Abstract
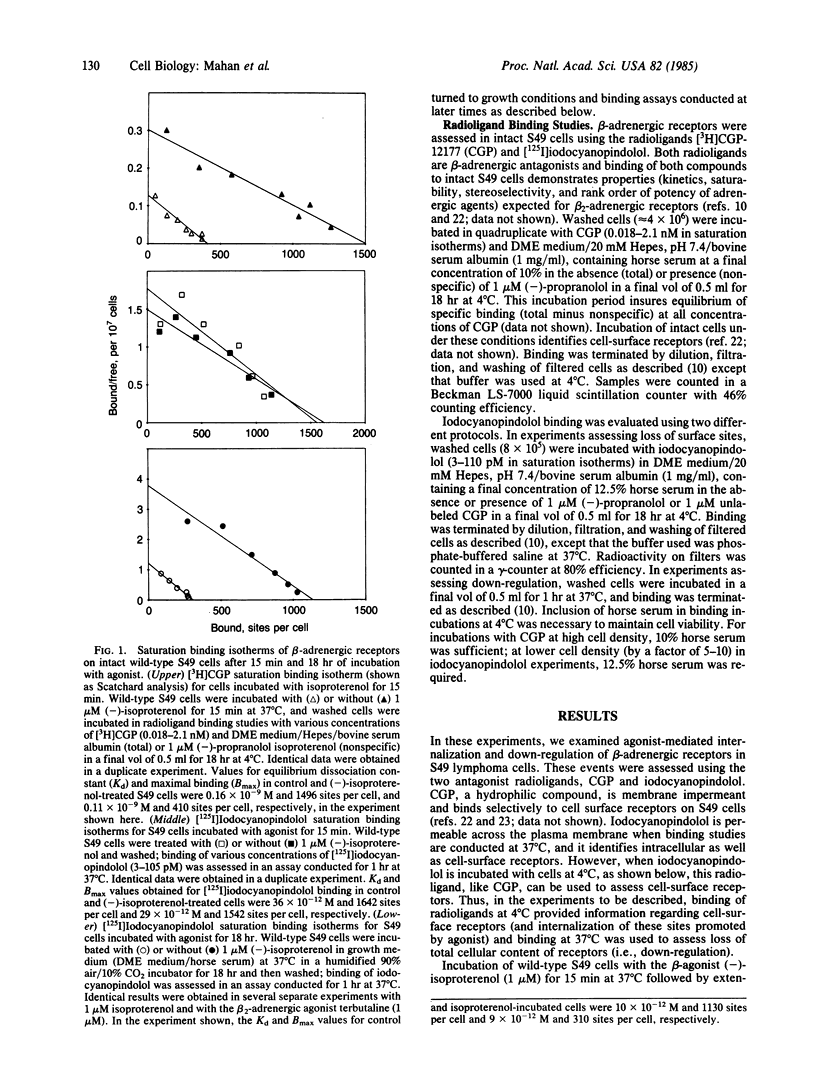
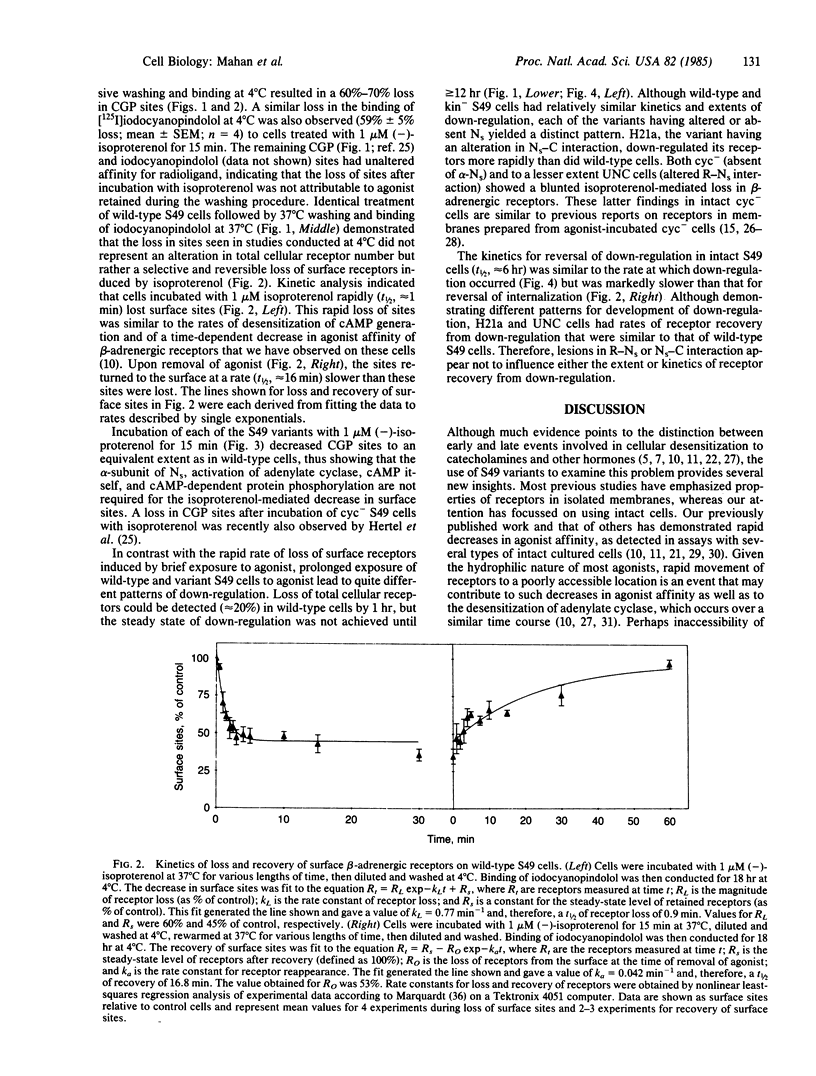
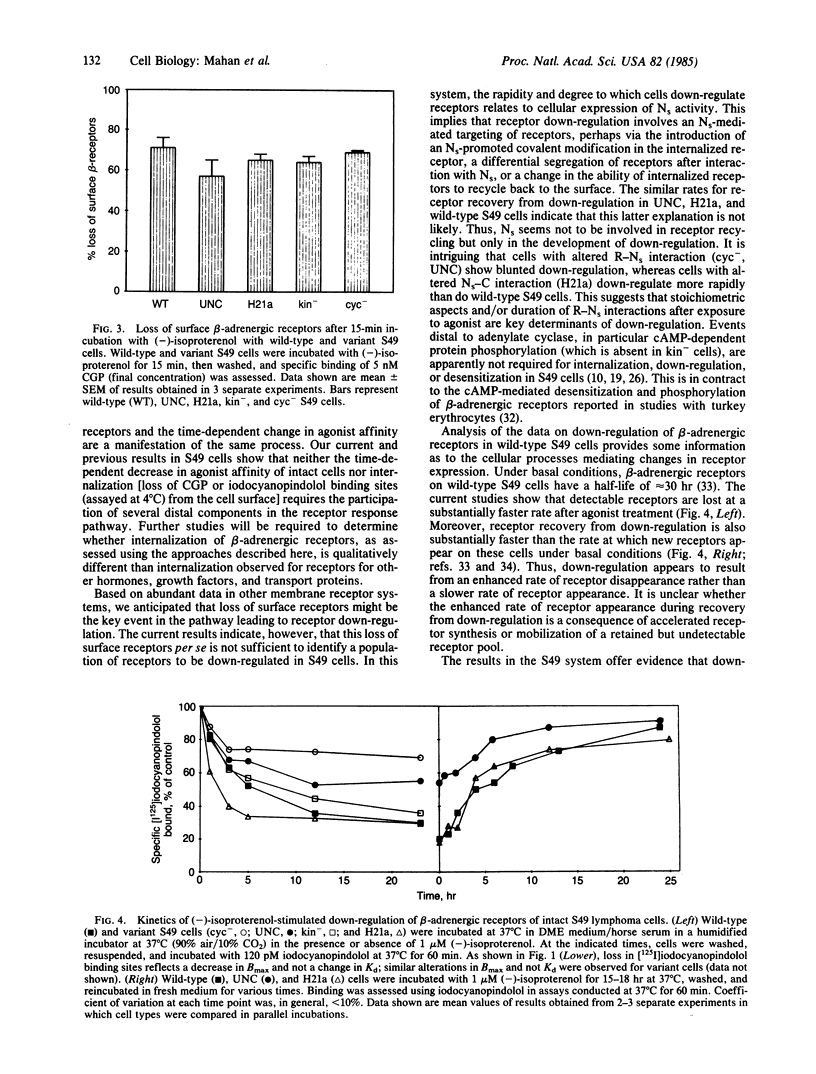
We have used wild-type and variants of the T-lymphoma cell line S49 to explore internalization and down-regulation of adenylate cyclase-linked beta-adrenergic receptors. Internalization was defined by the loss in "surface receptors" detected at 4 degrees C on intact cells by the antagonists [3H]CGP-12177 or [125I]iodocyanopindolol, whereas down-regulation was defined as the loss in total cellular content of receptors [( 125I]iodocyanopindolol binding assayed at 37 degrees C). In wild-type cells, the beta-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol induced a rapid (t 1/2, approximately equal to 1 min) and reversible loss in surface receptors. The surface sites were lost at a rate similar to the rate of desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor-mediated cyclic AMP generation of S49 cells. A series of S49 variants (cyc-, UNC, H21a) having lesions in NS (the guanine nucleotide binding protein that couples beta-receptors to adenylate cyclase) or with absent cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity (kin-), had a loss in surface sites that was equivalent to that of wild-type cells. By contrast, S49 variant cells having lesions in NS showed variable rates and extents of down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. In wild-type and kin- S49 cells, beta-receptors down-regulated with a t 1/2 of approximately equal to 4 hr. Down-regulation was blunted in the cyc- and UNC variants that have altered coupling of receptors to NS, but it was faster in the H21a variant that retains receptor-NS interaction. Recovery of receptors after down-regulation occurred at a similar rate (t 1/2, approximately equal to 6 hr) in wild-type, UNC, and H21a cells. These results demonstrate that internalization of beta-adrenergic receptors may be necessary, but is not sufficient, to explain agonist-induced receptor down-regulation in S49 cells. The variable expression in the development of down-regulation in S49 variants implies that receptor-NS interaction regulates the fate of receptors linked to the stimulation of adenylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Beiderman B., Steinberg F., Brothers V. M. Three adenylate cyclase phenotypes in S49 lymphoma cells produced by mutations of one gene. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;22(1):204–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Kaslow D., Kaslow H. R., Salomon M. R., Licko V. Hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Mutant phenotype with normally regulated beta-adrenergic receptors uncoupled with catalytic adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang D. M., Costa E. Evidence for internalization of the recognition site of beta-adrenergic receptors during receptor subsensitivity induced by (-)-isoproterenol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):3024–3028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdos J. J., Maguire M. E. Independent desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor-regulated magnesium transport and cyclic AMP accumulation. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(3):379–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Ross E. M., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylate cyclase permanently uncoupled from hormone receptors in a novel variant of S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor-linked adenylate cyclase. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Mar;35(1):5–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel C., Müller P., Portenier M., Staehelin M. Determination of the desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors by [3H]CGP-12177. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2160669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel C., Staehelin M., Perkins J. P. Evidence for intravesicular beta-adrenergic receptors in membrane fractions from desensitized cells: binding of the hydrophilic ligand CGP-12177 only in the presence of alamethicin. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(2):119–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Reynolds E. E., Molinoff P. B. Agonist-induced changes in the properties of beta-adrenergic receptors on intact S49 lymphoma cells. Time-dependent changes in the affinity of the receptor for agonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Tomkins G. M. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase: pivotal role in regulation of enzyme induction and growth. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):896–898. doi: 10.1126/science.171770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Kaslow H. R., Farfel Z., Bourne H. R. Genetic analysis of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;13:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. Polypeptide-binding membrane receptors: analysis and classification. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):14–20. doi: 10.1126/science.6259730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan L. C., Insel P. A. Use of superoxide dismutase and catalase to protect catecholamines from oxidation in tissue culture studies. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):208–216. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90327-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution of the activated 45,000-dalton (alpha) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11369–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones in cultured cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:239–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Molinoff P. B. Interactions of agonists and antagonists with beta-adrenergic receptors on intact L6 muscle cells. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(6):421–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E., Green D. A., Clark R. B. Photoaffinity labeling of the beta-adrenergic receptor from cultured lymphoma cells with [125I]iodoazidobenzylpindolol: loss of the label with desensitization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer L. S., Garrison J. C., Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase from uncoupled S49 lymphoma cells differs in charge from the wild type protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2641–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear M., Insel P. A., Melmon K. L., Coffino P. Agonist-specific refractoriness induced by isoproterenol. Studies with mutant cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7572–7576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Nambi P., Shorr R. G., Sawyer D. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Catecholamine-induced desensitization of turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase is associated with phosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3173–3177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Strulovici B., Nambi P., Lavin T. N., Briggs M. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor of frog erythrocytes. Recovery and characterization of the down-regulated receptors in sequestered vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3032–3038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Strulovici B., Nambi P., Lavin T. N., Briggs M. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor of frog erythrocytes. Recovery and characterization of the down-regulated receptors in sequestered vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3032–3038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin M., Hertel C. [3H]CGP-12177, a beta-adrenergic ligand suitable for measuring cell surface receptors. J Recept Res. 1983;3(1-2):35–43. doi: 10.3109/10799898309041921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J. Equilibrium model for insulin-induced receptor down-regulation. Regulation of insulin receptors in differentiated BC3H-1 myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2346–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Coffino P. Two-dimensional gel analysis of cyclic AMP effects in cultured S49 mouse lymphoma cells: protein modifications, inductions and repressions. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):719–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Y. F., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Catecholamine-specific desensitization of adenylate cyclase. Evidence for a multistep process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7410–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tell G. P., Haour F., Saez J. M. Hormonal regulation of membrane receptors and cell responsiveness: a review. Metabolism. 1978 Oct;27(10):1566–1592. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. High-affinity binding of agonists to beta-adrenergic receptors on intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3553–3557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Perkins J. P. Agonist-induced changes in beta-adrenergic receptors on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2227–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo G. L., Northup J. K., Perkins J. P., Harden T. K. Characterization of an altered membrane form of the beta-adrenergic receptor produced during agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13900–13908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Daalen Wetters T., Murtaugh M. P., Coffino P. Revertants of a trans-dominant S49 mouse lymphoma mutant that affects expression of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


