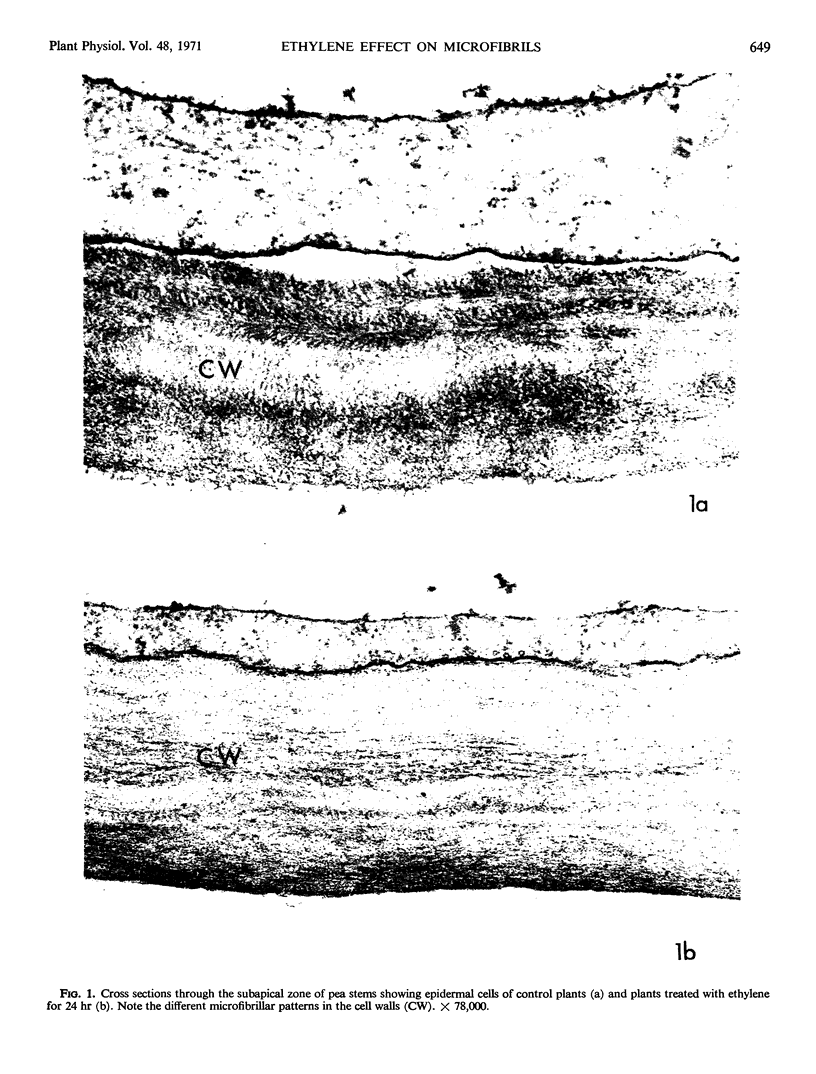
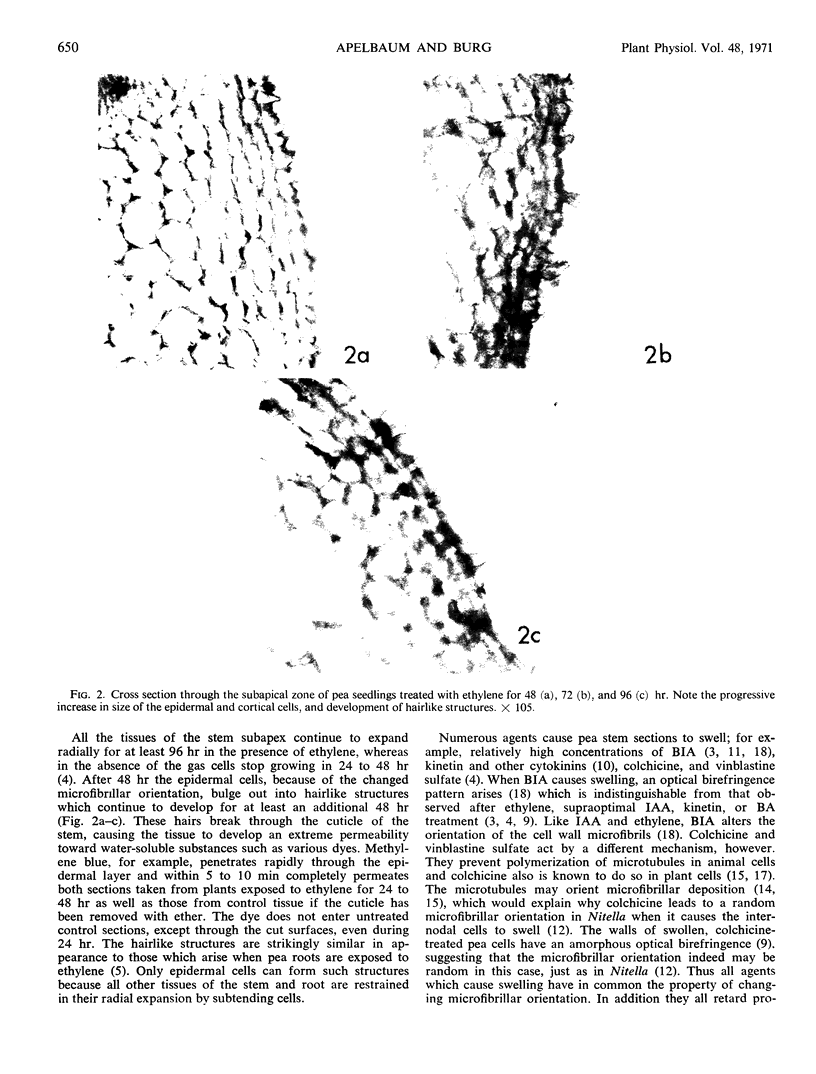
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burg S. P., Burg E. A. The interaction between auxin and ethylene and its role in plant growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):262–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick A. V., Burg S. P. An explanation of the inhibition of root growth caused by indole-3-acetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1967 Mar;42(3):415–420. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland R., Karlsnes A. M. A possible role of hydroxyproline-containing proteins in the cessation of cell elongation. Plant Physiol. 1967 May;42(5):669–671. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.5.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs Y., Lieberman M. Effects of Kinetin, IAA, and Gibberellin on Ethylene Production, and Their Interactions in Growth of Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1968 Dec;43(12):2029–2036. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.12.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]