Abstract
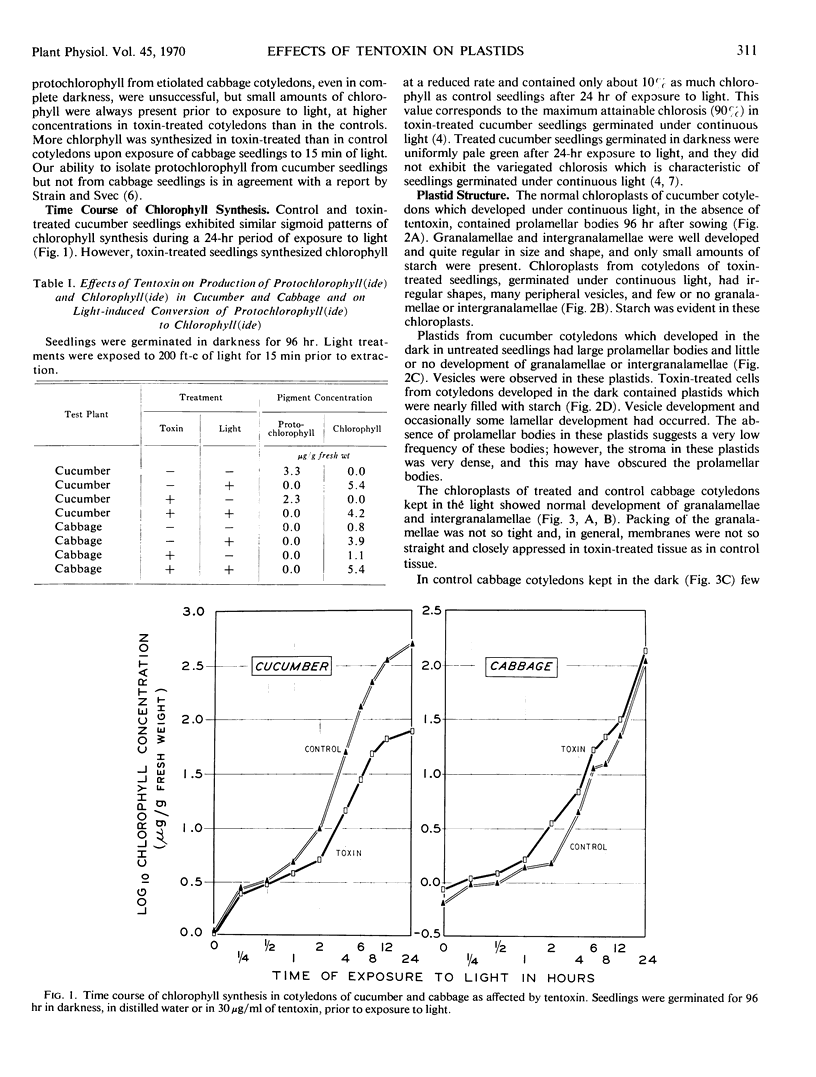
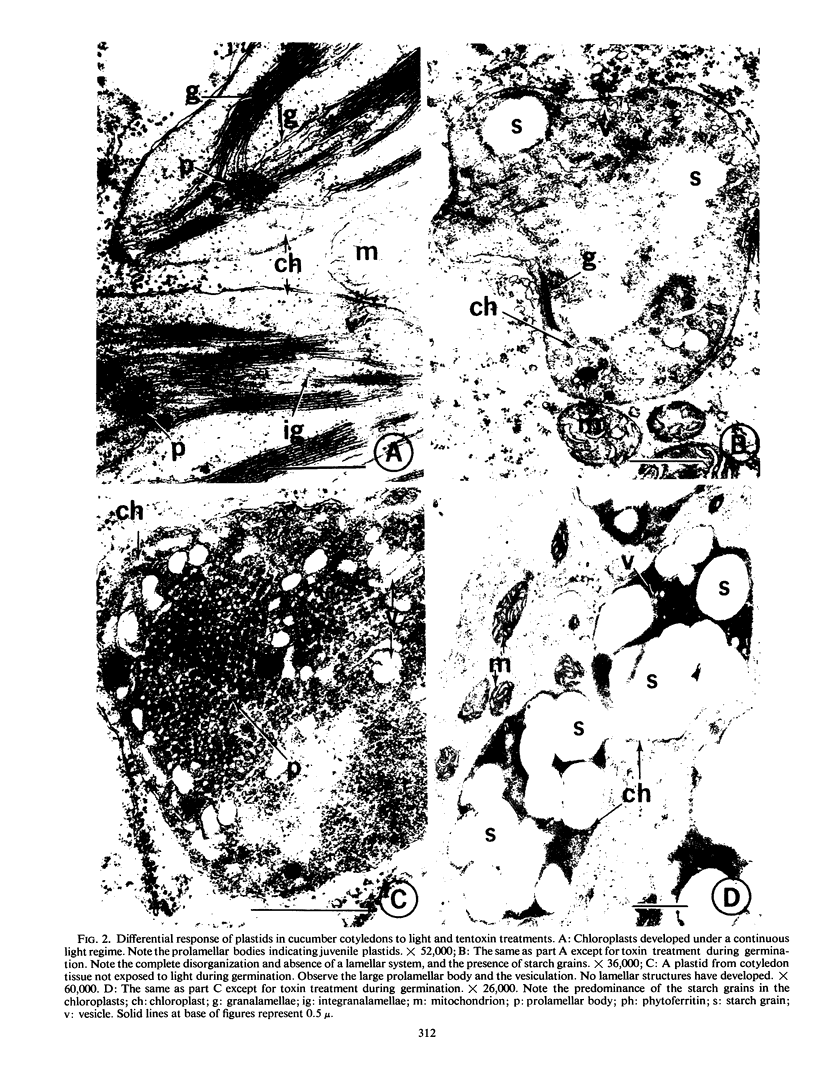
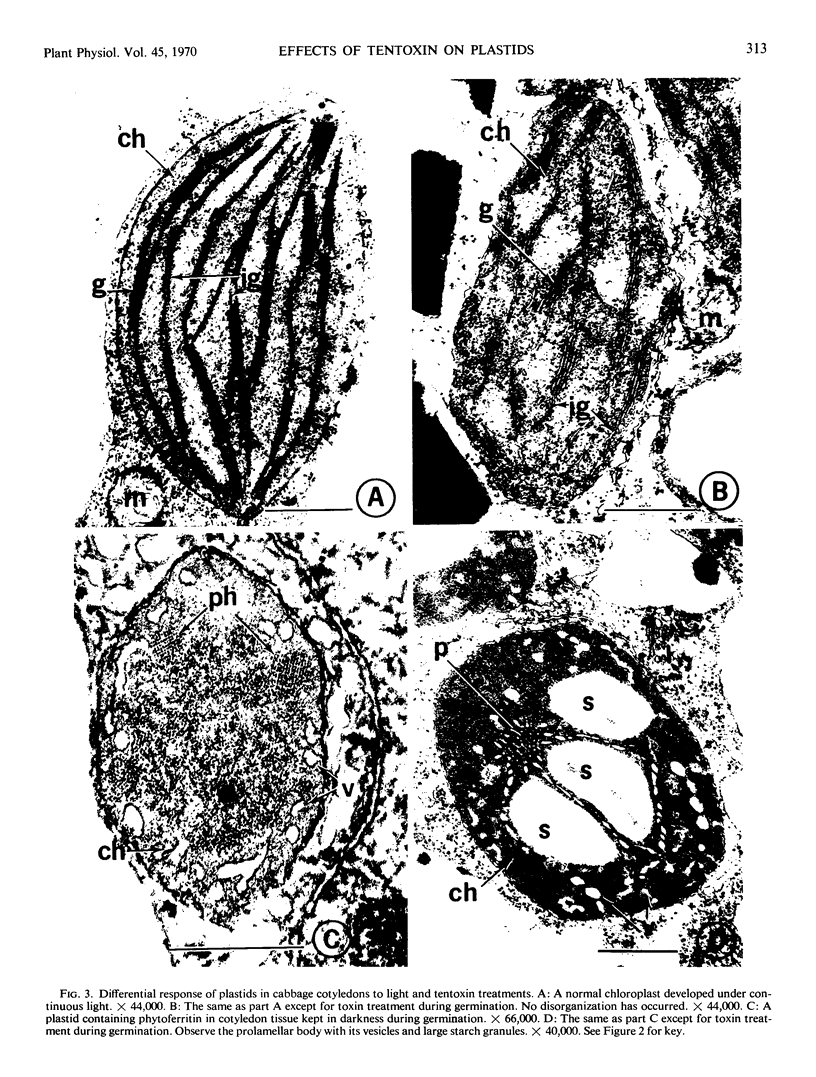
To determine if chlorosis caused by tentoxin, a toxin produced by Alternaria tenuis Nees., is due to interference with chlorophyll synthesis directly or to disruption of normal chloroplast development, the effects of the toxin on these processes in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) and cabbage (Brassica oleracea L., var. capitata) were studied. Cucumber cotyledons are highly sensitive to the toxin but exhibited no interference with the conversion of protochlorophyll(ide) to chlorophyll(ide) or with the general time course pattern of chlorophyll synthesis, although there was a 90% reduction in chlorophyll concentration. In cabbage, which shows no chlorosis in the presence of the toxin, there was a slight stimulation of chlorophyll synthesis in the presence of the toxin. Electron microscopy revealed that in cucumber, toxin treatment interferes with development of prolamellar bodies and lamellae, and results in deformed plastids. No such effects were noted in toxin-treated cabbage tissues. Plastids in toxin-treated cotyledons of both cucumber and cabbage contained more starch than plastids in nontreated tissues. It was concluded that tentoxin acts through disruption of normal plastid development, rather than through direct interference with chlorophyll synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- KOSKI V. M. Chlorophyll formation in seedlings of Zea mays L. Arch Biochem. 1950 Dec;29(2):339–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]