Abstract
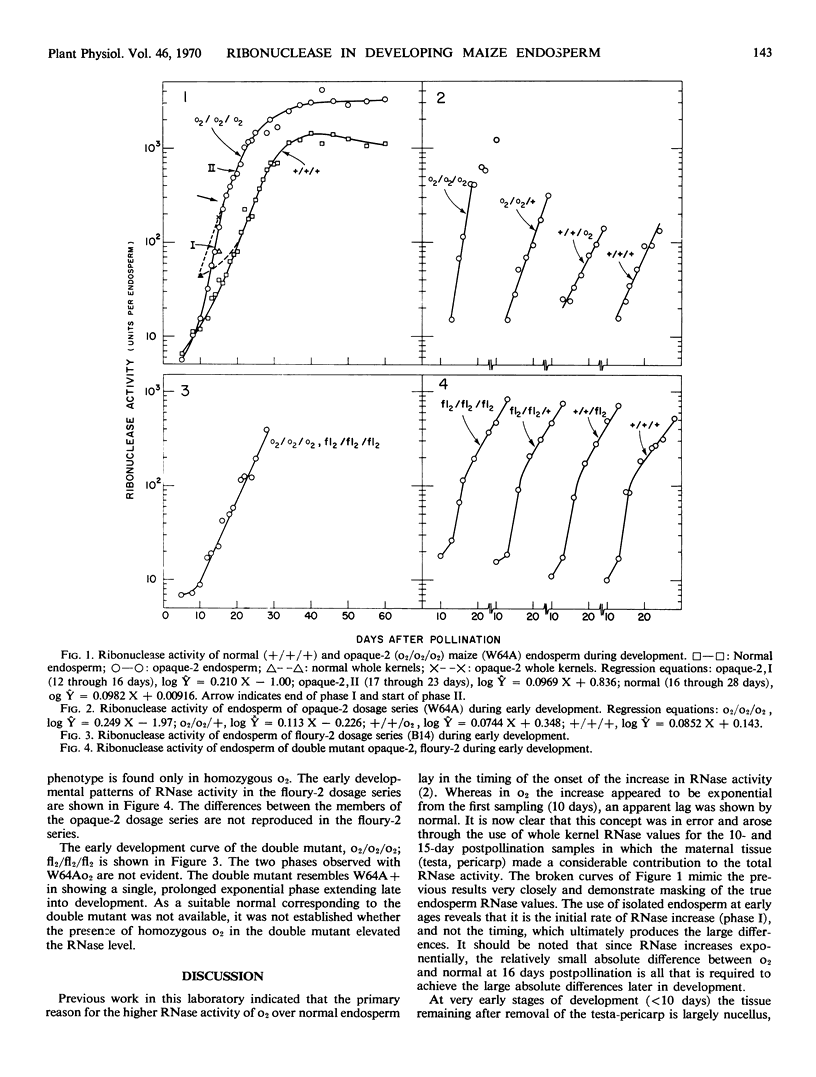
The elevated ribonuclease activity produced in the endosperm of a maize (Zea mays L.) inbred, W64A, by homozygous opaque-2, results from a more than doubled rate of ribonuclease accumulation occurring prior to 16 days post-pollination; after 16 days the rates in opaque-2 and normal are the same, suggesting that opaque-2 is no longer active. The pattern of ribonuclease increase in the opaque-2 dosage series indicates that opaque-2 is not fully recessive. Ribonuclease accumulation is not affected by floury-2 in a second inbred, B14. The results are discussed with reference to other proteins, notably zein, the net synthesis of which is affected by opaque-2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dalby A., Davies I. I. Ribonuclease activity in the developing seeds of normal and opaque-2 maize. Science. 1967 Mar 24;155(3769):1573–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3769.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTZ E. T., BATES L. S., NELSON O. E. MUTANT GENE THAT CHANGES PROTEIN COMPOSITION AND INCREASES LYSINE CONTENT OF MAIZE ENDOSPERM. Science. 1964 Jul 17;145(3629):279–280. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3629.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson O. E., Mertz E. T., Bates L. S. Second Mutant Gene Affecting the Amino Acid Pattern of Maize Endosperm Proteins. Science. 1965 Dec 10;150(3702):1469–1470. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3702.1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Alexander D. E. Ribonuclease activity in normal and opaque-2 mutant endosperm of maize. Science. 1967 Mar 24;155(3769):1575–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3769.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


