Abstract
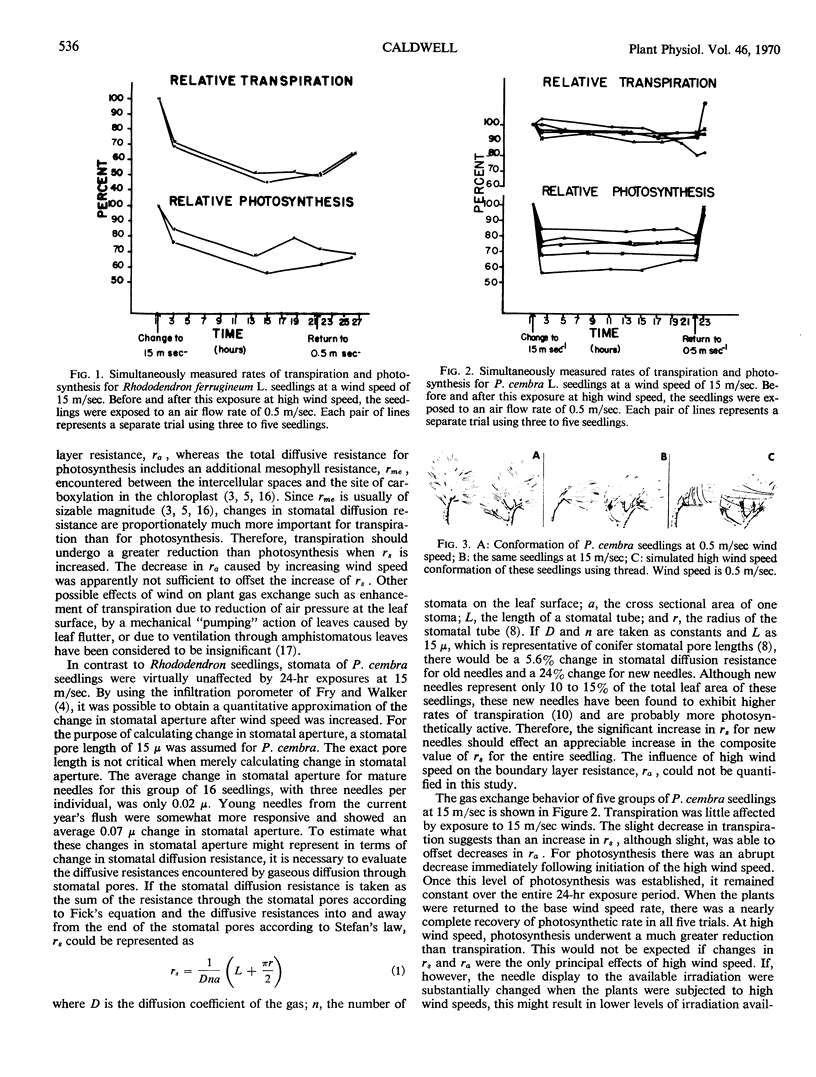
High altitude Rhododendron ferrugineum L. and Pinus cembra L. seedlings were exposed to winds at 15 meters per second for 24-hour periods. Wind-sensitive stomata of Rhododendron seedlings immediately initiated a closing response which resulted in decreased photosynthesis and an even greater reduction in transpiration. Stomatal aperture and transpiration rates of P. cembra were only slightly reduced by high speed winds. However, photosynthesis was substantially reduced because of changes in needle display to available irradiation.
Full text
PDF