Abstract
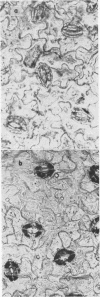
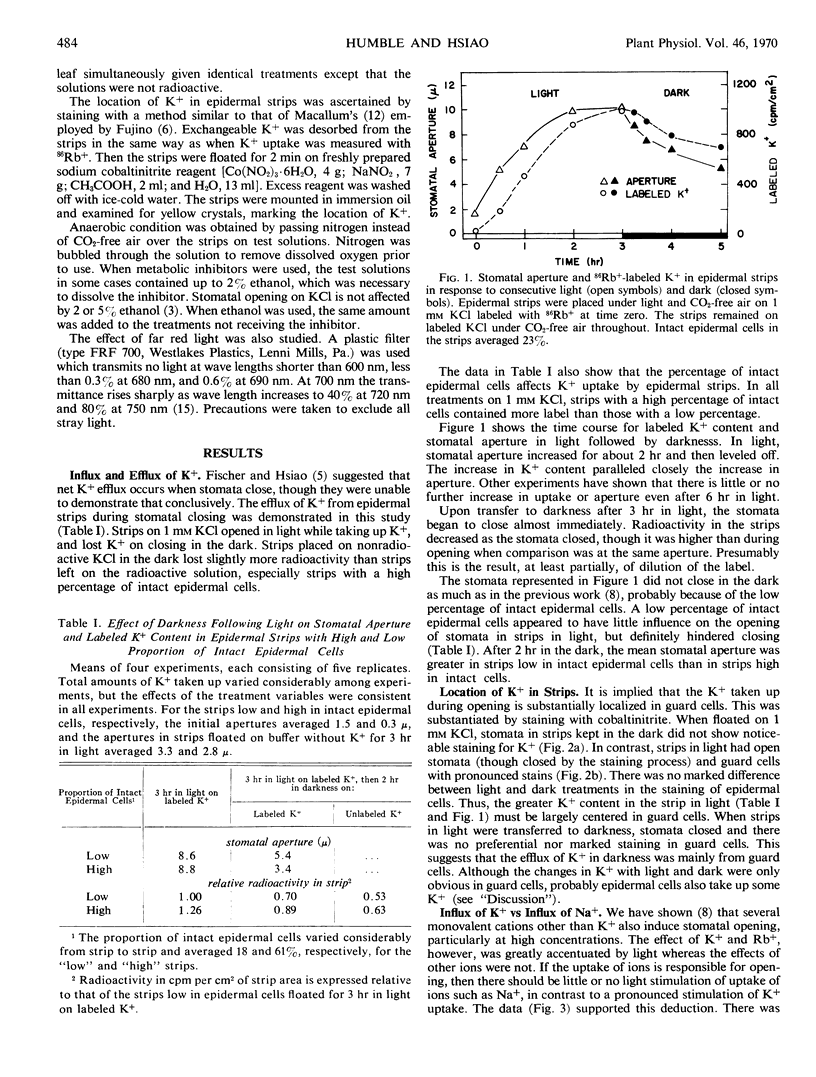
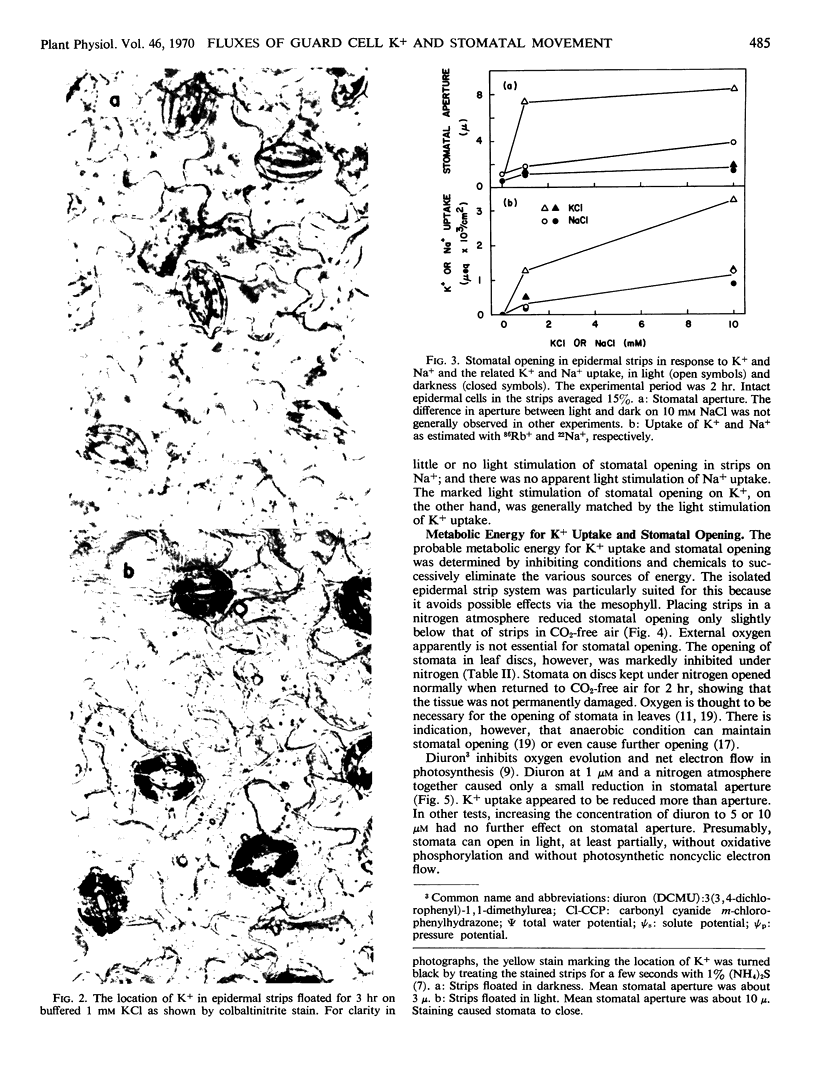
Stomata in epidermal strips of Vicia faba opened in light and closed in darkness when floated on dilute K+ solutions. Opening and closing, respectively, paralleled the fluxes of labeled K+ into and out of the strips. The gain and loss of K+ by the strips were shown by colbaltinitrite stain to be centered at guard cells. Intact epidermal cells, however, appeared to take up K+, complicating interpretation of the data.
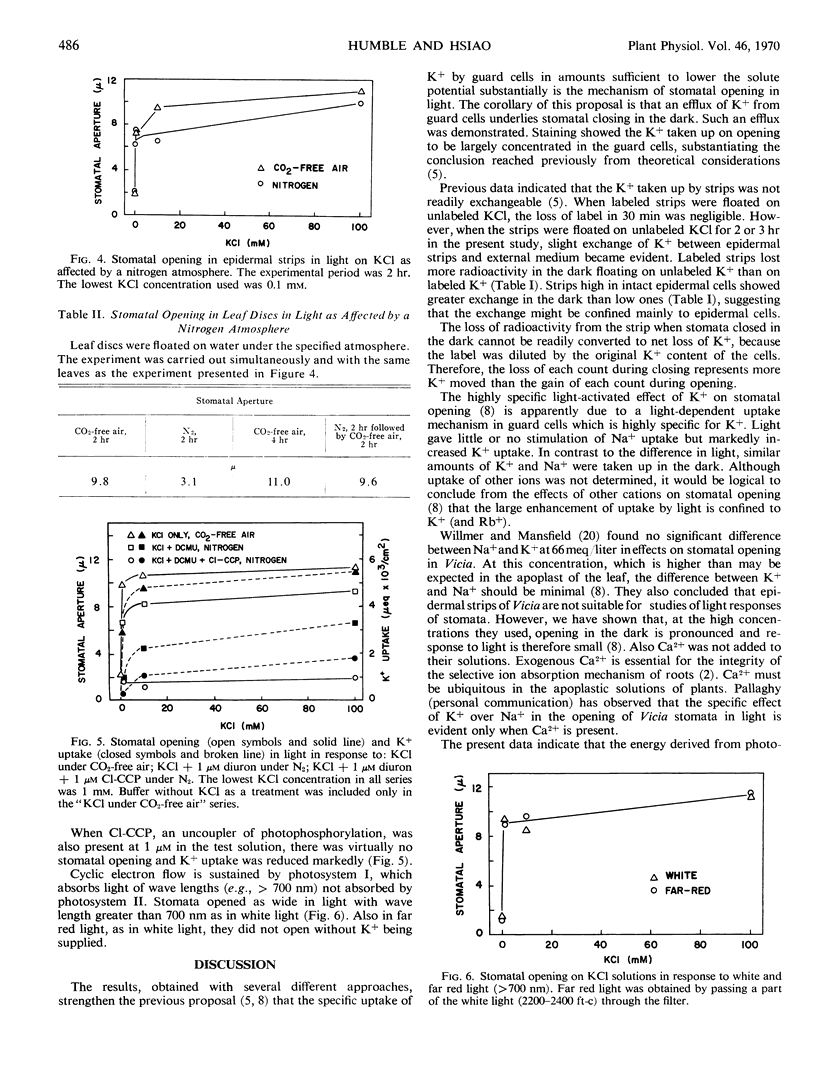
The specific requirement of K+ for stomatal opening in light appeared to be related to the specific uptake of K+. There was little or no light stimulation of opening in strips on Na+, nor was there stimulation of Na+ uptake. The marked light stimulation of opening on K+ was generally matched by stimulation of K+ uptake.
Anaerobiosis markedly reduced opening in leaf discs but not in strips. Under anaerobic conditions, opening in strips was not appreciably affected by 3(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (diuron) but was completely inhibited by carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone plus diuron. Inhibition of opening was generally correlated with inhibition of K+ uptake by the strips. Also stomata in strips opened well under far red light (>700 nanometers). These data suggest that photosystem I and cyclic electron flow can supply the necessary energy for K+ uptake and stomatal opening.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Epstein E. The essential role of calcium in selective cation transport by plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1961 Jul;36(4):437–444. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer R. A., Hsiao T. C. Stomatal Opening in Isolated Epidermal Strips of Vicia faba. II. Responses to KCl Concentration and the Role of Potassium Absorption. Plant Physiol. 1968 Dec;43(12):1953–1958. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.12.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer R. A. Stomatal Opening in Isolated Epidermal Strips of Vicia faba. I. Response to Light and to CO(2)-free Air. Plant Physiol. 1968 Dec;43(12):1947–1952. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.12.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humble G. D., Hsiao T. C. Specific requirement of potassium for light-activated opening of stomata in epidermal strips. Plant Physiol. 1969 Feb;44(2):230–234. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper P. J. Dependence upon Wavelength of Stomatal Movement in Epidermal Tissue of Senecio odoris. Plant Physiol. 1964 Nov;39(6):952–955. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.6.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACROBBIE E. A. THE NATURE OF THE COUPLING BETWEEN LIGHT ENERGY AND ACTIVE ION TRANSPORT IN NITELLA TRANSLUCENS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 25;94:64–73. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macallum A. B. On the distribution of potassium in animal and vegetable cells. J Physiol. 1905 Feb 28;32(2):95–198.3. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1905.sp001068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rains D. W. Kinetics and Energetics of Light-enhanced Potassium Absorption by Corn Leaf Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1968 Mar;43(3):394–400. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.3.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney B. L., Zelitch I. Direct determination of potassium ion accumulation in guard cells in relation to stomatal opening in light. Plant Physiol. 1969 Sep;44(9):1350–1354. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.9.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. A., Zelitch I. Some Effects of Metabolic Inhibitors, Temperature, & Anaerobic Conditions on Stomatal Movement. Plant Physiol. 1963 Jul;38(4):390–396. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.4.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]