Abstract
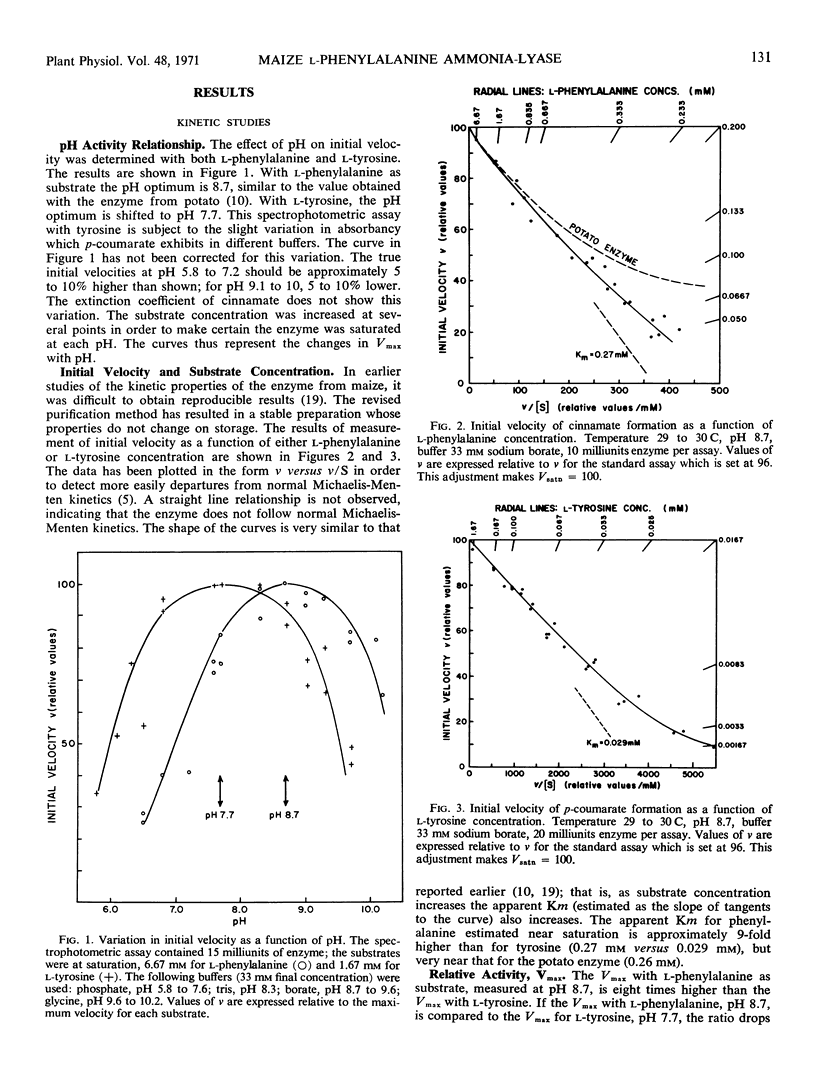
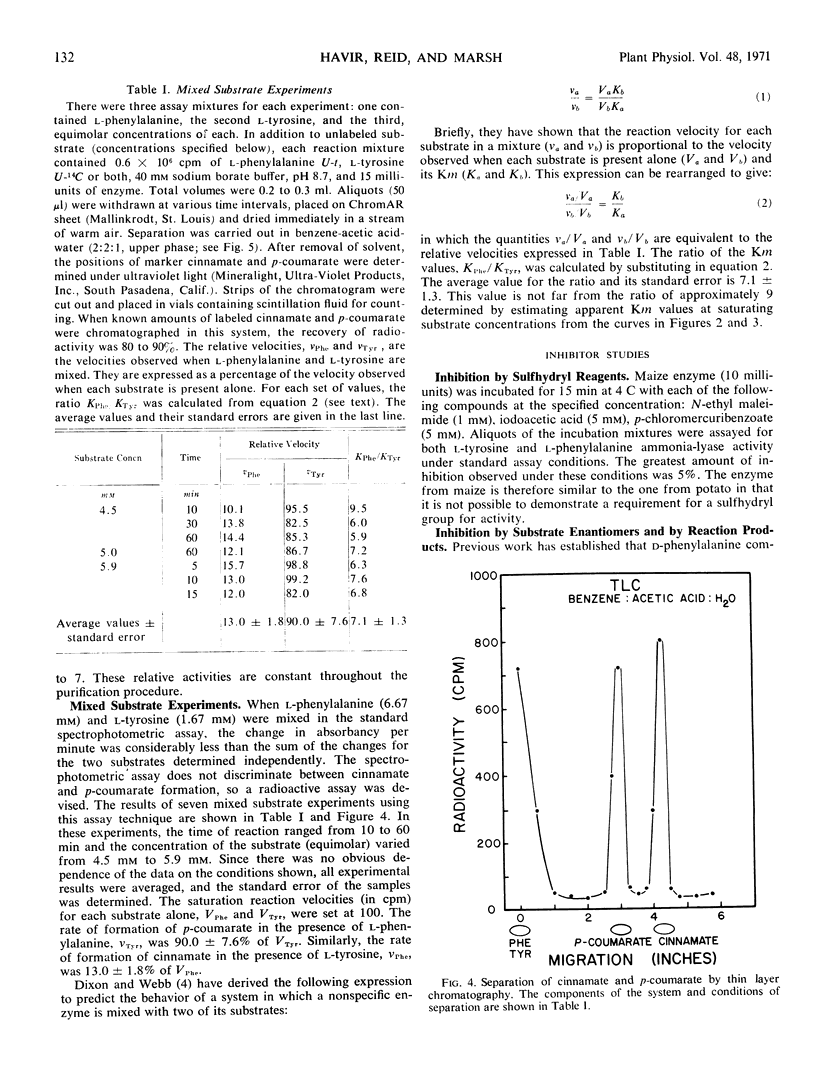
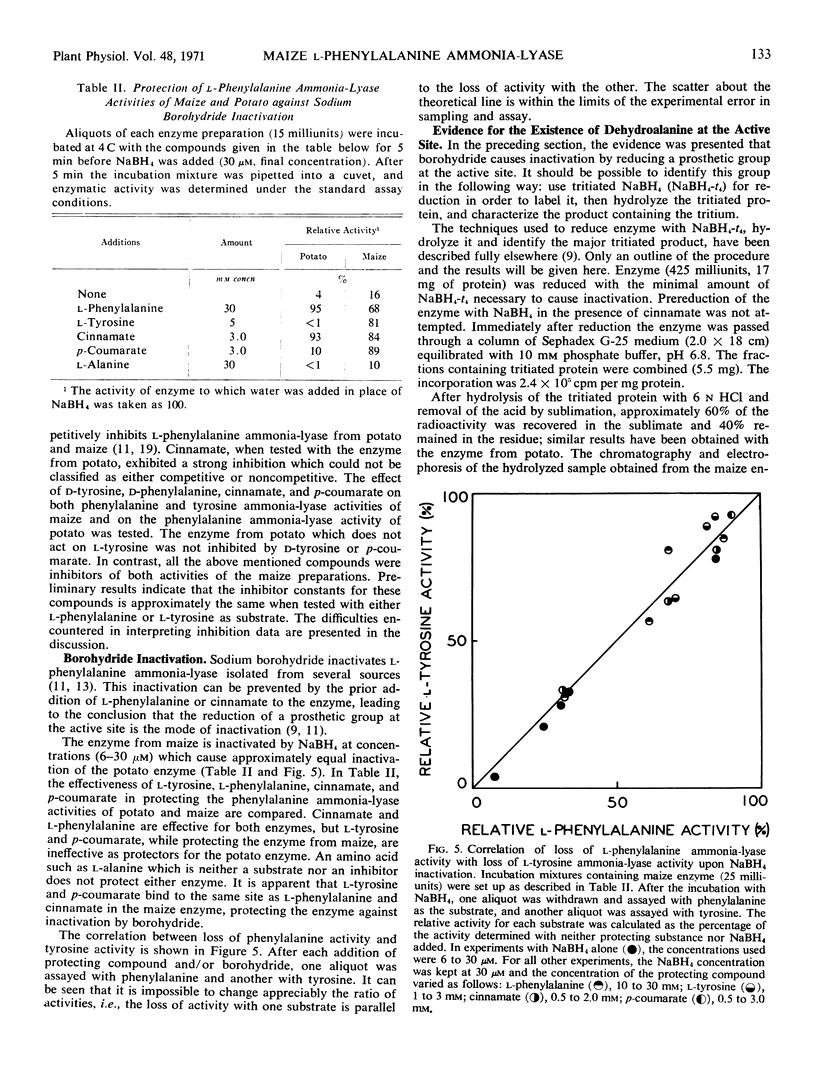
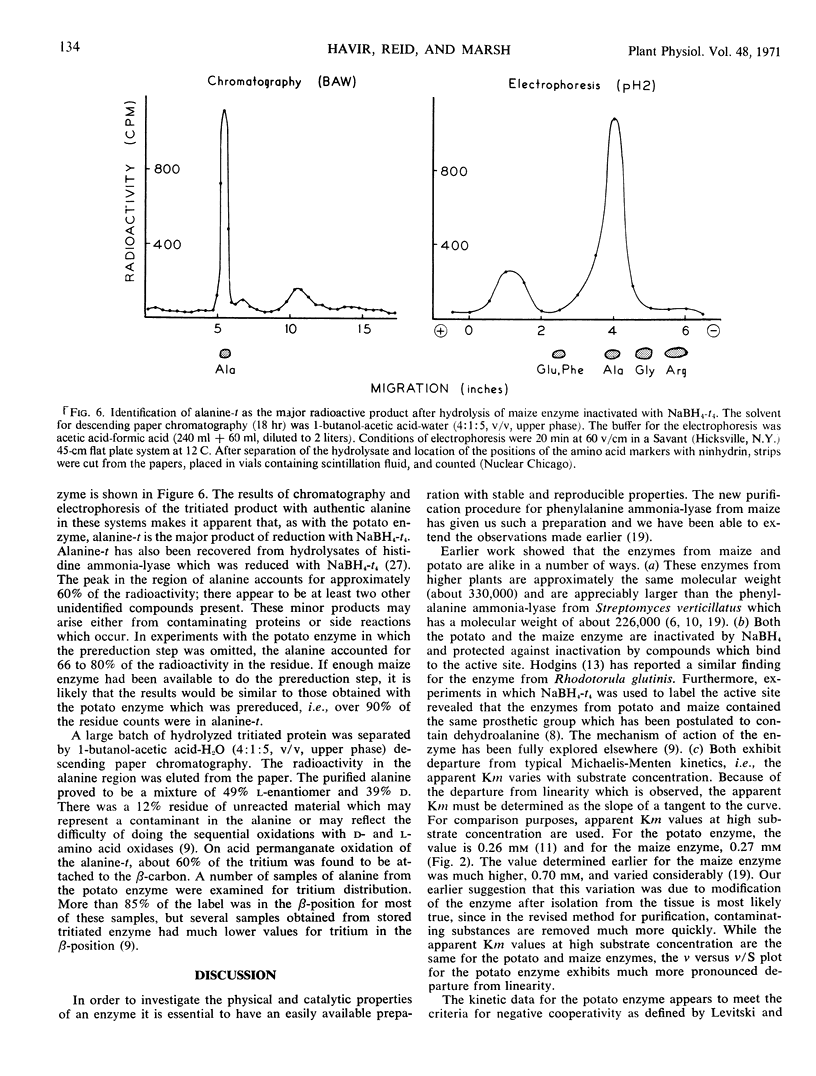
l-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (E.C. 4.3.1.5) from maize is active with l-tyrosine and l-phenylalanine and exhibits atypical Michaelis-Menten kinetics with both substrates. With phenylalanine as a substrate, the pH optimum is 8.7 and with tyrosine, 7.7. The estimated Km at high substrate concentrations is 0.27 mm for phenylalanine and 0.029 mm for tyrosine. However, the Vmax with phenylalanine is eight times higher than the Vmax with tyrosine when both are measured at pH 8.7, and 7 times higher when both are measured at their pH optima. The following evidence leads us to the conclusion that there is a common catalytic site for both substrates: (a) It is impossible to appreciably alter the ratio of the two activities during purification and isoelectric focusing. (b) The ratio of the products formed in mixed substrate experiments is in good agreement with the ratio predicted from the estimated Km values. (c) NaBH4 reduces both activities to the same degree and l-phenylalanine, l-tyrosine, cinnamate, and p-coumarate protect both activities against NaBH4 reduction to the same degree. In contrast, the enzyme isolated from potato, which does not act on l-tyrosine, is not protected against reduction by either l-tyrosine or p-coumarate. However, both enzymes appear to have a dehydroalanine-containing prosthetic group.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conway A., Koshland D. E., Jr Negative cooperativity in enzyme action. The binding of diphosphopyridine nucleotide to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4011–4023. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWD J. E., RIGGS D. S. A COMPARISON OF ESTIMATES OF MICHAELIS-MENTEN KINETIC CONSTANTS FROM VARIOUS LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:863–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emes A. V., Vining L. C. Partial purification and properties of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Streptomyces verticillatus. Can J Biochem. 1970 May;48(5):613–622. doi: 10.1139/o70-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson K. R., Havir E. A. L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. IV. Evidence that the prosthetic group contains a dehydroalanyl residue and mechanism of action. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havir E. A., Hanson K. R. L-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. I. Purification and molecular size of the enzyme from potato tubers. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1896–1903. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havir E. A., Hanson K. R. L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. II. Mechanism and kinetic properties of the enzyme from potato tubers. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1904–1914. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. L., Brown D. H., Brown B. I. Studies of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase. I. Purification and properties of the rat liver enzyme. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1403–1415. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOUKOL J., CONN E. E. The metabolism of aromatic compounds in higher plants. IV. Purification and properties of the phenylalanine deaminase of Hordeum vulgare. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2692–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Koshland D. E., Jr Negative cooperativity in regulatory enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1121–1128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh H. V., Jr, Havir E. A., Hanson K. R. L-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. 3. Properties of the enzyme from maize seedlings. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1915–1918. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K., Rao P. V., Towers G. H. Degradation of phenylalanine and tyrosine by Sporobolomyces roseus. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):507–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1060507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


