Abstract
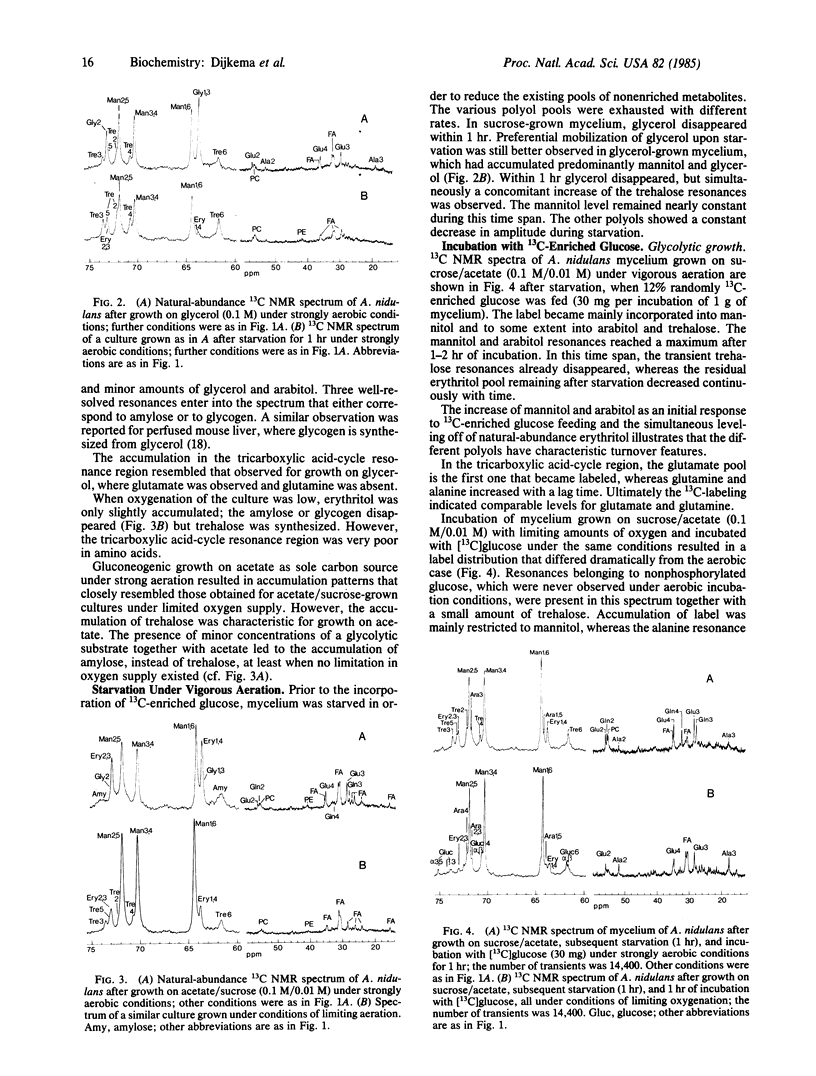
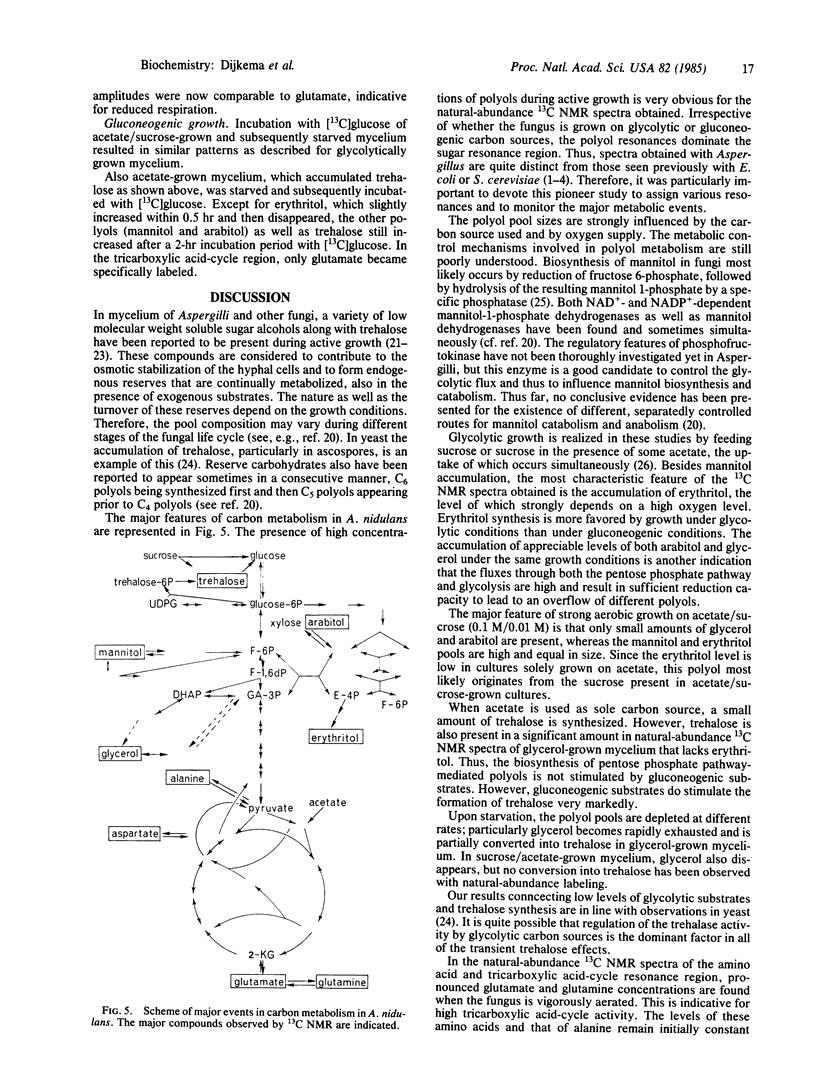
Natural-abundance high-resolution 13C NMR spectra (linewidth, 10 Hz) of the hyphal fungus Aspergillus nidulans have been obtained after growth on glycolytic or gluconeogenic carbon sources. Various polyols, some tricarboxylic acid-cycle intermediates and amino acids, and some phospholipids and fatty acyl compounds are present. The polyols found are mannitol, arabitol, erythritol, and glycerol. The nature of the carbon source has a pronounced effect on the pool sizes of the various polyols. All are present when the fungus is grown on sucrose or sucrose/acetate under strongly aerobic conditions. When grown on acetate, both arabitol and glycerol levels are low, whereas on glycerol erythritol is also hardly detectable. The effect of oxygen is most outspoken in glycolytically grown cultures. Limited oxygenation leads to low levels of arabitol and glycerol. Strong oxygenation changes the ratio of erythritol to mannitol, favoring the C4 polyol. An increase in oxygen supply leads to (i) stimulation of the fluxes through the pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis, (ii) an overflow of reduced metabolites both at the pentose phosphate pathway level (erythritol and arabitol) and at the C3 level of the glycolytic pathway (glycerol), and (iii) the usual accumulation of mannitol. Upon starvation, glycerol, the other three polyols, and the tricarboxylic acid-cycle intermediates and their associated amino acids disappear in this order. As in yeast, gluconeogenic substrates lead to the synthesis of trehalose, which also occurs when mycelium is grown on acetate/sucrose under limiting aeration. A transient formation of trehalose has been observed upon incubation of starved mycelium, cultured on different substrates, with [13C]glucose.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton J. K., Den Hollander J. A., Hopfield J. J., Shulman R. G. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study of trehalose mobilization in yeast spores. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):177–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.177-185.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canioni P., Alger J. R., Shulman R. G. Natural abundance Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of liver and adipose tissue of the living rat. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):4974–4980. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Glynn P., Shulman R. G. 13C NMR study of gluconeogenesis from labeled alanine in hepatocytes from euthyroid and hyperthyroid rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Ogawa S., Shulman R. G. 13C NMR studies of gluconeogenesis in rat liver cells: utilization of labeled glycerol by cells from euthyroid and hyperthyroid rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1603–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Rognstad R., Shulman R. G., Katz J. A comparison of 13C nuclear magnetic resonance and 14C tracer studies of hepatic metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3428–3432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Shulman R. G., McLaughlin A. C. Effects of ethanol on alanine metabolism in perfused mouse liver studied by 13C NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakin R. T., Morgan L. O. Carbon-13 nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectroscopy of whole cells and of cytochrome C from Neurospora crass grown with (S-Me-13C)methionine. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):529–535. doi: 10.1042/bj1520529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González R. G., Willis J., Aguayo J., Campbell P., Chylack L. T., Jr, Schleich T. 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance studies of sugar cataractogenesis in the single intact rabbit lens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1982 Jun;22(6):808–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H. Carbon balance of a mannitol fermentation and the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1206–1210. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1206-1210.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H. Mannitol acetyl phosphate phosphotransferase of Aspergillus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 17;29(3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga T., Okubo A., Fukami M., Yamazaki S., Toda S. Identification of beta-galactofuranosyl residues and their rapid internal motion in the Penicillium ochro-chloron cell wall probed by 13 C NMR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):524–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91551-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton R. S., MacKay M. A., Borowitzka L. J. The physical state of osmoregulatory solutes in unicellular algae. A natural-abundance carbon-13 nuclear-magnetic-resonance relaxation study. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 15;202(3):699–706. doi: 10.1042/bj2020699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. I., Baxter R. L. Applications of 13C NMR to metabolic studies. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:151–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. G., Brown T. R., Ugurbil K., Ogawa S., Cohen S. M., den Hollander J. A. Cellular applications of 31P and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1979 Jul 13;205(4402):160–166. doi: 10.1126/science.36664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Brown T. R., den Hollander J. A., Glynn P., Shulman R. G. High-resolution 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of glucose metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3742–3746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hollander J. A., Behar K. L., Shulman R. G. 13C NMR study of transamination during acetate utilization by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2693–2697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hollander J. A., Brown T. R., Ugurbil K., Shulman R. G. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of anaerobic glycolysis in suspensions of yeast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6096–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


