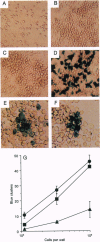
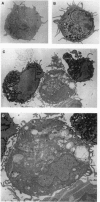
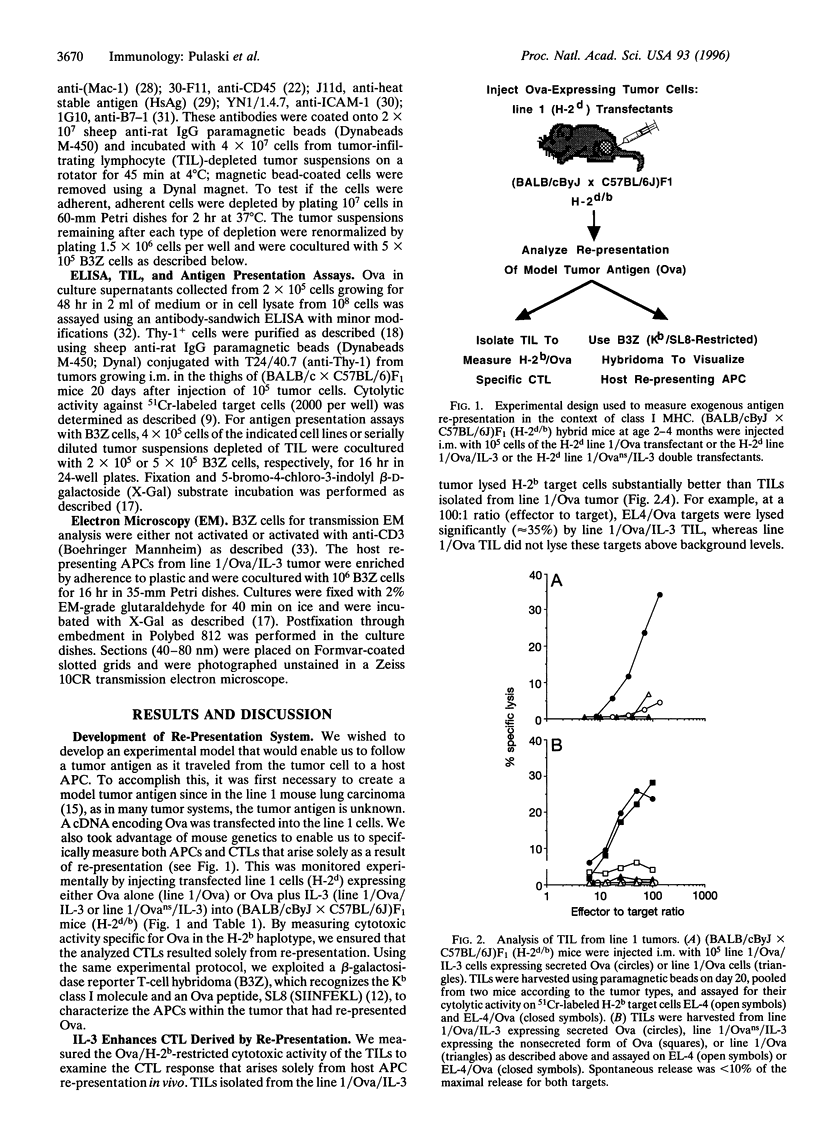
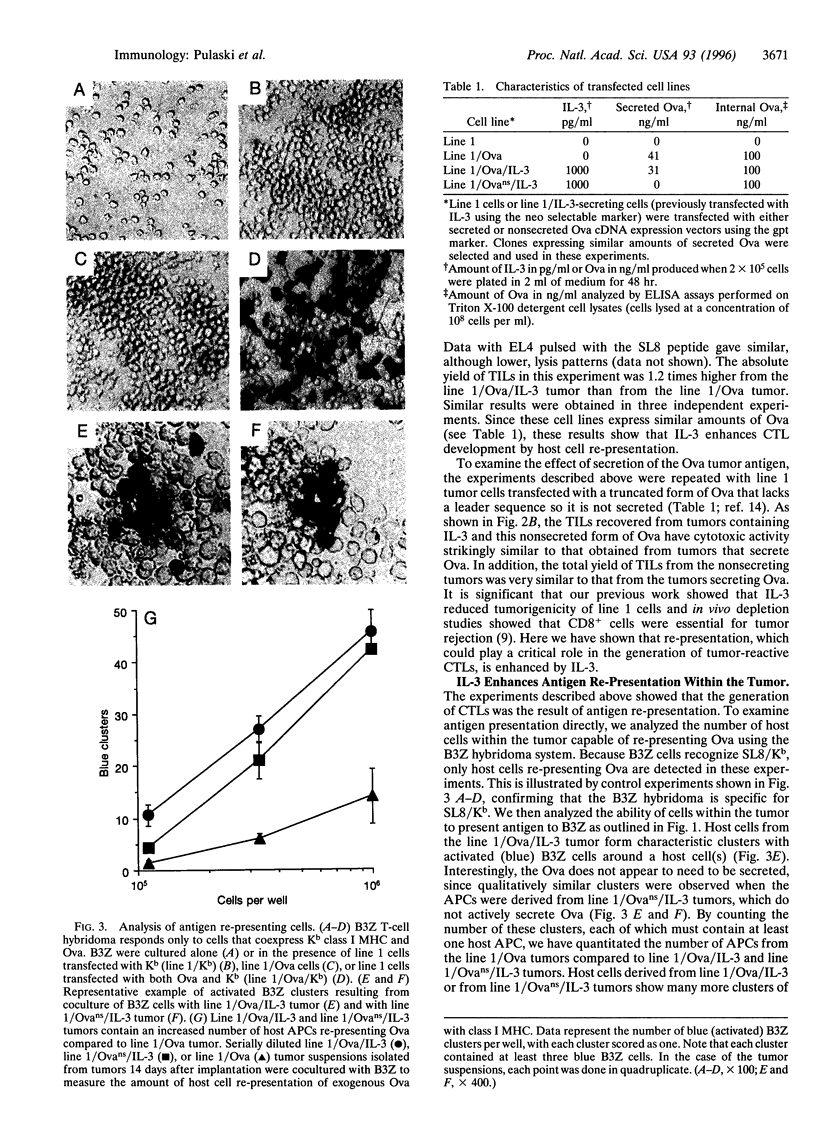
Abstract
We show that interleukin 3 (IL-3) enhances the generation of tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) through the stimulation of host antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The BALB/c (H-2d) spontaneous lung carcinoma line 1 was modified by gene transfection to express ovalbumin as a nominal "tumor antigen" and to secrete IL-3, a cytokine enhancing myeloid development. IL-3-transfected tumor cells are less tumorigenic than the parental cell line, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes isolated from these tumors contain increased numbers of tumor-specific CTLs. By using B3Z86/90.14 (B3Z), a unique T-cell hybridoma system restricted to ovalbumin/H-2b and implanting the tumors in (BALB/c x C57BL/6)F1 (H-2d/b) mice, we demonstrate that the IL-3-transfected tumors contain an increased number of a rare population of host cells that can process and "re-present" tumor antigen to CTLs. Electron microscopy allowed direct visualization of these host APCs, and these studies, along with surface marker phenotyping, indicate that these APCs are macrophage-like. The identification of these cells and their enhancement by IL-3 offers a new opportunity for tumor immunotherapy.
Full text
PDF

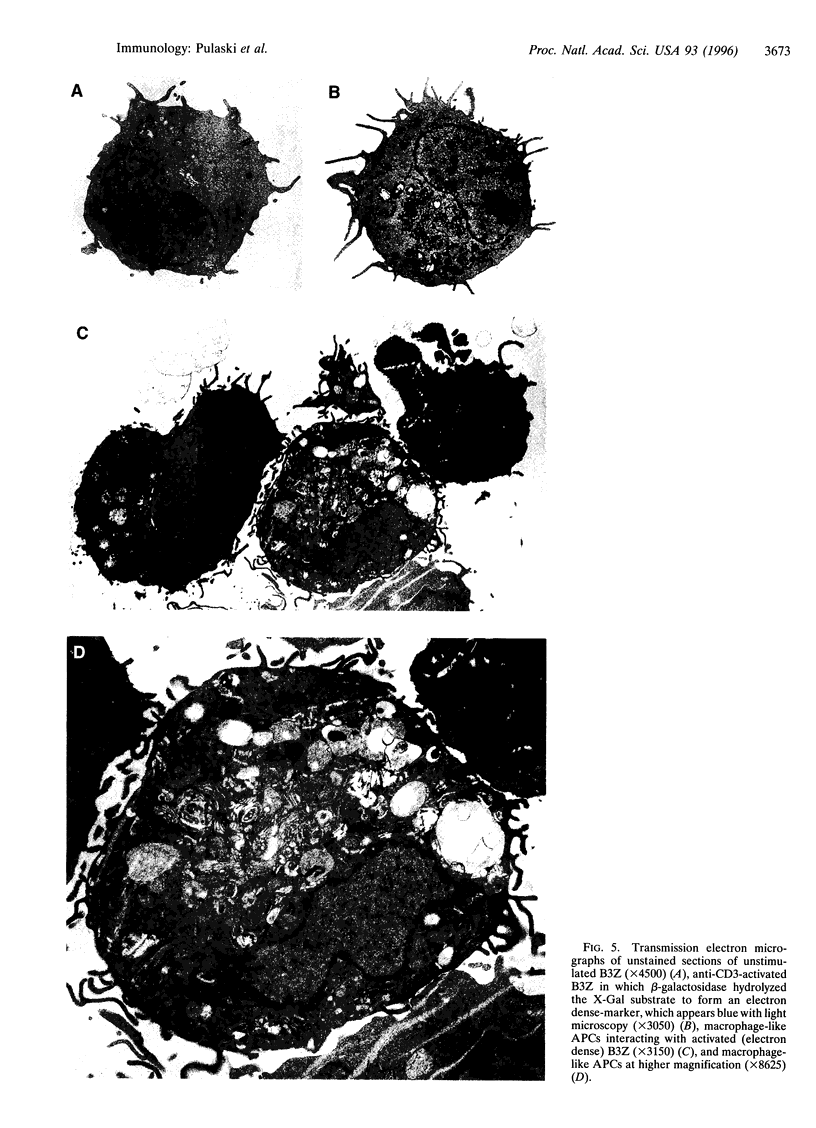

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. P. CD28-B7 interactions in T-cell activation. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994 Jun;6(3):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold D., Faath S., Rammensee H., Schild H. Cross-priming of minor histocompatibility antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells upon immunization with the heat shock protein gp96. J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):885–889. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J. Antigen presentation to cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vivo. J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):639–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J. Cross-priming for a secondary cytotoxic response to minor H antigens with H-2 congenic cells which do not cross-react in the cytotoxic assay. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1283–1288. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A., Dorf M. E., Springer T. A. A shared alloantigenic determinant on Ia antigens encoded by the I-A and I-E subregions: evidence for I region gene duplication. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2488–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blieden T. M., McAdam A. J., Frelinger J. G., Lord E. M. Mechanism of cytolytic T lymphocyte killing of a low class I-expressing tumor. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1433–1438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Guagliardi L. E. The cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:707–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Symington F. W., McKearn T. J., Sprent J. A monoclonal antibody discriminating between subsets of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Tizard R., Farber N. M., Cheung A., Ninfa E. G., Frey A. Z., Gash D. J., Chow E. P. Isolation of the bovine and human genes for Müllerian inhibiting substance and expression of the human gene in animal cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):685–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90783-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruijn M. L., Jackson M. R., Peterson P. A. Phagocyte-induced antigen-specific activation of unprimed CD8+ T cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1995 May;25(5):1274–1285. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Van Vliet E., Döpp E. A., van der Lelij A. A., Kraal G. Marginal zone macrophages identified by a monoclonal antibody: characterization of immuno- and enzyme-histochemical properties and functional capacities. Immunology. 1985 May;55(1):23–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H. Structure of peptides associated with class I and class II MHC molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:181–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Austyn J., Stahl P. D., Gordon S. Surface properties of bacillus Calmette-Guérin-activated mouse macrophages. Reduced expression of mannose-specific endocytosis, Fc receptors, and antigen F4/80 accompanies induction of Ia. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):60–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Fuller-Farrar J., Simon P. L., Hilfiker M. L., Stadler B. M., Farrar W. L. Thymoma production of T cell growth factor (Interleukin 2). J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2555–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Weissman I. L., Bevan M. J. Haplotype-specific suppression of cytotoxic T cell induction by antigen inappropriately presented on T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flechner E. R., Freudenthal P. S., Kaplan G., Steinman R. M. Antigen-specific T lymphocytes efficiently cluster with dendritic cells in the human primary mixed-leukocyte reaction. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jan;111(1):183–195. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Borriello F., Hodes R. J., Reiser H., Gribben J. G., Ng J. W., Kim J., Goldberg J. M., Hathcock K., Laszlo G. Murine B7-2, an alternative CTLA4 counter-receptor that costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2185–2192. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding L. R., Edwards C. B. H-2 antigen requirements in the in vitro induction of SV40-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1258–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. Y., Golumbek P., Ahmadzadeh M., Jaffee E., Pardoll D., Levitsky H. Role of bone marrow-derived cells in presenting MHC class I-restricted tumor antigens. Science. 1994 May 13;264(5161):961–965. doi: 10.1126/science.7513904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J., Rüsch E., Tada N., Kimura S., Hämmerling U. Localization of allodeterminants on H-2Kb antigens determined with monoclonal antibodies and H-2 mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4737–4741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen J., Shastri N. Measurement of ligand-induced activation in single viable T cells using the lacZ reporter gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3972–3976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke Y., Li Y., Kapp J. A. Ovalbumin injected with complete Freund's adjuvant stimulates cytolytic responses. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Feb;25(2):549–553. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Lee G., Watanabe T., Sun L., Scheid M. P. Antigens displayed on murine B lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2262–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Thorens B., de Kossodo S., Allet B., Eliason J. F., Thatcher D., Farber N., Vassalli P. Stimulation of hematopoiesis in vivo by recombinant bacterial murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1001–1005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics-Bankowski M., Rock K. L. A phagosome-to-cytosol pathway for exogenous antigens presented on MHC class I molecules. Science. 1995 Jan 13;267(5195):243–246. doi: 10.1126/science.7809629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancki D. W., Ma D. I., Havran W. L., Fitch F. W. Cell surface structures involved in T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1984 Oct;81:65–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb01105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K. P., Russell S. W., LeBlanc P. A., Caballero S. Heterogeneity among macrophages cultured from mouse bone marrow. Morphologic, cytochemical and flow cytometric analyses. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(3):693–701. doi: 10.1007/BF00219251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber M. I., Loken M. R., Stall A. M., Fitch F. W. I-A antigens on cloned alloreactive murine T lymphocytes are acquired passively. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2798–2803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord E. M., Keng P. C. Methods for using centrifugal elutriation to separate malignant and lymphoid cell populations. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 30;68(1-2):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam A. J., Pulaski B. A., Storozynsky E., Yeh K. Y., Sickel J. Z., Frelinger J. G., Lord E. M. Analysis of the effect of cytokines (interleukins 2, 3, 4, and 6, granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interferon-gamma) on generation of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes against a weakly immunogenic tumor. Cell Immunol. 1995 Oct 15;165(2):183–192. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. W., Carbone F. R., Bevan M. J. Introduction of soluble protein into the class I pathway of antigen processing and presentation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):777–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Freeman G. J., Gault A., Godfrey D., Nadler L. M., Glimcher L. H. Signalling through the MHC class II cytoplasmic domain is required for antigen presentation and induces B7 expression. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):266–268. doi: 10.1038/360266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonacs R., Humborg C., Tam J. P., Steinman R. M. Mechanisms of mouse spleen dendritic cell function in the generation of influenza-specific, cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):519–529. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt B., Eppler M., Leist T. P., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Virus-triggered acquired immunodeficiency by cytotoxic T-cell-dependent destruction of antigen-presenting cells and lymph follicle structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8252–8256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou J. M., Ashman R. B. Macrophages: current views on their differentiation, structure, and function. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1989 Jul-Aug;13(4):343–372. doi: 10.3109/01913128909048488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulaski B. A., McAdam A. J., Hutter E. K., Biggar S., Lord E. M., Frelinger J. G. Interleukin 3 enhances development of tumor-reactive cytotoxic cells by a CD4-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res. 1993 May 1;53(9):2112–2117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis e Sousa C., Germain R. N. Major histocompatibility complex class I presentation of peptides derived from soluble exogenous antigen by a subset of cells engaged in phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1995 Sep 1;182(3):841–851. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.3.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson S., Shastri N. LacZ inducible, antigen/MHC-specific T cell hybrids. Int Immunol. 1994 Mar;6(3):369–376. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastri N., Gonzalez F. Endogenous generation and presentation of the ovalbumin peptide/Kb complex to T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):2724–2736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1142–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suto R., Srivastava P. K. A mechanism for the specific immunogenicity of heat shock protein-chaperoned peptides. Science. 1995 Sep 15;269(5230):1585–1588. doi: 10.1126/science.7545313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei F. Inhibition of mixed lymphocyte response by a rat monoclonal antibody to a novel murine lymphocyte activation antigen (MALA-2). J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1403–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Golden L., Zakut R., Mellor A., Fahrner K., Kvist S., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the H-2kb gene: evidence for gene conversion as a mechanism for the generation of polymorphism in histocompatibilty antigens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuhas J. M., Pazmino N. H., Proctor J. O., Toya R. E. A direct relationship between immune competence and the subcutaneous growth rate of a malignant murine lung tumor. Cancer Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):722–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]