t − t0) denotes the expected number of detected photons for the time interval [t0, t].
From Corollary 4, it can be seen that for both the Airy and the Gaussian image functions, the fundamental limits of x0, y0 and v are independent of θ whereas the fundamental limit of φ is only independent of x0, y0 and φ. When the photon detection rate is assumed to be a constant, the expressions for the fundamental limit of the parameter estimates further simplify to expressions comprising some properties of the photon emission process of the single-molecule, parameters of the detection system and parameters of the trajectory. There are also several interesting common observations for both image functions. The fundamental limit exhibits an inverse square root dependence on the expected number of detected photons. This result is similar to the case of a stationary object [16]. As for δφ, and δv, not only are they inversely proportional to , the former is also inversely proportional to the distance moved by the object of interest v(t − t0) while the latter to the acquisition time interval (t − t0). The fundamental limit of the localization accuracy δx0 or δy0 derived here is twice that of δx0 or δy0 for a stationary object [16]. Therefore, in the case of an object moving in a straight line, we are able to estimate the unknown parameters δφ and δv at the expense of reducing the estimation accuracy of x0 and y0.
In the next corollary, we consider the case of a nonlinear trajectory, specifically a circular trajectory [24], [25]. The object is assumed to start moving at (x0, y0), which is angularly offset at ψ0 degrees with respect to the x axis. It revolves at a constant angular velocity ω at a fixed radius R about the center of its trajectory (xc, yc). For the corollary that follows, we derive the Fisher information matrix for the corresponding time interval [t0, t] using a similar approach to that of the linear trajectory. We also consider a special case where the length of the time interval [t0, t] is assumed to equal the period with respect to the angular velocity and the photon detection rate Λ of the image detection process is assumed to be a known constant.
Corollary 5. (Appendix D)
Let 𝒢(Λ, {fθ,τ}τ≥t0, ℝ2) be an image detection process. The parametric expressions for the circular trajectory of the object of interest for the time interval [t0, t] are given by xθ(τ) = xc + R cos(ω(τ − t0) + ψ0), yθ(τ) = yc + R sin(ω(τ − t0) + ψ0); t0 ≤ τ ≤ t, where (xc, yc) denotes the center of the circular trajectory R ω and ψ0, its radius, angular velocity, and angular offset of the starting point (x0, y0) from the x axis, respectively. For τ ≥ t0 and M > 0, assume that there exists a radially symmetric image function q(x, y) such that fθ,τ(x, y) = 1/M2q(x/M − xθ(τ), y/M − yθ(τ)), (x, y) ∈ ℝ2 with q(x, y) = q̃(r2) = q̃(x2 + y2), for a function q̃: ℝ → ℝ. Let .
| (6) |
For θ = (R, xc, yc, ω, ψ0) ∈ Θ, the Fisher information matrix of 𝒢 for the time interval [t0, t] is given by (6), where ψ: = ω(τ − t0) + ψ0, τ ≥ t0. In the case of the 2D Gaussian image function q(x, y) = 1/2πσ2 exp (−(x2 + y2)/2σ2), σ > 0, (x, y) ∈ ℝ2, γ = 1/σ. As for the Airy image function , (x, y) ∈ ℝ2, γ = 2πna/λ, where na and λ denote the numerical aperture and emission wavelength respectively and J1 denotes the first order Bessel function of the first kind.
-
Let Tp denote the length of the time interval [t0, t], i.e., Tp: = t − t0, and assume that Tp equals the period with respect to the angular velocity, i.e., Tp = 2π/ω. Assume also the photon detection rate to be a known constant, i.e., Λ(τ) = Λ0, t0 ≤ τ ≤ t. Then the fundamental limit δxc (δyc) of xc (yc) and the fundamental limits δR, δω and δψ0 of R, ω and ψ0 are given by
(7) where NTp: = Λ0Tp denotes the expected number of detected photons for the period Tp.
The general expression to calculate the Fisher information matrix I(θ) of 𝒢 corresponding to the time interval [t0, t] for an object with a circular trajectory is given in the first part of the above corollary. By taking the square root of diagonal elements of the inverse of Fisher information matrix, we obtain the fundamental limits of the parameter estimates. Unlike the linear trajectory case, it seems that no simple analytical expression is available for the fundamental limits in the case of a general circular trajectory.
However, in the special case where the length of the time interval [t0, t] is the period Tp with respect to the angular velocity and the photon detection rate is a known constant Λ0, the fundamental limit of θ = (R, xc, yc, ω, ψ0) simplifies to that shown in result 2 of Corollary 5 with analytical expressions given in (7). These expressions are given in terms of some properties of the photon emission process of the single-molecule, parameters of the detection system and parameters of the trajectory. Similar to the case of the linear trajectory, the fundamental limits for all the five parameters are dependent on the inverse square root of the expected number of detected photons and independent of the acquisition starting time. However, the fundamental limits of the δxc and δyc are periodic in nature and dependent on the angular offset of the starting point ψ0. On the other hand, the fundamental limits δω, δψ0 and δR are independent of ψ0. Moreover, both δω and δψ0 are inversely proportional to the radius of the circular trajectory and in addition, δω is inversely proportional to Tp.
III. Effects of Pixelation and Simulation Results
So far we have only considered a moving object where its image is acquired by a nonpixelated detector of infinite size without extraneous noise sources. In fluorescence single-molecule microscopy, CCD cameras are commonly used for acquiring images of fluorescent-labelled molecules. The detectors of CCD cameras are of finite size and pixelated, i.e., they consist of a matrix of light sensing elements (pixels) where photo-electrons are accumulated during an exposure interval. We will henceforth refer to it as a pixelated detector of finite size 𝒞p or in short, just a pixelated detector since a pixelated detector is always of finite size in practice.
As for the acquired data, it comprises the detected photons from the object of interest and noise from a variety of sources. The detected photons from the object of interest and the external background radiation introduce a Poisson signal from the object of interest and from the background component respectively. Hence we let denote an image detection process for the detected photons from the object of interest and for the background component. Readout noise, which is characterized as a Gaussian random process, further contributes to the degradation of the images acquired. As such, we consider two stochastic models for the pixelated detector, one purely in terms of Poisson random variables while the other is in terms of Poisson and Gaussian random variables. As for the photon distribution profile of 𝒢2, it is assumed to be independent of the time point τ and is denoted by f(2).
In the following theorem, we provide expressions to calculate the Fisher information matrix of the acquired data from a pixelated detector in terms of its image function, photon detection rate and object trajectory for two different scenarios: one where its acquired data comprise only Poisson random variables and the other, its acquired data comprise both Poisson and Gaussian random variables.
Theorem 6 (Appendix E)
Let and 𝒢(2) (Λ(2), {f(2)}, ℝ2) be two independent image detection processes for the object of interest and the background component, respectively. Let the pixelated detector 𝒞p be defined as a collection {C1, …, CNp} of open, disjoint subsets of ℝ2 such that , where Np denotes the total number of pixels. For θ ∈ Θ, assume that
-
A1)
the photon detection rates of 𝒢(1) and 𝒢(2) are known;
-
A2)there exists an image function such that for M > 0, the photon distribution profile of a moving object is given byand for q(2), which is assumed to be independent of the focus level and the orientation, the photon distribution profile f(2) of the background component is given by
- Let ℐθ,k = Sθ,k + Bk, k = 1, …, Np, where Sθ,k and Bk are Poisson random variables from the object of interest and background component, respectively. For θ ∈ Θ, the Fisher information matrix for {ℐθ,1, …, ℐθ,Np} for the time interval [t0, t] is given by
(8) (9) - Let ℐθ,k = Sθ,k + Bk + Wk, k = 1, …, Np, where Sθ, k and Bk are Poisson random variables from the object of interest and background component, respectively, and Wk denotes the Gaussian random variable with mean ηk and variance , which models the measurement noise. For θ ∈ Θ, the Fisher information matrix for {ℐθ,1, …, ℐθ,Np } for the time interval [t0, t] is given by (9). The Poisson-Gaussian mixture probability density function, pθ,k(z), is given by
We define the square roots of the diagonal elements of the inverse of the Fisher information matrix associated with a pixelated detector of finite size as the practical limits of the accuracy for the particular parameter vector, or in short just as the practical limits. The word “practical” is used here to differentiate it from the fundamental limit of the accuracy which is associated with a nonpixelated detector of infinite size. Moreover, for simplicity, the term “limit of the accuracy” is used when we refer to both the fundamental and practical limit of the accuracy.
In the following simulations, we use the results of Theorem 6 to show how extraneous noise sources, parameters of the detection system and parameters of the trajectory affect the practical limit of the accuracy of θ. The practical limits will be benchmarked against their corresponding fundamental limits.
Consider a single exposure/image for the time interval [t0, t]. The photon detection rate of a moving point source is assumed to be a known constant, i.e., , τ ≥ t0, and its image function to be a Gaussian, i.e., q(1)(x, y) = 1/2πσ2 exp(−((x/M − xθ(τ))2 + (y/M − yθ(τ))2)/2σ2), (x, y) ∈ ℝ2, τ ≥ t0. The photon detection rate of the background component is also assumed to be a known constant , τ ≥ t0, and the detected photons from the background component are assumed to be uniformly distributed. Since we are considering the 2D case where the image function is independence of zθ(τ) and oθ(τ), the column vectors p(1)(τ) and Vθ(τ) in Theorem 6 are reduced to p(1)(τ): = [x/M − xθ(τ) y/M − yθ(τ)]T and Vθ(τ): = [−∂xθ(τ)/∂θ − ∂yθ(τ)/∂θ]T. For both the linear and circular trajectories illustrated in Fig. 1, we consider the noise-free and the noise-corrupted cases. In our context, noise-free refers to the case where only “Poisson noise” or “shot noise” [26] from the object of interest is present. This noise arises due to the stochastic nature of the acquired data. As for the noise-corrupted case, it includes Poisson noise from the background component and Gaussian noise from the readout process.
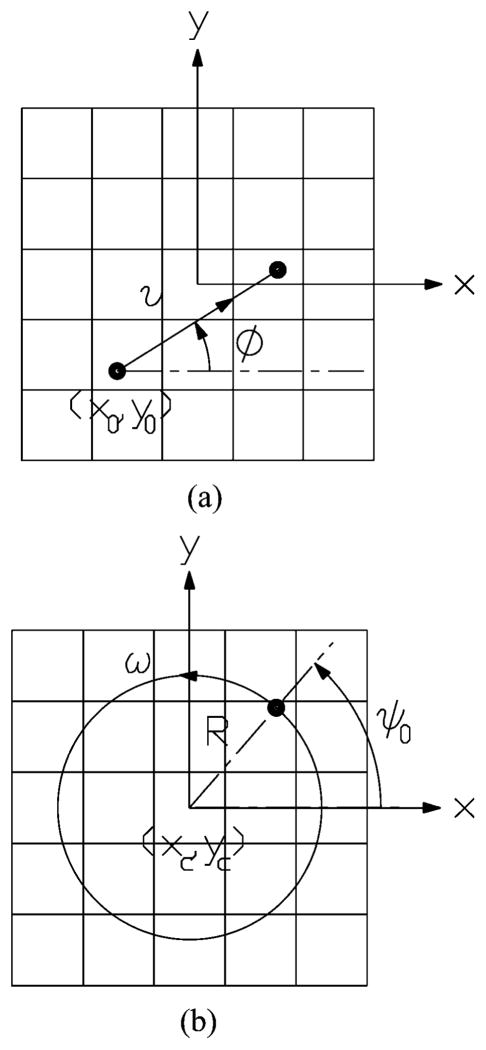
Fig. 1.
Schematic sketch of a linear trajectory and a circular trajectory.
A. Linear Trajectory
For the case of a linear trajectory, we assume that the object commences to move with a constant speed v from a given initial position (x0, y0) at an angle φ between the linear trajectory and the x axis. During the acquisition, the image of the object is well within the bounds of the pixelated detector, as shown in Fig. 1(a). Its parametric expressions are given by xθ(τ) = x0 + v(τ − t0) cos φ, yθ(τ) = y0 + v(τ − t0) sin φ, t0 ≤ τ ≤ t.
Then for θ = (x0, y0, φ, v) ∈ Θ, ∂μθ(k, t)/∂θ = [∂μθ(k, t)/∂x0 ∂μθ(k, t)/∂y0 ∂μθ(k, t)/∂φ ∂μθ(k, t)/∂v], where
| (10) |
To calculate the Fisher information matrix, we substitute the expressions in (10) into the results of Theorem 6. Inverting the Fisher information matrix and taking the square roots of the diagonal elements, we obtain the practical limits of θ = (x0, y0, φ, v).
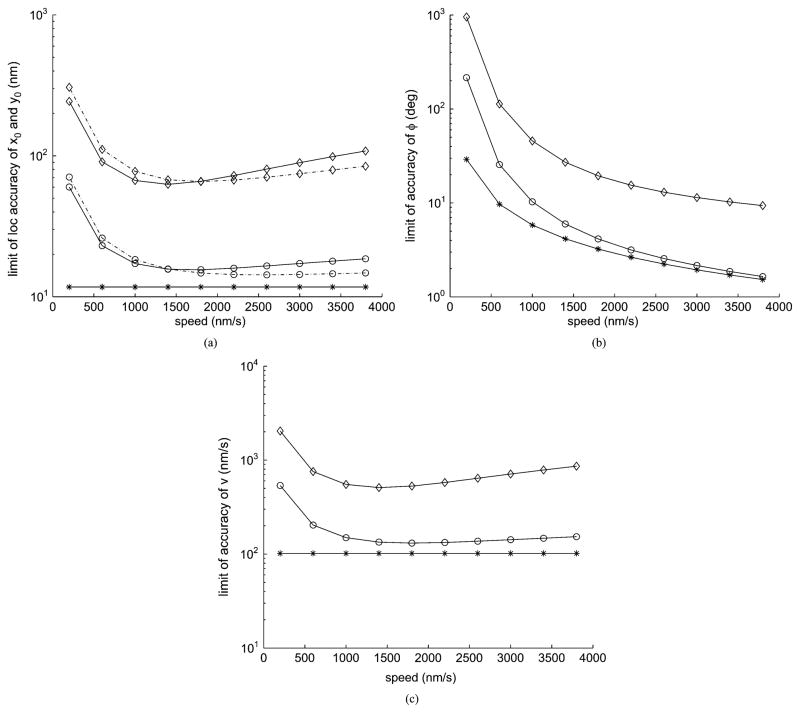
To study the effect of the speed of the object on the practical limit of θ, we fix the acquisition time and consider a range of speeds. It can be observed in Fig. 2(a) and (c) that the practical limits of x0, y0, and v improve initially but deteriorate subsequently as the speed increases. The improvement in the practical limit is due to the increase in the number of pixels that sample the image as the speed increases. Meanwhile, fewer photons are detected per pixel because the same number of photons is now distributed over a greater number of pixels. When the number of detected photons from the object decreases in relation to the photons from the extraneous noise sources, the practical limit deteriorates. The deterioration is more pronounced in the noise-corrupted case where the extraneous noise is present as compared to the noise-free case where only the Poisson signal is present. It can also be observed that there is a disparity between the practical limits of x0 and y0 in Fig. 2(a) as the trajectory influences the practical localization limits differently. For the practical limit of φ, it improves monotonically as the speed increases. Hence for a fixed acquisition time, the improvement in the practical limit is dependent on the tradeoff between the number of pixels that sample the image and the number of detected photons per pixel.
Fig. 2.
Limits of the accuracy of the parameter estimates as a function of the speed of a linearly moving object. (a) Practical limits of x0 (—) and y0 (– · –). (b) Practical limit of φ and (c) of v. (○) corresponds to the noise-free case and (◇) corresponds to the case where Poisson noise ( ) of 2 photons/pixel/s and Gaussian noise (σk) of 4 e−/pixel are present. Their corresponding fundamental limits (*) are included as the references. For the object in all plots σ = 83 nm, magnification M = 100, its direction of movement φ = 30°, and its starting coordinates are (x0, y0) = (−268.7, −268.7) nm. The photon detection rate , acquisition time is 0.2 s, pixel size is 4.03 μm × 4.03 μm and the array size is 31 × 31 pixels.
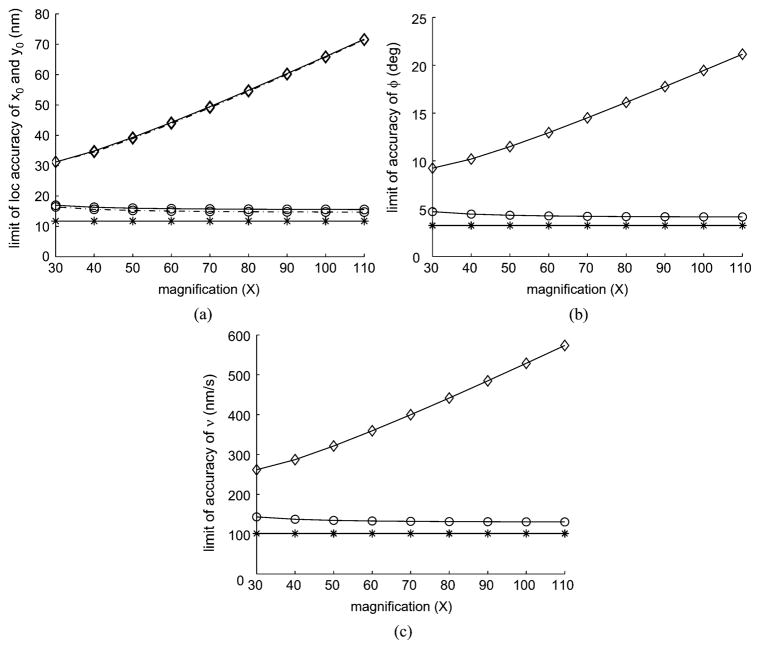
We next investigate the effect of magnification on the practical limit of θ. At low magnification, the photons from the object of interest are concentrated over a small number of pixels and the projected distance moved by the object in the pixel array is short. As the magnification increases, the image magnifies and the projected distance moved increases too. This causes the photons from the object of interest to be distributed over a larger number of pixels. Thus in the noise-free case, for a fixed acquisition time, the trade-off between the number of pixels that sample the image and the number of detected photons per pixel results in the improvement of the practical limit of θ as the magnification increases. However, in the noise-corrupted case, the practical limit deteriorates as the magnification increases and, as a result, the number of detected photons from the object decreases in relation to the photons from the extraneous noise sources, as shown in Fig. 3. It is noted that in the stationary case, the distribution of photons over the pixel array is due to the change in its image size whereas in the moving case, the distance moved by the object affects the photon distribution too.
Fig. 3.
Limits of the accuracy of the parameter estimates as a function of the magnification of a linearly moving object. (a) Practical limits of x0 (—) and y0 (– · –). (b) Practical limit of φ and (c) of v. (○)corresponds to the noise-free case and (◇) to the case where Poisson noise ( ) of 2 photons/pixel/s and Gaussian noise (σk) of 4 e−/pixel are present. Their corresponding fundamental limits (*) are included as reference. For the object in all plots σ = 83 nm, its direction of movement φ = 30°, its speed v = 1800 nm/s, and its starting coordinates are (x0, y0) = (− 127.3, −127.3) nm. The photon detection rate , acquisition time is 0.2 s, pixel size is 4.03 μm × 4.03 μm and the array size is 31 × 31 pixels.
We now benchmark the practical limits against the fundamental limits from Corollary 4. From Fig. 2, the practical limits of the accuracy of x0, y0 and v first approach and then deviate from their respective fundamental limits as the speed increases. Note that their fundamental limits remain constant throughout because they are independent of the speed of the object. As for the practical limit of φ, it approaches its fundamental limit, which improves monotonically as the speed increases. From Fig. 3, when the magnification increases, the practical limit of θ approaches its fundamental limit for the noise-free case while it deviates from its fundamental limit for the noise-corrupted case. It should be noted that the fundamental limit of θ is independent of magnification and thus it remains constant regardless of the magnification M.
For relatively low speeds, such as when the particle moves at 200 nm/s, the practical limits of both x0 and y0 are quite large for the noise-corrupted case in comparison to the fundamental limits, the actual values of the parameters and the sizes of the pixels in object space. For example, at this speed the practical limits are larger than 243 nm while the size of an area in the object space corresponding to a pixel in the detector is only about 40 nm × 40 nm. In this particular scenario it is clear that a parameter estimate would be highly questionable. For significantly larger speeds the practical limits that also account for extraneous noise are much lower, although they never reach even single pixel precision. In contrast, for the practical limits that are computed ignoring extraneous noise sources, the predicted accuracies are of acceptable levels, for speeds over around 1000 nm/s. They are not significantly above the fundamental limits. This suggests that, for this range of speeds, no significant improvements in accuracy can be achieved by changing the detector size, magnification and pixel size. This is in stark contrast to the range of speeds below 1000 nm/s. For these speeds the difference between the fundamental limit and the practical limit that excludes noise sources is rather large. Therefore changing the experimental conditions promises major improvements. However, for all speeds there is a significant difference between the practical limits that include extraneous noise sources and those without. This suggests, that in a concrete experimental setting, the extraneous noise sources have to be significantly reduced in order to obtain estimates that have accuracies close to what is theoretically possible as specified by the fundamental limit.
B. Circular Trajectory
For the case of a circular trajectory, we assume that the center of the circular trajectory is located at the center of the pixelated detector as shown in Fig. 1(b). Its parametric expressions are given by xθ(τ) = xc + R cos(ω(τ − t0) + ψ0), yθ(τ) = yc + R sin (ω(τ − t0) + ψ0), t0 ≤ τ ≤ t. For θ = (R, xc, yc, ω, ψ0) ∈ Θ, ∂μθ(k, t)/∂θ = [∂μθ(k, t)/∂R ∂μθ(k, t)/∂xc ∂μθ(k, t)/∂yc ∂μθ(k, t)/∂ω ∂μθ(k, t)/∂ψ0], where
| (11) |
To calculate the Fisher information matrix, we substitute the expressions in (11) into the results of Theorem 6. Inverting the Fisher information matrix and taking the square root of the diagonal elements, we obtain the practical limit of θ = (R, xc, yc, ω, ψ0).
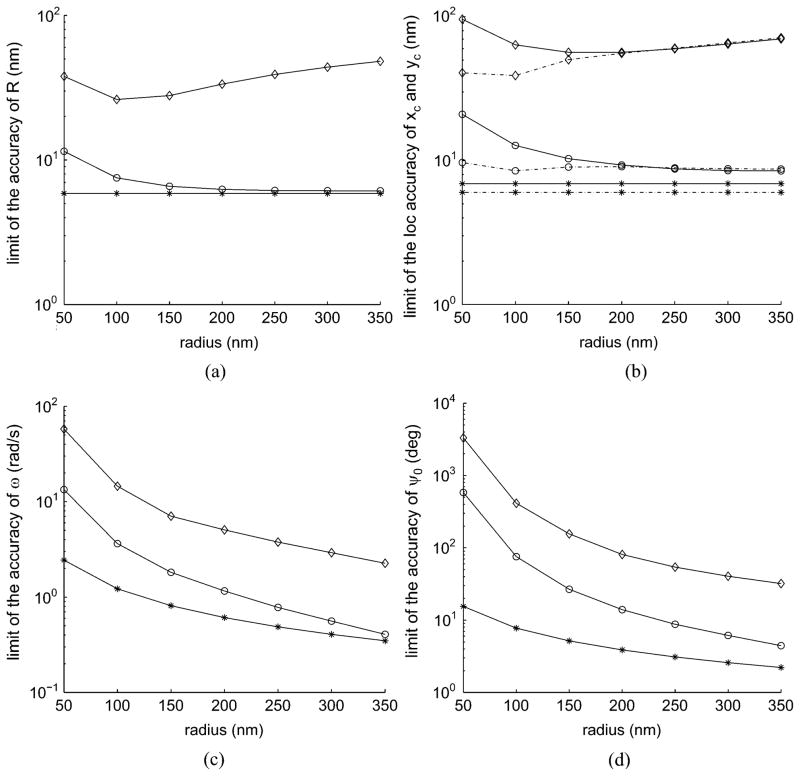
We first investigate the effect of the radius of the circular trajectory and then the effect of the angular offset of the starting point on the practical limit of θ. To investigate the dependence on the radius of the circular trajectory, we fix the constant angular velocity for a range of radii and also fix the acquisition time as one period with respect to the angular velocity. As the radius of the circular trajectory increases, for the noise-free case, the practical limits of R, xc and of yc approach their respective fundamental limits, whereas for the noise-corrupted case, they improve initially but deteriorate subsequently as shown in Fig. 4(a) and (b), respectively. Similar to the case of the linear trajectory, this improvement is due to the increase in the number of pixels that sample the image as the radius increases. Meanwhile, fewer photons are detected per pixel because the same number of photons is now distributed over a larger number of pixels. When the number of detected photons from the object decreases in relation to the photons from the extraneous noise sources, the practical limits deteriorate. For ω and ψ0, their practical limits improve as the radius of the circular trajectory increases, following the same trend of the fundamental limits.
Fig. 4.
Limits of the accuracy of the parameter estimates as a function of the radius of the circular trajectory. (a) Practical limit of R. Panel (b) of xc (—) and yc (– · –). Panel (c) of ω and (d) of ψ0. (○) corresponds to the noise-free case and (◇) to the case where Poisson noise ( ) of 2 photons/pixel/s and Gaussian noise (σk) of 4 e−/pixel are present. Their corresponding fundamental limits (*), which are independent of the pixel array, are included as reference. For the object in all plots, σ = 83 nm, magnification M = 100, angular offset of the starting point ψ0 = 20°, and the coordinates of xc and yc are (0, 0). The photon detection rate , period Tp = 0.2 s, pixel size is 4.03 μm × 4.03 μm and the array size is 31 × 31 pixels.
We notice that there is also a disparity between the practical limits of xc and yc, as shown in Fig. 4(b). This disparity diminishes as the radius of the circular trajectory increases. This phenomenon can also be observed in the case of the angular offset of the starting location as shown in Fig. 5(b) and (c). Hence, it is seen that the trajectory has a strong influence on the practical limit. As in the case of the linear trajectory, the practical limit of the accuracy for the circular case is also dependent on the tradeoff between the number of pixels that sample the image and the number of detected photons per pixel.
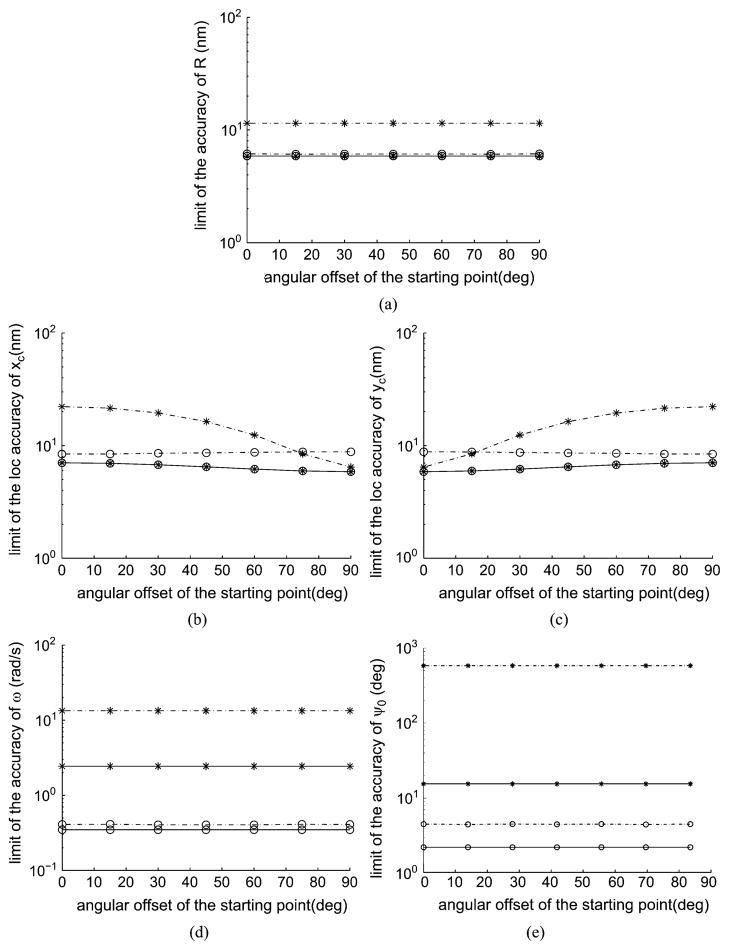
Fig. 5.
Limits of the accuracy of the parameter estimates as a function of the angular offset of the starting point ψ0 of an object with a circular trajectory. (a) Practical limit of R. Panel (b) of xc. Panel (c) of yc. Panel (d) of ω and (e) of ψ0. (○) corresponds to a radius of the circular trajectory of 350 nm while (*) corresponds to a radius of 50 nm. The line style (– · –) corresponds to the noise-free case while (—) refers to that of the fundamental limit. For the object in all plots σ = 83 nm, magnification M = 100, and the coordinates of xc and yc are (0, 0). The photon detection rate , period Tp = 0.2 s, pixel size is 4.03 μm × 4.03 μm and the array size is 31 × 31 pixels.
We now benchmark the practical limits against the fundamental limits of θ from Corollary 5. From Fig. 4, for the noise-corrupted case, the practical limits of R, xc and yc first approach and then deviate from their respective fundamental limits as the radius of the circular trajectory increases. Note that the fundamental limits of R, xc and yc are independent of the radius of the circular trajectory and hence they remain constant as the radius increases. As for the practical limits of ω and ψ0, they approach their respective fundamental limits, which improve monotonically as the radius increases. From Fig. 5, the practical limits of R, ω and ψ0 are almost independent of the angular offset of the starting point ψ0, and as the radius of the circular trajectory increases, they approach their respective fundamental limits which are independent of the angular offset of the starting point ψ0. However, the situation of the practical limits of xc and yc is quite different as their deviations from the respective fundamental limits are dependent on the angular offset of the starting point ψ0 and the radius of the circular trajectory. It should be noted that the fundamental limits of xc and yc are functions of the angular offset of the starting point ψ0.
IV. Conclusion
In this paper, we have investigated the performance of parameter estimation for moving single molecules imaged by fluorescence microscopy. The acquired data are modeled as a space-time random process where the detected photons are Poisson distributed. A nonpixelated detector of infinite size is first considered. We derive a general expression of the Fisher information matrix for parameter estimation in terms of its image function and object trajectory for an object moving in 3D space. We have shown that the Fisher information matrix can be obtained by integrating the corresponding time-invariant results with a weighting function that is associated with the derivative of the object trajectory with respect to the parameters concerned. For an object moving in the 2D focus plane, we have also shown that the Fisher information matrix is separable in terms of the spatial and temporal integrals. Furthermore, explicit CRLB expressions have been obtained when the object moves in the 2D focus plane with the object trajectory being either linear or circular and for two specific image functions: the Airy image function and the Gaussian image function.
We next consider a pixelated detector of finite size. From the simulations conducted, we have obtained insights into how extraneous noise sources, pixelation, parameters of the detection system, and parameters of the trajectory affect the limits of the accuracy of the estimated parameters. In the time-varying and linear trajectory case, the number of pixels that sample the image is proportional to the speed of the object while the number of detected photons per pixel is inversely proportional for a fixed acquisition time. Consequently, the practical limits of the parameter estimates depend on the tradeoff between the number of pixels that sample the image and the number of detected photons per pixel. As for the magnification, the distribution of photons over the pixel array in the time-varying case is dependent on both the image size and the projected distance moved by the object on the pixel array whereas in the time-invariant case, it is dependent only on the image size. In the time-varying and circular trajectory case, we have shown that the disparity between the practical limits of the center coordinates xc and yc diminishes as the radius of the circular trajectory increases. The effect of the angular offset of the starting point on the practical limits also diminishes as the radius increases. We also discuss the meanings and practical implication of the results obtained. We hope that these insights will enable the experimentalists to optimize their experimental setup in order to achieve the best possible accuracy. It should be noted that the results here are essentially independent of the application in single-molecule microscopy and can be applied to the general problem of tracking an object using quantum limited detectors.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01 GM071048 and R01 GM085575).
Biographies

Yau Wong received the M.Sc. (Mech. Eng.) and M.Sc. (Biomed. Eng.) degrees from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and Nanyang Technological University (NTU) in 1992 and 2005, respectively.
He is currently an academic staff lecturing at Nanyang Polytechnic and is concurrently pursuing his Ph.D. degree at the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at NTU. His current research interests include statistical signal processing and biomedical engineering.

Zhiping Lin (SM’00) received the B.Eng degree in control engineering from South China Institute of Technology, Canton, in 1982 and the Ph.D. degree in information engineering from the University of Cambridge, England, in 1987.
He was with the University of Calgary, Canada, from 1987 to 1988, with Shantou University, China, from 1988 to 1993, and with DSO National Laboratories, Singapore, from 1993 to 1999. Since February 1999, he has been an Associate Professor with Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore. He is also the Program Director of Bio-Signal Processing, Center for Signal Processing, NTU. His research interests include multidimensional systems and signal processing, statistical signal processing, and biomedical signal processing.
Dr. Lin is currently serving as the Editor-in-Chief of Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing and an Associate Editor of the IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems—Part II. He was an Associate Editor of Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing from 2000 to 2007. He was a Distinguished Lecturer of the IEEE Circuits and Systems Society for 2007–2008, and the Chair of the IEEE Circuits and Systems Singapore Chapter during 2007–2008.

Raimund J. Ober (S’87–M’88–SM’95) received the Ph.D. degree in engineering from Cambridge University, Cambridge, U.K., in 1987.
From 1987 to 1990, he was a Research Fellow with Girton College and the Engineering Department, Cambridge University. In 1990, he joined the University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, where he is currently a Professor with the Department of Electrical Engineering. He is also an Adjunct Professor with the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas. His research interests include the development of microscopy techniques for cellular investigations, in particular, at the single molecule level, the study of cellular trafficking pathways using microscopy investigations, and signal/image processing of bioengineering data.
Dr. Ober is an Associate Editor of Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing and Mathematics of Control, Signals, and Systems, and a past Associate Editor of the IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems and Systems and Control Letters.
Appendix A. Proof of Theorem 2
Let
and
where Vθ(τ) is independent of x and y. The photon distribution profile fθ,τ, in terms of the entries of p̃(τ), can then be rewritten as
| (12) |
We first show that the existence of ∂qzθ(τ),oθ(τ) (x/M − xθ(τ), y/M − yθ(τ))/∂p(τ) implies the existence of ∂qz̃θ(τ),õθ(τ)(x̃θ(x, τ), ỹθ(y, τ))/∂p̃(τ).
Using the chain rule, we have
Hence
Therefore, ∂qz̃θ(τ),õθ(τ) (x̃θ(x, τ), ỹθ(y, τ))/∂p̃(τ) exists.
Consequently, the partial derivative of fθ,τ(x, y) with respect to θ can be expressed as follows:
| (13) |
Substituting (12) and (13) into the expression of I(θ) in Theorem 1 and simplifying gives the following equation. Since dx = Mdx̃θ, dy = Mdỹθ and the assumption of |xθ(τ)| and |yθ(τ)| being uniformly bounded for θ ∈ Θ, t0 ≤ τ ≤ t, the expression becomes (14). Replacing the dummy variables x̃θ with x, and ỹθ with y in the above expression, respectively, and recalling that z̃θ(τ) = zθ(τ), and õθ(τ) = oθ(τ), we have p̃(τ) = p(τ) in (14) and, hence, obtain the desired result given in (1).□
| (14) |
Appendix B. Proof of Proposition 3
As the image function q is independent of zθ(τ) and oθ(τ), p(τ) and Vθ(τ) in Theorem 2 reduce to and Vθ(τ): = [−∂xθ(τ)/∂θ −∂yθ(τ)/∂θ]T, respectively, and the corresponding expression of I(θ) becomes
| (15) |
With the assumption of the image profile q(x, y) being radially symmetric and condition (A2), it can be readily shown that
| (16) |
since (∂q̃(x2 + y2)/∂(x2 + y2))2 is also radially symmetric, and that
| (17) |
Using the polar coordinate system, where x = r cos φ and y = r sin φ, φ, r ∈ ℝ, and with some algebraic manipulations, we have
| (18) |
Similarly, it can be shown that
| (19) |
Substituting (16)–(19) into (15) gives the equation below (14).□
Appendix C. Proof of Corollary 4
-
1)Since , the expression of I(θ) in Proposition 3 can be rewritten as
(20)
The linear trajectory of the object of interest for the time interval [t0, t] is given by
where (x0, y0) is the starting location of the object, φ is the direction of movement, i.e., the angle between the linear trajectory and the x axis and v is the constant speed of the object. Then for θ = (x0, y0, φ, v)
| (21) |
Hence, we obtain (21). By substituting (21) into (20), partitioning the matrix obtained and considering the limits of integration from 0 to t − t0, I(θ) can be expressed as
| (22) |
where a1(t), a2(t), and a3(t) are given in (4) and
As ai (t) ≢ 0, for i = 1, 2, 3 and B1(θ) is the 2×2 identity matrix I2, the inverse of the partitioned matrix I−1(θ) [27] is given by
| (23) |
where
Some simple algebraic manipulations give
| (24) |
| (25) |
| (26) |
By substituting (25) and (26) into the inverse Fisher information matrix I−1(θ) in (23) and taking the square root of its diagonal elements, we obtain the desired result given in (3). For the case of the 2D Gaussian image function, [15]. Hence by replacing γ with 1/σ in (3), we obtain the fundamental limit of the accuracy of θ. Similarly for the Airy profile, we replace γ with 2πna/λ[15].
-
2)For the special case where the photon detection rate is constant, i.e., Λ(τ) = Λ0, τ ≥ t0, Λ0 ∈ ℝ+, the integrals of the photon detection rate with respect to time for the expressions in (4) become
Substituting the above expressions into result 1 of this corollary and letting N = Λ0(t − t0), we obtain the desired result given in (5).□
Appendix D. Proof of Corollary 5
-
1)Since , the expression of I(θ) in Proposition 3 can be rewritten as
(27)
The parametric expressions of the moving object with circular trajectory are given by
where (xc, yc) is the center, R is the radius of the circle, ω is the constant angular velocity of the object and ψ0 is the angular offset of the starting point (x0, y0) from the x axis. Given that the unknown parameter vector is θ = (R, xc, yc, ω, ψ0), then we can readily express (28), where ψ = ω(τ − t0) + ψ0.
| (28) |
Substituting (28) into (27), we obtain the desired Fisher information matrix given in (6). For the case of the 2D Gaussian image function, [15] and by replacing γ with 1/σ, we obtain its Fisher information matrix I(θ). Similarly for the Airy profile, we obtain its Fisher information matrix by replacing γ with 2πna/λ[15].
-
2)Assuming Λ(τ) = Λ0, t0 ≤ τ ≤ t, and t = t0 + Tp where Tp = 2π/ω, we can further simplify the Fisher information matrix I(θ) in (6) after evaluating the following expressions:
(29) (30) (31)
Next
| (32) |
since it is the integration over one period of a cosine. Similarly, .
Using integration by parts and with some simplifications, we also have
| (33) |
| (34) |
Substituting (29)–(34) into (6) and making use of ω = 2π/Tp, we have the equation below (28), where NTp = Λ0Tp and
Hence I−1 (θ) is given by
| (35) |
| (36) |
Adopting the same approach to inverting the 4×4 matrix in (22), which has a similar structure as I1 (θ) here, we can readily obtain (36). Substituting in (36) into (35) and taking the square root of its diagonal elements, we obtain the fundamental limits of the accuracy of θ = (R, xc, yc, ω, ψ0) as given in (7).□
Appendix E. Proof of Theorem 6
-
1)Using condition (A1), the mean of the number of detected photons at the kth pixel due to the object of interest for the time interval [t0, t] is given by [16]
The above expression can then be expressed in terms of its image function as
| (37) |
The mean of the number of detected photons at the kth pixel due to the background component for the time interval [t0, t] is given by [16]
| (38) |
From [16], vθ(k, t) = μθ(k, t) + β(k, t). Substituting (37) and (38) into vθ(k, t) gives
| (39) |
| (40) |
The partial derivative of μθ(k, t) with respect to θ is expressed as shown in (40). Interchanging the operation of differentiation with that of integration for (40) and adopting a similar approach used in Theorem 2, the derivative of μθ(k, t) with respect to θ can be expressed as
| (41) |
Substituting (39) and (41) into [21]
we obtain the Fisher information matrix I(θ) in (8) for the pixelated detector 𝒞 where the detected photons from the object of interest and background component are independently Poisson distributed.
Contributor Information
Yau Wong, Email: wong0333@ntu.edu.sg, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798.
Zhiping Lin, Email: ezplin@ntu.edu.sg, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798.
Raimund J. Ober, Email: ober@utdallas.edu, The Erik Jonsson School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, TX 75083-0688 USA. He is also with the Department of Immunology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, TX 75235-8576 USA.
References
- 1.Zlatanova J, Van Holde K. Single-molecule biology: What is it and how does it work? Molec Cell. 2006 Nov;24(3):317–329. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moerner WE, Fromm DP. Methods of single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy and microscopy. Rev Scientif Instrum. 2003 Aug;74(8):3597–3619. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schütz GJ, Sonnleitner M, Hinterdorfer P, Schindler H. Single molecule microscopy of biomembranes (Review) Molec Membrane Biol. 2000;17:17–29. doi: 10.1080/096876800294452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Weiss S. Fluorescence spectroscopy of single biomolecules. Science. 1999 Mar;283:1676–1683. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5408.1676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Moerner WE. New directions in single-molecule imaging and analysis. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 2007 Jul;104:12596–12602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610081104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vonesch C, Aguet F, Vonesch JL, Unser M. The colored revolution of bioimaging. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2006 May;23:20–31. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yu J, Xiao J, Ren X, Lao K, Xie XS. Probing gene expression in live cells, one protein molecule at a time. Science. 2006 Mar;311:1600–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.1119623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lino R, Koyama I, Kusumi A. Single molecule imaging of green fluorescent proteins in living cells: E-Cadherin forms oligmers on the free cell surface. Biophys J. 2001 Jun;80:2667–2677. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76236-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Smith PR, Morrison IEG, Wilson KW, Fernández N, Cherry RJ. Anamalous diffusion of major histocompatability complex class I molecules on HeLa cells determined by single particle tracking. Biophys J. 1999 Jun;76:3331–3344. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77486-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Douglass AD, Vale RD. Single-molecule microscopy reveals plasma membrane microdomains created by protein-protein networks that exclude or trap signaling molecules in T cells. Cell. 2005 Jun;121:937–950. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kubitscheck U, Kückmann O, Kues T, Peters R. Imaging and tracking of single GFP molecules in solution. Biophys J. 2000 Apr;78(4):2170–2179. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76764-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Martin DS, Forstner MB, Käs JA. Apparent subdiffusion inherent to single particle tracking. Biophys J. 2002 Oct;83:2109–2117. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)73971-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Savin T, Doyle PS. Static and dynamic errors in particle tracking microrheology. Biophys J. 2005 Jan;88:623–638. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.042457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cheezum MK, Walker WF, Guilford WH. Quantitative comparison of algorithms for tracking single fluorescent particles. Biophys J. 2001 Oct;81:2378–2388. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75884-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ober RJ, Ram S, Ward ES. Localization accuracy in single-molecule microscopy. Biophys J. 2004 Feb;86:1185–1200. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74193-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ram S, Ward ES, Ober RJ. A stochastic analysis of performance limits for optical microscopes. Multidimens Syst Signal Process. 2006 Jan;17:27–57. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Thompson RE, Larson DR, Webb WW. Precise nanometer localization analysis for individual fluorescent probes. Biophys J. 2002 May;82:2775–2783. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75618-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kay SM. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall PTR; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zou Q, Lin Z, Ober RJ. The Cramer Rao lower bound for bilinear systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 2006 May;54:1666–1680. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yetik IS, Nehorai A. Performance bounds on image registration. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 2006 May;54:1737–1749. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Snyder DL, Miller MI. Random Point Processes in Time and Space. 2. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang B, Zerubia J, Olivo-Marin JC. Gaussian approximations of fluorescence microscope point-spread function models. Appl Opt. 2007 Apr;46(10):1819–1829. doi: 10.1364/ao.46.001819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Santos A, Young IT. Model-based resolution: Applying the theory in quantitative microscopy. Appl Opt. 2000 Jun;39(17):2948–2958. doi: 10.1364/ao.39.002948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cluzel P, Surette M, Leibler S. An ultrasensitive bacterial motor revealed by monitoring signaling proteins in single cells. Science. 2000 Mar;287(5458):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5458.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Diez S, Reuther C, Dinu C, Seidel R, Metig N, Pompe W, Howard J. Stretching and transporting DNA molecules using motor proteins. Nano Lett. 2003;3(9):1251–1254. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wolfe WL. Introduction to Imaging Spectrometers. Bellingham, WA: SPIE, The Int. Soc. Opt. Eng; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kraus AD. Matrices for Engineers. New York: Oxford Univ. Press; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ram S. PhD dissertation. The Univ. Texas; Arlington: Univ. Texas Southwestern Med. Center; Dallas, Dallas, TX: 2007. Resolution and localization in single molecule microscopy. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Michalet X, Siegmund OHW, Vallerga JV, Jelinsky P, Millaud JE, Weiss S. Detectors for single-molecule fluorescence imaging and spectroscopy. J Modern Opt. 2007 Feb;54(2–3):239–281. doi: 10.1080/09500340600769067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]