Abstract
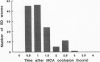
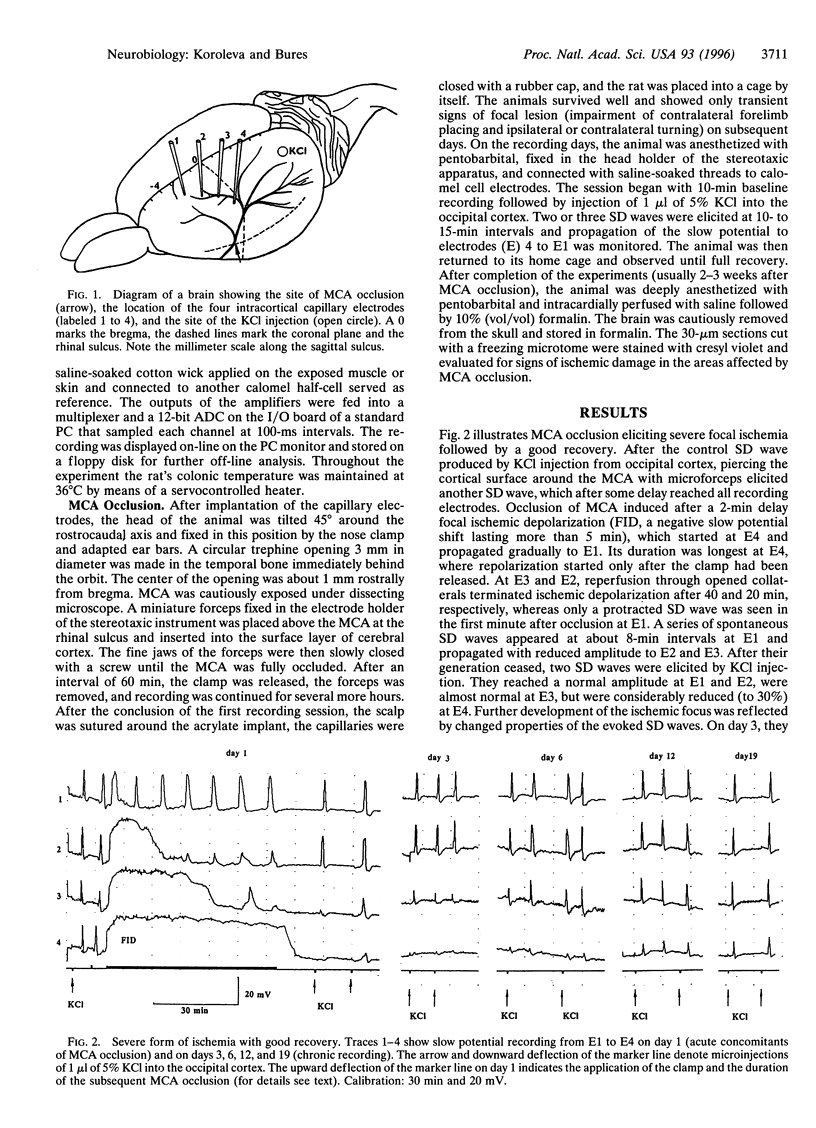
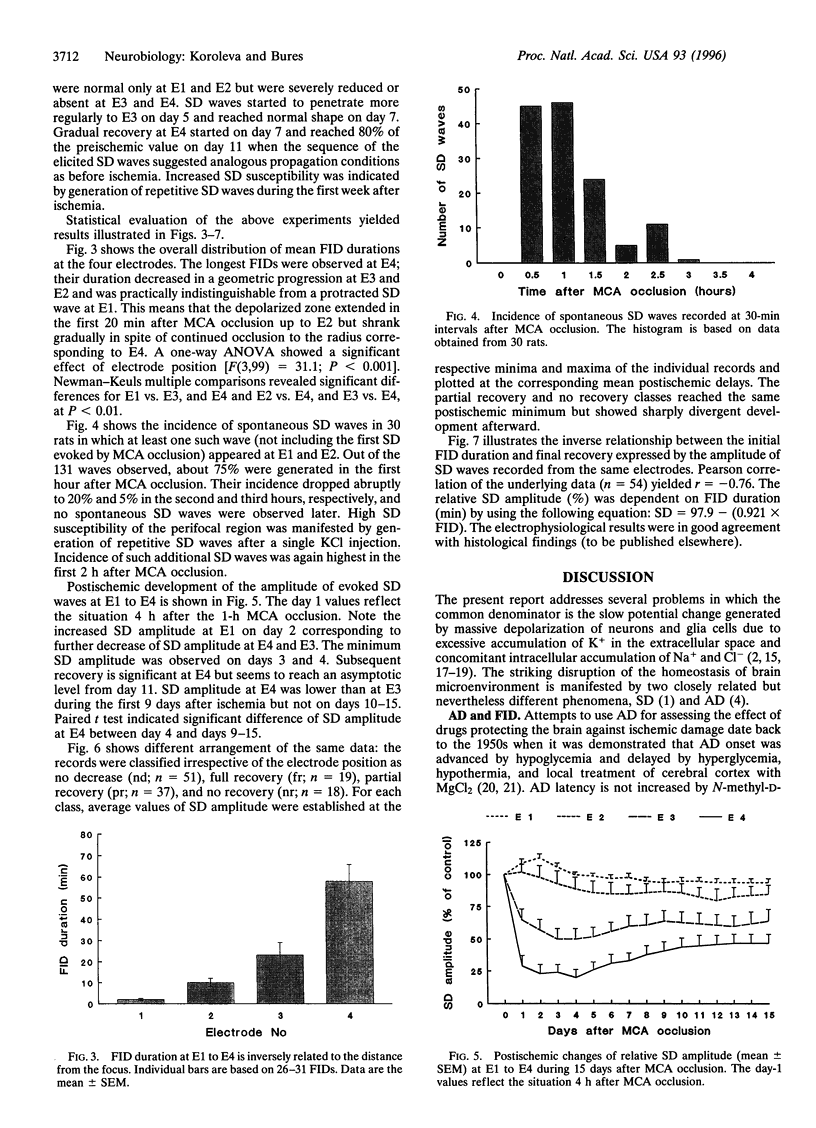
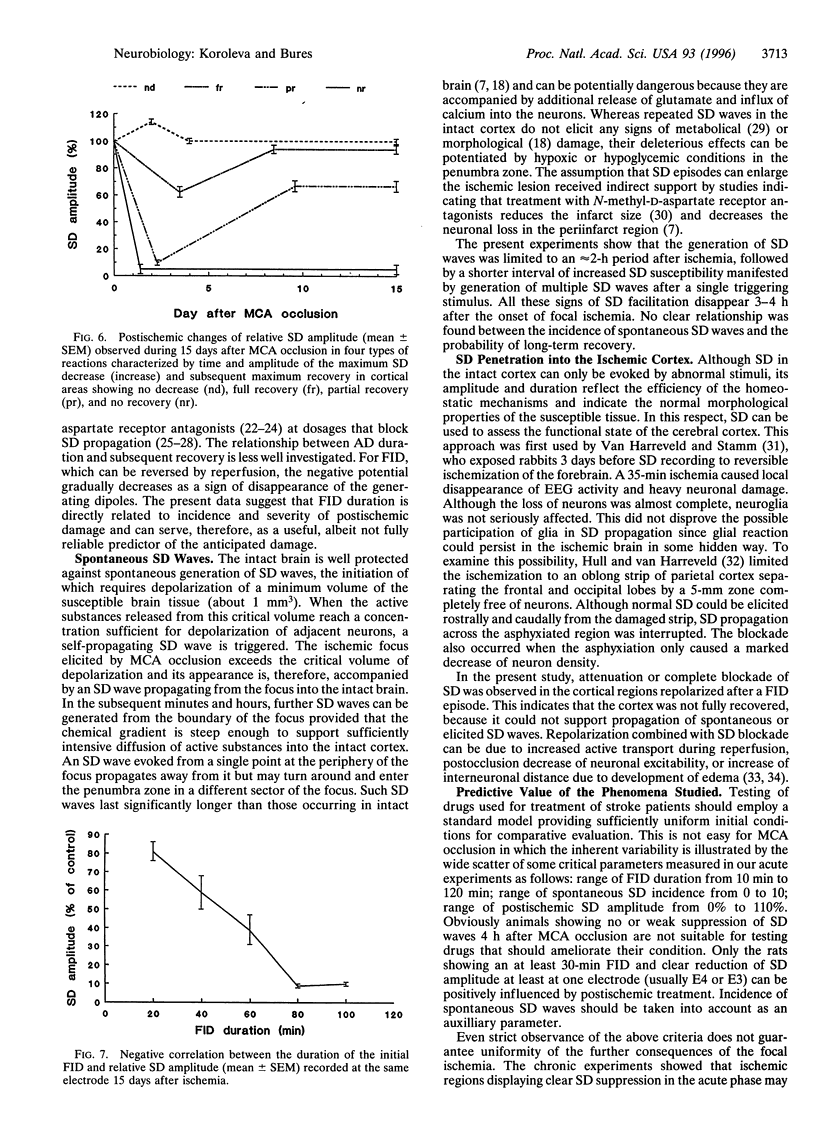
Slow potential recording was used for long-term monitoring of the penumbra zone surrounding an ischemic region produced by middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion in adult hooded rats (n = 32). Four capillary electrodes (El-E4) were chronically implanted at 2-mm intervals from AP -3, L 2 (El) to AP 0, L 5 (E4). Spontaneous or evoked slow potential waves of spreading depression (SD) were recorded during and 4 h after a 1-h MCA occlusion and at 2- to 3-day intervals afterward for 3 weeks. Duration of the initial focal ischemic depolarization was maximal at E4 and decreased with distance from the focus. SD waves in the penumbra zone were high at El and E2, low and prolonged at E3, and almost absent at E4. Amplitude of elicited SD waves was further reduced 3 days later and slowly increased in the following week. Cortical areas displaying marked reduction of SD waves in the first days after MCA occlusion either remained low or showed substantial (60%) recovery, the probability of which decreased with the duration of the initial focal ischemic depolarization and increased with the distance from the focus. It is concluded that the outcome of ischemia monitored by long-term SD recovery in the perifocal region can be partly predicted from the acute signs of MCA occlusion.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amemori T., Bures J. Ketamine blockade of spreading depression: rapid development of tolerance. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 11;519(1-2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90101-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENESOVA O., BURESOVA O., BURES J. Die Wirkung des Chlorpromazins und der Glykämie auf das elektrophysiologisch kontrollierte Uberleben der Hirnrinde bei verschiedenen Kopertemperaturen. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1957;231(6):550–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURES J., BURESOVA O. Die anoxische Terminaldepolarisation als Indicator der Vulnerabilität der Grosshirnrinde bei Anoxie und Ischämie. Pflugers Arch. 1957;264(4):325–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00364173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back T., Kohno K., Hossmann K. A. Cortical negative DC deflections following middle cerebral artery occlusion and KCl-induced spreading depression: effect on blood flow, tissue oxygenation, and electroencephalogram. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994 Jan;14(1):12–19. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A., Li H., Pulsinelli W. A. The N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, MK-801, fails to protect against neuronal damage caused by transient, severe forebrain ischemia in adult rats. J Neurosci. 1991 Apr;11(4):1049–1056. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-04-01049.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiamulera C., Terron A., Reggiani A., Cristofori P. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the progressive cerebral damage after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res. 1993 Mar 26;606(2):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90992-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. D., Feng Z. C., Leistra H., Watson B. D., Rosenthal M. Photothrombotic infarction triggers multiple episodes of cortical spreading depression in distant brain regions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994 Jan;14(1):20–28. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Andiné P., Hillered L., Persson L., Hagberg H. The effect of MK-801 on cortical spreading depression in the penumbral zone following focal ischaemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 May;12(3):371–379. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorelova N. A., Koroleva V. I., Amemori T., Pavlík V., Bures J. Ketamine blockade of cortical spreading depression in rats. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1987 Apr;66(4):440–447. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(87)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULL C. D., VANHARREVELD A. ABSENCE OF CONDUCTION OF SPREADING DEPRESSION THROUGH CORTICAL REGION DAMAGED BY ASPHYXIATION. Am J Physiol. 1964 Oct;207:921–924. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.4.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. J. Effect of anoxia on ion distribution in the brain. Physiol Rev. 1985 Jan;65(1):101–148. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. J., Nedergaard M. Brain ion homeostasis in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Pathol. 1988 Jul-Dec;9:195–209. doi: 10.1007/BF03160362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernándéz-Cáceres J., Macias-González R., Brozek G., Bures J. Systemic ketamine blocks cortical spreading depression but does not delay the onset of terminal anoxic depolarization in rats. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 29;437(2):360–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91652-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernándéz-Cáceres J., Macias-González R., Brozek G., Bures J. Systemic ketamine blocks cortical spreading depression but does not delay the onset of terminal anoxic depolarization in rats. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 29;437(2):360–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91652-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima T., Mies G., Hossmann K. A. Repeated negative DC deflections in rat cortex following middle cerebral artery occlusion are abolished by MK-801: effect on volume of ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 Sep;12(5):727–733. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritzen M., Hansen A. J. The effect of glutamate receptor blockade on anoxic depolarization and cortical spreading depression. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 Mar;12(2):223–229. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsberg P. J., Frerichs K. U., Burris J. A., Hallenbeck J. M., Feuerstein G. Cortical microcirculation in a new model of focal laser-induced secondary brain damage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Jan;11(1):88–98. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrannes R., Willems R., De Prins E., Wauquier A. Evidence for a role of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in cortical spreading depression in the rat. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 9;457(2):226–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90690-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard M., Astrup J. Infarct rim: effect of hyperglycemia on direct current potential and [14C]2-deoxyglucose phosphorylation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1986 Oct;6(5):607–615. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1986.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard M. Mechanisms of brain damage in focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988 Feb;77(2):81–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1988.tb05878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. K., Nehls D. G., Graham D. I., Teasdale G. M., McCulloch J. Focal cerebral ischaemia in the cat: treatment with the glutamate antagonist MK-801 after induction of ischaemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Oct;8(5):757–762. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siesjö B. K., Bengtsson F. Calcium fluxes, calcium antagonists, and calcium-related pathology in brain ischemia, hypoglycemia, and spreading depression: a unifying hypothesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Apr;9(2):127–140. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somjen G. G., Aitken P. G. The ionic and metabolic responses associated with neuronal depression of Leão's type in cerebral cortex and in hippocampal formation. An Acad Bras Cienc. 1984 Dec;56(4):495–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syková E., Svoboda J., Polák J., Chvátal A. Extracellular volume fraction and diffusion characteristics during progressive ischemia and terminal anoxia in the spinal cord of the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994 Mar;14(2):301–311. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HARREVELD A., STAMM J. S. Cerebral asphyxiation and spreading cortical depression. Am J Physiol. 1953 Apr;173(1):171–175. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.173.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyskocil F., Kritz N., Bures J. Potassium-selective microelectrodes used for measuring the extracellular brain potassium during spreading depression and anoxic depolarization in rats. Brain Res. 1972 Apr 14;39(1):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90802-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]